Tomcat源码阅读之Mapper分析
Mapper对于Tomcat或者jetty这种应用服务器来说应该算是非常重要的一个东西了。。
首先来说它是干嘛用的,听名字就基本上能猜出来,对于请求,对这个请求进行路由,交给应该负责处理这个请求的最终代码就是Mapp而应该干的或。。
对于servlet来说,对应的就是一次http请求该交给哪一个servlet来处理。
其实以前在看jetty的代码的时候就相当于看过了一种实现的方式,jetty采用的是一种类似于tries(字典树)的查询来进行请求的路由。。。感觉还算是蛮不错的吧。。毕竟字典树在做基于字符串的查询效率还是很高的。。
那么接下来来大体的来说一下tomcat是怎么实现的吧。。。嗯,最关键的就是:二分搜索,字符串也是可以排序的嘛,也就是字典序,那么也就可以做二分搜索咯。。。
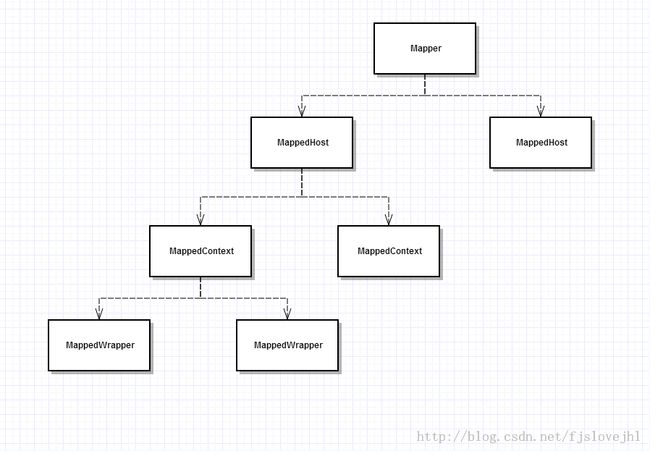
在开始具体的代码之前,先来看一个简略的结构图吧:
这个是整个Mapper的比较简单的总体的结构层次图吧,通过以前的分析我们知道,在tomcat服务器中,可以有多个service,每个service只能有一个engine,而一个engine可以部署多个host,一个host又可以部署多个context,而mapper对象是属于service所拥有的。。。也符合上面的层次图。。。
先来看看上面提到一些对象的定义吧,他们都是定义在Mapper里面的嵌套类:
protected abstract static class MapElement<T> {
public String name = null; //名字
public T object = null; //对应的对象,例如是host对象,context对象或者wrapper对象啥的
}
// ------------------------------------------------------- Host Inner Class
protected static final class MappedHost //对host的map信息
extends MapElement<Host> {
public ContextList contextList = null; //有一个contextlist
}
// ------------------------------------------------ ContextList Inner Class
protected static final class ContextList { //在mappedhost里面将会用其来存拥有的context的信息
public MappedContext[] contexts = new MappedContext[0]; //mappedcontext对象的数组
public int nesting = 0; //所有的context的path中,最多的斜线数目
}
// ---------------------------------------------------- Context Inner Class
protected static final class MappedContext extends MapElement<Context> { //对context的map的信息
public ContextVersion[] versions = new ContextVersion[0]; //版本的数组
}
protected static final class ContextVersion extends MapElement<Context> { //某个context的某个版本的具体信息
public String path = null; //path
public String[] welcomeResources = new String[0]; //welcome的数据
public WebResourceRoot resources = null; //操作当前web应用程序的资源
public MappedWrapper defaultWrapper = null; //默认的wrapper
public MappedWrapper[] exactWrappers = new MappedWrapper[0]; //对wrapper的精确的map
public MappedWrapper[] wildcardWrappers = new MappedWrapper[0]; //基于通配符的map
public MappedWrapper[] extensionWrappers = new MappedWrapper[0]; //基于扩展名的map
public int nesting = 0; // 属于这个context的所有servlet的path里面最大斜线数目
}
// ---------------------------------------------------- Wrapper Inner Class
protected static class MappedWrapper //对wrapper对象的map信息
extends MapElement<Wrapper> {
public boolean jspWildCard = false;
public boolean resourceOnly = false;
}
这里最基本的类型是MapElement,它是一个泛型吧,属性首先是名字,对于host来说,那么就是host的名字了,对于context来说那就是context的path了。。。。以此类推。。
然后是MappedHost的定义,这里其实也就稍微扩展了一下MapElement类型吧,加入了一个ContextList,看名字就知道它用于保存当前host所拥有的所有的host对象。。。ContextList的定义我们可以看到其实也是用数组来保存MappedContext对象的。。。
然后是MappedContext的定义,这里扩展了 一个ContextVersion的数组,因对于context来说,可能在时间段上同一个context可能会重新部署啥的,就涉及到不同的版本了。。当然一般情况下这个数组的长度都是为1的,也就是只有一个版本。。。
接下来就是ContextVersion定义了,可以将它理解为具体的一个context的map的信息,有path,defaultWrapper,以及wrapper的匹配什么的。。分为精确匹配,通配符匹配,和扩展名匹配。。
最后就是MappedWrapper了,扩展的东西不多吧。。主要是一些标记。。。
好啦,接下来来具体的看看Mapper的定义,先来看看它的重要的属性吧:
protected MappedHost[] hosts = new MappedHost[0]; // 对host的map信息
