Android 4.0 Service Framework
1 Android本地服务基本框架
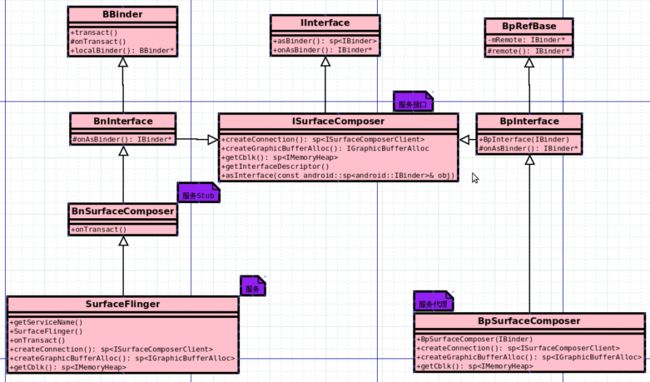
下图是Android本地服务基本框架类图,类图中指名了个类中主要成员以及成员函数,这些成员函数都是用来实现系统服务的。
图1-1 Native Service 类
(1)IBinder,BBinder BpBinder:IBinder类是对Android Binder的抽象,BBinder和BpBinder分别是它的两个子类。BBinder负责接收RPC代码和数据,并在Binder Driver内部生成Binder节点,其中Bpinder保存服务的Handle句柄,用于Binder Driver寻址
(2)IInterface,BnInterface BpInterface: Iinterface类提供类型转换功能,将服务或服务代理转换成IBinder类型,BnInterface和BpInterface是转换的实现,其中BnInterface将服务类转换成IBinder类型,BpInterface将服务代理类转换成IBinder类型
(3)ProcessState:用来管理Binder Driver
(4)IPCThreadState:用于支持服务Client,Service Server(Context Manager)与Binder Driver间的Binder IPC通信
(5)Parcel:当服务与服务代理之间进行Binder IPC通信时, Parcel负责保存Binder IPC数据
2 Android本地服务运行机制
本文将以SurfaceFlinger服务为例,来说明服务的运行机制,下图表示SurfaceFlinger服务的主要类
图2-1SurfaceFlinger服务类图
2.1服务接口<->creatConnection()
服务函数在服务接口类ISurfaceComposer类中声明,并在服务SurfaceFlinger类和服务代理类BpSurfaceComposer类中被实现,比如上面的creatConnection()服务函数,在服务接口中被声明,并且该函数在SurfaceFlinger服务类和BpSurfaceComposer代理类都得到实现。另外在服务接口中还有其他的成员函数。
在surfaceFlinger服务中存在ISurfaceComposer的服务接口,代码如下:frameworks/base/libs/gui/ISurfaceComposer.cpp
class ISurfaceComposer : public IInterface
{
public:
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(SurfaceComposer);/*关注这个宏*/
/************省略部分*******************/
/* create connection with surface flinger, requires
* ACCESS_SURFACE_FLINGER permission
* 利用这个接口和SurfaceFlinger服务创建连接,后面着重分析这个函数
*/
virtual sp<ISurfaceComposerClient> createConnection() = 0;
/* create a graphic buffer allocator
*/
virtual sp<IGraphicBufferAlloc> createGraphicBufferAlloc() = 0;
/* retrieve the control block */
virtual sp<IMemoryHeap> getCblk() const = 0;
/* open/close transactions.
*requires ACCESS_SURFACE_FLINGER permission
*/
virtual void setTransactionState(const Vector<ComposerState>& state,
int orientation, uint32_t flags) = 0;
/* Capture the specified screen. requires READ_FRAME_BUFFER permission
* This function will fail if there is a secure window on screen.
