【数据挖掘】最优化算法入门
简介
optimization用来解决以下问题:有多个变量协作,多种可能方法,输出很大程度上依赖各种变量的协作。
预测:通过尝试多种不同方法,并为它们打分来决定其效果。
#!/usr/bin/python
import time
import random
import math
#元组中存放的是人和其家乡
people = [('Seymour','BOS'),('Franny','DAL'),('Zooey','CAK'),('Walt','MIA'),
('Buddy','ORD'),('Les','OMA')]
destination='LGA'
flights={}
#将小时格式时间转换为分钟
def getminutes(t):
x=time.strptime(t,'%H:%M')
return x[3]*60+x[4]
#schedule.txt的文件格式:DAL,LGA,10:30,14:57,290
#其中DAL为起飞地、LGA为目的地,以及起飞时间、到达时间和价格
def loadflights(flightInfo):
fp = open(flightInfo,'r')
for line in fp.readlines():
origin,dest,depart,arrive,price=line.strip().split(',')
flights.setdefault((origin,dest),[])
flights[(origin,dest)].append((depart,arrive,price))
#r:[1,4,3,2,7,3,6,3,2,4,5,3],6个人乘坐的航班信息
#此列表代表了一个解决方案
#因为涉及到来回,所以r的长度为人数*2,所以第一和第二个元素代表了某人的去回的两趟
#航班信息
def printschedual(r):
for d in range(len(r)/2):
name=people[d][0]
origin=people[d][1]
out=flights[(origin,destination)][r[d]]
ret=flights[(destination,origin)][r[d+1]
print '%10s%10s %5s-%5s $%3s %5s-%5s $%3s' % (name,origin,\
out[0],out[1],out[2],\
ret[0],ret[1],ret[2])
代价函数
代价函数是使用最优化解决任何问题的关键。任何最优化的目标:找到一个输入集合(此例中就是航班信息),最小化代价函数。代价函数会考虑多个因素的影响,比如此例中会考虑到机票价格、等待时间、旅行时间、租车等。
#计算解决方案r的总成本,此例只考虑航班机票价格和等待时间两个因素
#每个人必须在目的地机场等待直到最晚到达的人到达,同时返回时他们同时达到机场,等候他们的航班
def schedulecost(r):
tprice=0#航班总价格之和
latestarrive=0#最晚到达
earliestdep=24*60#最早离开
for i in range(len(r)/2):
origin=people[i][0]
#去航班
outbound=flights[(origin,destination)][int(r[i])]
#回航班
returnf=flights[(destination,origin)][int(r[i+1])]
#航班票价
tprice+=outbound[2]
tprice+=returnf[2]
#记录最晚到达、最早离开时间
if latestarrive < getminutes(outbound[1]): latestarrive=getminutes(outbound[1])
if earliestdep > getminutes(returnf[0]):earliestdep=getminutes(returnf[0])
twaittime=0
for i in range(len(r)/2):
origin=people[i][0]
outbound=flights[(origin,destination)][int(r[i])]
returnf=flights[(destination,origin)][int(r[i+1])]
twaittime += latestarrive - getminutes(outbound[1])
twaittime += getminutes(returnf[0]) - earliestdep
return twaittime + tprice
随机搜索
#随机搜索并不是一个好的优化方法,但是它易于理解算法的思想
#domain是一个2元tuple的列表,tuple指定了变量的最大值和最小值
def randomoptimize(domain,costfunc):
best=999999999
bestr=None
for i in range(1000):#遍历1000次
#随机生成一个解决方案
r = [random.randint(domain[j][0],domain[j][1]) for j in range(len(domain))]
cost = costfunc(r)
#找到最小的代价
if cost < best:
best=cost
bestr=r
return bestr
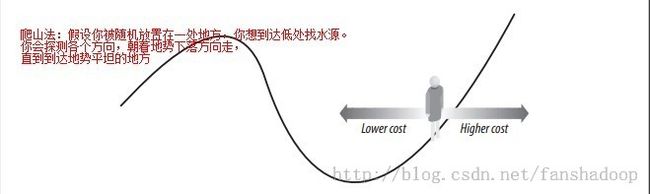
爬山法(Hill climbing)
随机搜索并不是有效的方法,它没有利用已经找到的好的解决方案,因为随机搜索在周围跳转,不能自动查找类似的解决方案。
