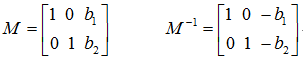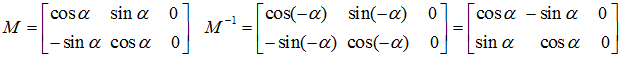【OpenCV】图像几何变换:旋转,缩放,斜切
参考文章:http://wiki.opencv.org.cn/index.php/Cv%E5%9B%BE%E5%83%8F%E5%A4%84%E7%90%86#WarpAffine
其他源码实现:http://blog.csdn.net/fengbingchun/article/details/17713429
几何变换
几何变换可以看成图像中物体(或像素)空间位置改变,或者说是像素的移动。
几何运算需要空间变换和灰度级差值两个步骤的算法,像素通过变换映射到新的坐标位置,新的位置可能是在几个像素之间,即不一定为整数坐标。这时就需要灰度级差值将映射的新坐标匹配到输出像素之间。最简单的插值方法是最近邻插值,就是令输出像素的灰度值等于映射最近的位置像素,该方法可能会产生锯齿。这种方法也叫零阶插值,相应比较复杂的还有一阶和高阶插值。
插值算法感觉只要了解就可以了,图像处理中比较需要理解的还是空间变换。
空间变换
空间变换对应矩阵的仿射变换。一个坐标通过函数变换的新的坐标位置:
所以在程序中我们可以使用一个2*3的数组结构来存储变换矩阵:
以最简单的平移变换为例,平移(b1,b2)坐标可以表示为:
因此,平移变换的变换矩阵及逆矩阵记为:
缩放变换:将图像横坐标放大(或缩小)sx倍,纵坐标放大(或缩小)sy倍,变换矩阵及逆矩阵为:
选择变换:图像绕原点逆时针旋转a角,其变换矩阵及逆矩阵(顺时针选择)为:
OpenCV中的图像变换函数
基本的放射变换函数:
- void cvWarpAffine(
- const CvArr* src,//输入图像
- CvArr* dst, //输出图像
- const CvMat* map_matrix, //2*3的变换矩阵
- int flags=CV_INTER_LINEAR+CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS, //插值方法的组合
- CvScalar fillval=cvScalarAll(0) //用来填充边界外的值
- );
- void cvGetQuadrangleSubPix(
- const CvArr* src, //输入图像
- CvArr* dst, // 提取的四边形
- const CvMat* map_matrix //2*3的变换矩阵
- );
即对应每个点的变换:
![]()
WarpAffine与 GetQuadrangleSubPix 不同的在于cvWarpAffine 要求输入和输出图像具有同样的数据类型,有更大的资源开销(因此对小图像不太合适)而且输出图像的部分可以保留不变。而 cvGetQuadrangleSubPix 可以精确地从8位图像中提取四边形到浮点数缓存区中,具有比较小的系统开销,而且总是全部改变输出图像的内容。
实践:图像旋转变换(原尺寸)
首先用cvWarpAffine实验将图像逆时针旋转degree角度。
- //逆时针旋转图像degree角度(原尺寸)
- void rotateImage(IplImage* img, IplImage *img_rotate,int degree)
- {
- //旋转中心为图像中心
- CvPoint2D32f center;
- center.x=float (img->width/2.0+0.5);
- center.y=float (img->height/2.0+0.5);
- //计算二维旋转的仿射变换矩阵
- float m[6];
- CvMat M = cvMat( 2, 3, CV_32F, m );
- cv2DRotationMatrix( center, degree,1, &M);
- //变换图像,并用黑色填充其余值
- cvWarpAffine(img,img_rotate, &M,CV_INTER_LINEAR+CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS,cvScalarAll(0) );
- }
这里我们将新的图像还保留原来的图像尺寸。这样的效果显然不太好,我们通过计算相应放大图像尺寸。
实践:图像旋转变换(保留原图内容,放大尺寸)
需要计算新图的尺寸,示意图如下:
所以新图size为(width*cos(a)+height*sin(a), height*cos(a)+width*sin(a))
- //旋转图像内容不变,尺寸相应变大
- IplImage* rotateImage1(IplImage* img,int degree){
- double angle = degree * CV_PI / 180.; // 弧度
- double a = sin(angle), b = cos(angle);
- int width = img->width;
- int height = img->height;
- int width_rotate= int(height * fabs(a) + width * fabs(b));
- int height_rotate=int(width * fabs(a) + height * fabs(b));
- //旋转数组map
- // [ m0 m1 m2 ] ===> [ A11 A12 b1 ]
- // [ m3 m4 m5 ] ===> [ A21 A22 b2 ]
- float map[6];
- CvMat map_matrix = cvMat(2, 3, CV_32F, map);
- // 旋转中心
- CvPoint2D32f center = cvPoint2D32f(width / 2, height / 2);
- cv2DRotationMatrix(center, degree, 1.0, &map_matrix);
- map[2] += (width_rotate - width) / 2;
- map[5] += (height_rotate - height) / 2;
- IplImage* img_rotate = cvCreateImage(cvSize(width_rotate, height_rotate), 8, 3);
- //对图像做仿射变换
- //CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS - 填充所有输出图像的象素。
- //如果部分象素落在输入图像的边界外,那么它们的值设定为 fillval.