*/
virtual status_t captureScreen(DisplayID dpy,
sp<IMemoryHeap>* heap,
uint32_t* width, uint32_t* height, PixelFormat* format,
uint32_t reqWidth, uint32_t reqHeight,
uint32_t minLayerZ, uint32_t maxLayerZ) = 0;
/***********省略部分*****************************************/
};
IsurfaceComposer类的主要特征如下:
-
(1)IsurfaceComposer类继承IInterface类
-
(2)使用DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(SurfaceComposer)构造asInterface函数
-
(3)声明createConnection()函数,通过该函数和SurfaceFlinger通信
(1)Iinterface类介绍:
frameworks/base/include/binder/IInterface.h
class IInterface : public virtual RefBase
{
public:
IInterface();
sp<IBinder> asBinder();//通过他调用onAsBinder
sp<const IBinder> asBinder() const;
protected:
virtual ~IInterface();
};
Iinterface类的主要功能是支持服务和IBinder类型之间的转换,Iinterface类通过asBinder()函数将ISurfaceComposer类型转换成IBinder类型,在进行IPC通信时,IBinder对象被保存到RPC数据中,然后传给BinderDriver,下面看Iinterface::asBinder()接口的实现。
frameworks/base/include/binder/IInterface.cpp
sp<IBinder> IInterface::asBinder()
{
return this ? onAsBinder() : NULL;
}
回到图1-1可一发现上述函数中的asBinder()接口分别在BnInterface类和BpInterface类中被实现,但是他们的实现各不相同,BnInterface和BpInterface是两个模板类,onAsBinder()也是个模板函数其实现如下:
frameworks/base/include/binder/IInterface.h
template<typename INTERFACE>
IBinder* BnInterface<INTERFACE>::onAsBinder()
{
return this;
}
template<typename INTERFACE>
inline IBinder* BpInterface<INTERFACE>::onAsBinder()
{
return remote();
}
由代码可以发现BnInterface中的onAsBinder()的实现是返回其本身,而BpInterface中的onAsBinder()实现是调用remote()函数,进而调用BpRefBase类的remote()函数最后返回mRemote变量,正好mRemote是IBinder类型。
(2)DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(SurfaceComposer)
在isurfaceComposer类中定义了DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(SurfaceComposer)宏
下面来分析Android中是怎么处理该宏的
frameworks/base/include/binder/IInterface.h
#define DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE) \
static const android::String16 descriptor; \
static android::sp<I##INTERFACE> asInterface( \
const android::sp<android::IBinder>& obj); \
virtual const android::String16& getInterfaceDescriptor() const;\
I##INTERFACE(); \
virtual ~I##INTERFACE();
#define DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(SurfaceComposer) \
static const android::String16 descriptor; \
static android::sp<ISurfaceComposer> asInterface( \
const android::sp<android::IBinder>& obj); \
virtual const android::String16& getInterfaceDescriptor() const; \
ISurfaceComposer(); \
virtual ~ISurfaceComposer();
经过DECLARE_META_INTERFACE宏预处理后我们可以得到asInterface()函数,那么它的实现在那里呢?在IInterface.h中还定义了另外一个宏用来实现该函数,代码如下:
frameworks/base/include/binder/IInterface.h
#define IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE, NAME) \
const android::String16 I##INTERFACE::descriptor(NAME); \
const android::String16& \
I##INTERFACE::getInterfaceDescriptor() const { \
return I##INTERFACE::descriptor; \
} \
android::sp<I##INTERFACE> I##INTERFACE::asInterface( \
const android::sp<android::IBinder>& obj) \
{ \
android::sp<I##INTERFACE> intr; \
if (obj != NULL) { \
intr = static_cast<I##INTERFACE*>( \
obj->queryLocalInterface( \
I##INTERFACE::descriptor).get()); \
if (intr == NULL) { \
intr = new Bp##INTERFACE(obj); \
