庖丁解牛-----winpcap源码彻底解密(一)
庖丁解牛-----winpcap源码彻底解密
原创:转载请注明出处;
最近忙一个项目,需要使用winpcap抓取网络数据包,调用winpcap提供的api进行抓包后,发现丢包情况比较严重,而且cpu占用率比较大。所以下定决心,对winpcap源码进行分析,因为对驱动和对Ndis网络驱动比较熟悉,所以分析源码还不是很费劲,其实winpcap底层的npf不过是一个Ndis协议驱动,所以它能做的工作就是捕获数据包,而不能做防火墙等使用,要做防火墙,一般使用的都是Ndis中间层过滤驱动,呵呵,不多说了,超出了本文的范围。下面分析源代码的一点经验,供大家分享,共同进步。
总的来说,winpcap主要有3个文件需要关注,wpcap.dll, parket.dll, npf.sys。其中wpcap和packet属于应用层的程序,npf属于内核层的程序,即npf就是一个Ndis的协议驱动。在本文中主要分析这几个文件和他们之间是怎么通信的,对于驱动的基础知识和Ndis驱动程序不在进行重点讲解,如果对本文的内容看不明白,大家可以在回过头学习驱动的知识,也可以和我交流。
首先我们从上往下层层分析,即先分析winpcap的wpcap.dll,然后分析parket.dll,最后分析底层的npf。对于大多数应用开发的人来说,使用wpcap.dll就足够了,因为它提供的api函数足够你捕获网络数据包,从而分析网络数据包,解析网络数据包。下面讲解下数据包的捕获流程。
数据包的捕获流程一般都分为以下几步:
1) 查找设备,也就是说查找网卡设备,调用的函数是pcap_findalldevs
2) 打开对应的网卡设备,调用的函数为pcap_open_live
3) 过滤数据包,在解析之前过滤数据包,可以减少解析的数据包数,增强数据包解析的能力,主要调用2个函数,pcap_compile编译过滤器,采用pcap_setfiter;
4) 获取数据包,主要的函数有pcap_loop,pcap_dispatch,pcap_next,pcap_next_ex这4个函数,这四个函数的区别可以参考winpcap的手册。
5) 关闭设备,pcap_freealldevs;
这是基本的数据包捕获流程,对一般的应用层的开发者来说,知道这些已经足够了。
但是当网络数据很大的时候,比如大块的文件传输,等,就需要考虑丢包情况了。下面介绍改善性能的api。怎样设置内核缓冲,怎样设置用户缓冲区,如何设置内核缓冲区到用户缓冲区的拷贝数据的最小值,即当内核缓冲区的数据达到这个值时,才能被上层的应用程序读走。在分析这些之前,必先知道数据包是怎么从网卡到达应用程序的。对于linux和windows系统,稍有不同,linux下采用libcap抓取网络数据包,windows采用winpcap抓取网络数据包。数据包从网卡到应用程序的过程如下:
图1:linux下数据包捕获流程
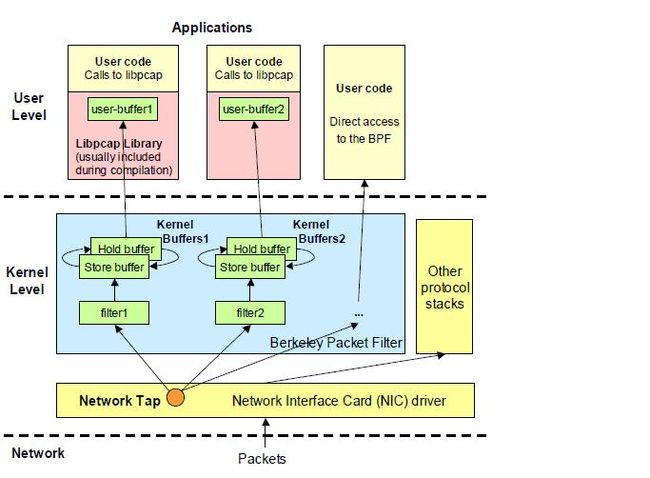
图2:winpcap数据包捕获流程
从linux和windows抓包过程可以看出,libcap和winpcap的不同之处如下:
(1)Libcap在BPF中采用2个缓冲区,即store buffer和hold buffer,从网卡拷贝的数据首先放入到store buffer ,然后再复制到hold buffer,就是一个乒乓操作经过hold buffer拷贝到应用程序的user buffer中,这两个缓冲区的大小一般为32k。而winpcap采用的是一个循环缓冲区,即内核缓冲区,kernel buffer,内核缓冲区的默认大小为1M,可以采用pcap_setbuff对内核缓冲区进行修改。
(2)libcap的内核缓冲区和用户缓冲区大小在应用层是不可以更改的,如果需要更改,必须修改内核代码,然后重新编译,而winpcap提供了修改内核缓冲区和用户缓冲区的api函数,用户可以方便的设置缓冲区的大小,用户缓冲区的默认大小为256k,可以使用pcap_setuserbuffer进行设置。
(3)从图中可以看出,libcap只有2层,内核层和用户层,而winpcap有3层,在用户层又分为packet.dll和wpcap.dll,这样层次更加清晰,方便用户的理解,当然用户可以直接调用wpcap.dll的api进行数据包操作,也可以调用packet.dll进行数据包操作。
