JSON知识总结- Gson(四)List和Map
1.List
简单使用
@Test
public void testList() {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("one");
list.add(122);
String json = gson.toJson(list);
System.out.println("json->" + json);
List list2 = gson.fromJson(json , List.class);
for(Object each : list2) {
System.out.println(each);
}
}
结果:
处理泛型:
class Person {
public int id;
public String name;
public Person(int _id , String _name) {
this.id = _id;
this.name = _name;
}
public String toString() {
return "id->" + id + ",name->" + name;
}
}
@Test
public void testList2() {
List<Person> persons = new ArrayList<Person>();
persons.add(new Person(1 , "one"));
persons.add(new Person(2 , "two"));
String json = gson.toJson(persons);
System.out.println("json->" + json);
Type type = new TypeToken<List<Person>>() {}.getType();
List<Person> anotherPersons = gson.fromJson(json , type);
for(Person each : anotherPersons) {
System.out.println(each);
}
}
结果:
2.Map
简单使用
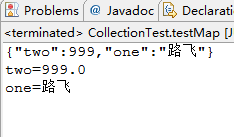
@Test
public void testMap() {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("one" , "路飞");
map.put("two" , 999);
String json = gson.toJson(map);
System.out.println(json);
Map map2 = gson.fromJson(json , Map.class);
for(Object each : map2.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(each);
}
}
结果显示:
使用泛型:
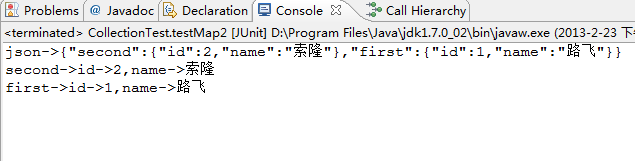
@Test
public void testMap2() {
Map<String , Person> map = new HashMap<String , Person>();
map.put("first" , new Person(1 , "路飞"));
map.put("second", new Person(2 , "索隆"));
String json = gson.toJson(map);
System.out.println("json->" + json);
Type type = new TypeToken<Map<String , Person>>() {}.getType();
Map<String , Person> map2 = gson.fromJson(json , type);
for(String key : map2.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + "->" + map2.get(key));
}
}