css网页编程【详解】
CSS(Cascading Style Sheets)
(下面例子中可能出现编码格式问题,只需将浏览器编码格式换成utf-8就可以)
一、CSS概述
CSS是层叠样式表(Cascading Style Sheets)用来定义网页的显示效果。可以解决html代码对样式定义的重复,提高了后期样式代码的可维护性,并增强了网
页的显示效果功能。简单一句话:CSS将网页内容和显示样式进行分离,提高了显示功能。
二、CSS与HTML相结合的四种方式
1、style属性方式
<span style="font-size:14px;"><p style="background-color:#FF0000; color:#FFFFFF">
p标签段落内容。
</p></span>
2、style标签方式
<span style="font-size:14px;"><style type=”text/css”>
p { color:#FF0000;}
</style></span>
3、导入方式
<span style="font-size:14px;"><style type="text/css">
@import url(myDiv.css)
</style></span>
注:导入语句必须放在style标签最前面(类似java中的导包)
4、链接方式
<span style="font-size:14px;"><link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="css_3.css" media="screen" /></span>例:(请仔细看注释,很有帮助)
<span style="font-size:14px;"><!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>html与css相结合的方式.html</title>
<!-- html与css相结合的第四种方式:用link标签导入css样式表文件 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="link.css">
<style type="text/css">
/*html与css相结合的第三种方式:用import导入css样式表文件*/
@import url(cor.css);/*导入css的语句必须在前面*/ /*cor.css相当于java中的配置文件,此处是配置样式*/
/* html与css相结合的第二种方式:添加style标签*/
p{
color:#0000ff;
background-color:#ff0000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>这是span标签中的内容</span>
<!-- html与css相结合的第一种方式:给html标签添加style属性 -->
<p style="color:#00ff00">
这是段落标签中的内容
</p>
<div>
这是div标签中的内容
</div>
</body>
</html>
</span>
cor.css
<span style="font-size:14px;">@CHARSET "UTF-8"; @import url(myDiv.css); @import url(mySpan.css);</span>myDiv.css
<span style="font-size:14px;">@CHARSET "UTF-8";
/*
* 这个是转义编码的用 因为一般的国内网页都是gb2312 的编码 如果想使用utf-8的编码的话
* 就加上那句话css里@charset "utf-8"的作用跟
* 网页中的<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html;
* charset=utf-8" /> 这句话是一样的
*/
div {
color:#0000FF;
background-color:#FF0000;
}
</span>
mySpan.css
<span style="font-size:14px;">@CHARSET "UTF-8";
span {
color:#00ff00;
background-color:#ffff00;
border:#0000ff 3px solid;
}
</span>
link.css
<span style="font-size:14px;">@CHARSET "UTF-8"
p {
color:#00FF00;
background-color:ffff00;
border:#0000ff 1px solid;
}</span>
三、相关语法
1、样式优先级
由上到下,由外到内。优先级由低到高。——总之,一般情况是以后加载为主,但还有细节优先级问题(后面会讲到)。
2、CSS代码格式
选择器名称 { 属性名:属性值;属性名:属性值;…….}
1)属性与属性之间用 分号 隔开
2)属性与属性值直接按用 冒号 连接
3)如果一个属性有多个值的话,那么多个值用 空格 隔开。
例:(请仔细看注释,很有帮助)
<html>
<head>
<title>cssDemo.html</title>
<style type="text/css">
ul{
list-style-position:inside;/*设置项目符号与文字位置,inside表示绘制的项目符号与文字在一起,默认为outside*/
list-style-image:url("house.png");
}
table{
border-bottom:#0c0 double 4px;
border-top:#0c0 double 4px;
border-left:#f00 dotted 4px;
border-right:#f00 dotted 4px;
border-collapse:collapse;/*设置或获取表明表格行和单元格边框是组合为单一边框还是像标准 HTML 那样分离。(就是相邻两个单元格边框是否合二为一)*/
}
table td{
border:#0cf solid 1px;
padding:20px;
}
div{
border:#0c0 solid 1px;
height:100px;
width:200px;
margin-top:50px;
padding:30px;
}
input{
border:none;
border-bottom:#00f solid 2px;
}
table#tid{/*这里一定要注意table 和 #tid之间千万不能有空格*/
border:#0c0 solid 1px;
border-collapse:collapse;
}
table#tid td{
padding:5px;
}
table input{
border:none;
}
table input:hover{
background-color:#f1e1ff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>无序列表项1</li>