(4)对数据包的捕获一般要经过3个内存的拷贝,首先是网卡拷贝到内核缓冲区,然后内核缓冲区拷贝到用户缓冲区,然后通过api将用户缓冲区的数据包读走,进行协议分析,然后把数据保存起来,放入应用程序开辟的内存中。这一点它们都是类似的。
(5) winpcap提供了直接从内核缓冲区将数据写入文件的方法,这样减少了数据包的拷贝次数,提高了收包的速度。
(6)如何将数据包从内核缓冲区直接提供给应用程序,这是提高数据包捕获性能的好方法?
读者可以尝试这样去做,可以降低cpu占用率和丢包率。
(7)libcap老的版本没有发送数据包的函数,winpcap有pcap_sendpacket发送数据包;
(8)winpcap采用pcap_setmintocopy设置每次从内核缓冲区拷贝到用户缓冲区的最小值,当内核缓冲区的数据小于这个值时,读操作不返回,直到超时为止;
下面由上到下对各个函数进行解析:
(1) pcap_findalldevs
intpcap_findalldevs(pcap_if_t **alldevsp,char *errbuf)
{
pcap_if_t *devlist =NULL;
intret = 0;
constchar *desc;
char *AdaptersName;
ULONGNameLength;
char *name;
if (!PacketGetAdapterNames(NULL, &NameLength))
{
DWORDlast_error =GetLastError();
if (last_error !=ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER)
{
snprintf(errbuf,PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE,
"PacketGetAdapterNames: %s",
pcap_win32strerror());
return (-1);
}
}
if (NameLength > 0)
AdaptersName = (char*)malloc(NameLength);
else
{
*alldevsp =NULL;
return 0;
}
if (AdaptersName ==NULL)
{
snprintf(errbuf,PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE,"Cannot allocate enough memory to list the adapters.");
return (-1);
}
if (!PacketGetAdapterNames(AdaptersName, &NameLength)) {
snprintf(errbuf,PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE,
"PacketGetAdapterNames: %s",
pcap_win32strerror());
free(AdaptersName);
return (-1);
}
/*
* "PacketGetAdapterNames()" returned a list of
* null-terminated ASCII interface name strings,
* terminated by a null string, followed by a list
* of null-terminated ASCII interface description
* strings, terminated by a null string.
* This means there are two ASCII nulls at the end
* of the first list.
*
* Find the end of the first list; that's the
* beginning of the second list.
