linux io schedule: CFQ
优先级
每个进程都会有一个IO优先级,CFQ调度器将会将其作为考虑的因素之一,来确定该进程的请求队列何时可以获取块设备的使用权。IO优先级从高到低可以分为三大类:RT(real time),BE(best try),IDLE(idle),其中RT和BE又可以再划分为8个子优先级。实际上,我们已经知道CFQ调度器的公平是针对于进程而言的,而只有同步请求(read或syn write)才是针对进程而存在的,他们会放入进程自身的请求队列,而所有同优先级的异步请求,无论来自于哪个进程,都会被放入公共的队列,异步请求的队列总共有8(RT)+8(BE)+1(IDLE)=17个。
调度器的结构
CFQ调度器在整个工作过程中所涉及到的结构比较多,我们可以把这些结构分为两类,一类是用来描述调度器本身相关的结构,由于CFQ将进程作为考虑对象,因此另一类结构就是特定于进程的结构,对于这些结构,我们只选择其内部的重要元素进行分析。和调度器相关的数据结构主要有两个,一个是描述调度器的struct cfq_data,一个是描述队列的struct cfq_queue。
struct cfq_data {
struct request_queue *queue;
/*
* rr list of queues with requests and the count of them
*/
struct cfq_rb_root service_tree;
/*
* Each priority tree is sorted by next_request position. These
* trees are used when determining if two or more queues are
* interleaving requests (see cfq_close_cooperator).
*/
struct rb_root prio_trees[CFQ_PRIO_LISTS];
unsigned int busy_queues;
int rq_in_driver[2];
int sync_flight;
/*
* queue-depth detection
*/
int rq_queued;
int hw_tag;
int hw_tag_samples;
int rq_in_driver_peak;
/*
* idle window management
*/
struct timer_list idle_slice_timer;
struct work_struct unplug_work;
struct cfq_queue *active_queue;
struct cfq_<strong style="color: black; background-color: rgb(160, 255, 255);">io</strong>_context *active_cic;
/*
* async queue for each priority case
*/
struct cfq_queue *async_cfqq[2][IOPRIO_BE_NR];
struct cfq_queue *async_idle_cfqq;
sector_t last_position;
/*
* tunables, see top of file
*/
unsigned int cfq_quantum;
unsigned int cfq_fifo_expire[2];
unsigned int cfq_back_penalty;
unsigned int cfq_back_max;
unsigned int cfq_slice[2];
unsigned int cfq_slice_async_rq;
unsigned int cfq_slice_idle;
unsigned int cfq_latency;
struct list_head cic_list;
/*
* Fallback dummy cfqq for extreme OOM conditions
*/
struct cfq_queue oom_cfqq;
unsigned long last_end_sync_rq;
};
queue:指向块设备对应的request_queue
service_tree:所有待调度的队列都被添加进该红黑树,等待调度获取时间片
prio_trees[CFQ_PRIO_LISTS]:对应8个优先级的红黑树,所有优先级类别为RT或BE的进程的同步请求队列,都会根据优先级添加至相应的红黑树
busy_queues:用于计算service_tree中有多少个队列在等待调度
active_queue:指向当前占有块设备的队列
async_cfqq[2][IOPRIO_BE_NR]:对应RT和BE优先级类的16个异步请求队列
async_idle_cfqq:对应优先级类别为IDLE的异步请求队列
cfq_quantum:用于计算在一个队列的时间片内,最多发放多少个请求到底层的块设备
cfq_fifo_expire[2]:同步、异步请求的响应期限时间
cfq_slice[2]:同步、异步请求队列的时间片长度
struct cfq_queue {
/* reference count */
atomic_t ref;
/* various state flags, see below */
unsigned int flags;
/* parent cfq_data */
struct cfq_data *cfqd;
/* service_tree member */
struct rb_node rb_node;
/* service_tree key */
unsigned long rb_key;
/* prio tree member */
struct rb_node p_node;
/* prio tree root we belong to, if any */
struct rb_root *p_root;
/* sorted list of pending requests */
struct rb_root sort_list;
/* if fifo isn't expired, next request to serve */
struct request *next_rq;
/* requests queued in sort_list */
int queued[2];
/* currently allocated requests */
int allocated[2];
/* fifo list of requests in sort_list */
struct list_head fifo;
unsigned long slice_end;
long slice_resid;
unsigned int slice_dispatch;
/* pending metadata requests */
int meta_pending;
/* number of requests that are on the dispatch list or inside driver */
int dispatched;
/* <strong style="color: black; background-color: rgb(160, 255, 255);">io</strong> prio of this group */
unsigned short ioprio, org_ioprio;
unsigned short ioprio_class, org_ioprio_class;
unsigned int seek_samples;
u64 seek_total;
sector_t seek_mean;
sector_t last_request_pos;
unsigned long seeky_start;
pid_t pid;
struct cfq_queue *new_cfqq;
};
cfqd:指向队列所属的cfq_data
rb_node:用于将队列插入service_tree
rb_key:红黑树节点关键值,用于确定队列在service_tree中的位置,该值要综合jiffies,进程的IO优先级等因素进行计算
p_node:用于将队列插入对应优先级的prio_tree
p_root:对应的prio_tree树根
sort_list:组织队列内的请求用的红黑树,按请求的起始扇区进行排序
fifo:组织队列内的请求用的链表头,按请求的响应期限排序
slice_end:指明时间片何时消耗完
slice_dispatch:在时间片内发送的请求数
ioprio:进程的当前IO优先级
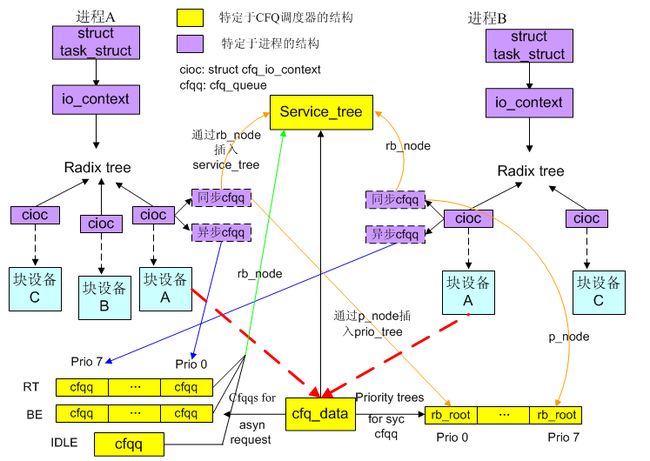
相对于进程的结构有struct io_context和struct cfq_io_context。io_context的核心结构是一个基数树,里面组织了进程所访问的所有块设备所对应的cfq_io_context。cfq_io_context中的核心结构是两个队列,也就是进程在一个CFQ调度器所关系到的队列,一个是同步的,一个是异步的,下面是我根据自己的理解画的一张关系图:
这一节暂时就分析道这里了,后面再结合代码来分析CFQ调度器的具体实现
