BNU 34986 Football on Table 解题报告(暴力)
Football on Table
Time Limit: 1000ms
Memory Limit: 65536KB
64-bit integer IO format:
%lld Java class name:
Main
Prev
Submit Status Statistics Discuss
Next
Type:
None Graph Theory 2-SAT Articulation/Bridge/Biconnected Component Cycles/Topological Sorting/Strongly Connected Component Shortest Path Bellman Ford Dijkstra/Floyd Warshall Euler Trail/Circuit Heavy-Light Decomposition Minimum Spanning Tree Stable Marriage Problem Trees Directed Minimum Spanning Tree Flow/Matching Graph Matching Bipartite Matching Hopcroft–Karp Bipartite Matching Weighted Bipartite Matching/Hungarian Algorithm Flow Max Flow/Min Cut Min Cost Max Flow DFS-like Backtracking with Pruning/Branch and Bound Basic Recursion IDA* Search Parsing/Grammar Breadth First Search/Depth First Search Advanced Search Techniques Binary Search/Bisection Ternary Search Geometry Basic Geometry Computational Geometry Convex Hull Pick's Theorem Game Theory Green Hackenbush/Colon Principle/Fusion Principle Nim Sprague-Grundy Number Matrix Gaussian Elimination Matrix Exponentiation Data Structures Basic Data Structures Binary Indexed Tree Binary Search Tree Hashing Orthogonal Range Search Range Minimum Query/Lowest Common Ancestor Segment Tree/Interval Tree Trie Tree Sorting Disjoint Set String Aho Corasick Knuth-Morris-Pratt Suffix Array/Suffix Tree Math Basic Math Big Integer Arithmetic Number Theory Chinese Remainder Theorem Extended Euclid Inclusion/Exclusion Modular Arithmetic Combinatorics Group Theory/Burnside's lemma Counting Probability/Expected Value Others Tricky Hardest Unusual Brute Force Implementation Constructive Algorithms Two Pointer Bitmask Beginner Discrete Logarithm/Shank's Baby-step Giant-step Algorithm Greedy Divide and Conquer Dynamic Programming Tag it!
"Bored? Let's play table football!"
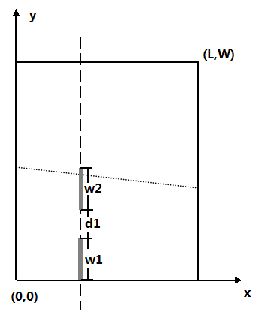
The table football is played on a rectangular table, usually contains m rows of players which are plastic, metal, wooden, or sometimes carbon-fibre figures mounted on vertical metal bars. After playing table football for hours, we decide to take a rest. And the state of the table remains random, that means each bar is placed at any legal position with equal possibilities (players can’t be outside the table and a bar is fixed at a row).
Now I'm wondering if the goal-keeper shoot a ball, what’s the possibility of this shoot turning to a goal? (If the ball did not touch any player, then I made a goal).
Let's assume there is a
i players on the i
th row (counted from left to right). And we know the width of each player and the distance between two players. (To simplify the problem, we ignore the thickness of the players, in other words, we consider the players as vertical segments. Then we treat the football as a point, moving along a straight line and will not touch the boundary of the table).
Input
The first line contains an integer T, which denotes the number of test cases.
For each test case:
- The first line contains two numbers L, W (1 ≤ L, W ≤ 108), denoting the length and the width of the table. (the lower left corner of the table is (0, 0) , and the top right corner of the table is (L, W)).
- The second line contains four number X, Y, dx, dy. (X, Y) denotes the initial position of the ball and (dx, dy) denotes the shooting direction. (X will always be zero, 0 ≤ Y ≤ W, dx> 0).
- The third line contains an integer m (1 ≤ m ≤ 10), the number of rows of the players.
- Following m blocks, for the ith block,
- The first line contains a number xi and an integer ai,(0<xi<L, 1 ≤ ai ≤ 100) denoteing the x-coordinate of the ith row and the number of players at the ith row.
- The second line contains ai numbers, the jth number wj denotes the width of the jth (from bottom to top) player at the ith row.
- The third line contains ai - 1 numbers, the jth number dj denotes the distance between the jth player and the (j+1)th player. If ai equals 1, this line will be a blank line.
We guarantee that ∑w
j + ∑d
j + 1< W
Output
For each case, first output the case number as " Case #x: ", and x is the case number. Then output the result rounded to 5 digits after the decimal point, representing the possibility of this shoot turning to a goal, in other words, that the ball does not touch any player.
Sample Input
2 8.0 10.0 0.0 5.0 2.0 -0.1 1 3.0 2 2.0 2.0 1.0 8.0 10.0 0.0 5.0 2.0 0.0 2 3.0 2 2.0 2.0 1.0 4.0 3 2.0 1.0 2.0 1.0 1.0
Sample Output
Case #1: 0.23000 Case #2: 0.13333
Hint
The black solid lines denote the table.
The dashed line denotes the bar.
The gray lines denote the players.
The dot-dashed line denote the trajectory of the ball.
Source
2014 ACM-ICPC Beijing Invitational Programming Contest
解题报告: 北京邀请赛上很简单的一题,当时我们没有做出来……原因很简单,我们当时计算板的长度,这样计算的答案一定过不了,要加上1e-8或者1e-7这样的小数修正精度。如果计算的是空白部分的长度,很简单就A了。代码如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
#define MEM(a) memset(a, 0, sizeof(a))
#define REP(i, n) for(int i=0;i<(n);++i)
typedef long long LL;
const int mod = 1e9+7;
double w[111];
double d[111];
int cas = 1;
void work()
{
double h;
double dx, dy;
double stay;
double tmp;
scanf("%lf%lf", &tmp, &h);
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &tmp, &stay, &dx, &dy);
double ans=1.0;
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while(t--)
{
double x;
int num;
scanf("%lf%d", &x, &num);
double sum = 0;
double sumd = 0;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++) scanf("%lf", w+i), sum += w[i];
for(int i=0;i<num-1;i++) scanf("%lf", d+i), sumd += d[i];
d[num-1] = 0;
double y = stay + x*dy/dx;
double shift = h - sum - sumd;
double yy = y - shift;
double part = 0;
double sta = 0, end = 0;
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
{
end += w[i];
sta = end;
end += d[i];
if(sta >= yy && end <= y)
part += d[i];
else if(sta >= yy && sta<=y && end>y)
part += y - sta;
else if(end <= y && end>=yy && sta<yy)
part += end - yy;
else if(sta<yy && end >y)
part += y - yy;
sta = end;
}
if(yy<0) part += -yy;
if(end<y) part += y-end;
ans *= part/shift;
}
printf("Case #%d: %.5lf\n", cas++, ans);
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--)
work();
}
就是这么坑~