IOS CoreData 使用(二)
实例背景描述:
在MKMapView视图上绘制多边形和圆形两种区域。首先从服务器上下载多个区域的JSon数据坐标,解析后存储到Core Data中。
一 创建模型视图
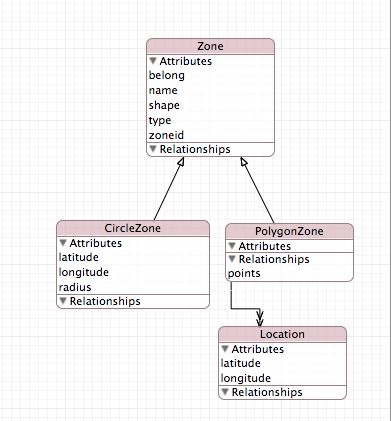
如下图所示,Zone是抽象类保存了圆形和多边形区域的共同属性,圆形和多边形区域继承自Zone Entity.多边形区域和Location一对多的关系。Location用来存储多边形的边界点。
编辑完视图后生成.h和.m文件。
二 解析存储数据
直接上代码
CircleZone *circleZone = nil;
PolygonZone *polygonZone = nil;Location *myLocation = nil;
for (count=0;count!=length;++count)
{
NSInteger shape = [[[allObjects objectAtIndex:count] objectForKey:@"Shape"] integerValue];
if (shape == 0) //多边形
{
polygonZone =(PolygonZone*)[NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:@"PolygonZone" inManagedObjectContext:self.myManageObjectContext];
NSDictionary* boundary = [[allObjects objectAtIndex:count] objectForKey:@"Boundary"];
NSArray* points = [boundary objectForKey:@"points"];
NSInteger pointsNum = points.count,i;
for (i=0; i!=pointsNum; i++)
{
CLLocationDegrees latitude = [[[points objectAtIndex:i] objectForKey:@"latitude"] doubleValue];
CLLocationDegrees longitude = [[[points objectAtIndex:i] objectForKey:@"longitude"] doubleValue];
CLLocationCoordinate2D location = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(latitude, longitude);
MKMapPoint point = MKMapPointForCoordinate(location);
myLocation = (Location*) [NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:@"Location" inManagedObjectContext:self.myManageObjectContext];
myLocation.longitude = [NSNumber numberWithDouble:longitude];
myLocation.latitude = [NSNumber numberWithDouble:latitude];
[polygonZone addPointsObject:myLocation];
}
}
else //圆形
{
//取半径
NSDictionary* boundary = [[allObjects objectAtIndex:count] objectForKey:@"Boundary"];
CLLocationDegrees radius = [[boundary objectForKey:@"radius"] doubleValue];
//取圆心坐标
NSDictionary* center = [boundary objectForKey:@"center"];
CLLocationDegrees latitude = [[center objectForKey:@"latitude"] doubleValue];
CLLocationDegrees longitude = [[center objectForKey:@"longitude"] doubleValue];
CLLocationCoordinate2D location = CLLocationCoordinate2DMake(latitude, longitude);
circleZone =(CircleZone*)[NSEntityDescription insertNewObjectForEntityForName:@"CircleZone" inManagedObjectContext:self.myManageObjectContext];
circleZone.longitude = [NSNumber numberWithDouble:longitude];
circleZone.latitude = [NSNumber numberWithDouble:latitude];
circleZone.radius = [NSNumber numberWithDouble:radius];
}
NSInteger Id = [[[allObjects objectAtIndex:count] objectForKey:@"Id"] integerValue];
NSString *name = [[allObjects objectAtIndex:count] objectForKey:@"Name"];
NSInteger belong = [[[allObjects objectAtIndex:count] objectForKey:@"Belong"] integerValue];
NSInteger type = [[[allObjects objectAtIndex:count] objectForKey:@"Type"] integerValue];
if (circleZone != nil) {
circleZone.zoneid = [NSNumber numberWithInt:Id];
circleZone.name = [NSString stringWithString:name];
circleZone.belong = [NSNumber numberWithInt:belong];
circleZone.shape = [NSNumber numberWithInt:shape];
else{
polygonZone.zoneid = [NSNumber numberWithInt:Id];
polygonZone.name = [NSString stringWithString:name];
polygonZone.belong = [NSNumber numberWithInt:belong];
polygonZone.shape = [NSNumber numberWithInt:shape];
}
NSError *error;
if ([self.myManageObjectContext save:&error] == NO )
{
NSLog(@"This was an error!");
}
else
{
NSLog(@"Save succeed!");
}
circleZone = nil;
polygonZone = nil;
}//for
注意加粗部分的代码,被插入到上下文中的托管对象在执行上下文的sava操作的时候才会将要保存的数据传到持久化调度器,然后持久化调度器才会将其保存到数据库中。为了提高程序的性能,我们在创建完左右对象后调用一次sava操作,如果每创建一个对象就调用一次save操作会比较耗时,降低程序执行效率。
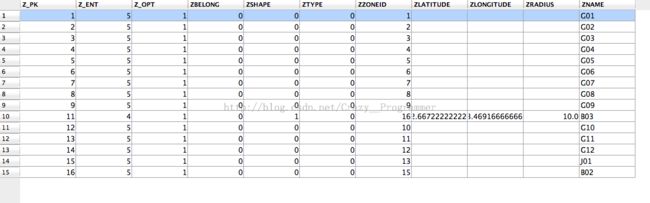
保存后我们可以查看一下Sqlite数据库中存储的数据情况:
观察发现圆形和多边形区域的类的基本属性多存储到了一个表中。
三 数据的处理
//***************
查询圆形区域 结果按照
zoneid升序顺序
***********
NSEntityDescription
*discription = [NSEntityDescription entityForName:@"Zone" inManagedObjectContext:self.objectContext];
NSFetchRequest *request = [[NSFetchRequest alloc] init];
NSSortDescriptor *sortDis = [[NSSortDescriptor alloc] initWithKey:@"zoneid" ascending:YES];
NSPredicate *predicate = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"shape = %@",[NSNumber numberWithInt:1]];
[request setSortDescriptors:@[sortDis]];
[request setPredicate:predicate];
[request setEntity:discription];
[request setEntity:discription];
NSError *error = nil;
NSArray *array = [self.objectContext executeFetchRequest:request error:&error];
//***************
修改对象
*******************
}
if ([array count]] > 0) {
Zone *zone = (Zone*)[array objectAtIndex:0];
zone.name = @"被修改了";
}
if (![self.objectContext save:&error])
{
NSLog(@"There was an error!");
}
Zone *zone = (Zone*)[array objectAtIndex:0];
zone.name = @"被修改了";
}
if (![self.objectContext save:&error])
{
NSLog(@"There was an error!");
}
}
//*************** 删除
对象
*******************
Zone *zone = nil;
if ([array count]] > 0) {
zone = (Zone*)[array objectAtIndex:0];
}
if (zone)
{
[self.objectContext deleteObject:zone];
}
if ([self.objectContext hasChanges])
{
if (![self.objectContext save:&error])
{
NSLog(@"There was an error!");
}
}