高级文本功能(二)
16.2 Creating Styled Text
在第15章中,我们已经了解了显示了普通文本与HTML。通过Swing文本组件-或者至少是JTextPane-我们也可以显示格式化文本,其中不同的文本块可以具有多种属性。这些属性也许包含粗体,斜体,不同的字体或是字符级别的颜色,或者是段落级别的对齐,就如现现代的字处理软件一样。
要支持这些功能,Swing提供了许多不同的接口与类,所有这些接口与类以特殊的StyledDocument的Document接口扩展开始。我们在第15章中介绍了Document接口,专注于PlainDocument实现类。StyledDocument接口,或者更确切的说是DefaultStyledDocument实现,管理Document内容的一系列格式与属性集合。
StyleDocument所用的各种格式初始时是由AttributeSet接口来描述的,他是一个只读属性的键/值对集合。一个属性的键也许是“当前的字体”,在这种情况下设置将是所用的字体。要实际修改字体,我们需要求助于MutableAttributeSet接口,他提供了添加也移除属性的功能。例如,如果我们有一个用于“粗体”的AttributeSet,我们可以使用MutableAttributeSet来添加斜体,下划线或是颜色设置。
对于AttributeSet的简单实现,有一个StyleContext.SmallAttributeSet类,他使用一个数组来管理属性集合。对于MutableAttributeSet接口的实现,有一个SimpleAttributeSet类,他使用Hashtable来管理属性。更为复杂的属性设置需要Style接口,他向属性集合添加由MutableAttributeSet定义的名字。实际的Style实现类是StyleContext.NamedStyle类。除了添加一个名字,Style接口添加功能来使得ChangeListener监视属性集合的变化。
为StyledDocument管理Style对象集合的类是StyleContext类。他是AbstractDocument.AttributeContext接口的一个实现,StyleContext使用StyleConstants类为常用的格式定义各种属性。当使用HTML文档时,StyleContext实际上是一个StyleSheet,这他也许会有助于我们理解整个布局。记住在这里所讨论的所有类与接口(除了StyleSheet)仅需要用来为一个特定的JTextPane设置Document数据模型。
16.2.1 StyledDocument接口与DefaultStyledDocument类
StyledDocument接口通过添加了存储文档内容格式的功能来扩展Document接口。这些格式可以描述字符或是段落属性,例如颜色,方向或是字体。
public interface StyledDocument extends Document {
public Style addStyle(String nm, Style parent);
public Color getBackground(AttributeSet attribute);
public Element getCharacterElement(int position);
public Font getFont(AttributeSet attribute);
public Color getForeground(AttributeSet attribute);
public Style getLogicalStyle(int position);
public Element getParagraphElement(int position);
public Style getStyle(String name);
public void removeStyle(String name);
public void setCharacterAttributes(int offset, int length, AttributeSet s,
boolean replace);
public void setLogicalStyle(int position, Style style);
public void setParagraphAttributes(int offset, int length, AttributeSet s,
boolean replace);
}
DefaultStyledDocument类是Swing组件所提供的StyledDocument接口的实现。他作为JTextPane组件的数据模型。
创建DefaultStyledDocument
我们可以使用下面所列的三种方法来创建DefaultStyledDocument:
public DefaultStyledDocument() DefaultStyledDocument document = new DefaultStyledDocument(); public DefaultStyledDocument(StyleContext styles) StyleContext context = new StyleContext(); DefaultStyledDocument document = new DefaultStyledDocument(context); public DefaultStyledDocument(AbstractDocument.Content content, StyleContext styles) AbstractDocument.Content content = new StringContent(); DefaultStyledDocument document = new DefaultStyledDocument(content, context);
我们可以在多个文档之间共享StyleContext或是使用默认的上下文环境。另外,我们可以使用AbstractDocument.Content的一个实现,GapContent或是StringContent预定义内容。存储实际的Document内容是这些Content实现的职责。
DefaultStyledDocument属性
除了具有默认的根元素来描述文档的内容以外,DefaultStyledDocument将可用的格式名字作为Enumeration。这是在DefaultStyledDocument级别所定义的两个属性,如表16-2所示。当然我们也可以获得DefaultStyledDocument的其他属性;然而,他们需要获取时的位置或是AttributeSet。
16.2.2 AttributeSet接口
AttributeSet接口描述了一个只读的键/值属性集合,允许我们访问一系列属性的描述性内容。如果属性集合缺少特定的键定义,AttributeSet通过在一个链中遍历解析属性的父属性定义。这使得AttributeSet定义一个核心属性集合,并且允许开发者(或者可能是用户)仅修改他们所希望修改的属性集合。除非我们希望有人修改默认全局设置,我们不应提供到解析父属性的直接访问。这样,我们就不会丢失任何的原始设置。
public interface AttributeSet {
// Constants
public final static Object NameAttribute;
public final static Object ResolveAttribute;
// Properties
public int getAttributeCount();
public Enumeration getAttributeNames();
public AttributeSet getResolveParent();
// Other methods
public boolean containsAttribute(Object name, Object value);
public boolean containsAttributes(AttributeSet attributes);
public AttributeSet copyAttributes();
public Object getAttribute(Object key);
public boolean isDefined(Object attrName);