protected String defaultHostName = null; // engine使用的默认的host名字
protected Map<Context, ContextVersion> contextObjectToContextVersionMap = //对context的map信息,key是context对象,value是contextVersion对象
new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
hosts数组,用于保存所有的host的map信息,然后又一个defaultHostName,在engine对象的定义中有一个defaultHostName属性,就是对应的这里。。。
然后就是一个map,用于将context对象与具体的contextVersion匹配起来。。。
好啦,接下来来看看如何在mapper中添加对一个host。。
//添加host的map信息,第一个参数是hsot的名字,第二个是别名,第三个是host对象
public synchronized void addHost(String name, String[] aliases,
Host host) {
MappedHost[] newHosts = new MappedHost[hosts.length + 1]; //创建MappedHost对象的数组,这里长度需要加1
MappedHost newHost = new MappedHost(); //创建一个MappedHost对象,用于保存host的map信息
ContextList contextList = new ContextList(); //ContextList对象,用于保存context
newHost.name = name; //设置名字
newHost.contextList = contextList; //设置
newHost.object = host; //设置对应的host对象
if (insertMap(hosts, newHosts, newHost)) { //这里需要复制以前的host的map信息,并维护好排序
hosts = newHosts; //指向新新的数组
}
for (int i = 0; i < aliases.length; i++) { //遍历这个host的所有的别名,为每一个别名都创建一次map信息,感觉这里做了挺多重复的事情
newHosts = new MappedHost[hosts.length + 1];
newHost = new MappedHost();
newHost.name = aliases[i];
newHost.contextList = contextList; //这里指向同一个contextList
newHost.object = host;
if (insertMap(hosts, newHosts, newHost)) {
hosts = newHosts;
}
}
}
代码应该很简单的吧,这里说白了扩展hosts数组,创建新的MappedHost对象,将其保存起来。。。然后对于最终保存的数组,mappedHost对象是按照name的排序好的。。这里就需要来具体的看一下insertMap方法了。。
private static final <T> boolean insertMap //将oldmap里面的信息保存到newMap,并且还要加入newElement,这里还要基于name进行排序
(MapElement<T>[] oldMap, MapElement<T>[] newMap, MapElement<T> newElement) {
int pos = find(oldMap, newElement.name); //在old里面,最近接新的元素的name的位置,这里返回的pos要么name相当,要么最左侧
if ((pos != -1) && (newElement.name.equals(oldMap[pos].name))) { //这里表示有名字相同的,那么失败
return false;
}
//分段拷贝,这样拷贝完了之后也是排好序的
System.arraycopy(oldMap, 0, newMap, 0, pos + 1); //对数组拷贝,这里相当于先拷贝小的
newMap[pos + 1] = newElement;
System.arraycopy
(oldMap, pos + 1, newMap, pos + 2, oldMap.length - pos - 1);
return true;
}
这里首先调用find方法,通过名字在old里面去寻找是否有相同的,如果有的话,那么返回相同的下标,如果没有的话就返回小于当前name的最大的一个,也就是最左侧的那个。。。然后再进行分段的拷贝,这样也就可以保证按照name的排序进行保存了。。。来看看find方法吧:
//在排序的element里面找与name最接近的,相等的或者小于name的最大的,也就是最左侧的
//这里其实就是一个二分查找
private static final <T> int find(MapElement<T>[] map, String name) {
int a = 0;
int b = map.length - 1;
// Special cases: -1 and 0
if (b == -1) {
return -1;
}
if (name.compareTo(map[0].name) < 0) {
return -1;
}
if (b == 0) {
return 0;
}
int i = 0;
while (true) {
i = (b + a) / 2;
int result = name.compareTo(map[i].name);
if (result > 0) {
a = i;
} else if (result == 0) {
return i;
} else {
b = i;
}
if ((b - a) == 1) {
int result2 = name.compareTo(map[b].name);
if (result2 < 0) {
return a;
} else {
return b;
}
}
}
}
就是一个基于字典序排序的二分搜索嘛。。。。。
好啦,接下来来看看如何添加一个context吧:
//为host添加context,其实也就是添加context的map信息,第一个参数是所属的host的名字,第二个是这个context的path(/examples啥的),第三个是版本,第三个是对应的context对象,接着是首页?,最后是root的资源引用