前文介绍了CFQ调度器的一些概念和结构之间的关系,这里再结合实际的代码,来分析CFQ的工作流程。CFQ调度器的定义如下:
- static struct elevator_type iosched_cfq = {
- .ops = {
- .elevator_merge_fn = cfq_merge,
- .elevator_merged_fn = cfq_merged_request,
- .elevator_merge_req_fn = cfq_merged_requests,
- .elevator_allow_merge_fn = cfq_allow_merge,
- .elevator_dispatch_fn = cfq_dispatch_requests,
- .elevator_add_req_fn = cfq_insert_request,
- .elevator_activate_req_fn = cfq_activate_request,
- .elevator_deactivate_req_fn = cfq_deactivate_request,
- .elevator_queue_empty_fn = cfq_queue_empty,
- .elevator_completed_req_fn = cfq_completed_request,
- .elevator_former_req_fn = elv_rb_former_request,
- .elevator_latter_req_fn = elv_rb_latter_request,
- .elevator_set_req_fn = cfq_set_request,
- .elevator_put_req_fn = cfq_put_request,
- .elevator_may_queue_fn = cfq_may_queue,
- .elevator_init_fn = cfq_init_queue,
- .elevator_exit_fn = cfq_exit_queue,
- .trim = cfq_free_io_context,
- },
- .elevator_attrs = cfq_attrs,
- .elevator_name = "cfq",
- .elevator_owner = THIS_MODULE,
- };
- static struct elevator_type iosched_cfq = {
- .ops = {
- .elevator_merge_fn = cfq_merge,
- .elevator_merged_fn = cfq_merged_request,
- .elevator_merge_req_fn = cfq_merged_requests,
- .elevator_allow_merge_fn = cfq_allow_merge,
- .elevator_dispatch_fn = cfq_dispatch_requests,
- .elevator_add_req_fn = cfq_insert_request,
- .elevator_activate_req_fn = cfq_activate_request,
- .elevator_deactivate_req_fn = cfq_deactivate_request,
- .elevator_queue_empty_fn = cfq_queue_empty,
- .elevator_completed_req_fn = cfq_completed_request,
- .elevator_former_req_fn = elv_rb_former_request,
- .elevator_latter_req_fn = elv_rb_latter_request,
- .elevator_set_req_fn = cfq_set_request,
- .elevator_put_req_fn = cfq_put_request,
- .elevator_may_queue_fn = cfq_may_queue,
- .elevator_init_fn = cfq_init_queue,
- .elevator_exit_fn = cfq_exit_queue,
- .trim = cfq_free_io_context,
- },
- .elevator_attrs = cfq_attrs,
- .elevator_name = "cfq",
- .elevator_owner = THIS_MODULE,
- };
可以看到CFQ调度器涉及到的操作函数还是比较多的,这里我只打算选一些和提交bio以及request相关的函数进行分析。在提交bio的时候,如果在通用层寻找可以合并bio的途径失败,要通过cfq_merge()来判断是否能够将bio插入到某个request的bio链表首部
- static struct request *
- cfq_find_rq_fmerge(struct cfq_data *cfqd, struct bio *bio)
- {
- struct task_struct *tsk = current;
- struct cfq_io_context *cic;
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq;
- //在进程的io_context中,找到进程特定于块设备的cfq_io_context
- cic = cfq_cic_lookup(cfqd, tsk->io_context);
- if (!cic)
- return NULL;
- //根据同步还是异步,确定cfq_queue
- cfqq = cic_to_cfqq(cic, cfq_bio_sync(bio));
- if (cfqq) {
- sector_t sector = bio->bi_sector + bio_sectors(bio);//得到末尾扇区号
- //从cfq_queue的红黑树中查找对应的节点
- return elv_rb_find(&cfqq->sort_list, sector);
- }
- return NULL;
- }
- static struct request *
- cfq_find_rq_fmerge(struct cfq_data *cfqd, struct bio *bio)
- {
- struct task_struct *tsk = current;
- struct cfq_io_context *cic;
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq;
- //在进程的io_context中,找到进程特定于块设备的cfq_io_context
- cic = cfq_cic_lookup(cfqd, tsk->io_context);
- if (!cic)
- return NULL;
- //根据同步还是异步,确定cfq_queue
- cfqq = cic_to_cfqq(cic, cfq_bio_sync(bio));
- if (cfqq) {
- sector_t sector = bio->bi_sector + bio_sectors(bio);//得到末尾扇区号
- //从cfq_queue的红黑树中查找对应的节点
- return elv_rb_find(&cfqq->sort_list, sector);
- }
- return NULL;
- }
cfq_find_rq_fmerge()进行实际的搜索工作,要确定bio的归属request,必须先确定进程的通信对象是谁(因为一个进程有可能和多个块设备通信),也就是要找到进程对应的cfq_io_context结构,其中包含了进程的同步请求队列和异步请求队列的地址,只要找到了相应的cfq_io_context,就可以通过bio的同异步性确定对应的cfq_queue了,最后再判断对应的cfq_queue中是否存在可以容纳bio的request。推导cfq_io_context的关键在于以块设备CFQ调度器的描述结构cfq_data的地址为关键值,在进程的io_context的基数树中进行搜索
- <SPAN style="FONT-SIZE: 12px">static struct request *
- cfq_find_rq_fmerge(struct cfq_data *cfqd, struct bio *bio)
- {
- struct task_struct *tsk = current;
- struct cfq_io_context *cic;
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq;
- //在进程的io_context中,找到进程特定于块设备的cfq_io_context
- cic = cfq_cic_lookup(cfqd, tsk->io_context);
- if (!cic)
- return NULL;
- //根据同步还是异步,确定cfq_queue
- cfqq = cic_to_cfqq(cic, cfq_bio_sync(bio));
- if (cfqq) {
- sector_t sector = bio->bi_sector + bio_sectors(bio);//得到末尾扇区号