public boolean isEqual(AttributeSet attr);
}
16.2.3 MutableAttributeSet接口
MutableAttributeSet接口描述了我们如何由属性集合中添加或是移除属性,以及如何设置解析父属性。
public interface MutableAttributeSet extends AttributeSet {
public void addAttribute(Object name, Object value);
public void addAttributes(AttributeSet attributes);
public void removeAttribute(Object name);
public void removeAttributes(AttributeSet attributes);
public void removeAttributes(Enumeration names);
public void setResolveParent(AttributeSet parent);
}
16.2.4 SimpleAttributeSet类
SimpleAttributeSet类是AttributeSet接口的第一个实现。当我们开始使用这个类时,我们最终将会看到如何创建显示在JTextPane中的多属性文本。SimpleAttributeSet类是依赖用于管理键/属性对的标准Hashtable的AttributeSet的一个特定实现。
创建SimpleAttributeSet
SimpleAttributeSet有两个构造函数:
public SimpleAttributeSet() SimpleAttributeSet attributeSet1 = new SimpleAttributeSet(); public SimpleAttributeSet(AttributeSet source) SimpleAttributeSet attributeSet2 = new SimpleAttributeSet(attributeSet1);
我们通常会创建一个空的SimpleAttributeSet,然后设置其属性。或者我们可以在构造函数中提供一个初始的设置集合。注意,这并不是解析父属性-他仅是一个初始化的数据结构。
SimpleAttributeSet属性
表16-3显示了SimpleAttributeSet的四个属性。他们提供了到属性集合的访问,使得我们可以了解属性是否存在,并且标记解析父属性。
使用SimpleAttributeSet
要创建SimpleAttributeSet所用的AttributeSet,我们需要查找我们要修改的属性的键。我们会在稍后讨论StyleConstants时了解一些助手方法。所有的键隐藏在StyleConstants的四个公开内联类中:CharacterConstants,ColorConstants,FontConstants与ParagraphConstants,如表16-4所示。
例如,要在创建DefaultStyledDocument之后填充JTextPane的StyledDocument,我们通过调用public void insertString(int offset, String contents, AttributeSet attributes)方法来向其中添加内容,该方法会抛出BadLocationException。然后我们可以修改属性集合并且添加更多的属性。所以,如果我们希望创建同时为粗体与斜体的内容,我们需要向SimpleAttributeSet中添加两个属性并将内容添加到文档中:
SimpleAttributeSet attributes = new SimpleAttributeSet();
attributes.addAttribute(StyleConstants.CharacterConstants.Bold, Boolean.TRUE);
attributes.addAttribute(StyleConstants.CharacterConstants.Italic, Boolean.TRUE);
// Insert content
try {
document.insertString(document.getLength(), "Hello, Java", attributes);
} catch (BadLocationException badLocationException) {
System.err.println("Oops");
}
图16-4显示程序运行的结果。
列表16-4显示了完整的示例源码。
package swingstudy.ch16;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTextPane;
import javax.swing.text.BadLocationException;
import javax.swing.text.DefaultStyledDocument;
import javax.swing.text.SimpleAttributeSet;
import javax.swing.text.StyleConstants;
import javax.swing.text.StyledDocument;
public class SimpleAttributeSample {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Runnable runner = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Simple Attributes");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
StyledDocument document = new DefaultStyledDocument();
SimpleAttributeSet attributes = new SimpleAttributeSet();
attributes.addAttribute(StyleConstants.CharacterConstants.Bold, Boolean.TRUE);
attributes.addAttribute(StyleConstants.CharacterConstants.Italic, Boolean.TRUE);
// Insert content
try {
document.insertString(document.getLength(), "Hello, Java", attributes);
}
catch(BadLocationException badLocationException) {
System.err.println("Bad Insert");
}
attributes = new SimpleAttributeSet();
attributes.addAttribute(StyleConstants.CharacterConstants.Bold, Boolean.FALSE);
attributes.addAttribute(StyleConstants.CharacterConstants.Italic, Boolean.FALSE);
attributes.addAttribute(StyleConstants.CharacterConstants.Foreground, Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
// Insert content
try {
document.insertString(document.getLength(), " - Good-bye Visual Basic", attributes);
}
catch(BadLocationException badLocationException) {
System.err.println("Bad Insert");
}
JTextPane textPane = new JTextPane(document);