} \
} \
return intr; \
} \
I##INTERFACE::I##INTERFACE() { } \
I##INTERFACE::~I##INTERFACE() { } \
当然了有定义就有实现的,在ISurfaceComposer.cpp中定义着相对应的宏,如下
IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(SurfaceComposer,"android.ui.ISurfaceComposer");
接着将这两个参数传进去进行处理
#define IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(SurfaceComposer, NAME) \
const android::String16 ISurfaceComposer::descriptor(NAME); \
const android::String16& \
ISurfaceComposer::getInterfaceDescriptor() const { \
return ISurfaceComposer::descriptor; \
} \
android::sp<ISurfaceComposer> IsurfaceComposer::asInterface( \
const android::sp<android::IBinder>& obj) \
{ \
android::sp<ISurfaceComposer> intr; \
if (obj != NULL) { \
intr = static_cast<ISurfaceComposer*>( \
obj->queryLocalInterface( \
ISurfaceComposer::descriptor).get()); \
if (intr == NULL) { \
intr = new BpSurfaceComposer(obj); \
} \
} \
return intr; \
} \
ISurfaceComposer::ISurfaceComposer() { } \
ISurfaceComposer::~ISurfaceComposer() { }
经过上面两步的处理可以得到IsurfaceComposer类对应的asInterface()函数的真身了
const String16 ISurfaceComposer::descriptor("android.ui.ISurfaceComposer")
const String16&
ISurfaceComposer::getInterfaceDescriptor() const {
/*直接返回android.ui.ISurfaceComposer*/
return ISurfaceComposer::descriptor;
}
sp<ISurfaceComposer> IsurfaceComposer::asInterface(const sp<IBinder>& obj)
{
sp<ISurfaceComposer> intr;
if (obj != NULL) {
intr = static_cast<ISurfaceComposer*>(
obj->queryLocalInterface(
ISurfaceComposer::descriptor).get());
if (intr == NULL) {
intr = new BpSurfaceComposer(obj);
}
}
return intr;
}
由此可知asInterface()函数的参数有两种类型,BBinder或BpBinder,它们都是IBinder类型。
如果参数是Bpinder类型,则IBinder的queryLocalInterface()将被调用,如下:
sp<IInterface> IBinder::queryLocalInterface(const String16& descriptor)
{
return NULL;
}
如果参数是BBinder类型,则BnInterface的queryLocalInterface将被调用,BnInterface的queryLocalInterface()函数是一个模板函数,如果参数值是ISurfaceComposer接口的名称"android.ui.ISurfaceComposer"则返回BnIntreface的实例。如下:
template<typename ISurfaceComposer>
inline sp<IInterface> BnInterface<ISurfaceComposer>::queryLocalInterface(
const String16& _descriptor)
{
if (_descriptor == IsurfaceComposer::descriptor)
/*返回BnInterface实例*/
return this;
return NULL;//否则
}
最后通过static_cast<ISurfaceComposer*>(BnInterface)将BnInterface类型转换成IsurfaceComposer类型的实例,最后由asInterface()函数将该实例返回
(3)服务函数createConnection()的声明
这个很简单了在frameworks/base/libs/gui/ISurfaceComposer.h中一行代码彻底搞定重要的是它的实现。后面会分析
2.3服务Stub
服务函数在服务类中被实现,比如上面说的createConnection()函数,它在SurfaceFlinger类中被实现,但是要怎么调用它?这时服务Stub类的作用来了也就是被SurfaceFlinger继承的BnSurfaceComposer,SurfaceFlinger类的定义如下:
frameworks/base/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
class SurfaceFlinger :
public BinderService<SurfaceFlinger>,
public BnSurfaceComposer,//服务Stub类
public IBinder::DeathRecipient,
protected Thread
{
public:
static char const* getServiceName() { return "SurfaceFlinger"; }
SurfaceFlinger();
void init();
virtual status_t onTransact(
uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags);
// ISurfaceComposer interface
virtual sp<ISurfaceComposerClient> createConnection();
/****************省略很多行代码**************************/
}