- //从cfq_queue的红黑树中查找对应的节点
- return elv_rb_find(&cfqq->sort_list, sector);
- }
- return NULL;
- }
- </SPAN>
- <span style="font-size: 12px;">static struct request *
- cfq_find_rq_fmerge(struct cfq_data *cfqd, struct bio *bio)
- {
- struct task_struct *tsk = current;
- struct cfq_io_context *cic;
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq;
- //在进程的io_context中,找到进程特定于块设备的cfq_io_context
- cic = cfq_cic_lookup(cfqd, tsk->io_context);
- if (!cic)
- return NULL;
- //根据同步还是异步,确定cfq_queue
- cfqq = cic_to_cfqq(cic, cfq_bio_sync(bio));
- if (cfqq) {
- sector_t sector = bio->bi_sector + bio_sectors(bio);//得到末尾扇区号
- //从cfq_queue的红黑树中查找对应的节点
- return elv_rb_find(&cfqq->sort_list, sector);
- }
- return NULL;
- }
- </span>
通过基数树寻找对应设备的cfq_io_context:
- <SPAN style="FONT-SIZE: 12px">static struct cfq_io_context *
- cfq_cic_lookup(struct cfq_data *cfqd, struct io_context *ioc)
- {
- struct cfq_io_context *cic;
- unsigned long flags;
- void *k;
- if (unlikely(!ioc))
- return NULL;
- rcu_read_lock();
- /*
- * we maintain a last-hit cache, to avoid browsing over the tree
- */
- //由于进程很有可能连续访问同一块设备,因此先将cic中的关键值直接与cfqd比较
- cic = rcu_dereference(ioc->ioc_data);
- if (cic && cic->key == cfqd) {
- rcu_read_unlock();
- return cic;
- }
- do {//在进程io_context的基数树中寻找对应访问的块设备的cfq_data结构
- cic = radix_tree_lookup(&ioc->radix_root, (unsigned long) cfqd);
- rcu_read_unlock();
- if (!cic)
- break;
- /* ->key must be copied to avoid race with cfq_exit_queue() */
- k = cic->key;
- if (unlikely(!k)) {
- cfq_drop_dead_cic(cfqd, ioc, cic);
- rcu_read_lock();
- continue;
- }
- //保存cic到ioc->ioc_data
- spin_lock_irqsave(&ioc->lock, flags);
- rcu_assign_pointer(ioc->ioc_data, cic);
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ioc->lock, flags);
- break;
- } while (1);
- return cic;
- }</SPAN>
- <span style="font-size: 12px;">static struct cfq_io_context *
- cfq_cic_lookup(struct cfq_data *cfqd, struct io_context *ioc)
- {
- struct cfq_io_context *cic;
- unsigned long flags;
- void *k;
- if (unlikely(!ioc))
- return NULL;
- rcu_read_lock();
- /*
- * we maintain a last-hit cache, to avoid browsing over the tree
- */
- //由于进程很有可能连续访问同一块设备,因此先将cic中的关键值直接与cfqd比较
- cic = rcu_dereference(ioc->ioc_data);
- if (cic && cic->key == cfqd) {
- rcu_read_unlock();
- return cic;
- }
- do {//在进程io_context的基数树中寻找对应访问的块设备的cfq_data结构
- cic = radix_tree_lookup(&ioc->radix_root, (unsigned long) cfqd);
- rcu_read_unlock();
- if (!cic)
- break;
- /* ->key must be copied to avoid race with cfq_exit_queue() */
- k = cic->key;
- if (unlikely(!k)) {
- cfq_drop_dead_cic(cfqd, ioc, cic);
- rcu_read_lock();
- continue;
- }
- //保存cic到ioc->ioc_data
- spin_lock_irqsave(&ioc->lock, flags);
- rcu_assign_pointer(ioc->ioc_data, cic);
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(&ioc->lock, flags);
- break;
- } while (1);
- return cic;
- }</span>
在通用层__make_request()函数中,如果bio找不到接收对象,那么就要重新创建一个request来接收它。分配一个request必须进行初始化,需要调用cfq_set_request()函数。和前面的过程比较类似的是,request要先找到接收它的cfq_queue,然后这里出现了一个问题,如果这个request是进程的第一个同步请求或者异步请求,那么就要分配新的cfq_queue来接收request。同步请求和异步请求的处理情况有点区别,因为进程独自拥有自己的同步请求队列,而进程的异步请求都是共享cfq_data中的异步请求队列的,所以只有当request是同步请求时才需要进行cfq_queue的分配
- static int
- cfq_set_request(struct request_queue *q, struct request *rq, gfp_t gfp_mask)
- {
- struct cfq_data *cfqd = q->elevator->elevator_data;
- struct cfq_io_context *cic;
- const int rw = rq_data_dir(rq);
- const bool is_sync = rq_is_sync(rq);
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq;
- unsigned long flags;
- might_sleep_if(gfp_mask & __GFP_WAIT);
- //获取进程特定于块设备的cfq_io_context结构
- cic = cfq_get_io_context(cfqd, gfp_mask);
- spin_lock_irqsave(q->queue_lock, flags);
- if (!cic)
- goto queue_fail;
- new_queue:
- cfqq = cic_to_cfqq(cic, is_sync);//根据同异步情况,获取进程中对应的cfq_queue
- if (!cfqq || cfqq == &cfqd->oom_cfqq) {//如果还没有相应的cfqq则进行分配
- cfqq = cfq_get_queue(cfqd, is_sync, cic->ioc, gfp_mask);//分配cfq_queue
- cic_set_cfqq(cic, cfqq, is_sync);//设置cic->cfqq[is_sync] = cfqq
- } else {
- /*
- * If the queue was seeky for too long, break it apart.
