关于USB-AUDIO使用ALSA编程的一点问题
转载自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-25272011-id-3153434.html
最近在调试一款原相PAP7501摄像头中的USB的麦克风,USB层走的应该是标准的UAC协议,具体可以见USB的官网:http://www.usb.org/developers/devclass_docs#approved,而音频部分则可以跑目前Linux标准的ALSA的PCM接口,对于硬件CODEC来说,与其是完全兼容的。
给出一份参考代码:
这个是仿照arecord写的一个简略的测试代码,保存为wav格式的。
1、recod.c
- /*
- This example reads from the default PCM device
- and writes to standard output for 5 seconds of data.
- */
- /* Use the newer ALSA API */
- #define ALSA_PCM_NEW_HW_PARAMS_API
- #include <alsa/asoundlib.h>
- /**************************************************************/
- #define ID_RIFF 0x46464952
- #define ID_WAVE 0x45564157
- #define ID_FMT 0x20746d66
- #define ID_DATA 0x61746164
- typedef unsigned long uint32_t;
- typedef unsigned short uint16_t;
- #define FORMAT_PCM 1
- static uint32_t totle_size = 0;
- struct wav_header {
- /* RIFF WAVE Chunk */
- uint32_t riff_id;
- uint32_t riff_sz;
- uint32_t riff_fmt;
- /* Format Chunk */
- uint32_t fmt_id;
- uint32_t fmt_sz;
- uint16_t audio_format;
- uint16_t num_channels;
- uint32_t sample_rate;
- uint32_t byte_rate; /* sample_rate * num_channels * bps / 8 */
- uint16_t block_align; /* num_channels * bps / 8 */
- uint16_t bits_per_sample;
- /* Data Chunk */
- uint32_t data_id;
- uint32_t data_sz;
- }__attribute__((packed));
- static struct wav_header hdr;
- /**************************************************************/
- int record_file(unsigned rate, unsigned channels, int fd, unsigned count)
- {
- long loops;
- int val;
- int rc;
- int size;
- snd_pcm_t *handle;
- snd_pcm_hw_params_t *params;
- int dir;
- snd_pcm_uframes_t frames;
- char *buffer; /* TODO */
- /* Open PCM device for recording (capture). */
- rc = snd_pcm_open(&handle, "plughw:0,0", SND_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE, 0);
- if (rc < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "unable to open pcm device: %s\n", snd_strerror(rc));
- exit(1);
- }
- /* Allocate a hardware parameters object. */
- snd_pcm_hw_params_alloca(¶ms);
- /* Fill it in with default values. */
- snd_pcm_hw_params_any(handle, params);
- /* Set the desired hardware parameters. */
- /* Interleaved mode */
- snd_pcm_hw_params_set_access(handle, params, SND_PCM_ACCESS_RW_INTERLEAVED);
- /* Signed 16-bit little-endian format */
- snd_pcm_hw_params_set_format(handle, params, SND_PCM_FORMAT_S16_LE);
- /* Two channels (stereo) */
- snd_pcm_hw_params_set_channels(handle, params, channels);
- /* rate bits/second sampling rate (CD quality) */
- snd_pcm_hw_params_set_rate_near(handle, params, &rate, &dir);
- /* Set period size to 32 frames. */
- frames = 320; /* 这边的大小也不是绝对的,可以调整 */
- snd_pcm_hw_params_set_period_size_near(handle, params, &frames, &dir);