*/
desc = &AdaptersName[0];
while (*desc !='/0' || *(desc + 1) !='/0')
desc++;
/*
* Found it - "desc" points to the first of the two
* nulls at the end of the list of names, so the
* first byte of the list of descriptions is two bytes
* after it.
*/
desc += 2;
/*
* Loop over the elements in the first list.
*/
name = &AdaptersName[0];
while (*name !='/0') {
/*
* Add an entry for this interface.
*/
if (pcap_add_if_win32(&devlist,name,desc, errbuf) == -1) {
/*
* Failure.
*/
ret = -1;
break;
}
name +=strlen(name) + 1;
desc +=strlen(desc) + 1;
}
if (ret != -1) {
/*
* We haven't had any errors yet; do any platform-specific
* operations to add devices.
*/
if (pcap_platform_finddevs(&devlist,errbuf) < 0)
ret = -1;
}
if (ret == -1) {
/*
* We had an error; free the list we've been constructing.
*/
if (devlist !=NULL) {
pcap_freealldevs(devlist);
devlist =NULL;
}
}
*alldevsp =devlist;
free(AdaptersName);
return (ret);
}
/获取可用网络适配器的一个列表与它们的描述
BOOLEANPacketGetAdapterNames(PTSTRpStr,PULONG BufferSize)
{
PADAPTER_INFOTAdInfo;
ULONG SizeNeeded = 0;
ULONG SizeNames = 0;
ULONG SizeDesc;
ULONG OffDescriptions;
TRACE_ENTER("PacketGetAdapterNames");
TRACE_PRINT_OS_INFO();
TRACE_PRINT2("Packet DLL version %s, Driver version %s",PacketLibraryVersion, PacketDriverVersion);
TRACE_PRINT1("PacketGetAdapterNames: BufferSize=%u", *BufferSize);
//
// Check the presence on some libraries we rely on, and load them if we found them
//f
PacketLoadLibrariesDynamically();
//d
// Create the adapter information list
//
TRACE_PRINT("Populating the adapter list...");
PacketPopulateAdaptersInfoList();
WaitForSingleObject(g_AdaptersInfoMutex,INFINITE);
if(!g_AdaptersInfoList)
{
ReleaseMutex(g_AdaptersInfoMutex);
*BufferSize = 0;
TRACE_PRINT("No adapters found in the system. Failing.");
SetLastError(ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER);
TRACE_EXIT("PacketGetAdapterNames");
returnFALSE; // No adapters to return
}
//
// First scan of the list to calculate the offsets and check the sizes
//
for(TAdInfo =g_AdaptersInfoList;TAdInfo !=NULL;TAdInfo =TAdInfo->Next)
{
if(TAdInfo->Flags !=INFO_FLAG_DONT_EXPORT)
{
// Update the size variables
SizeNeeded += (ULONG)strlen(TAdInfo->Name) + (ULONG)strlen(TAdInfo->Description) + 2;
SizeNames += (ULONG)strlen(TAdInfo->Name) + 1;
}
}
// Check that we don't overflow the buffer.