- */
- if (cfq_cfqq_coop(cfqq) && should_split_cfqq(cfqq)) {
- cfq_log_cfqq(cfqd, cfqq, "breaking apart cfqq");
- cfqq = split_cfqq(cic, cfqq);
- if (!cfqq)
- goto new_queue;
- }
- /*
- * Check to see if this queue is scheduled to merge with
- * another, closely cooperating queue. The merging of
- * queues happens here as it must be done in process context.
- * The reference on new_cfqq was taken in merge_cfqqs.
- */
- if (cfqq->new_cfqq)
- cfqq = cfq_merge_cfqqs(cfqd, cic, cfqq);
- }
- cfqq->allocated[rw]++;
- atomic_inc(&cfqq->ref);
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(q->queue_lock, flags);
- rq->elevator_private = cic;//保存cfq_io_context到request
- rq->elevator_private2 = cfqq;//保存cfq_queue到request
- return 0;
- queue_fail:
- if (cic)
- put_io_context(cic->ioc);
- cfq_schedule_dispatch(cfqd);
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(q->queue_lock, flags);
- cfq_log(cfqd, "set_request fail");
- return 1;
- }
- static int
- cfq_set_request(struct request_queue *q, struct request *rq, gfp_t gfp_mask)
- {
- struct cfq_data *cfqd = q->elevator->elevator_data;
- struct cfq_io_context *cic;
- const int rw = rq_data_dir(rq);
- const bool is_sync = rq_is_sync(rq);
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq;
- unsigned long flags;
- might_sleep_if(gfp_mask & __GFP_WAIT);
- //获取进程特定于块设备的cfq_io_context结构
- cic = cfq_get_io_context(cfqd, gfp_mask);
- spin_lock_irqsave(q->queue_lock, flags);
- if (!cic)
- goto queue_fail;
- new_queue:
- cfqq = cic_to_cfqq(cic, is_sync);//根据同异步情况,获取进程中对应的cfq_queue
- if (!cfqq || cfqq == &cfqd->oom_cfqq) {//如果还没有相应的cfqq则进行分配
- cfqq = cfq_get_queue(cfqd, is_sync, cic->ioc, gfp_mask);//分配cfq_queue
- cic_set_cfqq(cic, cfqq, is_sync);//设置cic->cfqq[is_sync] = cfqq
- } else {
- /*
- * If the queue was seeky for too long, break it apart.
- */
- if (cfq_cfqq_coop(cfqq) && should_split_cfqq(cfqq)) {
- cfq_log_cfqq(cfqd, cfqq, "breaking apart cfqq");
- cfqq = split_cfqq(cic, cfqq);
- if (!cfqq)
- goto new_queue;
- }
- /*
- * Check to see if this queue is scheduled to merge with
- * another, closely cooperating queue. The merging of
- * queues happens here as it must be done in process context.
- * The reference on new_cfqq was taken in merge_cfqqs.
- */
- if (cfqq->new_cfqq)
- cfqq = cfq_merge_cfqqs(cfqd, cic, cfqq);
- }
- cfqq->allocated[rw]++;
- atomic_inc(&cfqq->ref);
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(q->queue_lock, flags);
- rq->elevator_private = cic;//保存cfq_io_context到request
- rq->elevator_private2 = cfqq;//保存cfq_queue到request
- return 0;
- queue_fail:
- if (cic)
- put_io_context(cic->ioc);
- cfq_schedule_dispatch(cfqd);
- spin_unlock_irqrestore(q->queue_lock, flags);
- cfq_log(cfqd, "set_request fail");
- return 1;
- }
当一个request创建初始化,就要将其插入到相应的队列中,cfq_insert_request()函数完成这个功能,和deadline调度器相似,request会被放入两个队列里,一个是按照起始扇区号排列的红黑树(sort_list),一个是按响应期限排列的链表(fifo)
- static void cfq_insert_request(struct request_queue *q, struct request *rq)
- {
- struct cfq_data *cfqd = q->elevator->elevator_data;
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq = RQ_CFQQ(rq);
- cfq_log_cfqq(cfqd, cfqq, "insert_request");
- cfq_init_prio_data(cfqq, RQ_CIC(rq)->ioc);//根据ioc设定cfq_queue的优先级类和优先级
- cfq_add_rq_rb(rq);//将rq添加到cfq_queue的红黑树
- //设置期限值
- rq_set_fifo_time(rq, jiffies + cfqd->cfq_fifo_expire[rq_is_sync(rq)]);
- list_add_tail(&rq->queuelist, &cfqq->fifo);//添加至fifo
- cfq_rq_enqueued(cfqd, cfqq, rq);
- }
- static void cfq_insert_request(struct request_queue *q, struct request *rq)
- {
- struct cfq_data *cfqd = q->elevator->elevator_data;
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq = RQ_CFQQ(rq);
- cfq_log_cfqq(cfqd, cfqq, "insert_request");
- cfq_init_prio_data(cfqq, RQ_CIC(rq)->ioc);//根据ioc设定cfq_queue的优先级类和优先级
- cfq_add_rq_rb(rq);//将rq添加到cfq_queue的红黑树
- //设置期限值
- rq_set_fifo_time(rq, jiffies + cfqd->cfq_fifo_expire[rq_is_sync(rq)]);
- list_add_tail(&rq->queuelist, &cfqq->fifo);//添加至fifo
- cfq_rq_enqueued(cfqd, cfqq, rq);
- }
当一个request纳入一个新的bio后,要考虑能否和其他request进行合并,假如是将bio插入到链表的末尾,那么就要在sort_list中获取request后面的一个request(通过函数elv_rb_latter_request()来获取),然后判断前者的结束扇区和前者的起始扇区是否一样,这些工作都是再通用层代码中完成的,当两个request通过了通用层的审核和,并完成合并操作后,将调用cfq_merged_requests进行一些针对队列的额外工作
- tatic void
- cfq_merged_requests(struct request_queue *q, struct request *rq,
- struct request *next)
- {
- /*
- * reposition in fifo if next is older than rq
- */
- if (!list_empty(&rq->queuelist) && !list_empty(&next->queuelist) &&
- time_before(rq_fifo_time(next), rq_fifo_time(rq))) {
- list_move(&rq->queuelist, &next->queuelist);