textPane.setEditable(false);
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(textPane);
frame.add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setSize(300, 150);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
};
EventQueue.invokeLater(runner);
}
}概括来说,要指定文档的格式,只需要简单的设置属性集合,插入内容,然后为我们要添加到的每一个内容重复以上步骤。
16.2.5 StyleConstants类
StyleConstants类满是简化设置属性集合的助手方法。而且我们并不需要深入StyleConstants内联类的常量,因为通守StyleConstants级别的类常量就可以进行访问。
public static final Object Alignment; public static final Object Background; public static final Object BidiLevel; public static final Object Bold; public static final Object ComponentAttribute; public static final String ComponentElementName; public static final Object ComposedTextAttribute; public static final Object Family; public static final Object FirstLineIndent; public static final Object FontFamily; public static final Object FontSize; public static final Object Foreground; public static final Object IconAttribute; public static final String IconElementName; public static final Object Italic; public static final Object LeftIndent; public static final Object LineSpacing; public static final Object ModelAttribute; public static final Object NameAttribute; public static final Object Orientation; public static final Object ResolveAttribute; public static final Object RightIndent; public static final Object Size; public static final Object SpaceAbove; public static final Object SpaceBelow; public static final Object StrikeThrough; public static final Object Subscript; public static final Object Superscript; public static final Object TabSet; public static final Object Underline;
一些静态方法可以使得我们使用更符合逻辑的方法来修改MutableAttributeSet,而不需要我们了解更为隐蔽的AttributeSet名字。使用StyleConstants变量的ALIGN_CENTER,ALIGN_JSTIFIED,ALIGN_LEFT与ALIGN_RIGH可以作为int参数用于setAlignment()方法。其余的设置都是自解释的。
public static void setAlignment(MutableAttributeSet a, int align); public static void setBackground(MutableAttributeSet a, Color fg); public static void setBidiLevel(MutableAttributeSet a, int o); public static void setBold(MutableAttributeSet a, boolean b); public static void setComponent(MutableAttributeSet a, Component c); public static void setFirstLineIndent(MutableAttributeSet a, float i); public static void setFontFamily(MutableAttributeSet a, String fam); public static void setFontSize(MutableAttributeSet a, int s); public static void setForeground(MutableAttributeSet a, Color fg); public static void setIcon(MutableAttributeSet a, Icon c); public static void setItalic(MutableAttributeSet a, boolean b); public static void setLeftIndent(MutableAttributeSet a, float i); public static void setLineSpacing(MutableAttributeSet a, float i); public static void setRightIndent(MutableAttributeSet a, float i); public static void setSpaceAbove(MutableAttributeSet a, float i); public static void setSpaceBelow(MutableAttributeSet a, float i); public static void setStrikeThrough(MutableAttributeSet a, boolean b); public static void setSubscript(MutableAttributeSet a, boolean b); public static void setSuperscript(MutableAttributeSet a, boolean b); public static void setTabSet(MutableAttributeSet a, TabSet tabs); public static void setUnderline(MutableAttributeSet a, boolean b);
例如,我们并不需要使用下面的代码来使得SimpleAttributeSet成为粗体与斜体:
attributes.addAttribute(StyleConstants.CharacterConstants.Bold, Boolean.TRUE) attributes.addAttribute(StyleConstants.CharacterConstants.Italic, Boolean.TRUE)
相反,我们可以使用下面的方法来替代:
StyleConstants.setBold(attributes, true); StyleConstants.setItalic(attributes, true);
正如我们所看到的,后一种方法更易于阅读且更易于维护。
提示,除了修改AttributeSet对象的方法,StyleConstants类还提供了许多其他的方法可以使得我们检测AttributeSet的状态来确定某一个当前设置是否被允许或是禁止。