- /* Write the parameters to the driver */
- rc = snd_pcm_hw_params(handle, params);
- if (rc < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "unable to set hw parameters: %s\n", snd_strerror(rc));
- exit(1);
- }
- /* Use a buffer large enough to hold one period */
- snd_pcm_hw_params_get_period_size(params, &frames, &dir);/* 获取实际的frames */
-
- size = frames * 2; /* 2 bytes/sample, 1 channels */
- buffer = (char *) malloc(size);
- /* We want to loop for 20 seconds 时间不一定准确 */
- snd_pcm_hw_params_get_period_time(params, &val, &dir);
- loops = 20000000 / val;
-
- while (loops > 0) {
- loops--;
- rc = snd_pcm_readi(handle, buffer, frames);
- if (rc == -EPIPE) {
- /* EPIPE means overrun */
- fprintf(stderr, "overrun occurred\n");
- snd_pcm_prepare(handle);
- } else if (rc < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "error from read: %s\n", snd_strerror(rc));
- } else if (rc != (int)frames) {
- fprintf(stderr, "short read, read %d frames\n", rc);
- }
- rc = write(fd, buffer, size);
- totle_size += rc; /* totle data size */
- if (rc != size)
- fprintf(stderr, "short write: wrote %d bytes\n", rc);
- }
-
- lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET); /* 回到文件头,重新更新音频文件大小 */
- hdr.riff_sz = totle_size + 36;
- hdr.data_sz = totle_size;
-
- if (write(fd, &hdr, sizeof(hdr)) != sizeof(hdr)) {
- fprintf(stderr, "arec: cannot write header\n");
- return -1;
- }
-
- snd_pcm_drain(handle);
- snd_pcm_close(handle);
- free(buffer);
- return 0;
- }
- /**************************************************************/
- int rec_wav(const char *fn)
- {
- unsigned rate, channels;
- int fd;
- fd = open(fn, O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0664);
- if (fd < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "arec: cannot open '%s'\n", fn);
- return -1;
- }
- hdr.riff_id = ID_RIFF;
- hdr.riff_fmt = ID_WAVE;
- hdr.fmt_id = ID_FMT;
- hdr.audio_format = FORMAT_PCM;
- hdr.fmt_sz = 16;
- hdr.bits_per_sample = 16;
- hdr.num_channels = 1;
- hdr.data_sz = 0; /* TODO before record over */
- hdr.sample_rate = 16000;
- hdr.data_id = ID_DATA;
-
- hdr.byte_rate = hdr.sample_rate * hdr.num_channels * hdr.bits_per_sample / 8;
- hdr.block_align = hdr.num_channels * hdr.bits_per_sample / 8;
-
- if (write(fd, &hdr, sizeof(hdr)) != sizeof(hdr)) {
- fprintf(stderr, "arec: cannot write header\n");
- return -1;
- }
- fprintf(stderr,"arec: %d ch, %ld hz, %d bit, %s\n",
- hdr.num_channels, hdr.sample_rate, hdr.bits_per_sample,
- hdr.audio_format == FORMAT_PCM ? "PCM" : "unknown");
-
- return record_file(hdr.sample_rate, hdr.num_channels, fd, hdr.data_sz);
- }
- int main(int argc, char **argv)
- {
- if (argc != 2) {
- fprintf(stderr,"usage: arec <file>\n");