- rq_set_fifo_time(rq, rq_fifo_time(next));
- }
- cfq_remove_request(next);
- }
- tatic void
- cfq_merged_requests(struct request_queue *q, struct request *rq,
- struct request *next)
- {
- /*
- * reposition in fifo if next is older than rq
- */
- if (!list_empty(&rq->queuelist) && !list_empty(&next->queuelist) &&
- time_before(rq_fifo_time(next), rq_fifo_time(rq))) {
- list_move(&rq->queuelist, &next->queuelist);
- rq_set_fifo_time(rq, rq_fifo_time(next));
- }
- cfq_remove_request(next);
- }
这里主要是考察两个request的期限,因为合并时都是将后者合并入前者,因此当后者的期限时间小于前者时,要进行相应的调整,这一点和deadline调度器是一样的。
最后分析的依然是每个调度器最重要的函数--elevator_dispatch_fn
CFQ调度器在发送request到底层块设备时的流程大致如下:
1.选择一个cfq_queue
2.从cfq_queue中选择一个request进行发送
选择cfq_queue的思路如下:
1.如果当前的cfq_queue的时间片还没用完,则继续当前的cfq_queue
2.如果当前的cfq_queue的时间片消耗完了,则优先在对应的prio_tree中选择一个cfq_queue,该cfq_queue的第一个访问扇区与整个调度器最后处理的扇区之间的差值必须小于一个阈值,如果OK的话就选择这个cfq_queue
3.如果找不到这样的cfq_queue,再从service_tree中调度其他的cfq_queue
- <SPAN style="FONT-SIZE: 12px">static int cfq_dispatch_requests(struct request_queue *q, int force)
- {
- struct cfq_data *cfqd = q->elevator->elevator_data;
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq;
- if (!cfqd->busy_queues)
- return 0;
- if (unlikely(force))
- return cfq_forced_dispatch(cfqd);
- //先要选择一个队列
- cfqq = cfq_select_queue(cfqd);
- if (!cfqq)
- return 0;
- /*
- * Dispatch a request from this cfqq, if it is allowed
- */
- //从选择的cfq_queue中选择request进行分派
- if (!cfq_dispatch_request(cfqd, cfqq))
- return 0;
- cfqq->slice_dispatch++;
- cfq_clear_cfqq_must_dispatch(cfqq);
- /*
- * expire an async queue immediately if it has used up its slice. idle
- * queue always expire after 1 dispatch round.
- */
- /*如果service_tree中有其他队列等待调度,而刚刚发送请求的
- 队列是异步队列并且发送数已经超过了时间片的内最大请求数,
- 则将异步队列挂起,如果是idle队列则在发送一个请求后直接将队列挂起
- */
- if (cfqd->busy_queues > 1 && ((!cfq_cfqq_sync(cfqq) &&
- cfqq->slice_dispatch >= cfq_prio_to_maxrq(cfqd, cfqq)) ||
- cfq_class_idle(cfqq))) {
- cfqq->slice_end = jiffies + 1;
- cfq_slice_expired(cfqd, 0);
- }
- cfq_log_cfqq(cfqd, cfqq, "dispatched a request");
- return 1;
- }
- </SPAN>
- <span style="font-size: 12px;">static int cfq_dispatch_requests(struct request_queue *q, int force)
- {
- struct cfq_data *cfqd = q->elevator->elevator_data;
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq;
- if (!cfqd->busy_queues)
- return 0;
- if (unlikely(force))
- return cfq_forced_dispatch(cfqd);
- //先要选择一个队列
- cfqq = cfq_select_queue(cfqd);
- if (!cfqq)
- return 0;
- /*
- * Dispatch a request from this cfqq, if it is allowed
- */
- //从选择的cfq_queue中选择request进行分派
- if (!cfq_dispatch_request(cfqd, cfqq))
- return 0;
- cfqq->slice_dispatch++;
- cfq_clear_cfqq_must_dispatch(cfqq);
- /*
- * expire an async queue immediately if it has used up its slice. idle
- * queue always expire after 1 dispatch round.
- */
- /*如果service_tree中有其他队列等待调度,而刚刚发送请求的
- 队列是异步队列并且发送数已经超过了时间片的内最大请求数,
- 则将异步队列挂起,如果是idle队列则在发送一个请求后直接将队列挂起
- */
- if (cfqd->busy_queues > 1 && ((!cfq_cfqq_sync(cfqq) &&
- cfqq->slice_dispatch >= cfq_prio_to_maxrq(cfqd, cfqq)) ||
- cfq_class_idle(cfqq))) {
- cfqq->slice_end = jiffies + 1;
- cfq_slice_expired(cfqd, 0);
- }
- cfq_log_cfqq(cfqd, cfqq, "dispatched a request");
- return 1;
- }
- </span>
cfq_select_queue()用来选择一个队列,active_queue为当前运行的队列
- static struct cfq_queue *cfq_select_queue(struct cfq_data *cfqd)
- {
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq, *new_cfqq = NULL;
- /*先检查active_queue*/
- cfqq = cfqd->active_queue;
- if (!cfqq)//没有指定active_queue则跳转到new_queue去选择新的队列
- goto new_queue;
- /*
- * The active queue has run out of time, expire it and select new.
- */
- //指定了active_queue,这里检查该队列的时间片是否已经过去
- if (cfq_slice_used(cfqq) && !cfq_cfqq_must_dispatch(cfqq))
- goto expire;
- /*
- * The active queue has requests and isn't expired, allow it to
- * dispatch.
- */
- /*走到这里表示时间片尚在,这里检查cfq_queue的sort_list是否为空*/
- if (!RB_EMPTY_ROOT(&cfqq->sort_list))
- goto keep_queue;
- /*
- * If another queue has a request waiting within our mean seek
- * distance, let it run. The expire code will check for close
- * cooperators and put the close queue at the front of the service
- * tree. If possible, merge the expiring queue with the new cfqq.
- */
- //走到这里表示active_queue内已经没有请求了,因此要找一个最适合的cfq_queue
- new_cfqq = cfq_close_cooperator(cfqd, cfqq);
- if (new_cfqq) {
- if (!cfqq->new_cfqq)
- cfq_setup_merge(cfqq, new_cfqq);
- goto expire;
- }
- /*
- * No requests pending. If the active queue still has requests in
- * flight or is idling for a new request, allow either of these
- * conditions to happen (or time out) before selecting a new queue.
