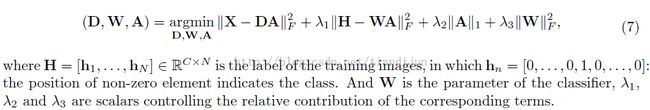图像分类的字典学习方法概述
1 字典学习(dictionary learning)
旨在从原始数据中找到一组特殊的稀疏信号,在机器视觉中称为视觉单词(visual words),这一组稀疏元素能够足够线性表示所有的原始信号。字典学习来源于压缩感知,后来广泛用于图像去噪、去雾、聚类、分类等方面。
两类:
1) 直接学习区分性的字典(directly forcing the dictionary discriminative)Track I
2)稀疏化系数,使得到的子弟那具有可区分性(making the sparse coefficients discriminative (usuallythrough simultaneously learning a classifier) to promote the discrimination ofthe dictionary.)Track II
2 字典学习的原理
假设为原始数据,字典学习的目的是通过下面的优化得到可区分性能很好表示原始数据的字典:
(1) Track I: Directly Making theDictionary Discriminative
The methods from Track I use the reconstruction error for the finalclassification, thus the learned dictionary ought to be as discriminative aspossible.
1)Meta-face learning
注:SRC(Sparse Representation-Based Classification)最开始用于鲁棒性人脸识别,C代表不同人脸个数,![]() 为原始训练样本,
为原始训练样本,![]() 是类的子集样本。SRC将原始数据当作完备字典,学习规则表达式如下:
是类的子集样本。SRC将原始数据当作完备字典,学习规则表达式如下:
SRC对于人脸是被效果很好,对噪声光照鲁棒性强,虽然不是直接涉及字典学习,但是用到了稀疏编码,开创了字典学习史上的先河,对大量数据处理速度问题有很大的改进和突破。
但是SRC将原始人脸图像作为完备字典,这种预定的字典会带有很多原始图像中的噪声等污染,而且字典冗余,当训练图像位数增加时,计算速度和事件遇到瓶颈问题。为此,提出了Meta-Face Learning方法。学习规则如下:
但是这样还是会遗漏子类的结构信息,如同类之间有共性,不同类间有差异性,为了使字典的可区分性更强,结构性更明显,可以再字典约束中加入规则项,极速那类间的关联度和相似度,体现结构特性。为此提出了Dictionary Learning with StructuredIncoherence方法。
3)Dictionary Learning with Structured Incoherence
Ramirez et al. note that the learned sub-dictionaries may share some common bases, i.e. some visual words from differentsub-dictionaries can be very coherent [8]. Undoubtedly, the coherence of the atomscan be used for reconstructing the query image interchangeably, and thereconstruction error based classifier will fail in identifying some queries. Tocircumvent this problem, they add an incoherence term term to drive thedictionaries associated to different classes as independent as possible.
(2) Track II: Making the CoefficientsDiscriminative
Track II is different from Track I in the way of discrimination. Contraryto Track I, it forces the sparse coefficients to be discriminative, andindirectly propagates the discrimination power to the overall dictionary. TrackII only need to learn an overall dictionary, instead of class-specificdictionaries.
2) Discriminative K-SVD forDictionary Learning
discriminative K-SVD (D-KSVD) tosimultaneously achieve a desired dictionary which has good representation powerwhile supporting optimal discrimination of the classes. D-KSVD adds a simplelinearregression as a penalty term to the conventional DL framework:
前两项可以合并一起,最后一项可以省略(原理见K-SVD,detailsin [13]).)
3) Label Consistent K-SVD
Jiang et al. propose alabel consistent K-SVD (LC-KSVD) method to learn a discriminative dictionaryfor sparse coding [5]. They introduce a label consistent constraint called“discriminative sparse-code error”, and combine it with the reconstructionerror and the classification error to form a unified objective function asbelow:
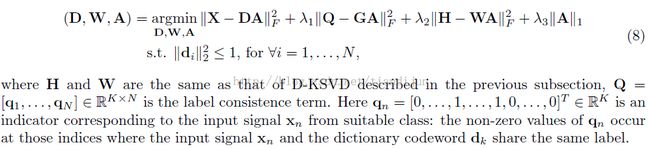
4) Fisher DiscriminantDictionary Learning
Yang et al. propose Fisher discrimination dictionary learning (Fisher DL) method based on the Fisher criterion to learn a structured dictionary [11], whose atomhas correspondence to the class label. The structured dictionaryis denoted as D = [D1, . . . ,DC], where Dc isthe class-specific sub-dictionary associated with the cth class.Denote the data set X = [X1, . . . ,XC], where Xc is the sub-set of the trainingsamplesfrom the cth class. Then they solve the following formulation overthe dictionary and the coefficients to derive the desired discriminativedictionary:
3 总结
回顾前面各种字典学习的方法,我们可以总结出字典学习规则的表达式如下:
第一部分是字典规则向,约束重构误差的;第二项是稀疏系数的可区分性约束,第三项和第四项是拉格朗如乘子的规则项.
References
[1] D. M. Bradley and J. A. Bagnell. Differentiablesparse coding. NIPS, 2008.
[2] B. Cheng, J. Yang, S. Yan, Y. Fu, and T. S.Huang. Learning with ℓ1-graph for image analysis.
IEEE Trans. Img. Proc., 19(4):858–866, Apr. 2010.
[3] M. Elad and M. Aharon. Image denoising vialearned dictionaries and sparse representation.
CVPR, 2006.
[4] M. Elad, M. Figueiredo, and Y. Ma. On the roleof sparse and redundant representations in
image processing. proceedings of IEEE, 98(6):972–982, 2010.
[5] Z. Jiang, Z. Lin, and L. S. Davis. Learning adiscriminative dictionary for sparse coding via
label consistent k-svd. CVPR,2011.
[6] J. Mairal, F. Bach, J. Ponce, G. Sapiro, and A.Zisserman. Supervised dictionary learning.
NIPS, 2008.
[7] R. Raina, A. Battle, H. Lee, B. Packer, and A.Y. Ng. Self-taught learning: transfer learning
from unlabeled data. ICML,2007.
[8] I. Ramirez, P. Sprechmann, and G. Sapiro.Classification and clustering via dictionary learning
with structured incoherence and shared features. CVPR, 2010.
[9] J. Wright, Y. Ma, J. Mairal, G. Sapiro, T.Huang, and S. Yan. sparse representation for computer vision and patternrecognition. proceedingsof IEEE, 98(6):1031–1044, 2010.
[10] J. Wright, A. Yang, A. Ganesh, S. Sastry, andY. Ma. Robust face recognition via sparse representation. PAMI, 2009.
[11] M. Yang, L. Zhang, X. Feng, and D. Zhang.Fisher discrimination dictionary learning for sparse
representation. ICCV,2011.
[12] M. Yang, L. Zhang, J. Yang, and D. Zhang.metaface learning for sparse representation based
face recognition. ICIP,2010.
[13] Q. Zhang and B. Li. Discriminative k-svd fordictionary learning in face recognition. CVPR,
2010.