public void addContextVersion(String hostName, Host host, String path,
String version, Context context, String[] welcomeResources,
WebResourceRoot resources) {
MappedHost[] hosts = this.hosts;
int pos = find(hosts, hostName); //根据host的名字来查找相应的mapedHost对象的下标
if( pos <0 ) { //如果没有,那么添加这个host
addHost(hostName, new String[0], host); //
hosts = this.hosts;
pos = find(hosts, hostName); //重新获取下标
}
if (pos < 0) {
log.error("No host found: " + hostName);
}
MappedHost mappedHost = hosts[pos]; //获取mappedHost对象
if (mappedHost.name.equals(hostName)) { //名字肯定要相等了
int slashCount = slashCount(path); //获取path里面的斜线的数量
synchronized (mappedHost) {
MappedContext[] contexts = mappedHost.contextList.contexts; //获取相应的host的mappedContext的数组
// Update nesting
if (slashCount > mappedHost.contextList.nesting) {
mappedHost.contextList.nesting = slashCount; //记录最大的context的path里面的斜线的数目
}
int pos2 = find(contexts, path); //在context数组里面获取一个位置,这里要么返回相当的path,要么返回左侧的
if (pos2 < 0 || !path.equals(contexts[pos2].name)) { //如果有path相等的,那么不幸
MappedContext newContext = new MappedContext(); //创建context的map信息
newContext.name = path;
MappedContext[] newContexts = new MappedContext[contexts.length + 1]; //将数组变大
if (insertMap(contexts, newContexts, newContext)) { //更新mappedContext对象的数组
mappedHost.contextList.contexts = newContexts; //指向新的数组
}
pos2 = find(newContexts, path); //获取新的下标
}
MappedContext mappedContext = mappedHost.contextList.contexts[pos2]; //获取刚刚加入的MappedContext对象
ContextVersion[] contextVersions = mappedContext.versions; //获取版本信息
ContextVersion[] newContextVersions =
new ContextVersion[contextVersions.length + 1]; //这里会初始化将contextVersion的数组为1,初始化的时候contextVersion的数组长度为0
ContextVersion newContextVersion = new ContextVersion(); //创建一个ContextVersion对象
newContextVersion.path = path; //设置path
newContextVersion.name = version; // 设置version的名字
newContextVersion.object = context; //保存context对象
newContextVersion.welcomeResources = welcomeResources; //保存welcomeResources
newContextVersion.resources = resources; //保存WebResourceRoot对象
if (insertMap(contextVersions, newContextVersions, newContextVersion)) { //更新mappedContext的contextVersion的数组
mappedContext.versions = newContextVersions; //指向新的数组
contextObjectToContextVersionMap.put( //key是context,value是ContextVersion
context, newContextVersion);
}
}
}
}
这个代码其实跟前面添加host差不多太对,只不过多了一个层次,首先更具hostName来查找要添加到的mappedHost对象,然后我们知道在mappedHost中有一个contextList,其实也就是一个MappedContext对象数组,然后接着就根据当年context的名字,创建一个新的MappedContext对象根据context的path的排序加入到contextList数组里面就好了,这里也就完成了将某个context加入到某个host的map过程。。。
那么最后就是如何加入wrapper对象了。。。
//添加warpper,首先是所属的host的名字,接着是contextpath,接着是context版本,接着是warpper的path,然后是warpper对象
public void addWrapper(String hostName, String contextPath, String version,
String path, Wrapper wrapper, boolean jspWildCard,
boolean resourceOnly) {
MappedHost[] hosts = this.hosts;
int pos = find(hosts, hostName); //根据host的名字,查找mappedHost对象的下标
if (pos < 0) {
return;
}
MappedHost host = hosts[pos]; //获取mapedHost对象