- */
- if (timer_pending(&cfqd->idle_slice_timer) ||
- (cfqq->dispatched && cfq_cfqq_idle_window(cfqq))) {
- cfqq = NULL;
- goto keep_queue;
- }
- expire:
- cfq_slice_expired(cfqd, 0);//将时间片消耗完的active_queue重新插入service_tree
- new_queue:
- cfqq = cfq_set_active_queue(cfqd, new_cfqq);//设定new_cfqq为新的active_tree接收时间片
- keep_queue:
- return cfqq;
- }
- static struct cfq_queue *cfq_select_queue(struct cfq_data *cfqd)
- {
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq, *new_cfqq = NULL;
- /*先检查active_queue*/
- cfqq = cfqd->active_queue;
- if (!cfqq)//没有指定active_queue则跳转到new_queue去选择新的队列
- goto new_queue;
- /*
- * The active queue has run out of time, expire it and select new.
- */
- //指定了active_queue,这里检查该队列的时间片是否已经过去
- if (cfq_slice_used(cfqq) && !cfq_cfqq_must_dispatch(cfqq))
- goto expire;
- /*
- * The active queue has requests and isn't expired, allow it to
- * dispatch.
- */
- /*走到这里表示时间片尚在,这里检查cfq_queue的sort_list是否为空*/
- if (!RB_EMPTY_ROOT(&cfqq->sort_list))
- goto keep_queue;
- /*
- * If another queue has a request waiting within our mean seek
- * distance, let it run. The expire code will check for close
- * cooperators and put the close queue at the front of the service
- * tree. If possible, merge the expiring queue with the new cfqq.
- */
- //走到这里表示active_queue内已经没有请求了,因此要找一个最适合的cfq_queue
- new_cfqq = cfq_close_cooperator(cfqd, cfqq);
- if (new_cfqq) {
- if (!cfqq->new_cfqq)
- cfq_setup_merge(cfqq, new_cfqq);
- goto expire;
- }
- /*
- * No requests pending. If the active queue still has requests in
- * flight or is idling for a new request, allow either of these
- * conditions to happen (or time out) before selecting a new queue.
- */
- if (timer_pending(&cfqd->idle_slice_timer) ||
- (cfqq->dispatched && cfq_cfqq_idle_window(cfqq))) {
- cfqq = NULL;
- goto keep_queue;
- }
- expire:
- cfq_slice_expired(cfqd, 0);//将时间片消耗完的active_queue重新插入service_tree
- new_queue:
- cfqq = cfq_set_active_queue(cfqd, new_cfqq);//设定new_cfqq为新的active_tree接收时间片
- keep_queue:
- return cfqq;
- }
cfq_close_cooperator查找一个在扇区地址上满足要求的队列,这个操作只对同步请求队列有效
- static struct cfq_queue *cfq_close_cooperator(struct cfq_data *cfqd,
- struct cfq_queue *cur_cfqq)
- {
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq;
- if (!cfq_cfqq_sync(cur_cfqq))
- return NULL;
- if (CFQQ_SEEKY(cur_cfqq))
- return NULL;
- /*
- * We should notice if some of the queues are cooperating, eg
- * working closely on the same area of the disk. In that case,
- * we can group them together and don't waste time idling.
- */
- //根据扇区的差值,寻找一个最接近的节点
- cfqq = cfqq_close(cfqd, cur_cfqq);
- if (!cfqq)
- return NULL;
- /*
- * It only makes sense to merge sync queues.
- */
- if (!cfq_cfqq_sync(cfqq))
- return NULL;
- if (CFQQ_SEEKY(cfqq))
- return NULL;
- return cfqq;
- }
- static struct cfq_queue *cfq_close_cooperator(struct cfq_data *cfqd,
- struct cfq_queue *cur_cfqq)
- {
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq;
- if (!cfq_cfqq_sync(cur_cfqq))
- return NULL;
- if (CFQQ_SEEKY(cur_cfqq))
- return NULL;
- /*
- * We should notice if some of the queues are cooperating, eg
- * working closely on the same area of the disk. In that case,
- * we can group them together and don't waste time idling.
- */
- //根据扇区的差值,寻找一个最接近的节点
- cfqq = cfqq_close(cfqd, cur_cfqq);
- if (!cfqq)
- return NULL;
- /*
- * It only makes sense to merge sync queues.
- */
- if (!cfq_cfqq_sync(cfqq))
- return NULL;
- if (CFQQ_SEEKY(cfqq))
- return NULL;
- return cfqq;
- }
cfqq_close执行实际的工作
- static struct cfq_queue *cfqq_close(struct cfq_data *cfqd,
- struct cfq_queue *cur_cfqq)
- {
- struct rb_root *root = &cfqd->prio_trees[cur_cfqq->org_ioprio];
- struct rb_node *parent, *node;
- struct cfq_queue *__cfqq;
- sector_t sector = cfqd->last_position;//这里区最后访问的扇区
- if (RB_EMPTY_ROOT(root))
- return NULL;
- /*
- * First, if we find a request starting at the end of the last
- * request, choose it.
- */
- //首先试图在同优先级的红黑树中寻找与最近访问的扇区相接的另一个cfq_queue
- __cfqq = cfq_prio_tree_lookup(cfqd, root, sector, &parent, NULL);
- if (__cfqq)//如果找到了的话则选定该cfq_queue进行调度
- return __cfqq;
- /*
- * If the exact sector wasn't found, the parent of the NULL leaf
- * will contain the closest sector.