BnSurfaceComposer服务Stub类有什么作用?
frameworks/base/libs/gui/ISurfaceComposer.cpp
class BnSurfaceComposer : public BnInterface<ISurfaceComposer>
{
public:
/*
*@ code:RPC代码 如CREATE_CONNECTION等
*@ data:RPC数据
*@ reply:响应数据
*/
virtual status_t onTransact( uint32_t code,
const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply,
uint32_t flags = 0);
};
BnSurfaceComposer服务Stub类负责分析SurfaceFlinger服务中使用的RPC代码,并调用SurfaceFlinger类中的相应的函数
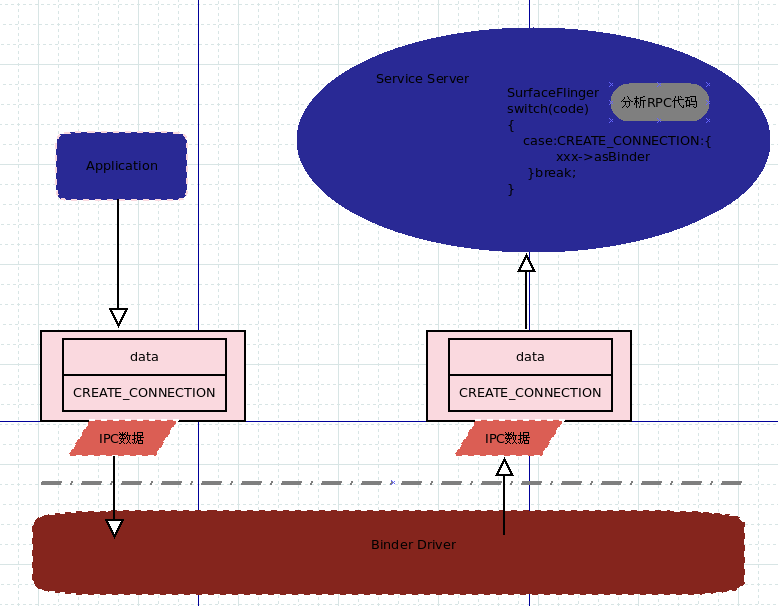
图2-3 RPC数据与RPC代码应用
再回过头去看看BnSurfaceComposer,SurfaceFlinger,BnInterface,ISurfaceComposer之间的关系如下图:
图2-4
3 Service Manager运行机制
ServiceManager的运行机制包括三步
(1)ServiceManager Init
-
Create ProcessState
-
Create BpBinder
-
Create BpServiceManager
(2)Register XXX Service
(3)Get xxx service information
3.1 Service Manager Init
以surfaceflinger的main函数为例进行代码分析
frameworks/base/cmds/surfaceflinger/main_surfaceflinger.cpp
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
SurfaceFlinger::publishAndJoinThreadPool();
return 0;
}
frameworks/base/include/binder/BinderService.h
template<typename SERVICE>
class BinderService
{
public:
/****************省略部分**************/
static void publishAndJoinThreadPool() {
sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());/*(a)*/
/*return BpServiceManager(b)(c)*/
sp<IServiceManager> sm(defaultServiceManager());
/****************省略部分**************/
}
/****************省略部分**************/
};
(a)CreateProcessState
frameworks/base/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::self()
{
/*on first the gProcess is NULL*/
if (gProcess != NULL) /*gProcess是一个全局变量用来保存ProcessState对象*/
return gProcess;
AutoMutex _l(gProcessMutex);
if (gProcess == NULL) /*构建ProcessState实例并保存到gProcess中*/
gProcess = new ProcessState;
return gProcess;
}
ProcessState::ProcessState()
: mDriverFD(open_driver())/*open the Binder Driver*/
, mVMStart(MAP_FAILED)/*保存mmap映射后的起始地址*/
, mManagesContexts(false)
, mBinderContextCheckFunc(NULL)
, mBinderContextUserData(NULL)
, mThreadPoolStarted(false)
, mThreadPoolSeq(1)
{
if (mDriverFD >= 0) {
#if !defined(HAVE_WIN32_IPC)
/*进行内存映射*/
mVMStart = mmap(0, BINDER_VM_SIZE, PROT_READ,
MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE, mDriverFD, 0);
if (mVMStart == MAP_FAILED) {
close(mDriverFD);
mDriverFD = -1;
}
#else
mDriverFD = -1;
#endif
}
}
ProcessState构造函数的主要功能是打开BinderDriver设备,并将返回的文件描述符保存到mDriverFD成员变量当中,对BinderDriver调用mmap进行内存映射,将映射后的起始地址保存到mVMStart成员变量中,该区域用于保存BinderDriver接收BinderRPC数据
(b)CreateBpBinder
在publishAndJoinThreadPool()函数的第2行代码中调用了IserviceManager的defaultServiceManager()函数,用于创建BpServiceManager实例对象。下面来分析defaultServiceManager()函数的实现。
frameworks/base/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp
sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager()
{
if (gDefaultServiceManager != NULL) return gDefaultServiceManager;
/*gDefaultServiceManager是一个全局变量,用于保存ServiceManager实例*/
{
AutoMutex _l(gDefaultServiceManagerLock);
if (gDefaultServiceManager == NULL) {
gDefaultServiceManager = interface_cast<IServiceManager>(
ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL));
}
/*interface_cast<IServiceManager>(new BpBinder(0))*/
}
