Solr与数据库结合实现全文检索
一下给出了一个简单的实例展示了如何将Solr与数据库结合实现全文检索。生产环境下,会有很大差别,这里的配置仅作为调试或是开发所用。
1. 安装Java JDK 和Tomcat
第一步骤就是安装jdk 和Server 服务器Tomcat,这个也挺简单,这里就省略了。
2. 配置Solr Core
将Solr自带的一个例子复制一份,我这里演示的版本是Solr最新版本Solr 4.2.0.
修改需要与DB融合的shema.xml 和 solrconfig文件,修改细节如下:
假设目标表的结构如下所示:
可以这样来配置的schema.xml :
<!-- core 'customer' schema field definition --> <field name="customer_id" type="int" indexed="true" stored="true" required="true" multiValued="false"/> <field name="name" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="sex" type="string" indexed="true" stored="false"/> <field name="level" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true"/> <field name="address" type="string" indexed="true" multiValued="true" stored="true"/>修改uniqueKeys配置:
<!-- Field to use to determine and enforce document uniqueness.
Unless this field is marked with required="false", it will be a required field
<uniqueKey>id</uniqueKey>
-->
<uniqueKey>customer_id</uniqueKey>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!--
Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
(the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
-->
<!--
This is the Solr schema file. This file should be named "schema.xml" and
should be in the conf directory under the solr home
(i.e. ./solr/conf/schema.xml by default)
or located where the classloader for the Solr webapp can find it.
This example schema is the recommended starting point for users.
It should be kept correct and concise, usable out-of-the-box.
For more information, on how to customize this file, please see
http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SchemaXml
PERFORMANCE NOTE: this schema includes many optional features and should not
be used for benchmarking. To improve performance one could
- set stored="false" for all fields possible (esp large fields) when you
only need to search on the field but don't need to return the original
value.
- set indexed="false" if you don't need to search on the field, but only
return the field as a result of searching on other indexed fields.
- remove all unneeded copyField statements
- for best index size and searching performance, set "index" to false
for all general text fields, use copyField to copy them to the
catchall "text" field, and use that for searching.
- For maximum indexing performance, use the StreamingUpdateSolrServer
java client.
- Remember to run the JVM in server mode, and use a higher logging level
that avoids logging every request
-->
<schema name="example" version="1.5">
<!-- attribute "name" is the name of this schema and is only used for display purposes.
version="x.y" is Solr's version number for the schema syntax and
semantics. It should not normally be changed by applications.
1.0: multiValued attribute did not exist, all fields are multiValued
by nature
1.1: multiValued attribute introduced, false by default
1.2: omitTermFreqAndPositions attribute introduced, true by default
except for text fields.
1.3: removed optional field compress feature
1.4: autoGeneratePhraseQueries attribute introduced to drive QueryParser
behavior when a single string produces multiple tokens. Defaults
to off for version >= 1.4
1.5: omitNorms defaults to true for primitive field types
(int, float, boolean, string...)
-->
<fields>
<!-- Valid attributes for fields:
name: mandatory - the name for the field
type: mandatory - the name of a field type from the
<types> fieldType section
indexed: true if this field should be indexed (searchable or sortable)
stored: true if this field should be retrievable
docValues: true if this field should have doc values. Doc values are
useful for faceting, grouping, sorting and function queries. Although not
required, doc values will make the index faster to load, more
NRT-friendly and more memory-efficient. They however come with some
limitations: they are currently only supported by StrField, UUIDField
and all Trie*Fields, and depending on the field type, they might
require the field to be single-valued, be required or have a default
value (check the documentation of the field type you're interested in
for more information)
multiValued: true if this field may contain multiple values per document
omitNorms: (expert) set to true to omit the norms associated with
this field (this disables length normalization and index-time
boosting for the field, and saves some memory). Only full-text
fields or fields that need an index-time boost need norms.
Norms are omitted for primitive (non-analyzed) types by default.
termVectors: [false] set to true to store the term vector for a
given field.
When using MoreLikeThis, fields used for similarity should be
stored for best performance.
termPositions: Store position information with the term vector.
This will increase storage costs.
termOffsets: Store offset information with the term vector. This
will increase storage costs.
required: The field is required. It will throw an error if the
value does not exist
default: a value that should be used if no value is specified
when adding a document.
-->
<!-- field names should consist of alphanumeric or underscore characters only and
not start with a digit. This is not currently strictly enforced,
but other field names will not have first class support from all components
and back compatibility is not guaranteed. Names with both leading and
trailing underscores (e.g. _version_) are reserved.
-->
<field name="sku" type="text_en_splitting_tight" indexed="true" stored="true" omitNorms="true"/>
<field name="manu" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true" omitNorms="true"/>
<field name="cat" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<field name="features" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<field name="includes" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true" termVectors="true" termPositions="true" termOffsets="true" />
<field name="weight" type="float" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="price" type="float" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="popularity" type="int" indexed="true" stored="true" />
<field name="inStock" type="boolean" indexed="true" stored="true" />
<field name="store" type="location" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<!-- Common metadata fields, named specifically to match up with
SolrCell metadata when parsing rich documents such as Word, PDF.