<li>无序列表项2</li>
<li>无序列表项3</li>
<li>无序列表项4</li>
</ul>
<table>
<tr><td>内容11</td><td>内容12</td></tr>
<tr><td>内容21</td><td>内容22</td></tr>
</table>
<div>这是一个div中的文字</div>
<hr/>
姓名:<input type="text" /> 成绩:<input type="text" />
<p>输入成绩:</p>
<table id="tid">
<tr><td><input type="text"></td><td><input type="text"></td></tr>
<tr><td><input type="text"></td><td><input type="text"></td></tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
现象:

四、选择器
就是指定CSS要作用的标签,那个标签的名称就是选择器。意为:选择哪个容器(标签本身就是封装数据的容器)。
1、选择器种类
1) html标签名选择器。使用的就是html的标签名。
2) class选择器。其实使用的是标签中的class属性。
3) id选择器。其实使用的是标签的中的id属性。
每一个标签都定义了class属性和id属性。用于对标签进行标识,方便对标签进行操作。
在定义的中,多个标签的class属性值可以相同,而id值要唯一,因为JavaScript中经常用。
2、选择器优先级
标签名选择器 < class选择器 < id选择器 < style属性
例:(请仔细看注释,很有帮助)
<span style="font-size:14px;"><!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>选择器优先级的演示</title>
<!-- [ 标签 < class < id < style ] -->
<style type="text/css">
div{
background:#ffff00;
color:#0000FF;
}
div.a{
background:#ad5a5a;
}
/*接在div后面写 可以直接写出“.*”
.b{
background:#00ffff;
}
*/
#pid{
background:#e800e8;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span class="b">This is "span label" content ! </span>
<div> This is "div label" content !---two </div>
<!-- "div标签选择器"所设的样式不起作用,说明优先级:标签 < class -->
<div class="a"> This is "div label" content !---one </div>
<!-- class所设的样式不起作用,说明优先级:class < id -->
<div class="a" id="pid"> This is "div label" content !---three </div>
<div class="b"> This is "div label" content !---five </div>
<span> This is "span label" content !---two </span>
<!-- id所设的样式不起作用,说明优先级:id < style -->
<span id="pid" style="color:#ffffff;background:#000000"> This is "span label" content !---three </span>
</body>
</html>
</span>
五、扩展选择器
1、关联选择器
标签是可以嵌套的,要让相同标签中的不同标签显示不同样式,就可以用此选择器。
<span style="font-size:14px;">p { color:#00FF00;}
p b { color:#FF000;}
<p>P标签<b>csdn博客频道</b>段落样式</p>
<p>P标签段落</p> </span>
2、组合选择器
对多个选择器进行相同样式的定义。例如,我们想对“div中的<b>标签”和“类名为cc”的区域设置相同的样式,则可以定义如下的组合选择器:
.cc, div b{/*不同选择器之间用逗号分开*/
background-color:#0000ff;
color:#fff;
}
3、伪元素选择器
其实就在html中预先定义好的一些选择器,称为伪元素。
格式:标签名:伪元素。类名 标签名。类名:伪元素。
1)超链接a标签中的伪元素
a:link 超链接未点击状态。
a:visited 被访问后的状态。
a:hover 光标移到超链接上的状态(未点击)。
a:active 点击超链接时的状态。
使用顺序: L – V – H – A(巧记:驴打哈,个人:绿化)
2)段落p标签中的伪元素
p:first-line 段落的第一行文本。
p:first-letter 段落中的第一个字母。
3)自定义伪元素
:focus 具有焦点的元素
div:hover{
background-color:#f00;
color:#fff;
}例:(请仔细看注释,很有帮助)
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
<title>扩展选择器的演示</title>
<style type="text/css">
div{
background:#ffff00;
color:#0000FF;
}
.b{
text-decoration:line-through;
font-style:italic;
font-size:25px;
}
/*关联选择器:设置div标签中的b标签容器的样式*/
div b{
background:#ff0000;
}
/*组合选择器:给几个选择器设置相同的样式*/
span b,.c{
color:#ff00ff;
}
/*L-V-H-A 绿化*/
/*伪元素选择器:html中预先定义好的一些选择器,称为伪元素*/
a:link{/*未点击前的样式*/
background-color:#0066ff;
color:#ffffff;
text-decoration:none;
font-size:18px;
}
a:visited{/*点击之后的样式*/
background-color:#999999;
color:#000000;
text-decoration:line-through;
}
a:hover{/*鼠标悬停时的样式*/
background-color:#06f;
color:#000000;
font-size:25px;
}
a:active{/*鼠标点击时(点下去不松)的样式*/
