谈谈SQL数据库中滥用临时表、排序的解决方案优化(举例:汉字转拼音函数)
游标、临时表、触发器、COLLATE等等……
无可厚非、这些都是好东西,我为什么今天要花时间来写这些东西呢?
是因为我发现慢慢的很多人用久了这些东西之后会形成一种习惯,不管解决什么问题动不动都会把它们搬出来,由此我看到了很多漂亮的代码在性能效率面前却显得不那么优秀。
好了废话不多说开始进入正题吧。
今天的案例
场景:
需要通过用户输入的姓名关键字来搜索用户。用户输入关键字'x'来搜索用户(数据来源于表[Name字段中]或内存[List<UserInfo>]中)
要求:
得到的结果排序应为:
x
xia
xiao
yx
即:
- 包含x字母的结果均应显示出来
- 首字母匹配的结果应该排在前面(如x开头)
- 在条件2相同的前提下更短的结果应排在前面(如x排在xia前面)
补充:
如果能一起解决中文问题最好,如搜索'x'
得到的结果排序应为:
x
xiani
夏荣
肖小笑
杨星
即将汉字的拼音首字母纳入在内,不知SQL Server是否支持这一特性的搜索?
感谢[学习的脚步]这位网友提出来的问题
其实要解决这个问题不难,无非就是汉字转拼音首字母
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
先给出解决方案一
---------------------准备工作 开始-------------------------------
if object_id('zhuisuos')is not null
drop table zhuisuos
go
create table zhuisuos
(
name varchar(100)
)
insert into zhuisuos values('追索')
insert into zhuisuos values('追索2')
insert into zhuisuos values('xia')
insert into zhuisuos values('dxc')
insert into zhuisuos values('x')
insert into zhuisuos values('xx')
insert into zhuisuos values('xiani')
insert into zhuisuos values('yx')
insert into zhuisuos values('夏荣')
insert into zhuisuos values('肖小笑')
insert into zhuisuos values('杨星')
go
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--建立汉字转拼音首字母函数
if object_id('fn_getpy1')is not null
drop function fn_getpy1
go
GO
create function [dbo].fn_getpy1
(@str nvarchar(4000))
returns nvarchar(4000)
as
begin
declare @str_len int,@result nvarchar(4000)
declare @zhuisuo table
(firstspell nchar(1) collate Chinese_PRC_CI_AS,
letter nchar(1))
set @str_len=len(@str)
set @result= ' '
insert into @zhuisuo
(firstspell,letter)
select '吖 ', 'A ' union all select '八 ', 'B ' union all
select '嚓 ', 'C ' union all select '咑 ', 'D ' union all
select '妸 ', 'E ' union all select '发 ', 'F ' union all
select '旮 ', 'G ' union all select '铪 ', 'H ' union all
select '丌 ', 'J ' union all select '咔 ', 'K ' union all
select '垃 ', 'L ' union all select '嘸 ', 'M ' union all
select '拏 ', 'N ' union all select '噢 ', 'O ' union all
select '妑 ', 'P ' union all select '七 ', 'Q ' union all
select '呥 ', 'R ' union all select '仨 ', 'S ' union all
select '他 ', 'T ' union all select '屲 ', 'W ' union all
select '夕 ', 'X ' union all select '丫 ', 'Y ' union all
select '帀 ', 'Z '
while @str_len> 0
begin
select top 1 @result=letter+@result,@str_len=@str_len-1
from @zhuisuo
where firstspell <=substring(@str,@str_len,1)
order by firstspell desc
if @@rowcount=0
select @result=substring(@str,@str_len,1)+@result,@str_len=@str_len-1
end
return(@result)
end
---------------------准备工作 结束-------------------------------
--正式查询
declare @str varchar(10)
set @str='x'
create table #result
(name varchar(100) null,id int null,lens int null)
insert into #result
select name,1,len(name) from zhuisuos
where name like @str+'%'
insert into #result
select name,2,len(name) from zhuisuos
where name like '%'+@str+'%' and name not like @str+'%'