if (host.name.equals(hostName)) { //这里名字必须是相等的才行了
MappedContext[] contexts = host.contextList.contexts; //获取mappedContext的数组
int pos2 = find(contexts, contextPath); //找到相应的mappedContext的下标
if (pos2 < 0) { //找不到
log.error("No context found: " + contextPath );
return;
}
MappedContext context = contexts[pos2]; //获取所属的mappedContext对象
if (context.name.equals(contextPath)) { //这里必须相等才行了
ContextVersion[] contextVersions = context.versions; //获取context的版本数组
int pos3 = find(contextVersions, version); //寻找对一个的version的位置
if( pos3<0 ) {
log.error("No context version found: " + contextPath + " " +
version);
return;
}
ContextVersion contextVersion = contextVersions[pos3]; //获取对应的version的map信息
if (contextVersion.name.equals(version)) { //这里也要相等才行
addWrapper(contextVersion, path, wrapper, jspWildCard, //在这个里面添加warrper对象
resourceOnly);
}
}
}
}
/**
* Adds a wrapper to the given context.
*
* @param context The context to which to add the wrapper
* @param path Wrapper mapping
* @param wrapper The Wrapper object
* @param jspWildCard true if the wrapper corresponds to the JspServlet
* @param resourceOnly true if this wrapper always expects a physical
* resource to be present (such as a JSP)
* and the mapping path contains a wildcard; false otherwise
*/
//将某个wrapper放到某个对应的context,第二个参数是servlet要map的path,后面是wrapper对象,第一个参数是应该加到的contextVersion对象
protected void addWrapper(ContextVersion context, String path,
Wrapper wrapper, boolean jspWildCard, boolean resourceOnly) {
synchronized (context) {
MappedWrapper newWrapper = new MappedWrapper(); // 创建一个mappedWrapper对象
newWrapper.object = wrapper;
newWrapper.jspWildCard = jspWildCard;
newWrapper.resourceOnly = resourceOnly;
if (path.endsWith("/*")) { // 如果path的map是通配符类型的
// Wildcard wrapper
newWrapper.name = path.substring(0, path.length() - 2); //将/*去掉
MappedWrapper[] oldWrappers = context.wildcardWrappers; // 获取通配符匹配的mappedWrapper数组
MappedWrapper[] newWrappers = //将长度加1
new MappedWrapper[oldWrappers.length + 1];
if (insertMap(oldWrappers, newWrappers, newWrapper)) {
context.wildcardWrappers = newWrappers;
int slashCount = slashCount(newWrapper.name);
if (slashCount > context.nesting) {
context.nesting = slashCount; //更新当前context拥有的servlet的path里面最多的斜线数目
}
}
} else if (path.startsWith("*.")) { //表示是扩展名的mapper
// Extension wrapper
newWrapper.name = path.substring(2);
MappedWrapper[] oldWrappers = context.extensionWrappers; //获取扩展名匹配的mappedWrapper的数组
MappedWrapper[] newWrappers =
new MappedWrapper[oldWrappers.length + 1];
if (insertMap(oldWrappers, newWrappers, newWrapper)) {
context.extensionWrappers = newWrappers;
}
} else if (path.equals("/")) { // 表示是默认的wrapper
// Default wrapper
newWrapper.name = "";
context.defaultWrapper = newWrapper;
} else { //最后就是精确的map了
// Exact wrapper
if (path.length() == 0) {
// Special case for the Context Root mapping which is
// treated as an exact match
newWrapper.name = "/";
} else {
newWrapper.name = path;
}
MappedWrapper[] oldWrappers = context.exactWrappers; //获取精确的map