// Note: 2 is the number of additional separators needed inside the list
if(SizeNeeded + 2 > *BufferSize ||pStr == NULL)
{
ReleaseMutex(g_AdaptersInfoMutex);
TRACE_PRINT1("PacketGetAdapterNames: input buffer too small, we need %u bytes", *BufferSize);
*BufferSize =SizeNeeded + 2; // Report the required size
TRACE_EXIT("PacketGetAdapterNames");
SetLastError(ERROR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER);
returnFALSE;
}
OffDescriptions =SizeNames + 1;
//
// Second scan of the list to copy the information
//
for(TAdInfo =g_AdaptersInfoList,SizeNames = 0,SizeDesc = 0;TAdInfo !=NULL;TAdInfo =TAdInfo->Next)
{
if(TAdInfo->Flags !=INFO_FLAG_DONT_EXPORT)
{
// Copy the data
StringCchCopyA(
((PCHAR)pStr) +SizeNames,
*BufferSize -SizeNames,
TAdInfo->Name);
StringCchCopyA(
((PCHAR)pStr) +OffDescriptions + SizeDesc,
*BufferSize -OffDescriptions -SizeDesc,
TAdInfo->Description);
// Update the size variables
SizeNames += (ULONG)strlen(TAdInfo->Name) + 1;
SizeDesc += (ULONG)strlen(TAdInfo->Description) + 1;
}
}
// Separate the two lists
((PCHAR)pStr)[SizeNames] = 0;
// End the list with a further /0
((PCHAR)pStr)[SizeNeeded + 1] = 0;
ReleaseMutex(g_AdaptersInfoMutex);
TRACE_EXIT("PacketGetAdapterNames");
returnTRUE;
}
pcap_findalldevs为wpcap.dll中查找设备列表的函数,里面调用Packet.dll中的PacketGetAdapterNames获取设备列表。它调用PacketPopulateAdaptersInfoList函数,函数PacketPopulateAdaptersInfoList()创建适配器的链表g_AdaptersInfoList。该函数先释放掉g_AdaptersInfoList中旧的内容,然后调用PacketGetAdaptersNPF()函数用新的信息填充该链表。而PacketGetAdaptersNPF调用PacketAddAdapterNPF,从注册表中获取设备信息。PacketAddAdapterNPF又调用PacketRequest,将请求发送到NPF,
{
Result=(BOOLEAN)DeviceIoControl(AdapterObject->hFile,(DWORD)Set ? (DWORD)BIOCSETOID : (DWORD)BIOCQUERYOID,OidData,sizeof(PACKET_OID_DATA)-1+OidData->Length,OidData,
sizeof(PACKET_OID_DATA)-1+OidData->Length,&BytesReturned,NULL);
}
所有的应用程序和驱动之间通信,最终都是调用DeviceIoControl,WriteFile和ReadFile,Npf中和DeviceIoControl对应的就是NPF_IoControl。
(2) pcap_open_live
pcap_t *
pcap_open_live(constchar *source, int snaplen, intpromisc,int to_ms, char *errbuf)
{
pcap_t *p;
intstatus;
p =pcap_create(source,errbuf);
if (p ==NULL)
return (NULL);
status =pcap_set_snaplen(p,snaplen); //设置最大包长
if (status < 0)
gotofail;
status =pcap_set_promisc(p,promisc); //是否混杂模式
if (status < 0)
gotofail;
status =pcap_set_timeout(p,to_ms); //设置超时
if (status < 0)
gotofail;
/*
* Mark this as opened with pcap_open_live(), so that, for
* example, we show the full list of DLT_ values, rather
* than just the ones that are compatible with capturing
* when not in monitor mode. That allows existing applications
* to work the way they used to work, but allows new applications
* that know about the new open API to, for example, find out the
* DLT_ values that they can select without changing whether
* the adapter is in monitor mode or not.