Some fields are multiValued only because Tika currently may return
multiple values for them. Some metadata is parsed from the documents,
but there are some which come from the client context:
"content_type": From the HTTP headers of incoming stream
"resourcename": From SolrCell request param resource.name
<field name="id" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" required="true" multiValued="false" />
-->
<field name="title" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<field name="subject" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="description" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="comments" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="author" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="keywords" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="category" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="resourcename" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="url" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="content_type" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<field name="last_modified" type="date" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="links" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<!-- Main body of document extracted by SolrCell.
NOTE: This field is not indexed by default, since it is also copied to "text"
using copyField below. This is to save space. Use this field for returning and
highlighting document content. Use the "text" field to search the content. -->
<field name="content" type="text_general" indexed="false" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<!-- catchall field, containing all other searchable text fields (implemented
via copyField further on in this schema -->
<field name="text" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="false" multiValued="true"/>
<!-- catchall text field that indexes tokens both normally and in reverse for efficient
leading wildcard queries. -->
<field name="text_rev" type="text_general_rev" indexed="true" stored="false" multiValued="true"/>
<!-- non-tokenized version of manufacturer to make it easier to sort or group
results by manufacturer. copied from "manu" via copyField -->
<field name="manu_exact" type="string" indexed="true" stored="false"/>
<field name="payloads" type="payloads" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="_version_" type="long" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<!-- core 'customer' schema field definition -->
<field name="customer_id" type="int" indexed="true" stored="true" required="true" multiValued="false"/>
<field name="name" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="sex" type="string" indexed="true" stored="false"/>
<field name="level" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<field name="address" type="string" indexed="true" multiValued="true" stored="true"/>
<!--
Some fields such as popularity and manu_exact could be modified to
leverage doc values:
<field name="popularity" type="int" indexed="true" stored="true" docValues="true" default="0" />
<field name="manu_exact" type="string" indexed="false" stored="false" docValues="true" default="" />
Although it would make indexing slightly slower and the index bigger, it
would also make the index faster to load, more memory-efficient and more
NRT-friendly.
-->
<!-- Dynamic field definitions allow using convention over configuration
for fields via the specification of patterns to match field names.
EXAMPLE: name="*_i" will match any field ending in _i (like myid_i, z_i)
RESTRICTION: the glob-like pattern in the name attribute must have
a "*" only at the start or the end. -->
<dynamicField name="*_i" type="int" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_is" type="int" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_s" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" />
<dynamicField name="*_ss" type="string" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_l" type="long" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_ls" type="long" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_t" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_txt" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_en" type="text_en" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_b" type="boolean" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_bs" type="boolean" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_f" type="float" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_fs" type="float" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_d" type="double" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_ds" type="double" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<!-- Type used to index the lat and lon components for the "location" FieldType -->
<dynamicField name="*_coordinate" type="tdouble" indexed="true" stored="false" />
<dynamicField name="*_dt" type="date" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_dts" type="date" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_p" type="location" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<!-- some trie-coded dynamic fields for faster range queries -->
<dynamicField name="*_ti" type="tint" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_tl" type="tlong" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_tf" type="tfloat" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_td" type="tdouble" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_tdt" type="tdate" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_pi" type="pint" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="*_c" type="currency" indexed="true" stored="true"/>
<dynamicField name="ignored_*" type="ignored" multiValued="true"/>
<dynamicField name="attr_*" type="text_general" indexed="true" stored="true" multiValued="true"/>
<dynamicField name="random_*" type="random" />
<!-- uncomment the following to ignore any fields that don't already match an existing
field name or dynamic field, rather than reporting them as an error.
alternately, change the type="ignored" to some other type e.g. "text" if you want
unknown fields indexed and/or stored by default -->
<!--dynamicField name="*" type="ignored" multiValued="true" /-->
</fields>
<!-- Field to use to determine and enforce document uniqueness.
Unless this field is marked with required="false", it will be a required field
<uniqueKey>id</uniqueKey>
-->
<uniqueKey>customer_id</uniqueKey>
<!-- DEPRECATED: The defaultSearchField is consulted by various query parsers when
parsing a query string that isn't explicit about the field. Machine (non-user)
generated queries are best made explicit, or they can use the "df" request parameter
which takes precedence over this.
Note: Un-commenting defaultSearchField will be insufficient if your request handler
in solrconfig.xml defines "df", which takes precedence. That would need to be removed.
<defaultSearchField>text</defaultSearchField> -->
<!-- DEPRECATED: The defaultOperator (AND|OR) is consulted by various query parsers
when parsing a query string to determine if a clause of the query should be marked as
required or optional, assuming the clause isn't already marked by some operator.
The default is OR, which is generally assumed so it is not a good idea to change it
globally here. The "q.op" request parameter takes precedence over this.