MappedWrapper[] newWrappers = //更新map数组
new MappedWrapper[oldWrappers.length + 1];
if (insertMap(oldWrappers, newWrappers, newWrapper)) {
context.exactWrappers = newWrappers;
}
}
}
}
这里可能就别context更多了一个层次,首先找到相应的mappedHost对象,然后找到相应的mappedContext对象,然后再擦入。。
然后这里在擦入的时候还有一点不一样的地方,因为servlet的map可能有多重,例如通配符匹配,精确匹配,扩展名匹配啥的。。这个都要区分进行。。上面的注释应该算是蛮清楚的吧。。。
好啦,如何添加map信息算是有一定的了解了吧。。那么接下来来看看如何来检索吧,也就是给一个http请求路径,然后检索出对应的host,context以及wrapper对象。。。
在httpprocessor中,如果生成了一个http请求,会将请求交给adapter对象来处理。。。而在adapter里面就会调当前servcie对象的mapper对象来对请求进行路由。。。其实也就是调用如下的方法:
//第一个是host的名字,第二个是请求路径,例如/examples/servlets/servlet/HelloWorldExample,第三个是版本,默认使用最后的版本,最后是保存map信息的地方
public void map(MessageBytes host, MessageBytes uri, String version,
MappingData mappingData)
throws Exception {
if (host.isNull()) {
host.getCharChunk().append(defaultHostName);
}
host.toChars();
uri.toChars();
internalMap(host.getCharChunk(), uri.getCharChunk(), version,
mappingData);
}
对于最后map出来的信息,也就是哪一个host,context,wrapper会保存在mappingData参数中。。。
// 第一个参数是host的名字,第二个参数访问的path,第三个参数是version,最后保存map信息
private final void internalMap(CharChunk host, CharChunk uri,
String version, MappingData mappingData) throws Exception {
uri.setLimit(-1);
MappedContext[] contexts = null;
MappedContext context = null;
ContextVersion contextVersion = null;
int nesting = 0;
// Virtual host mapping
if (mappingData.host == null) {
MappedHost[] hosts = this.hosts; //获取当前所有的host
int pos = findIgnoreCase(hosts, host); //这里找到所属的host的下标
if ((pos != -1) && (host.equalsIgnoreCase(hosts[pos].name))) { //如果能够找到的话
mappingData.host = hosts[pos].object; //保存map到的host
contexts = hosts[pos].contextList.contexts; //所有的context
nesting = hosts[pos].contextList.nesting;
} else { //如果不能找到,那么就用默认的host
if (defaultHostName == null) {
return;
}
pos = find(hosts, defaultHostName);
if ((pos != -1) && (defaultHostName.equals(hosts[pos].name))) {
mappingData.host = hosts[pos].object;
contexts = hosts[pos].contextList.contexts;
nesting = hosts[pos].contextList.nesting;
} else {
return;
}
}
}
// Context mapping
if (mappingData.context == null && contexts != null) {
int pos = find(contexts, uri); //通过访问的path来找相应的context
if (pos == -1) {
return; // 找不到
}
int lastSlash = -1;
int uriEnd = uri.getEnd(); //刚开始end就是字符串的最后了
int length = -1;
boolean found = false;
while (pos >= 0) { //这里表示找到了可能可用的context
if (uri.startsWith(contexts[pos].name)) { // 如果path的开头与context的名字相等
length = contexts[pos].name.length(); //获取context的name的长度
if (uri.getLength() == length) { //如果path的长度就等等与context的名字,那么表示path与context的名字相等
found = true; //找到了context
break;
} else if (uri.startsWithIgnoreCase("/", length)) { // 如果path在context的名字后面就是“/”了,那么也行
found = true;
break;
}
}
//到这里表示刚开始找到的context的不满足
if (lastSlash == -1) {
lastSlash = nthSlash(uri, nesting + 1);
} else {
lastSlash = lastSlash(uri);
}
uri.setEnd(lastSlash);
pos = find(contexts, uri);
}
uri.setEnd(uriEnd); //恢复end
if (!found) { //找不到相应的context