/*return BpserviceManger*/
return gDefaultServiceManager;
}
在第一次执行的时候应该gDefaultServiceManager为NULL,上述代码首先通过ProcessState实例对象调用ProcessState的getContextObject()函数,该函数返回BpBinder然后再使用interface_cast<IServiceManager>(newBpBinder(0))转换成IServiceManager类型,最后将生成的BpserviceManger保存到gDefaultServiceManager全局变量当中
首先来分析ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL)
frameworks/base/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp
/*The caller value is NULL Or 0 return IBinder instance*/
sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getContextObject(const sp<IBinder>& caller)
{
return getStrongProxyForHandle(0);/*0 is Context Manger Handle*/
}
从代码中我们可以看到它把工作交给了getStrongProxyForHandle(0),其中将服务的Handle值做为参数传递进去,当Handle的值为0的时候,表明它是ContextManager服务的Handle,其实ServiceManager就好比是ContextManager的代理。
sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle(int32_t handle)
{
sp<IBinder> result;
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
handle_entry* e = lookupHandleLocked(handle);
if (e != NULL) {
IBinder* b = e->binder;
if (b == NULL || !e->refs->attemptIncWeak(this)) {
b = new BpBinder(handle); /*看到了吧BpBinder就是在这里生成的*/
e->binder = b;
if (b) e->refs = b->getWeakRefs();
result = b;
} else {
result.force_set(b);
e->refs->decWeak(this);
}
}
return result;
}
由此可知由于我们传入的Handle值为0,所以该BpBinder对象中持有ServiceManager的服务Handle
(c)CreateBpServiceManager
这个过程其实在2.1中已经说过,这里简单的说说interface_cast<IServiceManager>
template<typename INTERFACE>
inline sp<INTERFACE> interface_cast(const sp<IBinder>& obj)
{
return INTERFACE::asInterface(obj);
}
这是一个模板代码段,当在(b)中被调用的时候INTERFACE将会被IServiceManager所替代,经过转换最终将调用IServiceManager的asInterface()函数,不是么?不过该函数并不存在的它是有两个宏扩展而来的
/*ServiceManager.h*/
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager)
/*ServiceManager.cpp*/
IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager,"android.os.IServiceManager");
下面看asInterface()真身,其转化过程请看2.1节
sp<ServiceManager> IsurfaceComposer::asInterface(const sp<IBinder>& obj)
{
sp<ServiceManager> intr;
if (obj != NULL) {
intr = static_cast<ServiceManager*>(
obj->queryLocalInterface(
ServiceManager::descriptor).get());
if (intr == NULL) { /*这里的obj是BpBinder吧*/
intr = new BpServiceManager(obj);
}
}
return intr;
}
这里关心一下BpServiceManager的构造函数,我第一次看这代码的时候,发现什么都没做。。。
frameworks/base/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp
class BpServiceManager : public BpInterface<IServiceManager>
{
public:
BpServiceManager(const sp<IBinder>& impl)
: BpInterface<IServiceManager>(impl)/*不要忽略这个地方了*/
{
}
/............../
}
由此可知,在构造BpServiceManager实例的时候,传入BpBinder实例对象指针,并且该实例指针持有ContexManager的服务Handle,同时在构建BpBinder的时候BpBinder实例被保存到BpServiceManager父类BpRefBase的mRemote成员变量当中去了,它的获取流程如下:
---->BpServiceManager子类
---->BpInterface::onAsBinder()父类
---->BpRefBase::remote()父父类
---->returnmRemote
3.2 Registration XXX Service
在3.1中已经说了ServiceManager的运行机制,接下来看Android中一个服务是怎么向ServiceManager注册的,这里将以Surfaceflinger服务为例
还是回到surfaceflinger的main函数,现在已经到publishAndJoinThreadPool()函数的第4行代码了
sm->addService(String16(SERVICE::getServiceName()), newSERVICE());
此时sm是不是就是defaultServiceManager()返回的BpServiceManager实例?SERVICE是不是SurfaceFlinger?