*/
p->oldstyle = 1;
status =pcap_activate(p);
if (status < 0)
gotofail;
return (p);
fail:
if (status ==PCAP_ERROR || status ==PCAP_ERROR_NO_SUCH_DEVICE ||
status == PCAP_ERROR_PERM_DENIED)
strlcpy(errbuf,p->errbuf,PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE);
else
snprintf(errbuf,PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE,"%s: %s",source,
pcap_statustostr(status));
pcap_close(p);
return (NULL);
}
该函数设置最大的包长,设置超时时间,设置混杂模式等。Pcap_open_live调用pcap_activate,pcap_activate定义如下:
Intpcap_activate(pcap_t *p)
{
intstatus;
status =p->activate_op(p);
if (status >= 0)
p->activated = 1;
return (status);
}
Pcap_activate调用activate_op,该函数是回调函数, p->activate_op = pcap_activate_win32;即pcap_activate调用pcap_activate_win32函数,pcap_activate_win32函数调用PacketOpenAdapter,同时函数设置PacketSetBuff和if(PacketSetMinToCopy(p->adapter,16000)==FALSE),设置设置最小copysize=16k。PacketOpenAdapter中调用使用NPF device driver打开网卡(adapter),同样调用PacketRequest,调用DeviceIoControl,即对应驱动中的NPF_IoControl。
(3) pcap_setfilter
Intpcap_setfilter(pcap_t *p,struct bpf_program *fp)
{
returnp->setfilter_op(p,fp);
}
p->setfilter_op =pcap_setfilter_win32_npf;
pcap_setfilter调用pcap_setfilter_win32_npf设置过滤器;
staticint
pcap_setfilter_win32_npf(pcap_t *p, struct bpf_program *fp)
{
if(PacketSetBpf(p->adapter,fp)==FALSE){
/*
* Kernel filter not installed.
* XXX - fall back on userland filtering, as is done
* on other platforms?
*/
snprintf(p->errbuf,PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE,"Driver error: cannot set bpf filter: %s",pcap_win32strerror());
return (-1);
}
/*
* Discard any previously-received packets, as they might have
* passed whatever filter was formerly in effect, but might
* not pass this filter (BIOCSETF discards packets buffered
* in the kernel, so you can lose packets in any case).
*/
p->cc = 0;
return (0);
}
BOOLEANPacketSetBpf(LPADAPTERAdapterObject,structbpf_program *fp)
{
DWORDBytesReturned;
BOOLEANResult;
TRACE_ENTER("PacketSetBpf");
#ifdefHAVE_WANPACKET_API
if (AdapterObject->Flags ==INFO_FLAG_NDISWAN_ADAPTER)
{
Result =WanPacketSetBpfFilter(AdapterObject->pWanAdapter, (PUCHAR)fp->bf_insns,fp->bf_len * sizeof(struct bpf_insn));
TRACE_EXIT("PacketSetBpf");
returnResult;
}
#endif
#ifdefHAVE_AIRPCAP_API
if(AdapterObject->Flags ==INFO_FLAG_AIRPCAP_CARD)
{
Result = (BOOLEAN)g_PAirpcapSetFilter(AdapterObject->AirpcapAd,
(char*)fp->bf_insns,
fp->bf_len *sizeof(structbpf_insn));
TRACE_EXIT("PacketSetBpf");
returnResult;
}
#endif// HAVE_AIRPCAP_API
#ifdefHAVE_NPFIM_API
if(AdapterObject->Flags == INFO_FLAG_NPFIM_DEVICE)
{
Result = (BOOLEAN)g_NpfImHandlers.NpfImSetBpfFilter(AdapterObject->NpfImHandle,
fp->bf_insns,
fp->bf_len * sizeof(struct bpf_insn));
TRACE_EXIT("PacketSetBpf");
return TRUE;
}
#endif// HAVE_NPFIM_API
#ifdefHAVE_DAG_API
if(AdapterObject->Flags & INFO_FLAG_DAG_CARD)
{
// Delegate the filtering to higher layers since it's too expensive here
TRACE_EXIT("PacketSetBpf");
return TRUE;
}
#endif// HAVE_DAG_API
if (AdapterObject->Flags ==INFO_FLAG_NDIS_ADAPTER)
{
//调用DeviceIoControl设置过滤器
Result = (BOOLEAN)DeviceIoControl(AdapterObject->hFile,BIOCSETF,(char*)fp->bf_insns,fp->bf_len*sizeof(structbpf_insn),NULL,0,&BytesReturned,NULL);
}
else
{
TRACE_PRINT1("Request to set BPF filter on an unknown device type (%u)",AdapterObject->Flags);
Result =FALSE;
}
TRACE_EXIT("PacketSetBpf");
returnResult;
}
对应驱动的NPF_IoControl。