<solrQueryParser defaultOperator="OR"/> -->
<!-- copyField commands copy one field to another at the time a document
is added to the index. It's used either to index the same field differently,
or to add multiple fields to the same field for easier/faster searching. -->
<copyField source="cat" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="name" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="manu" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="features" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="includes" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="manu" dest="manu_exact"/>
<!-- Copy the price into a currency enabled field (default USD) -->
<copyField source="price" dest="price_c"/>
<!-- Text fields from SolrCell to search by default in our catch-all field -->
<copyField source="title" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="author" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="description" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="keywords" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="content" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="content_type" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="resourcename" dest="text"/>
<copyField source="url" dest="text"/>
<!-- Create a string version of author for faceting -->
<copyField source="author" dest="author_s"/>
<!-- Above, multiple source fields are copied to the [text] field.
Another way to map multiple source fields to the same
destination field is to use the dynamic field syntax.
copyField also supports a maxChars to copy setting. -->
<!-- <copyField source="*_t" dest="text" maxChars="3000"/> -->
<!-- copy name to alphaNameSort, a field designed for sorting by name -->
<!-- <copyField source="name" dest="alphaNameSort"/> -->
<types>
<!-- field type definitions. The "name" attribute is
just a label to be used by field definitions. The "class"
attribute and any other attributes determine the real
behavior of the fieldType.
Class names starting with "solr" refer to java classes in a
standard package such as org.apache.solr.analysis
-->
<!-- The StrField type is not analyzed, but indexed/stored verbatim.
It supports doc values but in that case the field needs to be
single-valued and either required or have a default value.
-->
<fieldType name="string" class="solr.StrField" sortMissingLast="true" />
<!-- boolean type: "true" or "false" -->
<fieldType name="boolean" class="solr.BoolField" sortMissingLast="true"/>
<!-- sortMissingLast and sortMissingFirst attributes are optional attributes are
currently supported on types that are sorted internally as strings
and on numeric types.
This includes "string","boolean", and, as of 3.5 (and 4.x),
int, float, long, date, double, including the "Trie" variants.
- If sortMissingLast="true", then a sort on this field will cause documents
without the field to come after documents with the field,
regardless of the requested sort order (asc or desc).
- If sortMissingFirst="true", then a sort on this field will cause documents
without the field to come before documents with the field,
regardless of the requested sort order.
- If sortMissingLast="false" and sortMissingFirst="false" (the default),
then default lucene sorting will be used which places docs without the
field first in an ascending sort and last in a descending sort.
-->
<!--
Default numeric field types. For faster range queries, consider the tint/tfloat/tlong/tdouble types.
These fields support doc values, but they require the field to be
single-valued and either be required or have a default value.
-->
<fieldType name="int" class="solr.TrieIntField" precisionStep="0" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="float" class="solr.TrieFloatField" precisionStep="0" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="long" class="solr.TrieLongField" precisionStep="0" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="double" class="solr.TrieDoubleField" precisionStep="0" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<!--
Numeric field types that index each value at various levels of precision
to accelerate range queries when the number of values between the range
endpoints is large. See the javadoc for NumericRangeQuery for internal
implementation details.
Smaller precisionStep values (specified in bits) will lead to more tokens
indexed per value, slightly larger index size, and faster range queries.
A precisionStep of 0 disables indexing at different precision levels.
-->
<fieldType name="tint" class="solr.TrieIntField" precisionStep="8" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="tfloat" class="solr.TrieFloatField" precisionStep="8" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="tlong" class="solr.TrieLongField" precisionStep="8" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<fieldType name="tdouble" class="solr.TrieDoubleField" precisionStep="8" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<!-- The format for this date field is of the form 1995-12-31T23:59:59Z, and
is a more restricted form of the canonical representation of dateTime
http://www.w3.org/TR/xmlschema-2/#dateTime
The trailing "Z" designates UTC time and is mandatory.
Optional fractional seconds are allowed: 1995-12-31T23:59:59.999Z
All other components are mandatory.
Expressions can also be used to denote calculations that should be
performed relative to "NOW" to determine the value, ie...
NOW/HOUR
... Round to the start of the current hour
NOW-1DAY
... Exactly 1 day prior to now
NOW/DAY+6MONTHS+3DAYS
... 6 months and 3 days in the future from the start of
the current day
Consult the DateField javadocs for more information.
Note: For faster range queries, consider the tdate type
-->
<fieldType name="date" class="solr.TrieDateField" precisionStep="0" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<!-- A Trie based date field for faster date range queries and date faceting. -->
<fieldType name="tdate" class="solr.TrieDateField" precisionStep="6" positionIncrementGap="0"/>
<!--Binary data type. The data should be sent/retrieved in as Base64 encoded Strings -->
<fieldtype name="binary" class="solr.BinaryField"/>
<!--
Note:
These should only be used for compatibility with existing indexes (created with lucene or older Solr versions).