将其转换变成如下:
sm->addService(String16(SurfaceFlinger::getServiceName()),newSurfaceFlinger());/*是不是?*/
将其转换变成如下:sm->addService(String16(SurfaceFlinger::getServiceName()),newSurfaceFlinger());
上述代码通过defaultServiceManager()返回的BpServiceManager对象调用它本身的addService()成员函数,将SurfaceFlinger的服务名称以及新生成的SurfaceFlinger的实例指针传入到函数当中。下面这图体现了SurfaceFlinger向ServiceManager注册的过程
图 3-2 SurfaceFlinger注册流程
接下来来分析BpServiceManager的addService()函数
virtual status_t addService(const String16& name,
const sp<IBinder>& service)
{
Parcel data, reply;
/*return android.os.IServiceManager*/
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor());
/*************************************************************
*26* "android.os.IServiceManager" *14 * "SurfaceFlinger" *
************************************************************/
/*set the service name to data*/
data.writeString16(name);
data.writeStrongBinder(service);
/*remote() :return BpBinder*/
status_t err = remote()->
transact(ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, &reply);
/*等待着回应?*/
return err == NO_ERROR ? reply.readExceptionCode() : err;
}
功能如下:
-
调用IServiceManager的getInterfaceDescriptor方法返回”android.os.IserviceManager”然后调用Parcel的writeInterfaceToken函数将ServiceManager服务的名称写入到data当中,并且按照字符串的长度以及字符串本身的顺序将其进行保存
-
调用Parcel的writeString16将SurfaceFlinger服务的名称”SurfaceFlinger”保存到data中
-
调用writeStrongBinder将SurfaceFlinger实例按照flat_binder_object结构体的形式将其保存到data当中,其中writeStrongBinder方法是调用flatten_binder()对Surfaceflinger实例进行保存的
-
最后调用BpRefBase类的remote()函数获取保存在IBinder中mRemote成员变量(mRemote保存着上面我们获得的BpBinder没错吧)从而可以解释成调用BpBinder的transact()函数将BinderRPC数据发送到BinderDriver中去
然后再看writeStrongBinder()和transact()是怎么实现的
frameworks/base/libs/binder/Parcel.cpp
status_t Parcel::writeStrongBinder(const sp<IBinder>& val)
{
return flatten_binder(ProcessState::self(), val, this);
}
/*Elvira <[email protected]> for Debug
*Because SurfaceFlinger inheritance BBinder
*so local is not null
*/
status_t flatten_binder(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const sp<IBinder>& binder, Parcel* out)
{
flat_binder_object obj;
obj.flags = 0x7f | FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS;
if (binder != NULL) {
/*用来判断当前传进来的binder参数是否是BBinder对象
*当然了这时我们传入的是new Surfaceflinger()是吧
* Surfaceflinger肯定是BBinder了因为继承的关系嘛
*/
IBinder *local = binder->localBinder();
if (!local) {//因为这时候不为NULL所以跳向else分支
BpBinder *proxy = binder->remoteBinder();
if (proxy == NULL) {
LOGE("null proxy");
}
const int32_t handle = proxy ? proxy->handle() : 0;
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE;
obj.handle = handle;
obj.cookie = NULL;
} else {
//根据这个在BinderDriver中生成新的节点
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
obj.binder = local->getWeakRefs();/*目前对C++的Weak还不是很懂*/
obj.cookie = local;/*这里用来保存new Surfaceflinger()实例*/
}
} else {
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
obj.binder = NULL;
obj.cookie = NULL;
}
/*最后调用它将flat_binder_object结构保存到data当中了吧*/
return finish_flatten_binder(binder, obj, out);
}
在上面这段代码中引出了flat_binder_object数据结构我们不妨看看它,他是在BinderDriver中定义的,它的定义形式如下:
drivers/staging/android/binder.h
struct flat_binder_object {
/* 8 bytes for large_flat_header. */
unsigned long type;/*see BINDER_TYPE_*/
unsigned long flags;
/* 8 bytes of data. */
union {
void *binder; /* local object */
signed long handle; /* remote object 这个用来保存handle值*/
};
/* extra data associated with local object */
void *cookie;/*保存服务实例指针*/
};
到这里我们发送给BinderDriver的RPC数据就已经准备好了,接下来肯定就是将这些东西附加上Binder协议正式的发送到BinderDriver了。然后再返回到addService函数当中,分析一下BpBinder的transact()函数了,transact()这一层次就是所谓的IPC层,生成真正的BinderIPC数据
transact()是BpBinder类中的一个成员函数,代码如下:
frameworks/base/libs/binder/BpBinder.cpp
status_t BpBinder::transact(
uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
{
// Once a binder has died, it will never come back to life.