- return -1;
- }
- return rec_wav(argv[1]);
- }
样本长度(sample):样本是记录音频数据最基本的单位,常见的有8位和16位。
通道数(channel):该参数为1表示单声道,2则是立体声。
桢(frame):桢记录了一个声音单元,其长度为样本长度与通道数的乘积。
采样率(rate):每秒钟采样次数,该次数是针对桢而言。
周期(period):音频设备一次处理所需要的桢数,对于音频设备的数据访问以及音频数据的存储,都是以此为单位。
交错模式(interleaved):是一种音频数据的记录方式,在交错模式下,数据以连续桢的形式存放,即首先记录完桢1的左声道样本和右声道样本(假设为立体声格式),再开始桢2的记录。而在非交错模式下,首先记录的是一个周期内所有桢的左声道样本,再记录右声道样本,数据是以连续通道的方式存储。不过多数情况下,我们只需要使用交错模式就可以了。
具体可以参照:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-25272011-id-3151136.html
一开始我犯过一个错误就是rc = snd_pcm_readi(handle, buffer, frames),这个函数的参数3的单位应该是帧大小,而一个帧的大小是根据你的量化位数和声道数决定的,对于本代码,是16bit单声道,自然一个帧大小是2字节,起初我将申请的buffer大小传给了这个参数,结果必然导致“卡顿”或者“快进”,“卡顿”是因为我在项目中是实时传输,会导致阻塞,毕竟数据量大了一倍,“快进”则是因为缓冲区的大小是实际读取数据的一半,有一半的数据在buffer中被自己给覆盖掉了,所以要慎重啊。
2、Makefile
- exe = record
- src = record.c
- CC = arm-linux-gcc
- INC = -I/nfs/usr/local/arm-alsa/include
- LDFLAGS = -lpthread -L/nfs/usr/local/arm-alsa/lib -lasound
- $(exe) : $(src) FORCE
- $(CC) -o $@ $(src) $(LDFLAGS) $(INC)
- FORCE:
- clean:
- rm -f ./*.o $(exe)
此处的alsa-lib库就是之前介绍的安装的库的路径,编译可以引用该路径的库,而运行之后库的路径可不受限制,按照你定义的环境变量找到即可。
对于内核的配置则在
- Device Drivers --->
- <*> Sound card support --->
- <*> Advanced Linux Sound Architecture --->
- [*] USB sound devices --->
- <*> USB Audio/MIDI driver
对于这款USB麦克风,我正常的去录音的时候,上层的直观感觉就是卡顿,这个与上面提到的是有区别的,因为同样的代码在arm上是好的,所以就怀疑是底层读慢了,(我们的应用背景是开发板实时录音,通过USB-WIFI发到上位机同步播放)很明显的是读取音频数据慢了。而同样的代码跑硬件的CODEC是很好的,不卡顿,所以很有可能问题出在USB上。我们刚好有USB的协议分析仪,我们USB是跑的全速模式,其描述符为
- Interface Descriptor:
- bLength 9
- bDescriptorType 4
- bInterfaceNumber 3
- bAlternateSetting 0
- bNumEndpoints 0
- bInterfaceClass 1
- bInterfaceSubClass 2
- bInterfaceProtocol 0
- iInterface 0
- Interface Descriptor:
- bLength 9
- bDescriptorType 4
- bInterfaceNumber 3
- bAlternateSetting 1
- bNumEndpoints 1
- bInterfaceClass 1
- bInterfaceSubClass 2
- bInterfaceProtocol 0
- iInterface 0
- AudioStreaming Interface Descriptor:
- bLength 7
- bDescriptorType 36
- bDescriptorSubtype 1 (AS_GENERAL)
- bTerminalLink 3
- bDelay 1 frames
- wFormatTag 1 PCM
- AudioStreaming Interface Descriptor:
- bLength 11
- bDescriptorType 36
- bDescriptorSubtype 2 (FORMAT_TYPE)
- bFormatType 1 (FORMAT_TYPE_I)
- bNrChannels 1
- bSubframeSize 2
- bBitResolution 16
- bSamFreqType 1 Discrete
- tSamFreq[ 0] 16000
- Endpoint Descriptor:
- bLength 9
- bDescriptorType 5
- bEndpointAddress 0x83 EP 3 IN
- bmAttributes 5
- Transfer Type Isochronous
- Synch Type Asynchronous
- Usage Type Data
- wMaxPacketSize 0x0020 1x 32 bytes
- bInterval 4
- bRefresh 0
- bSynchAddress 0
- AudioControl Endpoint Descriptor:
- bLength 7
- bDescriptorType 37
- bDescriptorSubtype 1 (EP_GENERAL)
- bmAttributes 0x01
- Sampling Frequency
- bLockDelayUnits 0 Undefined
- wLockDelay 0 Undefined