Use Trie based fields instead. As of Solr 3.5 and 4.x, Trie based fields support sortMissingFirst/Last
Plain numeric field types that store and index the text
value verbatim (and hence don't correctly support range queries, since the
lexicographic ordering isn't equal to the numeric ordering)
-->
<fieldType name="pint" class="solr.IntField"/>
<fieldType name="plong" class="solr.LongField"/>
<fieldType name="pfloat" class="solr.FloatField"/>
<fieldType name="pdouble" class="solr.DoubleField"/>
<fieldType name="pdate" class="solr.DateField" sortMissingLast="true"/>
<!-- The "RandomSortField" is not used to store or search any
data. You can declare fields of this type it in your schema
to generate pseudo-random orderings of your docs for sorting
or function purposes. The ordering is generated based on the field
name and the version of the index. As long as the index version
remains unchanged, and the same field name is reused,
the ordering of the docs will be consistent.
If you want different psuedo-random orderings of documents,
for the same version of the index, use a dynamicField and
change the field name in the request.
-->
<fieldType name="random" class="solr.RandomSortField" indexed="true" />
<!-- solr.TextField allows the specification of custom text analyzers
specified as a tokenizer and a list of token filters. Different
analyzers may be specified for indexing and querying.
The optional positionIncrementGap puts space between multiple fields of
this type on the same document, with the purpose of preventing false phrase
matching across fields.
For more info on customizing your analyzer chain, please see
http://wiki.apache.org/solr/AnalyzersTokenizersTokenFilters
-->
<!-- One can also specify an existing Analyzer class that has a
default constructor via the class attribute on the analyzer element.
Example:
<fieldType name="text_greek" class="solr.TextField">
<analyzer class="org.apache.lucene.analysis.el.GreekAnalyzer"/>
</fieldType>
-->
<!-- A text field that only splits on whitespace for exact matching of words -->
<fieldType name="text_ws" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- A general text field that has reasonable, generic
cross-language defaults: it tokenizes with StandardTokenizer,
removes stop words from case-insensitive "stopwords.txt"
(empty by default), and down cases. At query time only, it
also applies synonyms. -->
<fieldType name="text_general" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="stopwords.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true" />
<!-- in this example, we will only use synonyms at query time
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="index_synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/>
-->
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="stopwords.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true" />
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- A text field with defaults appropriate for English: it
tokenizes with StandardTokenizer, removes English stop words
(lang/stopwords_en.txt), down cases, protects words from protwords.txt, and
finally applies Porter's stemming. The query time analyzer
also applies synonyms from synonyms.txt. -->
<fieldType name="text_en" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<!-- in this example, we will only use synonyms at query time
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="index_synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/>
-->
<!-- Case insensitive stop word removal.
add enablePositionIncrements=true in both the index and query
analyzers to leave a 'gap' for more accurate phrase queries.
-->
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory"
ignoreCase="true"
words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"
enablePositionIncrements="true"
/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.EnglishPossessiveFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/>
<!-- Optionally you may want to use this less aggressive stemmer instead of PorterStemFilterFactory:
<filter class="solr.EnglishMinimalStemFilterFactory"/>
-->
<filter class="solr.PorterStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory"
ignoreCase="true"
words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"
enablePositionIncrements="true"
/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.EnglishPossessiveFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/>
<!-- Optionally you may want to use this less aggressive stemmer instead of PorterStemFilterFactory:
<filter class="solr.EnglishMinimalStemFilterFactory"/>
-->
<filter class="solr.PorterStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- A text field with defaults appropriate for English, plus
aggressive word-splitting and autophrase features enabled.
This field is just like text_en, except it adds
WordDelimiterFilter to enable splitting and matching of
words on case-change, alpha numeric boundaries, and
non-alphanumeric chars. This means certain compound word
cases will work, for example query "wi fi" will match
document "WiFi" or "wi-fi".
-->
<fieldType name="text_en_splitting" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100" autoGeneratePhraseQueries="true">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/>
<!-- in this example, we will only use synonyms at query time
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="index_synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/>
-->
<!-- Case insensitive stop word removal.
add enablePositionIncrements=true in both the index and query
analyzers to leave a 'gap' for more accurate phrase queries.