- //CV_WARP_INVERSE_MAP - 指定 map_matrix 是输出图像到输入图像的反变换,
- cvWarpAffine( img,img_rotate, &map_matrix, CV_INTER_LINEAR | CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS, cvScalarAll(0));
- return img_rotate;
- }
实践:图像旋转变换(保留原图内容,放大尺寸)-2
试一下用cvGetQuadrangleSubPix函数:
- //旋转图像内容不变,尺寸相应变大
- IplImage* rotateImage2(IplImage* img, int degree)
- {
- double angle = degree * CV_PI / 180.;
- double a = sin(angle), b = cos(angle);
- int width=img->width, height=img->height;
- //旋转后的新图尺寸
- int width_rotate= int(height * fabs(a) + width * fabs(b));
- int height_rotate=int(width * fabs(a) + height * fabs(b));
- IplImage* img_rotate = cvCreateImage(cvSize(width_rotate, height_rotate), img->depth, img->nChannels);
- cvZero(img_rotate);
- //保证原图可以任意角度旋转的最小尺寸
- int tempLength = sqrt((double)width * width + (double)height *height) + 10;
- int tempX = (tempLength + 1) / 2 - width / 2;
- int tempY = (tempLength + 1) / 2 - height / 2;
- IplImage* temp = cvCreateImage(cvSize(tempLength, tempLength), img->depth, img->nChannels);
- cvZero(temp);
- //将原图复制到临时图像tmp中心
- cvSetImageROI(temp, cvRect(tempX, tempY, width, height));
- cvCopy(img, temp, NULL);
- cvResetImageROI(temp);
- //旋转数组map
- // [ m0 m1 m2 ] ===> [ A11 A12 b1 ]
- // [ m3 m4 m5 ] ===> [ A21 A22 b2 ]
- float m[6];
- int w = temp->width;
- int h = temp->height;
- m[0] = b;
- m[1] = a;
- m[3] = -m[1];
- m[4] = m[0];
- // 将旋转中心移至图像中间
- m[2] = w * 0.5f;
- m[5] = h * 0.5f;
- CvMat M = cvMat(2, 3, CV_32F, m);
- cvGetQuadrangleSubPix(temp, img_rotate, &M);
- cvReleaseImage(&temp);
- return img_rotate;
- }

实践:图像放射变换(通过三点确定变换矩阵)
在OpenCV 2.3的参考手册中《opencv_tutorials》介绍了另一种确定变换矩阵的方法,通过三个点变换的几何关系映射实现变换。
变换示意图如下:
即通过三个点就可以确定一个变换矩阵。(矩形变换后一定为平行四边形)
以下是基于OpenCV 2.3的代码(需至少2.0以上版本的支持)
- int main( )
- {
- Point2f srcTri[3];
- Point2f dstTri[3];
- Mat rot_mat( 2, 3, CV_32FC1 );
- Mat warp_mat( 2, 3, CV_32FC1 );
- Mat src, warp_dst, warp_rotate_dst;
- //读入图像
- src = imread( "baboon.jpg", 1 );
- warp_dst = Mat::zeros( src.rows, src.cols, src.type() );
- // 用3个点确定A仿射变换
- srcTri[0] = Point2f( 0,0 );
- srcTri[1] = Point2f( src.cols - 1, 0 );
- srcTri[2] = Point2f( 0, src.rows - 1 );
- dstTri[0] = Point2f( src.cols*0.0, src.rows*0.33 );
- dstTri[1] = Point2f( src.cols*0.85, src.rows*0.25 );
- dstTri[2] = Point2f( src.cols*0.15, src.rows*0.7 );
- warp_mat = getAffineTransform( srcTri, dstTri );
- warpAffine( src, warp_dst, warp_mat, warp_dst.size() );
- /// 旋转矩阵
- Point center = Point( warp_dst.cols/2, warp_dst.rows/2 );
- double angle = -50.0;
- double scale = 0.6;
- rot_mat = getRotationMatrix2D( center, angle, scale );
- warpAffine( warp_dst, warp_rotate_dst, rot_mat, warp_dst.size() );
- ////OpenCV 1.0的形式
- //IplImage * img=cvLoadImage("baboon.jpg");
- //IplImage *img_rotate=cvCloneImage(img);
- //CvMat M =warp_mat;
- //cvWarpAffine(img,img_rotate, &M,CV_INTER_LINEAR+CV_WARP_FILL_OUTLIERS,cvScalarAll(0) );
- //cvShowImage("Wrap2",img_rotate);
- namedWindow( "Source", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
- imshow( "Source", src );
- namedWindow( "Wrap", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
- imshow( "Wrap", warp_dst );
- namedWindow("Wrap+Rotate", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
- imshow( "Wrap+Rotate", warp_rotate_dst );
- waitKey(0);
- return 0;
- }
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/7616044
实验代码下载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/xiaowei_cqu/4339856
写在最后的一点点闲话
之前一直用的2.1的版本,后来装了2.3,只是听说2.3很强大,但我刚开始学,用的也基础,完全没感觉出不同。直到今天忽然看到了2.3的手册,才发现从2.0开始函数和基本结构都有了很大的改变,而我一直还是用的1.0风格的函数(比如cvMat,cvLoadImage)。我的两个学习工具《Learnning OpenCV》和《OpenCV中文参考手册》都是基于1.0的,这也是我到今天才看到Mat,然后直接被惊艳到了。
别人总结出来的东西能帮助我们在一开始迅速入门,但要学深,学精,终归还是要自己去努力挖的。