def hillclimb(domain,costfunc):
#初始化,随机生成一个解决方案
sol = [random.randint(domain[j][0],domain[j][1]) for j in range(len(domain))]
while True:
neighbors=[]#创建sol的所有邻居,通过修改sol[j]的值
for j in range(len(domain)):
if sol[j] > domain[j][0]:#大于最小
neighbors.append(sol[0:j]+[sol[j]+1]+sol[j+1:])#将sol[j]元素加1
if sol[j]<domain[j][1]:#小于最大
neighbors.append(sol[0:j]+[sol[j]-1]+sol[j+1:])#将sol[j]元素减1
best=current=costf(sol)#当前sol的代价
for i in range(len(neighbors)):
cost=costf(neighbors[j])
if cost < best:
best=cost
sol=neighbors[j]
#若没有提高,则返回
if best == current:
break
return sol
模拟退火法
算法思想:
1)开始以随机一个解决方案,使用一个变量代表温度,此变量开始很高,逐渐变低2)在每次迭代,解决方案中的一个数字被随机选择,且朝一个方向改变。
3)如果新的代价低,则新的解决方案成为当前的解决方案,这点很像爬山法。然而,如果代价更高的话,新的解决方案以一定可能性任然是当前的解决方案,主要是尝试避免本地最小问题。
def annealingoptimize(domain,costf,t=10000.0,cool=0.95,step=1):
#初始化解决方案
vec = [float(random.randint(domain[i][0],domain[i][1])) for i in range(len(domain))]
while t > 0.1:
#随机选择一个
i=random.randint(0,len(domain)-1)
#随机选择一个方向变换
direction=random.randint(-step,step)
#复制集合
vecb=vec[:]
vecb[i]+=direction
#若变更后的vecb[i]小于最小值domain[i][0],vecb[i]变更为最小值
#若变更后的vecb[i]大于最大值domain[i][1],vecb[i]变更为最大值
if vecb[i]<domain[i][0]: vecb[i]=domain[i][0]
elif vecb[i]>domain[i][1]: vecb[i]=domain[i][1]
#计算变更前后的代价
ea=costf(vec)
eb=costf(vecb)
p=pow(math.e,(-eb-ea)/t)
#变更后的代价小于变更前的代价或随机数小于某概率p,变更解决方案
if (eb<ea or random.random()<p):
vec=vecb
#降温
t=t*cool
return vec
基因算法
#基因算法
def geneticoptimize(domain,costf,popsize=50,step=1,
mutprod=0.2,elite=0.2,maxiter=100):
#变异操作,随机选择vec中的一个元素进行处理,增大或减小,最后返回编译后的vec
def mutate(vec):
i=random.randint(0,len(domain)-1)
if random.random()<0.5 and vec[i]>domain[i][0]:
return vec[0:i]+[vec[i]-step]+vec[i+1:]
elif vec[i]<domain[i][1]:
return vec[0:i]+[vec[i]+step]+vec[i+1:]
#结合操作,将r1和r2在随机位置前后结合成新的解决方案
def crossover(r1,r2):
i=random.randint(1,len(domain)-2)
return r1[0:i]+r2[i:]
#构建初始化物种,pop物种大小
pop=[]
for i in range(popsize):
vec=[random.randint(domain[i][0],domain[i][1]) for i in range(len(domain))]
pop.append(vec)
#最终优胜者的个数
topelite=int(elite*popsize)
#主循环
for i in range(maxiter):
scores=[(costf(v),v) for v in pop]#为初始物种计算代价
scores.sort()
ranked=[v for (s,v) in scores]#排序后的解决方案
pop=ranked[0:topelite]#选取前topelite个解决方案
while len(pop)<popsize:#添加变异或组合后的解决方案,最终保持优胜者个数不变
if random.random()<mutprob:
# Mutation
c=random.randint(0,topelite)
pop.append(mutate(ranked[c]))
else:
# Crossover
c1=random.randint(0,topelite)
c2=random.randint(0,topelite)
pop.append(crossover(ranked[c1],ranked[c2]))
return scores[0][1]