- */
- //parent保存了最接近的节点的父节点,如果没找到相邻的cfq_queue,获取父节点对应的cfq_queue
- __cfqq = rb_entry(parent, struct cfq_queue, p_node);
- /*如果__cfqq的下一个派送请求(next_rq指定)的扇区地址和调度器最后派送的请求的结束扇区之间的间隙满足要求,
- 则选定该cfq_queue*/
- if (cfq_rq_close(cfqd, cur_cfqq, __cfqq->next_rq))
- return __cfqq;
- /* 前面都不成功,则根据next_rq和sector的大小关系,
- 来选择最接近的比__cfqq的起始扇区大的节点或者小的节点*/
- if (blk_rq_pos(__cfqq->next_rq) < sector)
- node = rb_next(&__cfqq->p_node);
- else
- node = rb_prev(&__cfqq->p_node);
- if (!node)
- return NULL;
- //这里再把选择的节点进行一次间隙的判断,如果间隙小于阈值,则选择该节点,否则返回NULL
- __cfqq = rb_entry(node, struct cfq_queue, p_node);
- if (cfq_rq_close(cfqd, cur_cfqq, __cfqq->next_rq))
- return __cfqq;
- return NULL;
- }
- static struct cfq_queue *cfqq_close(struct cfq_data *cfqd,
- struct cfq_queue *cur_cfqq)
- {
- struct rb_root *root = &cfqd->prio_trees[cur_cfqq->org_ioprio];
- struct rb_node *parent, *node;
- struct cfq_queue *__cfqq;
- sector_t sector = cfqd->last_position;//这里区最后访问的扇区
- if (RB_EMPTY_ROOT(root))
- return NULL;
- /*
- * First, if we find a request starting at the end of the last
- * request, choose it.
- */
- //首先试图在同优先级的红黑树中寻找与最近访问的扇区相接的另一个cfq_queue
- __cfqq = cfq_prio_tree_lookup(cfqd, root, sector, &parent, NULL);
- if (__cfqq)//如果找到了的话则选定该cfq_queue进行调度
- return __cfqq;
- /*
- * If the exact sector wasn't found, the parent of the NULL leaf
- * will contain the closest sector.
- */
- //parent保存了最接近的节点的父节点,如果没找到相邻的cfq_queue,获取父节点对应的cfq_queue
- __cfqq = rb_entry(parent, struct cfq_queue, p_node);
- /*如果__cfqq的下一个派送请求(next_rq指定)的扇区地址和调度器最后派送的请求的结束扇区之间的间隙满足要求,
- 则选定该cfq_queue*/
- if (cfq_rq_close(cfqd, cur_cfqq, __cfqq->next_rq))
- return __cfqq;
- /* 前面都不成功,则根据next_rq和sector的大小关系,
- 来选择最接近的比__cfqq的起始扇区大的节点或者小的节点*/
- if (blk_rq_pos(__cfqq->next_rq) < sector)
- node = rb_next(&__cfqq->p_node);
- else
- node = rb_prev(&__cfqq->p_node);
- if (!node)
- return NULL;
- //这里再把选择的节点进行一次间隙的判断,如果间隙小于阈值,则选择该节点,否则返回NULL
- __cfqq = rb_entry(node, struct cfq_queue, p_node);
- if (cfq_rq_close(cfqd, cur_cfqq, __cfqq->next_rq))
- return __cfqq;
- return NULL;
- }
如果找到了这样的队列,则在cfq_set_active_queue()函数中设定该队列为运行队列,否则就从service_tree中调度时间点最邻近的队列
- static struct cfq_queue *cfq_set_active_queue(struct cfq_data *cfqd,
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq)
- {
- if (!cfqq)//假如没指定cfqq,则从service_tree中最前的节点
- cfqq = cfq_get_next_queue(cfqd);
- __cfq_set_active_queue(cfqd, cfqq);//设定active_queue为cfqq
- return cfqq;
- }
- static struct cfq_queue *cfq_set_active_queue(struct cfq_data *cfqd,
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq)
- {
- if (!cfqq)//假如没指定cfqq,则从service_tree中最前的节点
- cfqq = cfq_get_next_queue(cfqd);
- __cfq_set_active_queue(cfqd, cfqq);//设定active_queue为cfqq
- return cfqq;
- }
队列选择完毕,下面要通过cfq_dispatch_request()函数在队列中选择合适的request进行发送
- static bool cfq_dispatch_request(struct cfq_data *cfqd, struct cfq_queue *cfqq)
- {
- struct request *rq;
- BUG_ON(RB_EMPTY_ROOT(&cfqq->sort_list));
- //先判断是否确定发放cfqq里的请求
- if (!cfq_may_dispatch(cfqd, cfqq))
- return false;
- /*
- * follow expired path, else get first next available
- */
- /*这里先检查fifo中的请求,如果fifo为空或者fifo中第一个请求的期限还没到,则不会获取到request*/
- rq = cfq_check_fifo(cfqq);
- if (!rq)//如果fifo中获取rq失败,则考虑备选的next_rq,next_rq总是从扇区的连续性上考虑的
- rq = cfqq->next_rq;
- /*
- * insert request into driver dispatch list
- */
- cfq_dispatch_insert(cfqd->queue, rq);//将rq插入到设备的请求队列
- if (!cfqd->active_cic) {
- struct cfq_io_context *cic = RQ_CIC(rq);
- atomic_long_inc(&cic->ioc->refcount);
- cfqd->active_cic = cic;
- }
- return true;
- }
- static bool cfq_dispatch_request(struct cfq_data *cfqd, struct cfq_queue *cfqq)
- {
- struct request *rq;
- BUG_ON(RB_EMPTY_ROOT(&cfqq->sort_list));
- //先判断是否确定发放cfqq里的请求
- if (!cfq_may_dispatch(cfqd, cfqq))
- return false;
- /*
- * follow expired path, else get first next available
- */
- /*这里先检查fifo中的请求,如果fifo为空或者fifo中第一个请求的期限还没到,则不会获取到request*/
- rq = cfq_check_fifo(cfqq);
- if (!rq)//如果fifo中获取rq失败,则考虑备选的next_rq,next_rq总是从扇区的连续性上考虑的
- rq = cfqq->next_rq;
- /*
- * insert request into driver dispatch list
- */
- cfq_dispatch_insert(cfqd->queue, rq);//将rq插入到设备的请求队列
- if (!cfqd->active_cic) {
- struct cfq_io_context *cic = RQ_CIC(rq);
- atomic_long_inc(&cic->ioc->refcount);
- cfqd->active_cic = cic;
- }
- return true;
- }
在发送具体的request之前,先要确定是否适合为该队列发放请求,主要是判断队列在时间片内发送的请求数有没有超额
- static bool cfq_may_dispatch(struct cfq_data *cfqd, struct cfq_queue *cfqq)
- {
- unsigned int max_dispatch;
- /*
- * Drain async requests before we start sync IO
- */
- //如果cfqq可以被idle并且设备有异步请求处理,则不进行新的同步请求的发放
- if (cfq_cfqq_idle_window(cfqq) && cfqd->rq_in_driver[BLK_RW_ASYNC])
- return false;
- /*
- * If this is an async queue and we have sync IO in flight, let it wait
- */
- //如果发放的是异步请求并且request_queue中还有同步请求在等待提交,则不方法
- if (cfqd->sync_flight && !cfq_cfqq_sync(cfqq))
- return false;
- //默认max_dispatch为预定的cfq_quantum,也就是说cfqq在时间片内最多dispatch
- //cfq_quantum个请求
- max_dispatch = cfqd->cfq_quantum;
- //如果cfqq的优先级类为idle,则在时间片内只能dispatch一个请求
- if (cfq_class_idle(cfqq))
- max_dispatch = 1;
- /*
- * Does this cfqq already have too much IO in flight?