if (contexts[0].name.equals("")) { //如果有根context,那么就用它,因为有可能就直接访问类似于 www.baidu.com/aa.do?aa=1这种地址,就是根context
context = contexts[0];
}
} else {
context = contexts[pos];
}
if (context != null) { //设置context
mappingData.contextPath.setString(context.name);
}
}
if (context != null) { //这里主要是处理context的版本
ContextVersion[] contextVersions = context.versions;
int versionCount = contextVersions.length;
if (versionCount > 1) {
Context[] contextObjects = new Context[contextVersions.length]; //默认是用最新的了
for (int i = 0; i < contextObjects.length; i++) {
contextObjects[i] = contextVersions[i].object;
}
mappingData.contexts = contextObjects; //设置map出来的context
}
if (version == null) {
// Return the latest version
contextVersion = contextVersions[versionCount - 1];
} else {
int pos = find(contextVersions, version);
if (pos < 0 || !contextVersions[pos].name.equals(version)) {
// Return the latest version
contextVersion = contextVersions[versionCount - 1];
} else {
contextVersion = contextVersions[pos];
}
}
mappingData.context = contextVersion.object;
}
// Wrapper mapping 找到相应的wrapper
if ((contextVersion != null) && (mappingData.wrapper == null)) {
internalMapWrapper(contextVersion, uri, mappingData);
}
}
/**
* Wrapper mapping.
*/
//wrapper的mapping信息,这里的path还带有前面的context的名字
private final void internalMapWrapper(ContextVersion contextVersion,
CharChunk path,
MappingData mappingData)
throws Exception {
int pathOffset = path.getOffset(); //当前path的游标
int pathEnd = path.getEnd(); //获取end
int servletPath = pathOffset; //servlet的path的游标,这里刚开始设置为path的一样
boolean noServletPath = false;
//这里主要是为了将前面的context的略过
int length = contextVersion.path.length(); //获取context的名字的长度
if (length != (pathEnd - pathOffset)) { //表示在context的名字后面还有servlet的名字啥的
servletPath = pathOffset + length; //将servlet的匹配游标向前加上context的名字长度
} else {
noServletPath = true; //表示在url里面没有指定特定的servlet
path.append('/'); //在path后面加上/
pathOffset = path.getOffset();
pathEnd = path.getEnd();
servletPath = pathOffset+length; //还是将servletpath的游标加上context的长度
}
path.setOffset(servletPath); //设置path的游标
// Rule 1 -- Exact Match
MappedWrapper[] exactWrappers = contextVersion.exactWrappers; //首先进行精确的匹配
internalMapExactWrapper(exactWrappers, path, mappingData);
// Rule 2 -- Prefix Match
//接下来是前缀匹配
boolean checkJspWelcomeFiles = false;
MappedWrapper[] wildcardWrappers = contextVersion.wildcardWrappers;
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) { //如果精确的匹配没有找到
internalMapWildcardWrapper(wildcardWrappers, contextVersion.nesting,
path, mappingData);
if (mappingData.wrapper != null && mappingData.jspWildCard) {
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
if (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/') {
/*
* Path ending in '/' was mapped to JSP servlet based on
* wildcard match (e.g., as specified in url-pattern of a
* jsp-property-group.
* Force the context's welcome files, which are interpreted
* as JSP files (since they match the url-pattern), to be
* considered. See Bugzilla 27664.