insert into #result
select name,3,len(name) from zhuisuos
where dbo.fn_getpy1 (name) like @str+'%' and name not like @str+'%' and name not like '%'+@str+'%'
insert into #result
select name,4,len(name) from zhuisuos
where dbo.fn_getpy1 (name) like '%'+@str+'%' and dbo.fn_getpy1 (name) not like @str+'%'
and name not like @str+'%' and name not like '%'+@str+'%'
select name from #result
order by id,lens
drop table #result
这个解决方案已经满足查询要求
其它都不管 我们重点来看看这次写的这个函数
象这样的汉字转拼音函数在网上一搜一大把 今天我就要举例几个方案让大家对优化及开销有个清楚的概念
解决方案一写的函数实在是太糟糕了(以上及接下来举出的案例并无冒犯任何雷同及原创代码之意,还请多多包涵)
为什么这么说呢
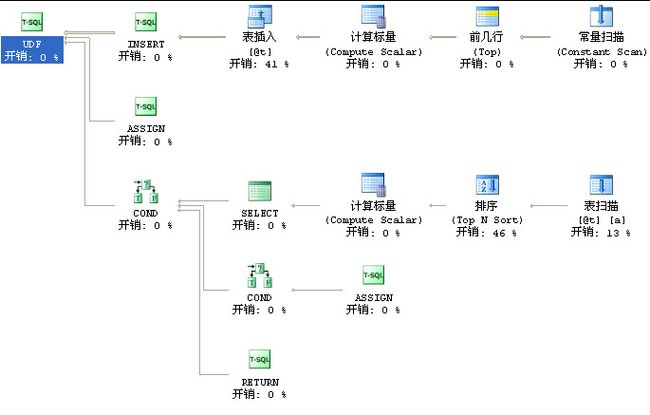
这是它的执行计划
它用了临时表并且排序
表插入开销0.01 表扫描开销0.003 表排序0.011
估计总开销0.0246
实际执行:我拿1万行数据调用此函数花了我20几秒、一个查询操作你愿意等20多秒吗
所以看到这样的执行计划实在很抱歉
解决方案二
create function [dbo].[fn_getpy2](@Str varchar(500)='')
returns varchar(500)
as
begin
declare @strlen int,@return varchar(500),@ii int
declare @n int,@c char(1),@chn nchar(1)
select @strlen=len(@str),@return='',@ii=0
set @ii=0
while @ii<@strlen
begin
select @ii=@ii+1,@n=63,@chn=substring(@str,@ii,1)
if @chn>'z'
select @n = @n +1
,@c = case chn when @chn then char(@n) else @c end
from(
select top 27 * from (
select chn = '吖'
union all select '八'
union all select '嚓'
union all select '咑'
union all select '妸'
union all select '发'
union all select '旮'
union all select '铪'
union all select '丌' --because have no 'i'
union all select '丌'
union all select '咔'
union all select '垃'
union all select '嘸'
union all select '拏'
union all select '噢'
union all select '妑'
union all select '七'
union all select '呥'
union all select '仨'
union all select '他'
union all select '屲' --no 'u'
union all select '屲' --no 'v'
union all select '屲'
union all select '夕'
union all select '丫'
union all select '帀'
union all select @chn) as a
order by chn COLLATE Chinese_PRC_CI_AS
) as b
else set @c=@chn
set @return=@return+@c
end
return(@return)
end
这是很聪明的一个解决方案,它巧妙的运用了排序使其利用序号位置int ASCII 代码转换为字母
这个方案能很漂亮的将汉字转为拼音
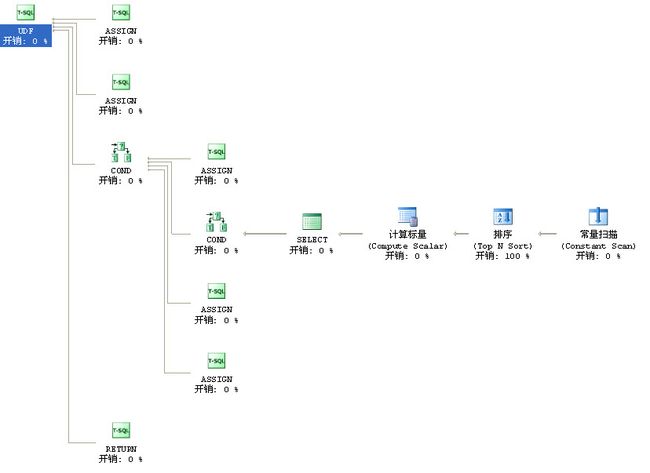
那么我们来看看它的执行计划是怎样的
看完之后也不得不为这个漂亮之举感到惋惜
排序开销0.01156
总估计开销大概0.01159
实际执行:我拿1万行数据调用此函数花了10几秒
当然它比解决方案一效率要高出一倍之多
解决方案三
既然解决方案一大部分开销花在表插入及排序上面那么我们把里面的临时表拿出来新建一个物理表并且建上主键让它聚集索引会怎样呢
create function [dbo].[fn_getpy3]
(@str nvarchar(4000))
returns nvarchar(4000)
as
begin
declare @str_len int,@result nvarchar(4000)
set @str_len=len(@str)
set @result= ' '
while @str_len> 0
begin
select top 1 @result=letter+@result,@str_len=@str_len-1
from transition_spell
where firstspell <=substring(@str,@str_len,1)
order by firstspell desc
if @@rowcount=0
select @result=substring(@str,@str_len,1)+@result,@str_len=@str_len-1
end
return(@result)
end
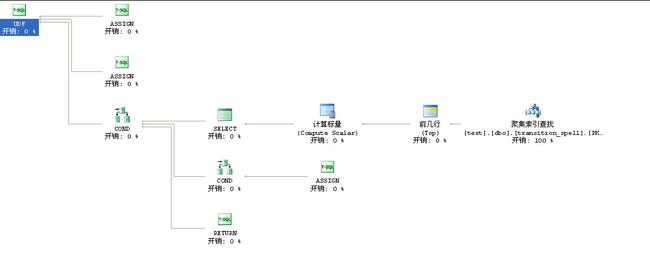
物理建表代码我就没有提供了 直接参考解决方案一临时表
果然,此方案总开销只花了0.003
实际执行:我拿1万行数据调用此函数花了4~5秒左右
没有了临时表,没有了插入,没有了排序这个简单的方法比漂亮的解决方案二效率更高
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
现在仔细想想 有没有什么方法能让它连聚集索引都不需要呢 这样岂不连0.003的开销都没有了?