if (mAlive) {
status_t status = IPCThreadState::self()->transact(
mHandle, code, data, reply, flags);
if (status == DEAD_OBJECT) mAlive = 0;
return status;
}
return DEAD_OBJECT;
}
由此可知,从BpServiceManager中的addService()经过包装的Parcel类型的RPC代码和数据都被传递到这里来了吧,并且BpBinder::transact()把所有的工作都交接给了IPCThreadState::self()->transact()同时将BpBinder对象中持有的mHandle值也随之传递进来,在这里mHandle应该是等于0的代表着ServiceManager的handle值,下面来看它的实现
frameworks/base/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
status_t IPCThreadState::transact(int32_t handle,
uint32_t code, const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
{
//代码去掉一些无关信息
status_t err = data.errorCheck();/*检查传进来的参数是否有效*/
flags |= TF_ACCEPT_FDS;/*0x10 allow replies with file descriptors*/
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
//这一句是关键这一句创建binder_transaction_data数据结构
err = writeTransactionData(BC_TRANSACTION, flags,
handle, code, data, NULL);
}
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
if (reply) reply->setError(err);
return (mLastError = err);
}
if ((flags & TF_ONE_WAY) == 0) {//这一句成立内核bind.h中定义了该宏
if (reply) {
err = waitForResponse(reply);//然后调用这一句
} else {
Parcel fakeReply;
err = waitForResponse(&fakeReply);
}
} else {
err = waitForResponse(NULL, NULL);
}
return err;
}
从这个函数的代码来看,总的来说就是先向BinderDriver先数据了,然后再等待BinderDriver的回应,具体的过程就先放一放这个函数,先分析一下该函数调用的另一个函数writeTransactionData()是怎么实现的
/*binder.h*/
struct binder_transaction_data {
/* The first two are only used for bcTRANSACTION and brTRANSACTION,
* identifying the target and contents of the transaction.
*/
union {
size_t handle;/* target descriptor of command transaction */
void *ptr; /* target descriptor of return transaction */
} target;/*它保存着目标服务的实例指针以及目标服务的handle值*/
void *cookie;/*target object cookie 指向flat_binder_object */
unsigned int code; /* transaction command */
/* General information about the transaction. */
unsigned int flags;
pid_t sender_pid;
uid_t sender_euid;
size_t data_size; /* number of bytes of data */
size_t offsets_size; /* number of bytes of offsets */
/* If this transaction is inline, the data immediately
* follows here; otherwise, it ends with a pointer to
* the data buffer.
*/
union {
struct {
/* transaction data */
const void *buffer;
/* offsets from buffer to flat_binder_object structs */
const void *offsets;/*表示flat_binder_object在data中偏移*/
} ptr;
uint8_t buf[8];
} data;
};
frameworks/base/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
status_t IPCThreadState::writeTransactionData(int32_t cmd, uint32_t binderFlags,int32_t handle, uint32_t code,
const Parcel& data, status_t* statusBuffer)
{
binder_transaction_data tr;/*该结构是在内核中定义的*/
/*init the binder_transaction_data */
/*(A)*/
tr.target.handle = handle;/*这里我们是向ServiceManager目标服务注册吧?*/
tr.code = code;/*RPC代码ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION表示我是要注册*//*(B)*/
tr.flags = binderFlags;/*TF_ACCEPT_FDS*/
tr.cookie = 0;
tr.sender_pid = 0;
tr.sender_euid = 0;
const status_t err = data.errorCheck();
if (err == NO_ERROR) {//这些东西都应该能看懂,不过理解它的含义恐怕还是要结合驱动
tr.data_size = data.ipcDataSize();/*IPC数据大小()*//*(C)*/
tr.data.ptr.buffer = data.ipcData();/*(D)*/
tr.offsets_size = data.ipcObjectsCount()*sizeof(size_t);/*(E)*/
tr.data.ptr.offsets = data.ipcObjects();/*(F)*/
} else if (statusBuffer) {
tr.flags |= TF_STATUS_CODE;
*statusBuffer = err;
tr.data_size = sizeof(status_t);
tr.data.ptr.buffer = statusBuffer;
tr.offsets_size = 0;
tr.data.ptr.offsets = NULL;
} else {
return (mLastError = err);
}
/*cmd BC_TRANSACTION表示Binder协议,协议部分主要有RC_XX和BR_XX组成*/
mOut.writeInt32(cmd);
mOut.write(&tr, sizeof(tr));/*写入binder_transaction_data数据*/
return NO_ERROR;
}
到这里Binder协议BC_TRANSACTION与binder_transaction_data数据结构到mOut中了,其中IPCThreadState持有mOut和mIn两个成员变量,他们都是Parcel类型,其中mOut用来发送数据,mIn用来接收数据。现在可以总结一下了所谓的BinderIPC数据是不是就是由Binder协议部分再加上binder_transaction_data数据结构组成的啊,为了弄明白上面代码中的(A)(B)(C)(D)(E)(F)下面给出一个图。好好的理解这图大有裨益。
图3-3binder_transaction_data数据结构(注册的时候)
再回到IPCThreadState::transact()中的waitForResponse()函数,用于发送请求和接收回复
status_t IPCThreadState::waitForResponse(Parcel *reply,
