用 FragmentTabHost 实现底部菜单
先不多说,上几张效果图看看:
好了,效果图看了,是不是感觉挺不错的呢,那么我们就来实现它吧,其实也不难,底部用到了FragmentTabHost,然后图片和文字的变色用到了selector背景选择器。那么接下来就来一步一步的实现吧。
首先我们来看一张图,解释一下底部的原理:
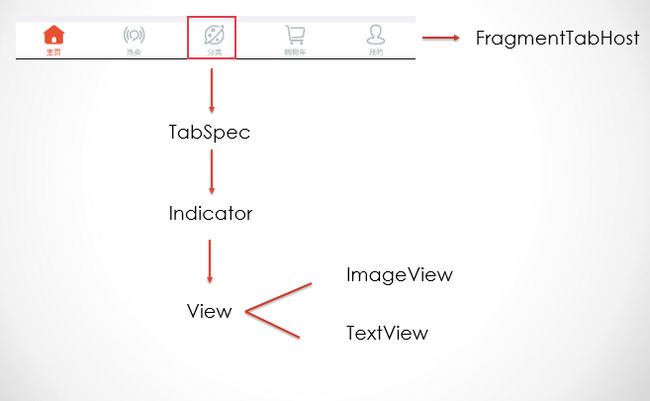
在这里我们可以看到,底部是一个FragmentTabHost,然后在这个FragmentTabHost中添加TabSpec,然后由indicator组成。下面首先看看TabSpec的官方解释:
A tab has a tab indicator, content, and a tag that is used to keep track of it. This builder helps choose among these options. For the tab indicator, your choices are: 1) set a label 2) set a label and an icon For the tab content, your choices are: 1) the id of a View 2) a TabHost.TabContentFactory that creates the View content. 3) an Intent that launches an Activity.
大概意思就是说有一个选项卡指示器,帮助我们在选项卡中进行选择,我们可以放入图片和文字那么我们来说下这个View,也就是说图标和文字是同一个View,包含了一个ImageView和一个TextView,那么我们首先来创建这个View吧。
tab_indicator.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_marginTop="3dp" android:layout_gravity="center" android:gravity="center" android:orientation="vertical" android:paddingBottom="3dp">
<ImageView android:id="@+id/icon_tab" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView android:textColor="@color/selector_color_text" android:id="@+id/text_indicator" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="2dp"/>
</LinearLayout>说到了tabhost,我们首先看看这个布局文件如何创建的吧,也就是说上代码:
activity_main.xml:
//这个官方的文档中也没有给出例子,还是我没有找到呢,不过网上的大都都是以下这样写的,tabcontent这个只是一个假的,真的是realtabcontent。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical">
<FrameLayout android:id="@+id/realtabcontent" android:layout_weight="1" android:background="@color/bg_color" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dip"/>
<com.example.ruolan.letgo.widget.FragmentTabHost android:id="@android:id/tabhost" android:background="@color/white" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<FrameLayout android:layout_weight="0" // android:id="@android:id/tabcontent" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="0dp"></FrameLayout>
</com.example.ruolan.letgo.widget.FragmentTabHost>
</LinearLayout>当然了哈,这里的FragmentTabHost并不是官方的哈,而是找的一个文件(我可没有那么大的本事)
那么好了,既然布局文件已经创建了,我们就开始实现我们需要的功能吧:
在实现之前我们先要知道FragmentTabHost用法的用法:
那么就先来看看官方给的例子吧:
private FragmentTabHost mTabHost;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
mTabHost = new FragmentTabHost(getActivity());
mTabHost.setup(getActivity(), getChildFragmentManager(), R.id.fragment1);
mTabHost.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("simple").setIndicator("Simple"),
FragmentStackSupport.CountingFragment.class, null);
mTabHost.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("contacts").setIndicator("Contacts"),
LoaderCursorSupport.CursorLoaderListFragment.class, null);
mTabHost.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("custom").setIndicator("Custom"),
LoaderCustomSupport.AppListFragment.class, null);
mTabHost.addTab(mTabHost.newTabSpec("throttle").setIndicator("Throttle"),
LoaderThrottleSupport.ThrottledLoaderListFragment.class, null);
return mTabHost;
}可以看得出来,有三步:
第一步是:activity继承FragmentActivity
第二步是:调用setup()方法
第三步是:添加tabSpec
**好了,既然知道了怎么使用,下面我们就先实现一个吧:
主要的代码:**
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
mTabHost = (FragmentTabHost) findViewById(android.R.id.tabhost);
//调用setup()方法
mTabHost.setup(this,getSupportFragmentManager(),R.id.realtabcontent);
//新建TabSpec
TabHost.TabSpec tabSpec = mTabHost.newTabSpec("主页");
//创建新的View,也就是刚才前面讲的View
View view = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.tab_indicator,null);
img = (ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.icon_tab);
text = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.text_indicator);
img.setBackgroundResource(R.mipmap.icon_home);
text.setText(R.string.home);
tabSpec.setIndicator(view);
//添加tabSpec,这里我们要传三个参数
//分别是tabSpec、class、null
mTabHost.addTab(tabSpec,HomeFragment.class,null);
是不是有点小激动了,我刚开始实现的时候也是很激动的,以前自己想都不敢想,不过实现之后,想想就是这么一回事(万事开头难)。