-->
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory"
ignoreCase="true"
words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"
enablePositionIncrements="true"
/>
<filter class="solr.WordDelimiterFilterFactory" generateWordParts="1" generateNumberParts="1" catenateWords="1" catenateNumbers="1" catenateAll="0" splitOnCaseChange="1"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.PorterStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory"
ignoreCase="true"
words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"
enablePositionIncrements="true"
/>
<filter class="solr.WordDelimiterFilterFactory" generateWordParts="1" generateNumberParts="1" catenateWords="0" catenateNumbers="0" catenateAll="0" splitOnCaseChange="1"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.PorterStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Less flexible matching, but less false matches. Probably not ideal for product names,
but may be good for SKUs. Can insert dashes in the wrong place and still match. -->
<fieldType name="text_en_splitting_tight" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100" autoGeneratePhraseQueries="true">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="false"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_en.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.WordDelimiterFilterFactory" generateWordParts="0" generateNumberParts="0" catenateWords="1" catenateNumbers="1" catenateAll="0"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.KeywordMarkerFilterFactory" protected="protwords.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.EnglishMinimalStemFilterFactory"/>
<!-- this filter can remove any duplicate tokens that appear at the same position - sometimes
possible with WordDelimiterFilter in conjuncton with stemming. -->
<filter class="solr.RemoveDuplicatesTokenFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Just like text_general except it reverses the characters of
each token, to enable more efficient leading wildcard queries. -->
<fieldType name="text_general_rev" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="stopwords.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true" />
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.ReversedWildcardFilterFactory" withOriginal="true"
maxPosAsterisk="3" maxPosQuestion="2" maxFractionAsterisk="0.33"/>
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.SynonymFilterFactory" synonyms="synonyms.txt" ignoreCase="true" expand="true"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="stopwords.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true" />
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- charFilter + WhitespaceTokenizer -->
<!--
<fieldType name="text_char_norm" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100" >
<analyzer>
<charFilter class="solr.MappingCharFilterFactory" mapping="mapping-ISOLatin1Accent.txt"/>
<tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
-->
<!-- This is an example of using the KeywordTokenizer along
With various TokenFilterFactories to produce a sortable field
that does not include some properties of the source text
-->
<fieldType name="alphaOnlySort" class="solr.TextField" sortMissingLast="true" omitNorms="true">
<analyzer>
<!-- KeywordTokenizer does no actual tokenizing, so the entire
input string is preserved as a single token
-->
<tokenizer class="solr.KeywordTokenizerFactory"/>
<!-- The LowerCase TokenFilter does what you expect, which can be
when you want your sorting to be case insensitive
-->
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory" />
<!-- The TrimFilter removes any leading or trailing whitespace -->
<filter class="solr.TrimFilterFactory" />
<!-- The PatternReplaceFilter gives you the flexibility to use
Java Regular expression to replace any sequence of characters
matching a pattern with an arbitrary replacement string,
which may include back references to portions of the original
string matched by the pattern.
See the Java Regular Expression documentation for more
information on pattern and replacement string syntax.
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.6.0/docs/api/java/util/regex/package-summary.html
-->
<filter class="solr.PatternReplaceFilterFactory"
pattern="([^a-z])" replacement="" replace="all"
/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<fieldtype name="phonetic" stored="false" indexed="true" class="solr.TextField" >
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.DoubleMetaphoneFilterFactory" inject="false"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldtype>
<fieldtype name="payloads" stored="false" indexed="true" class="solr.TextField" >
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.WhitespaceTokenizerFactory"/>
<!--
The DelimitedPayloadTokenFilter can put payloads on tokens... for example,
a token of "foo|1.4" would be indexed as "foo" with a payload of 1.4f
Attributes of the DelimitedPayloadTokenFilterFactory :
"delimiter" - a one character delimiter. Default is | (pipe)
"encoder" - how to encode the following value into a playload
float -> org.apache.lucene.analysis.payloads.FloatEncoder,
integer -> o.a.l.a.p.IntegerEncoder
identity -> o.a.l.a.p.IdentityEncoder
Fully Qualified class name implementing PayloadEncoder, Encoder must have a no arg constructor.
-->
<filter class="solr.DelimitedPayloadTokenFilterFactory" encoder="float"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldtype>
<!-- lowercases the entire field value, keeping it as a single token. -->
<fieldType name="lowercase" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.KeywordTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory" />
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!--
Example of using PathHierarchyTokenizerFactory at index time, so
queries for paths match documents at that path, or in descendent paths
-->
<fieldType name="descendent_path" class="solr.TextField">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizer class="solr.PathHierarchyTokenizerFactory" delimiter="/" />
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizer class="solr.KeywordTokenizerFactory" />
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!--
Example of using PathHierarchyTokenizerFactory at query time, so
queries for paths match documents at that path, or in ancestor paths
-->
<fieldType name="ancestor_path" class="solr.TextField">
<analyzer type="index">
<tokenizer class="solr.KeywordTokenizerFactory" />
</analyzer>
<analyzer type="query">
<tokenizer class="solr.PathHierarchyTokenizerFactory" delimiter="/" />
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- since fields of this type are by default not stored or indexed,
any data added to them will be ignored outright. -->
<fieldtype name="ignored" stored="false" indexed="false" multiValued="true" class="solr.StrField" />
<!-- This point type indexes the coordinates as separate fields (subFields)
If subFieldType is defined, it references a type, and a dynamic field
definition is created matching *___<typename>. Alternately, if
subFieldSuffix is defined, that is used to create the subFields.
Example: if subFieldType="double", then the coordinates would be
indexed in fields myloc_0___double,myloc_1___double.
Example: if subFieldSuffix="_d" then the coordinates would be indexed
in fields myloc_0_d,myloc_1_d
The subFields are an implementation detail of the fieldType, and end
users normally should not need to know about them.