status_t *acquireResult)
{
int32_t cmd;
int32_t err;
while (1) {
if ((err=talkWithDriver()) < NO_ERROR) break;
err = mIn.errorCheck();
if (err < NO_ERROR) break;
if (mIn.dataAvail() == 0) continue;
cmd = mIn.readInt32();
switch (cmd) {
case BR_REPLY:
{
binder_transaction_data tr;
err = mIn.read(&tr, sizeof(tr));
if (err != NO_ERROR) goto finish;
if (reply) {
if ((tr.flags & TF_STATUS_CODE) == 0) {
reply->ipcSetDataReference(
reinterpret_cast<const uint8_t*>(tr.data.ptr.buffer),
tr.data_size,
reinterpret_cast<const size_t*>(tr.data.ptr.offsets),
tr.offsets_size/sizeof(size_t),
freeBuffer, this);
}
}
}
default:
err = executeCommand(cmd);
if (err != NO_ERROR) goto finish;
break;
}
}
return err;
}
IPCThreadState::waitForResponse通过调用talkWithDriver()函数,将保存在mOut中的BinderIPC数据传递给BinderDriver,并将来自BinderDriver的BinderIPC数据保存到mIn中。在从BinderDriver接收到的Binder协议当中保存着BR_REPLY,我们看看当Binder协议为BR_REPLY的时候是怎么处理的,它将调用ipcSetDataReference进行处理,先看看talkWithDriver()是怎么实现的
frameworks/base/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp
将代码进行整容就变成下面这些了
status_t IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver(bool doReceive)
{
binder_write_read bwr;
const bool needRead = mIn.dataPosition() >= mIn.dataSize();
const size_t outAvail = (!doReceive || needRead) ? mOut.dataSize() : 0;
bwr.write_size = outAvail;
bwr.write_buffer = (long unsigned int)mOut.data();
if (doReceive && needRead) {
bwr.read_size = mIn.dataCapacity();
bwr.read_buffer = (long unsigned int)mIn.data();
} else {
bwr.read_size = 0;
bwr.read_buffer = 0;
}
if ((bwr.write_size == 0) && (bwr.read_size == 0)) return NO_ERROR;
bwr.write_consumed = 0;
bwr.read_consumed = 0;
status_t err;
do {
#if defined(HAVE_ANDROID_OS)
if (ioctl(mProcess->mDriverFD, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr) >= 0)
err = NO_ERROR;
else
err = -errno;
#else
err = INVALID_OPERATION;
#endif
} while (err == -EINTR);
return err;
}
到这个地方的时候我觉得有必要配合Binder驱动才能解释得清楚了。。。好的让我们看看
ioctl(mProcess->mDriverFD, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr)
是怎么操作Binder设备的,呵呵说到驱动这可是我最喜欢的工作啊,如果时间够,我一定再好好的分析一下Binder驱动的整个过程
/******************************************************************/
struct binder_write_read {
signed long write_size; /* bytes to write */
signed long write_consumed; /* bytes consumed by driver */
unsigned long write_buffer;
signed long read_size; /* bytes to read */
signed long read_consumed; /* bytes consumed by driver */
unsigned long read_buffer;
};
static long binder_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd,
unsigned long arg)
{
int ret;
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data;
struct binder_thread *thread;
unsigned int size = _IOC_SIZE(cmd);
void __user *ubuf = (void __user *)arg;
ret = wait_event_interruptible(binder_user_error_wait,
binder_stop_on_user_error < 2);
if (ret)
return ret;
mutex_lock(&binder_lock);
thread = binder_get_thread(proc);
if (thread == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err;
}
switch (cmd) {
case BINDER_WRITE_READ: {
struct binder_write_read bwr;
if (size != sizeof(struct binder_write_read)) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
if (copy_from_user(&bwr, ubuf, sizeof(bwr))) {
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
if (bwr.write_size > 0) {
ret = binder_thread_write(proc, thread,
(void __user *)bwr.write_buffer,
bwr.write_size, &bwr.write_consumed);
if (ret < 0) {
bwr.read_consumed = 0;
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr)))
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
}
if (bwr.read_size > 0) {
ret = binder_thread_read(proc, thread,
(void __user *)bwr.read_buffer, bwr.read_size,
&bwr.read_consumed, filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK);
if (!list_empty(&proc->todo))
wake_up_interruptible(&proc->wait);
if (ret < 0) {
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr)))
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
}
if (copy_to_user(ubuf, &bwr, sizeof(bwr))) {
ret = -EFAULT;
goto err;
}
break;
}
}