刚才写出了解决方案四就实现了这一点
create function [dbo].[fn_getpy4]
(@str nvarchar(4000))
returns nvarchar(4000)
as
begin
declare @str_len int,@result nvarchar(4000) ,@crs nvarchar(1)
set @str_len=len(@str)
set @result= ' '
while @str_len> 0
begin
set @crs=substring(@str,@str_len,1)
-- @result=b+@result
select @str_len=@str_len-1,@result=
case when @crs>='吖' and @crs<'八'then 'A'
when @crs>='八' and @crs<'嚓' then 'B'
when @crs>='嚓' and @crs<'咑' then 'C'
when @crs>='咑' and @crs<'妸' then 'D'
when @crs>='妸' and @crs<'发' then 'E'
when @crs>='发' and @crs<'旮' then 'F'
when @crs>='旮' and @crs<'铪' then 'G'
when @crs>='铪' and @crs<'丌' then 'H'
when @crs>='丌' and @crs<'咔' then 'J'
when @crs>='咔' and @crs<'垃' then 'K'
when @crs>='垃' and @crs<'嘸' then 'L'
when @crs>='嘸' and @crs<'拏' then 'M'
when @crs>='拏' and @crs<'噢' then 'N'
when @crs>='噢' and @crs<'妑' then 'O'
when @crs>='妑' and @crs<'七' then 'P'
when @crs>='七' and @crs<'呥' then 'Q'
when @crs>='呥' and @crs<'仨' then 'R'
when @crs>='仨' and @crs<'他' then 'S'
when @crs>='他' and @crs<'屲' then 'T'
when @crs>='屲' and @crs<'夕' then 'W'
when @crs>='夕' and @crs<'丫' then 'X'
when @crs>='丫' and @crs<'帀' then 'Y'
when @crs>='帀' then 'Z'
else @crs end+@result
end
return(@result)
end
估计运算开销 0
实际执行:1万行数据调用此函数只花了1~2秒
这样就满足了?
其实解决方案四还有优化的空间、不过这次仅仅只是代码及逻辑上的优化
解决方案五
create function [dbo].[fn_getpy5]
(@str nvarchar(4000))
returns nvarchar(4000)
as
begin
declare @str_len int,@result nvarchar(4000) ,@crs nvarchar(1)
set @str_len=len(@str)
set @result= ' '
while @str_len> 0
begin
set @crs=substring(@str,@str_len,1)
select @str_len=@str_len-1,@result=
case
when @crs>='帀' then 'Z'
when @crs>='丫' then 'Y'
when @crs>='夕' then 'X'
when @crs>='屲' then 'W'
when @crs>='他' then 'T'
when @crs>='仨' then 'S'
when @crs>='呥' then 'R'
when @crs>='七' then 'Q'
when @crs>='妑' then 'P'
when @crs>='噢' then 'O'
when @crs>='拏' then 'N'
when @crs>='嘸' then 'M'
when @crs>='垃' then 'L'
when @crs>='咔' then 'K'
when @crs>='丌' then 'J'
when @crs>='铪' then 'H'
when @crs>='旮' then 'G'
when @crs>='发' then 'F'
when @crs>='妸' then 'E'
when @crs>='咑' then 'D'
when @crs>='嚓' then 'C'
when @crs>='八' then 'B'
when @crs>='吖' then 'A'
else @crs end+@result
end
return(@result)
end
估计运算开销 0
实际执行:1万行数据调用此函数0~1秒
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
好了,这些方案我都写完了、简单的总结一下。
其实不管你写了多少年的SQL有的时候不要养成一种先入为主、自作聪明的观念。
一个优秀的解决方案也许只需最简单的代码就能达到理想的效果。
所以谨以此篇文章来希望让更多的人看到,其实我们生活当中经常所遇到的问题往往都是我们无限的把它复杂化,严重化了。
退一步海阔天空、换个角度想想吧!