- /************************************************************************/
- Interface Descriptor:
- bLength 9
- bDescriptorType 4
- bInterfaceNumber 3
- bAlternateSetting 2
- bNumEndpoints 1
- bInterfaceClass 1
- bInterfaceSubClass 2
- bInterfaceProtocol 0
- iInterface 0
- AudioStreaming Interface Descriptor:
- bLength 7
- bDescriptorType 36
- bDescriptorSubtype 1 (AS_GENERAL)
- bTerminalLink 3
- bDelay 1 frames
- wFormatTag 1 PCM
- AudioStreaming Interface Descriptor:
- bLength 11
- bDescriptorType 36
- bDescriptorSubtype 2 (FORMAT_TYPE)
- bFormatType 1 (FORMAT_TYPE_I)
- bNrChannels 1
- bSubframeSize 2
- bBitResolution 16
- bSamFreqType 1 Discrete
- tSamFreq[ 0] 48000
- Endpoint Descriptor:
- bLength 9
- bDescriptorType 5
- bEndpointAddress 0x83 EP 3 IN
- bmAttributes 5
- Transfer Type Isochronous
- Synch Type Asynchronous
- Usage Type Data
- wMaxPacketSize 0x0060 1x 96 bytes
- bInterval 4
- bRefresh 0
- bSynchAddress 0
- AudioControl Endpoint Descriptor:
- bLength 7
- bDescriptorType 37
- bDescriptorSubtype 1 (EP_GENERAL)
- bmAttributes 0x01
- Sampling Frequency
- bLockDelayUnits 0 Undefined
- wLockDelay 0 Undefined
看到描述符,顺便插一句,对照端点大小计算一下,蓝色字体,这款USB-AUDIO只支持16K和48K的16bit单声道录音,拿16K为例,1s数据量应该是16K*16/8=32KB,对应于端点的大小32B*1000=32KB,也就是说全速模式下应该是每帧(1ms)请求一次才对,而对于图中的红色字体,说明的意思是全速模式下的ISO传输请求间隔参数是4,对应我们的USB的控制器,意思即为每8帧才发起一次ISO请求,抓包验证确实如此,这一点确实比较诡异,问题可能就出在这里:
但是对于几乎同样的驱动版本,我们611的是2.6.32.9而arm的是2.6.32.2,其sound目录下的usbaudio.c基本是相同的,描述符又是相同的,所以上层获取描述符进行的配置应该也是相同的,唯一的区别就是USB的控制器,我们611的是musb,而arm的是OHCI,我们musb对这个bInterval的配置是
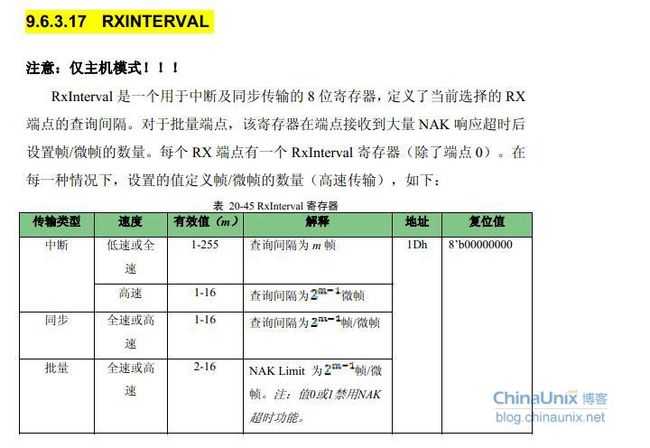
因此驱动固然是8帧请求一次。我在OHCI的控制器中未找到类似的寄存器,猜想可能是OHCI默认的就是ISO传输每一帧会保证一次,其抓包图如下:
所以只好强制去修改musb的驱动配置,/drivers/usb/musb/musb_host.c
- 2013 /* precompute rxtype/txtype/type0 register */
- 2014 type_reg = (qh->type << 4) | qh->epnum;
- 2015 switch (urb->dev->speed) {
- 2016 case USB_SPEED_LOW:
- 2017 type_reg |= 0xc0;
- 2018 break;
- 2019 case USB_SPEED_FULL:
- 2020 type_reg |= 0x80;
- 2021 break;
- 2022 default:
- 2023 type_reg |= 0x40;
- 2024 }
- 2025 qh->type_reg = type_reg;
- 2026
- 2027 /* Precompute RXINTERVAL/TXINTERVAL register */
- 2028 switch (qh->type) {
- 2029 case USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_INT:
- 2030 /*
- 2031 * Full/low speeds use the linear encoding,
- 2032 * high speed uses the logarithmic encoding.
- 2033 */
- 2034 if (urb->dev->speed <= USB_SPEED_FULL) {
- 2035 interval = max_t(u8, epd->bInterval, 1);
- 2036 break;
- 2037 }
- 2038 /* FALLTHROUGH */
- 2039 case USB_ENDPOINT_XFER_ISOC:
- 2040 /* ISO always uses logarithmic encoding */
- 2041 //interval = min_t(u8, epd->bInterval, 16);
- 2042 interval = min_t(u8, epd->bInterval, 1); //JGF
- 2043 break;
- 2044 default:
这样USB就是每帧请求一次,同样的代码,效果和2440的也一样了。