16.2.6 TabStop and TabSet类
用于存储AttributeSet值的一个关键常量是ParagraphConstants.TabSet属性。TabSet类表示一个TabStop对象的集合,其中的每一个定义了tab位置,对象方式以及导引。如果我们希望为JTextPane定义我们自己的tab定位,我们需要创建一个TabStop对象集合,为每一个tab定位创建一个TabSet,然后将TabSet关联到MutableAttributeSet。
创建TabStop
TabStop类并不是通常意义上的JavaBean组件;他并没有一个无参数的构造函数。相反,我们必须以像素指定tab定位的位置。他有两个构造函数:
public TabStop(float position) TabStop stop = new TabStop(40); public TabStop(float position, int align, int leader) TabStop stop = new TabStop(40, TabStop.ALIGN_DECIMAL, TabStop.LEAD_DOTS);
注意,尽管由技术上来说可以指定,但是TabStop构造函数的leader参数当前被预定义的文本组件所忽略。
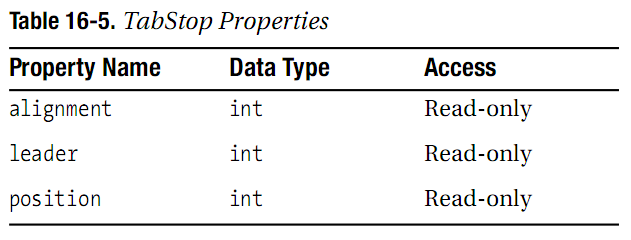
TabStop属性
表16-5显示了TabStop的三个属性,每一个都可以通过构造函数初始化。
四个对齐设置是通过表16-6中的四个常量来指定的。图16-5显示了不同的设置。
注意,尽管ALIGN_BAR与ALIGN_LEFT由技术上来说是不同的常量,但是当前他们的对齐设置会产生相同的结果。他们是为RTF规范所定义的。
使用TabStop对象
一旦我们拥有了一个TabStop对象或是一个TabStop对象集合,我们将对象以TabStop对象数组的形式传递给TabSet构造函数,如下所示:
TabSet tabset = new TabSet(new TabStop[] {tabstop})
作为一个示例,列表16-5显示了产生图16-5的TabStop对象程序的源码。
/**
*
*/
package swingstudy.ch16;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JScrollPane;
import javax.swing.JTextPane;
import javax.swing.text.BadLocationException;
import javax.swing.text.DefaultStyledDocument;
import javax.swing.text.SimpleAttributeSet;
import javax.swing.text.StyleConstants;
import javax.swing.text.StyledDocument;
import javax.swing.text.TabSet;
import javax.swing.text.TabStop;
/**
* @author mylxiaoyi
*
*/
public class TabSample {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Runnable runner = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Tab Attributes");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
StyledDocument document = new DefaultStyledDocument();
int positions[] = {TabStop.ALIGN_BAR, TabStop.ALIGN_CENTER, TabStop.ALIGN_DECIMAL,
TabStop.ALIGN_LEFT, TabStop.ALIGN_RIGHT };
String strings[] = {"\tBAR\n", "\tCENTER\n", "\t3.14159265\n",
"\tLEFT\n", "\tRIGHT\n" };
SimpleAttributeSet attributes = new SimpleAttributeSet();
for(int i=0, n=positions.length; i<n; i++) {
TabStop tabstop = new TabStop(150, positions[i], TabStop.LEAD_DOTS);
try {
int position = document.getLength();
document.insertString(position, strings[i], null);
TabSet tabset = new TabSet(new TabStop[] {tabstop});
StyleConstants.setTabSet(attributes, tabset);
document.setParagraphAttributes(position, 1, attributes, false);
}
catch(BadLocationException badLocationExeption) {
System.err.println("Bad Location");
}
}
JTextPane textPane = new JTextPane(document);
textPane.setEditable(false);
JScrollPane scrollPane = new JScrollPane(textPane);
frame.add(scrollPane, BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setSize(300, 150);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
};
EventQueue.invokeLater(runner);
}
}除了指定位置与对齐方式,我们还可以指定我们希望使用哪种字符作为导引字符显示在通过tab字符所创建的空白空间中。默认情况下并不存在任何内容;所以是常量LEAD_NONE。其他的TabStop值可以创建句点线,等号,连字符,细线或是下划线:LEAD_DOTS,LEAD_EQUALS,LEAD_HYPHENS,LEAD_THICKLINE或是LEAD_UNDERLINE。不幸的是,这个选项可用但是并不被支持。虽然非标准的Swing组件也许会支持这种功能,但是标准的Swing组件当前并不支持不同的导引字符串。
16.2.7 Style接口
Style接口是一种指定AttributeSet的加强方法。他为MutableAttributeSet添加了一个名字以及为了监视属性设置的变化将ChangeListener关联到Style的能力。例如,我们可以以下面的方式来配置粗体斜体格式:
String BOLD_ITALIC = "BoldItalic"; Style style = (Style)document.getStyle(StyleContext.DEFAULT_STYLE); StyleConstants.setBold(style, true); StyleConstants.setItalic(style, true); document.addStyle(BOLD_ITALIC, null);
稍后,我们可以将这个种格式关联到文本:
style = document.getStyle(BOLD_ITALIC); document.insertString(document.getLength(), "Hello, Java", style);
16.2.8 StyleContext类
StyleContext类管理格式化文档的格式。借助于StyleContext.NamedStyle类,我们可以使用JTextPane仅做他自己的事情,因为StyleContext知道某些事情何时完成。对于HTMl文档,StyleContext就变为更为特殊的StyleSheet。