-->
<fieldType name="point" class="solr.PointType" dimension="2" subFieldSuffix="_d"/>
<!-- A specialized field for geospatial search. If indexed, this fieldType must not be multivalued. -->
<fieldType name="location" class="solr.LatLonType" subFieldSuffix="_coordinate"/>
<!-- An alternative geospatial field type new to Solr 4. It supports multiValued and polygon shapes.
For more information about this and other Spatial fields new to Solr 4, see:
http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SolrAdaptersForLuceneSpatial4
-->
<fieldType name="location_rpt" class="solr.SpatialRecursivePrefixTreeFieldType"
geo="true" distErrPct="0.025" maxDistErr="0.000009" units="degrees" />
<!-- Money/currency field type. See http://wiki.apache.org/solr/MoneyFieldType
Parameters:
defaultCurrency: Specifies the default currency if none specified. Defaults to "USD"
precisionStep: Specifies the precisionStep for the TrieLong field used for the amount
providerClass: Lets you plug in other exchange provider backend:
solr.FileExchangeRateProvider is the default and takes one parameter:
currencyConfig: name of an xml file holding exchange rates
solr.OpenExchangeRatesOrgProvider uses rates from openexchangerates.org:
ratesFileLocation: URL or path to rates JSON file (default latest.json on the web)
refreshInterval: Number of minutes between each rates fetch (default: 1440, min: 60)
-->
<fieldType name="currency" class="solr.CurrencyField" precisionStep="8" defaultCurrency="USD" currencyConfig="currency.xml" />
<!-- some examples for different languages (generally ordered by ISO code) -->
<!-- Arabic -->
<fieldType name="text_ar" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<!-- for any non-arabic -->
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ar.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<!-- normalizes ﻯ to ﻱ, etc -->
<filter class="solr.ArabicNormalizationFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.ArabicStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Bulgarian -->
<fieldType name="text_bg" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_bg.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.BulgarianStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Catalan -->
<fieldType name="text_ca" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<!-- removes l', etc -->
<filter class="solr.ElisionFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" articles="lang/contractions_ca.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ca.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Catalan"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- CJK bigram (see text_ja for a Japanese configuration using morphological analysis) -->
<fieldType name="text_cjk" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<!-- normalize width before bigram, as e.g. half-width dakuten combine -->
<filter class="solr.CJKWidthFilterFactory"/>
<!-- for any non-CJK -->
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.CJKBigramFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Czech -->
<fieldType name="text_cz" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_cz.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.CzechStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Danish -->
<fieldType name="text_da" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_da.txt" format="snowball" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Danish"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- German -->
<fieldType name="text_de" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_de.txt" format="snowball" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.GermanNormalizationFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.GermanLightStemFilterFactory"/>
<!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.GermanMinimalStemFilterFactory"/> -->
<!-- more aggressive: <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="German2"/> -->
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Greek -->
<fieldType name="text_el" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<!-- greek specific lowercase for sigma -->
<filter class="solr.GreekLowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="false" words="lang/stopwords_el.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.GreekStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Spanish -->
<fieldType name="text_es" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_es.txt" format="snowball" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SpanishLightStemFilterFactory"/>
<!-- more aggressive: <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Spanish"/> -->
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Basque -->
<fieldType name="text_eu" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_eu.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Basque"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Persian -->
<fieldType name="text_fa" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<!-- for ZWNJ -->
<charFilter class="solr.PersianCharFilterFactory"/>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.ArabicNormalizationFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.PersianNormalizationFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_fa.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Finnish -->
<fieldType name="text_fi" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_fi.txt" format="snowball" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Finnish"/>
<!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.FinnishLightStemFilterFactory"/> -->
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- French -->
<fieldType name="text_fr" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<!-- removes l', etc -->
<filter class="solr.ElisionFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" articles="lang/contractions_fr.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_fr.txt" format="snowball" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.FrenchLightStemFilterFactory"/>
<!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.FrenchMinimalStemFilterFactory"/> -->
<!-- more aggressive: <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="French"/> -->
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Irish -->
<fieldType name="text_ga" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<!-- removes d', etc -->
<filter class="solr.ElisionFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" articles="lang/contractions_ga.txt"/>
<!-- removes n-, etc. position increments is intentionally false! -->
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/hyphenations_ga.txt" enablePositionIncrements="false"/>
<filter class="solr.IrishLowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ga.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Irish"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Galician -->
<fieldType name="text_gl" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_gl.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.GalicianStemFilterFactory"/>
<!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.GalicianMinimalStemFilterFactory"/> -->
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Hindi -->
<fieldType name="text_hi" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<!-- normalizes unicode representation -->
<filter class="solr.IndicNormalizationFilterFactory"/>
<!-- normalizes variation in spelling -->
<filter class="solr.HindiNormalizationFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_hi.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.HindiStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Hungarian -->
<fieldType name="text_hu" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_hu.txt" format="snowball" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Hungarian"/>
<!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.HungarianLightStemFilterFactory"/> -->
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Armenian -->
<fieldType name="text_hy" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_hy.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Armenian"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Indonesian -->
<fieldType name="text_id" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_id.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<!-- for a less aggressive approach (only inflectional suffixes), set stemDerivational to false -->
<filter class="solr.IndonesianStemFilterFactory" stemDerivational="true"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Italian -->
<fieldType name="text_it" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<!-- removes l', etc -->
<filter class="solr.ElisionFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" articles="lang/contractions_it.txt"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_it.txt" format="snowball" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.ItalianLightStemFilterFactory"/>
<!-- more aggressive: <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Italian"/> -->
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Japanese using morphological analysis (see text_cjk for a configuration using bigramming)
NOTE: If you want to optimize search for precision, use default operator AND in your query
parser config with <solrQueryParser defaultOperator="AND"/> further down in this file. Use
OR if you would like to optimize for recall (default).