那么接下来的四个,其实如果不想麻烦的话,就是cory代码,实现其余的四个,不过是不是感觉有点浪费呢,让我cory五份,多么不好哈,太麻烦了哈,哈哈,那么我们就来建一个bean类吧,看看需要什么参数吧。大家也看到了,我们需要三个参数,就是Class–>Fragment , title—-> 文字 image –>图片
创建想必大家都会创建,我就不多说了,直接上代码:
package com.example.ruolan.letgo.bean;
/** * Created by ruolan on 2015/11/29. */
public class Tab {
private int title;
private int image;
private Class fragment;
public Tab(int title, int image, Class fragment) {
this.title = title;
this.image = image;
this.fragment = fragment;
}
public int getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(int title) {
this.title = title;
}
public Class getFragment() {
return fragment;
}
public void setFragment(Class fragment) {
this.fragment = fragment;
}
public int getImage() {
return image;
}
public void setImage(int image) {
this.image = image;
}
}
那么我们的activity中的代码也需要改了,也就是我们的专业名词(封装)。
private void initTab() {
//虽然说要简便,不过该少的还是不能少的哈,最少你得创建这5个tab吧
Tab home = new Tab(R.string.home,R.drawable.selector_icon_home,HomeFragment.class);
Tab hot = new Tab(R.string.hot,R.drawable.selector_icon_hot, HotFragment.class);
Tab category = new Tab(R.string.category,R.drawable.selector_icon_category,CategoryFragment.class);
Tab cart = new Tab(R.string.cart,R.drawable.selector_icon_cart,CartFragment.class);
Tab mine = new Tab(R.string.mine,R.drawable.selector_icon_mine,MineFragment.class);
//mTabs是一个list数组,需要存放我们创建的五个tab
mTabs.add(home);
mTabs.add(hot);
mTabs.add(category);
mTabs.add(cart);
mTabs.add(mine);
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
mTabHost = (FragmentTabHost) findViewById(android.R.id.tabhost);
//调用setup()方法
mTabHost.setup(this, getSupportFragmentManager(), R.id.realtabcontent);
//遍历这个数组,把每个都设置好,
for (Tab tab:mTabs) {
TabHost.TabSpec tabSpec = mTabHost.newTabSpec(getString(tab.getTitle()));
tabSpec.setIndicator(builderIndiator(tab));
mTabHost.addTab(tabSpec,tab.getFragment(),null);
}
//去掉分割线
mTabHost.getTabWidget().setShowDividers(LinearLayout.SHOW_DIVIDER_NONE);
mTabHost.setCurrentTab(0);
}
//既然说到了代码良好,好看,那么我们就重新创建一个方法
private View builderIndiator(Tab tab){
View view = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.tab_indicator, null);
img = (ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.icon_tab);
text = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.text_indicator);
img.setBackgroundResource(tab.getImage());
text.setText(tab.getTitle());
return view;
}当然这里当我们点击图片的时候,图片是可以变色的,文字也会可以变色的,这个就要使用selector背景选择器了。当然我们首先看看selector的状态:
1.android:state_pressed="true/false"
true:表示按下状态下使用,false:表示非按下状态下使用。
2.android:state_focused="true/false"
ture:表示聚焦状态使用(例如使用滚动球/D-pad聚焦Button),false:表示非聚集状态下使用。
3.android:state_selected="true/false"
true:表示被选中状态下使用,false:表示非选中下使用
4.android:state_active="true/false"
true:表示可勾选状态时使用,false:表示不可勾选状态下使用
5. android:state_checkable="true/false"
true:表示勾选状态下使用,false:表示非勾选状态使用
6.android:state_checked="true/false"
true:表示勾选状态下使用,false:表示非勾选状态使用
7. android:state_enabled="true/false"
true:表示可用状态使用(能接收触摸/点击事件),false:表示不可用状态使用
8. android:state_window_focused="true/false"
true:表示应用程序窗口有焦点时使用(应用程序在前台),false:表示无焦点时使用
当然我们最常用的还是前面三种:
如果是图片的背景选择器,我们首先在res/drawable文件目录下(我用的是AS)创建:
selector_icon_home.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:state_focused="true" android:drawable="@mipmap/icon_home_press"/>
<item android:state_selected="true" android:drawable="@mipmap/icon_home_press"/>
<item android:drawable="@mipmap/icon_home"/>
</selector>上面的使用的时候直接在使用图片资源的时候使用。
文字的背景选择器,这个要在res/color目录下
selector_color_text.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:color="#eb4f38" android:state_selected="true"/>
<item android:color="#eb4f38" android:state_active="true"/>
<item android:color="#a9b7b7" android:state_activated="false"/>
<item android:color="#a9b7b7" android:state_active="false"/>
</selector>这个在布局文件textview中使用 android:textColor=”@color/selector_color_text”
好了,最后就在onCreate()方法中调用initTab()方法就行了,运行的效果图就是刚开始的那个效果图,我就不上了,最后这个小的项目已经上传至我的github,可以下载源码。下载地址:https://github.com/wuyinlei/FragmentTabHost.git,如果有不对的地方,还请大神们指点迷津,我也是刚刚使用的哈。