hdu 1022 Train Problem I 栈
Train Problem I
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3121 Accepted Submission(s): 1148
Problem Description
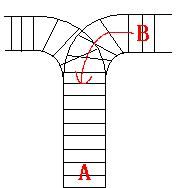
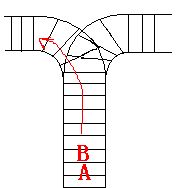
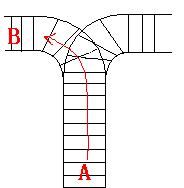
As the new term comes, the Ignatius Train Station is very busy nowadays. A lot of student want to get back to school by train(because the trains in the Ignatius Train Station is the fastest all over the world ^v^). But here comes a problem, there is only one railway where all the trains stop. So all the trains come in from one side and get out from the other side. For this problem, if train A gets into the railway first, and then train B gets into the railway before train A leaves, train A can't leave until train B leaves. The pictures below figure out the problem. Now the problem for you is, there are at most 9 trains in the station, all the trains has an ID(numbered from 1 to n), the trains get into the railway in an order O1, your task is to determine whether the trains can get out in an order O2.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case consists of an integer, the number of trains, and two strings, the order of the trains come in:O1, and the order of the trains leave:O2. The input is terminated by the end of file. More details in the Sample Input.
Output
The output contains a string "No." if you can't exchange O2 to O1, or you should output a line contains "Yes.", and then output your way in exchanging the order(you should output "in" for a train getting into the railway, and "out" for a train getting out of the railway). Print a line contains "FINISH" after each test case. More details in the Sample Output.
Sample Input
3 123 321 3 123 312
Sample Output
Yes. in in in out out out FINISH No. FINISH
For the first Sample Input, we let train 1 get in, then train 2 and train 3. So now train 3 is at the top of the railway, so train 3 can leave first, then train 2 and train 1. In the second Sample input, we should let train 3 leave first, so we have to let train 1 get in, then train 2 and train 3. Now we can let train 3 leave. But after that we can't let train 1 leave before train 2, because train 2 is at the top of the railway at the moment. So we output "No.".HintHint
设进出两个顺序分别为order1和order2,如果此时栈为空或者当前的栈顶元素不等于order2[i],就让order1[j]入栈,同时将"in"记录入q队列中。else如果此时栈顶元素等于order2[i],就将此栈顶元素弹出(sk.pop()),并将"out"记录入q队列。不断进行上面上面两个判断,直到两个数组遍历完,或者在中途中达不到目标顺序,使程序停止。#include<iostream> #include<queue> #include<stack> #include<string> using namespace std; int n; int i,j; char order1[12],order2[12]; void cal() { stack<char>sk; queue<string>q; for(i=0,j=0;i<n&&j<=n;) { if(sk.empty()||sk.top()!=order2[i]) { if(j==n) { cout<<"No./nFINISH"<<endl; return; } sk.push(order1[j++]); q.push("in"); } else { sk.pop(); q.push("out"); i++; } } cout<<"Yes."<<endl; string ch; while(!q.empty()) { ch=q.front(); cout<<ch<<endl; q.pop(); } cout<<"FINISH"<<endl; } int main() { while(cin>>n) { cin>>order1>>order2; cal(); } return 0; }上面代码较为简略了,后来又写了一次,下面代码比较清晰:#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<vector> #include"functional" #include<memory.h> #include<vector> #include"numeric" #include"algorithm" using namespace std; #define min(a,b)a>b?b:a #define N 12 #define IN 0 #define OUT 1 char o1[N],o2[N]; int seq[N*2]; int idx; int cal(int n) { int c1=0,c2=0; vector<char> V; //V.push_back(o1[c1++]); while(c1<=n) { while(!V.empty()&&V.back()==o2[c2]) { V.pop_back(); seq[idx++]=OUT; c2++; } while((V.empty()||V.back()!=o2[c2])&&c1<=n) { V.push_back(o1[c1]); seq[idx++]=IN; c1++; } } if(c2<n) return false; return true; } int main() { int n; while(cin>>n) { idx=0; cin>>o1>>o2; if(cal(n)) { cout<<"Yes."<<endl; for(int i=0;i<n*2;i++) if(seq[i]==IN) cout<<"in"<<endl; else cout<<"out"<<endl; } else cout<<"No."<<endl; cout<<"FINISH"<<endl; } return 0; }