*/
mappingData.wrapper = null;
checkJspWelcomeFiles = true;
} else {
// See Bugzilla 27704
mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars(buf, path.getStart(),
path.getLength());
mappingData.pathInfo.recycle();
}
}
}
if(mappingData.wrapper == null && noServletPath) {
// The path is empty, redirect to "/"
mappingData.redirectPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), pathOffset, pathEnd-pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd - 1);
return;
}
// Rule 3 -- Extension Match
//最后是扩展名的匹配了
MappedWrapper[] extensionWrappers = contextVersion.extensionWrappers;
if (mappingData.wrapper == null && !checkJspWelcomeFiles) {
internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path, mappingData,
true);
}
// Rule 4 -- Welcome resources processing for servlets
//最后是首页匹配了
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) {
boolean checkWelcomeFiles = checkJspWelcomeFiles;
if (!checkWelcomeFiles) {
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
checkWelcomeFiles = (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/');
}
if (checkWelcomeFiles) {
for (int i = 0; (i < contextVersion.welcomeResources.length)
&& (mappingData.wrapper == null); i++) {
path.setOffset(pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
path.append(contextVersion.welcomeResources[i], 0,
contextVersion.welcomeResources[i].length());
path.setOffset(servletPath);
// Rule 4a -- Welcome resources processing for exact macth
internalMapExactWrapper(exactWrappers, path, mappingData);
// Rule 4b -- Welcome resources processing for prefix match
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) {
internalMapWildcardWrapper
(wildcardWrappers, contextVersion.nesting,
path, mappingData);
}
// Rule 4c -- Welcome resources processing
// for physical folder
if (mappingData.wrapper == null
&& contextVersion.resources != null) {
String pathStr = path.toString();
WebResource file =
contextVersion.resources.getResource(pathStr);
if (file != null && file.isFile()) {
internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path,
mappingData, true);
if (mappingData.wrapper == null
&& contextVersion.defaultWrapper != null) {
mappingData.wrapper =
contextVersion.defaultWrapper.object;
mappingData.requestPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(),
path.getLength());
mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(),
path.getLength());
mappingData.requestPath.setString(pathStr);
mappingData.wrapperPath.setString(pathStr);
}
}
}
}
path.setOffset(servletPath);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
}
}
/* welcome file processing - take 2
* Now that we have looked for welcome files with a physical
* backing, now look for an extension mapping listed
* but may not have a physical backing to it. This is for
* the case of index.jsf, index.do, etc.
* A watered down version of rule 4
*/
if (mappingData.wrapper == null) {
boolean checkWelcomeFiles = checkJspWelcomeFiles;
if (!checkWelcomeFiles) {
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
checkWelcomeFiles = (buf[pathEnd - 1] == '/');
}
if (checkWelcomeFiles) {
for (int i = 0; (i < contextVersion.welcomeResources.length)
&& (mappingData.wrapper == null); i++) {
path.setOffset(pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
path.append(contextVersion.welcomeResources[i], 0,
contextVersion.welcomeResources[i].length());
path.setOffset(servletPath);
internalMapExtensionWrapper(extensionWrappers, path,
mappingData, false);
}
path.setOffset(servletPath);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
}
}
// Rule 7 -- Default servlet
if (mappingData.wrapper == null && !checkJspWelcomeFiles) {
if (contextVersion.defaultWrapper != null) {
mappingData.wrapper = contextVersion.defaultWrapper.object;
mappingData.requestPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength());
mappingData.wrapperPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength());
}
// Redirection to a folder
char[] buf = path.getBuffer();
if (contextVersion.resources != null && buf[pathEnd -1 ] != '/') {
String pathStr = path.toString();
WebResource file =
contextVersion.resources.getResource(pathStr);
if (file != null && file.isDirectory()) {
// Note: this mutates the path: do not do any processing
// after this (since we set the redirectPath, there
// shouldn't be any)
path.setOffset(pathOffset);
path.append('/');
mappingData.redirectPath.setChars
(path.getBuffer(), path.getStart(), path.getLength());
} else {
mappingData.requestPath.setString(pathStr);
mappingData.wrapperPath.setString(pathStr);
}
}
}
path.setOffset(pathOffset);
path.setEnd(pathEnd);
}
代码是在太多了吧,其实这里最关键的也就是一个二分搜索的过程。。。具体的细节就不交代了。。有兴趣自己看看就好了。。。
那么到这里位置tomcat如何对请求进行路由,就算是比较清楚了。。。用基于字典序的二分搜索,应该效率也不差吧。。。