- */
- //如果队列发放下去的请求数超额
- if (cfqq->dispatched >= max_dispatch) {
- /*
- * idle queue must always only have a single IO in flight
- */
- if (cfq_class_idle(cfqq))//如果是idle优先级,则不能进行发放
- return false;
- /*
- * We have other queues, don't allow more IO from this one
- */
- if (cfqd->busy_queues > 1)//如果有其他的队列在等待发放请求,则不进行发放
- return false;
- /*
- * Sole queue user, allow bigger slice
- */
- //如果service_tree中只有该队列,且优先级高于idle,则扩宽max_dispatch的限制
- max_dispatch *= 4;
- }
- /*
- * Async queues must wait a bit before being allowed dispatch.
- * We also ramp up the dispatch depth gradually for async IO,
- * based on the last sync IO we serviced
- */
- /*下面根据最后一次发送的同步请求和现在的时间间隔以及同步请求时间片的值,计算出
- depth,根据depth重置max_dispatch,这里的意图应该是在从同步请求的发送转为
- 异步请求的发送时,延迟一下异步请求的发送*/
- if (!cfq_cfqq_sync(cfqq) && cfqd->cfq_latency) {
- unsigned long last_sync = jiffies - cfqd->last_end_sync_rq;
- unsigned int depth;
- depth = last_sync / cfqd->cfq_slice[1];
- if (!depth && !cfqq->dispatched)
- depth = 1;
- if (depth < max_dispatch)
- max_dispatch = depth;
- }
- /*
- * If we're below the current max, allow a dispatch
- */
- return cfqq->dispatched < max_dispatch;
- }
- static bool cfq_may_dispatch(struct cfq_data *cfqd, struct cfq_queue *cfqq)
- {
- unsigned int max_dispatch;
- /*
- * Drain async requests before we start sync IO
- */
- //如果cfqq可以被idle并且设备有异步请求处理,则不进行新的同步请求的发放
- if (cfq_cfqq_idle_window(cfqq) && cfqd->rq_in_driver[BLK_RW_ASYNC])
- return false;
- /*
- * If this is an async queue and we have sync IO in flight, let it wait
- */
- //如果发放的是异步请求并且request_queue中还有同步请求在等待提交,则不方法
- if (cfqd->sync_flight && !cfq_cfqq_sync(cfqq))
- return false;
- //默认max_dispatch为预定的cfq_quantum,也就是说cfqq在时间片内最多dispatch
- //cfq_quantum个请求
- max_dispatch = cfqd->cfq_quantum;
- //如果cfqq的优先级类为idle,则在时间片内只能dispatch一个请求
- if (cfq_class_idle(cfqq))
- max_dispatch = 1;
- /*
- * Does this cfqq already have too much IO in flight?
- */
- //如果队列发放下去的请求数超额
- if (cfqq->dispatched >= max_dispatch) {
- /*
- * idle queue must always only have a single IO in flight
- */
- if (cfq_class_idle(cfqq))//如果是idle优先级,则不能进行发放
- return false;
- /*
- * We have other queues, don't allow more IO from this one
- */
- if (cfqd->busy_queues > 1)//如果有其他的队列在等待发放请求,则不进行发放
- return false;
- /*
- * Sole queue user, allow bigger slice
- */
- //如果service_tree中只有该队列,且优先级高于idle,则扩宽max_dispatch的限制
- max_dispatch *= 4;
- }
- /*
- * Async queues must wait a bit before being allowed dispatch.
- * We also ramp up the dispatch depth gradually for async IO,
- * based on the last sync IO we serviced
- */
- /*下面根据最后一次发送的同步请求和现在的时间间隔以及同步请求时间片的值,计算出
- depth,根据depth重置max_dispatch,这里的意图应该是在从同步请求的发送转为
- 异步请求的发送时,延迟一下异步请求的发送*/
- if (!cfq_cfqq_sync(cfqq) && cfqd->cfq_latency) {
- unsigned long last_sync = jiffies - cfqd->last_end_sync_rq;
- unsigned int depth;
- depth = last_sync / cfqd->cfq_slice[1];
- if (!depth && !cfqq->dispatched)
- depth = 1;
- if (depth < max_dispatch)
- max_dispatch = depth;
- }
- /*
- * If we're below the current max, allow a dispatch
- */
- return cfqq->dispatched < max_dispatch;
- }
通过检查后,则要正式开始选择request,选择的原则是:如果fifo中的第一个请求期限已到,则选择该请求,否则选择next_rq指针指定的请求,该指针指向的请求总是从物理扇区的连续性上考虑的。最后调用cfq_dispatch_insert()函数将request插入到request_queue中去,等待块设备的响应
- static void cfq_dispatch_insert(struct request_queue *q, struct request *rq)
- {
- struct cfq_data *cfqd = q->elevator->elevator_data;
- struct cfq_queue *cfqq = RQ_CFQQ(rq);
- cfq_log_cfqq(cfqd, cfqq, "dispatch_insert");
- cfqq->next_rq = cfq_find_next_rq(cfqd, cfqq, rq);//选择一个扇区间隙最近的请求赋给next_rq作为下一个请求的备选
- cfq_remove_request(rq);//将rq从sort_list和fifo中移除
- cfqq->dispatched++;
- elv_dispatch_sort(q, rq);//将rq分派到request queue的请求队列等候响应
- if (cfq_cfqq_sync(cfqq))
- cfqd->sync_flight++;
- }