-->
<fieldType name="text_ja" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100" autoGeneratePhraseQueries="false">
<analyzer>
<!-- Kuromoji Japanese morphological analyzer/tokenizer (JapaneseTokenizer)
Kuromoji has a search mode (default) that does segmentation useful for search. A heuristic
is used to segment compounds into its parts and the compound itself is kept as synonym.
Valid values for attribute mode are:
normal: regular segmentation
search: segmentation useful for search with synonyms compounds (default)
extended: same as search mode, but unigrams unknown words (experimental)
For some applications it might be good to use search mode for indexing and normal mode for
queries to reduce recall and prevent parts of compounds from being matched and highlighted.
Use <analyzer type="index"> and <analyzer type="query"> for this and mode normal in query.
Kuromoji also has a convenient user dictionary feature that allows overriding the statistical
model with your own entries for segmentation, part-of-speech tags and readings without a need
to specify weights. Notice that user dictionaries have not been subject to extensive testing.
User dictionary attributes are:
userDictionary: user dictionary filename
userDictionaryEncoding: user dictionary encoding (default is UTF-8)
See lang/userdict_ja.txt for a sample user dictionary file.
Punctuation characters are discarded by default. Use discardPunctuation="false" to keep them.
See http://wiki.apache.org/solr/JapaneseLanguageSupport for more on Japanese language support.
-->
<tokenizer class="solr.JapaneseTokenizerFactory" mode="search"/>
<!--<tokenizer class="solr.JapaneseTokenizerFactory" mode="search" userDictionary="lang/userdict_ja.txt"/>-->
<!-- Reduces inflected verbs and adjectives to their base/dictionary forms (辞書形) -->
<filter class="solr.JapaneseBaseFormFilterFactory"/>
<!-- Removes tokens with certain part-of-speech tags -->
<filter class="solr.JapanesePartOfSpeechStopFilterFactory" tags="lang/stoptags_ja.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<!-- Normalizes full-width romaji to half-width and half-width kana to full-width (Unicode NFKC subset) -->
<filter class="solr.CJKWidthFilterFactory"/>
<!-- Removes common tokens typically not useful for search, but have a negative effect on ranking -->
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ja.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true" />
<!-- Normalizes common katakana spelling variations by removing any last long sound character (U+30FC) -->
<filter class="solr.JapaneseKatakanaStemFilterFactory" minimumLength="4"/>
<!-- Lower-cases romaji characters -->
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Latvian -->
<fieldType name="text_lv" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_lv.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.LatvianStemFilterFactory"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Dutch -->
<fieldType name="text_nl" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_nl.txt" format="snowball" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.StemmerOverrideFilterFactory" dictionary="lang/stemdict_nl.txt" ignoreCase="false"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Dutch"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Norwegian -->
<fieldType name="text_no" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_no.txt" format="snowball" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Norwegian"/>
<!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.NorwegianLightStemFilterFactory"/> -->
<!-- singular/plural: <filter class="solr.NorwegianMinimalStemFilterFactory"/> -->
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Portuguese -->
<fieldType name="text_pt" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_pt.txt" format="snowball" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.PortugueseLightStemFilterFactory"/>
<!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.PortugueseMinimalStemFilterFactory"/> -->
<!-- more aggressive: <filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Portuguese"/> -->
<!-- most aggressive: <filter class="solr.PortugueseStemFilterFactory"/> -->
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Romanian -->
<fieldType name="text_ro" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ro.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Romanian"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Russian -->
<fieldType name="text_ru" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_ru.txt" format="snowball" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Russian"/>
<!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.RussianLightStemFilterFactory"/> -->
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Swedish -->
<fieldType name="text_sv" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_sv.txt" format="snowball" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Swedish"/>
<!-- less aggressive: <filter class="solr.SwedishLightStemFilterFactory"/> -->
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Thai -->
<fieldType name="text_th" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.LowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.ThaiWordFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="true" words="lang/stopwords_th.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
<!-- Turkish -->
<fieldType name="text_tr" class="solr.TextField" positionIncrementGap="100">
<analyzer>
<tokenizer class="solr.StandardTokenizerFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.TurkishLowerCaseFilterFactory"/>
<filter class="solr.StopFilterFactory" ignoreCase="false" words="lang/stopwords_tr.txt" enablePositionIncrements="true"/>
<filter class="solr.SnowballPorterFilterFactory" language="Turkish"/>
</analyzer>
</fieldType>
</types>
<!-- Similarity is the scoring routine for each document vs. a query.
A custom Similarity or SimilarityFactory may be specified here, but
the default is fine for most applications.
For more info: http://wiki.apache.org/solr/SchemaXml#Similarity
-->
<!--
<similarity class="com.example.solr.CustomSimilarityFactory">
<str name="paramkey">param value</str>
</similarity>
-->
</schema>
solrconfig.xml配置如下:
指定加载的jar包:
<lib dir="../../../contrib/extraction/lib" regex=".*\.jar" />
<lib dir="../../../dist/" regex="solr-cell-\d.*\.jar" />
<lib dir="../../../contrib/clustering/lib/" regex=".*\.jar" />
<lib dir="../../../dist/" regex="solr-clustering-\d.*\.jar" />
<lib dir="../../../contrib/langid/lib/" regex=".*\.jar" />
<lib dir="../../../dist/" regex="solr-langid-\d.*\.jar" />
<lib dir="../../../contrib/velocity/lib" regex=".*\.jar" />
<lib dir="../../../dist/" regex="solr-velocity-\d.*\.jar" />
<lib dir="./lib/" regex=".*\.jar" /> 将修要用到的jar包,"
mysql-connection>*\.jar" 和导入依赖的“apache-solr-dataimporthandler.*\.jar”放在与config同级的目录下
<requestHandler name="/dev/dataimport" class="org.apache.solr.handler.dataimport.DataImportHandler">
<lst name="defaults">
<str name="config">db-data-dev-config.xml</str>
</lst>
</requestHandler>
接下来,配置数据源文件 db-data-dev-config.xml(与solrconfig.xml同一目录下) 。
<dataConfig>
<dataSource type="JdbcDataSource" driver="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" batchSize="-1" url="jdbc:mysql://localhost/pythondb?autoReconnect=true" user="elite" password="elite"/>
<document name="customer">
<entity name="customer"
query="select c.* from customer c">
<field name="customer_id" column="id" />
</entity>
</document>
</dataConfig>
3. 配置Tomcat
在tomcat下建立一个指向Solr Core实例的Context,具体路径“conf\Catalina\localhost”下。比如,这里建立的文件名称是solr.xml。配置信息如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <Context docBase="F:/openSource/solr/solr-4.2.0/example-1/solr/solr-4.2.0.war"> <Environment name="solr/home" type="java.lang.String" value="F:/openSource/solr/solr-4.2.0/example-1/solr" override="true"/> </Context>
必须将要用到的war包放到指定的位置,这个路径指定对了就好。
4. 运行服务
DOS环境下,进入到Tomcat的bin目录下,输入命令:
startup.bat
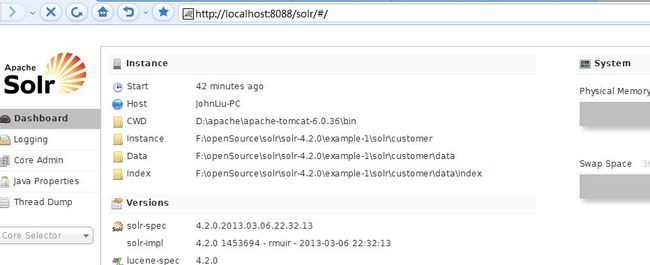
接着道浏览器中具体的路径,得到如下结果证明配置基本正确。
最后,导入数据库中的数据,即根据数据库表中的数据建立索引。
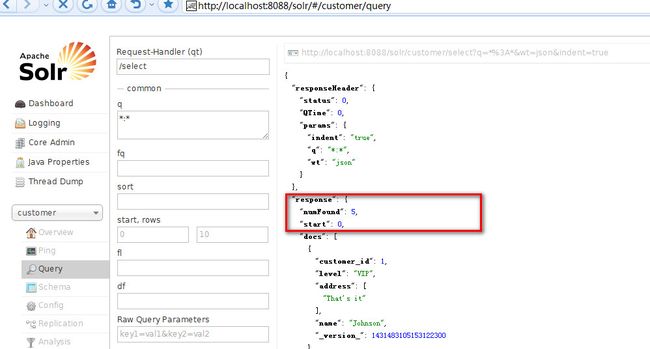
直接在浏览器中输入:http://localhost:8088/solr/customer/dev/dataimport?command=full-import。
到控制太查看具体的结果,有如下结果证明配置成功。
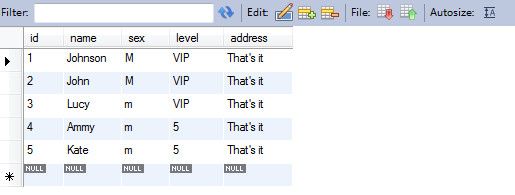
数据库中的数据如下所示:
- 顶
- 0
- 踩
- 0
- 上一篇深入解析Solr 4.2.0 solrconfig.xml 配置(下)
- 下一篇优化Solr schemalXML 设置