background-color:#000;
color:#fff;
font-size:32px;
}
p:first-letter{/*首字母(或第一个汉字)伪元素*/
font-size:36px;
color:#f00;
}
div:hover{
background-color:#f00;
color:#fff;
}
input:focus{/*鼠标点击的样式*/
background-color:#09f;
color:#fff;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>
这是一个div标签中的文字<b>这是第一组粗体字</b>
</div>
<b>这是第二章粗体字</b>
<br>
<span>
这是一个span标签中的文字<b>这是第三组粗体字</b>
</span>
<br>
<b class="c">这是第四组粗体字</b>
<br>
<a href="http:www.hncu.net" target="_blank">演示超链接伪元素选择器</a>
<p>这是段落标签中的文字。。。</p>
<div class="b">这是div标签中的文字</div>
用户名:<input type="text"/><br/>
密 码:<input type="password"/><br/>
</body>
</html>
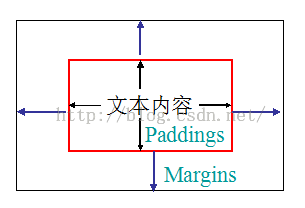
六、CSS的盒子模型
1、CSS布局——基本概念
◇边框(border)
上 border-top
下 border-bottom
左 border-left
右 border-right
◇内补丁(Paddings):内边距
上 padding-top
下 padding-bottom
左 padding-left
右 padding-right
◇外补丁(Margins):外边距
上 margin-top
下 margin-bottom
左 margin-left
右 margin-right
2、CSS布局——漂浮
◇ float : none | left | right
none : 默认值。对象不飘浮
left : 文本流向对象的右边
right : 文本流向对象的左边
◇ clear : none | left | right | both
none : 默认值。允许两边都可以有浮动对象
left : 不允许左边有浮动对象
right : 不允许右边有浮动对象
both : 不允许有浮动对象
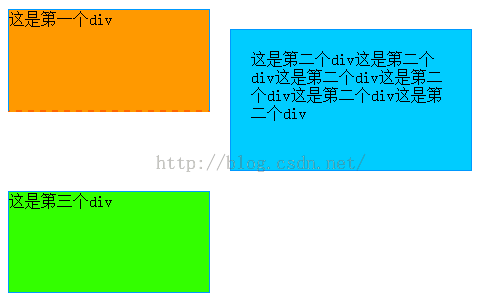
例:(请仔细看注释,很有帮助)
<html>
<head>
<title>box_div</title>
<style type="text/css">
div{
border:#09f solid 1px;
height:100px;
width:200px;
}
#div_1{
border-bottom:#f60 2px dashed;
background-color:#f90;
float:left;/*float:表示以流的形式布局,且从左开始*/
}
#div_2{
margin:20px; /*div框外:四个方向*/
/*margin:20px 100px;div框外:上下20px和左右100px*/
/*margin:20px 100px 200px;div框外:上20px,左右100px,下200px*/
/*margin-left:30px;
margin-top:25px;单个设置四个方向*/
padding:20px 20px;/*div里面的内容与内边框的距离*/
background-color:#0cf;
float:left;
}
#div_3{
background-color:#3f0;
float:left;
clear:left;/*表示其左边不能放任何其他的东西*/
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div_1">这是第一个div</div>
<div id="div_2">这是第二个div这是第二个div这是第二个div这是第二个div这是第二个div这是第二个div</div>
<div id="div_3">这是第三个div</div>
</body>
</html>
3、CSS布局——定位
◇ position : static | absolute | fixed | relative
static : 默认值。无特殊定位,对象遵循HTML定位规则。
absolute : 将对象从文档流中拖出,使用 left , right , top , bottom 等属性相对于其最接近的一个最有定位设置的父对象进行绝对定位。如果不存在这样的父对象,则依据 body 对象。而其层叠通过 z-index 属性定义。
fixed : 未支持。对象定位遵从绝对(absolute)方式。但是要遵守一些规范。
relative : 对象不可层叠,但将依据 left , right , top , bottom 等属性在正常文档流中偏移位置。
例:(请仔细看注释,很有帮助)
<html>
<head>
<title>box_div2</title>
<style type="text/css">
div{
border:#09f solid 1px;
height:100px;
width:200px;
}
#div_1{
background-color:#f90;
float:left;
position:absolute;/*absolute:所谓绝对位置,就是说定了在哪就在那(没有商量的余地),不会再因其它样式改变*/
top:150px;
left:120px;
}
#div_2{
background-color:#0cf;
float:left;
width:300px;
}
#div_3{
background-color:#3f0;
float:left;
clear:left;
}
#div_4{
background-color:#3f0;
clear:both;
position:relative;/*相对于absolute要弱点,表示先要根据正常的排列流动,然后再根据top、left定位*/
top:20px;
}
#div_5{
background-color:#0cf;
float:left;
width:300px;
}
#div_6{
background-color:#3f0;
float:left;
clear:left;
}
#div_0{
position:absolute;
top:200px;
left:200px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="div_1">这是一个div中的文字1</div>
<div id="div_2">这是一个div中的文字2</div>
<div id="div_3">这是一个div中的文字3</div>
<hr/>
<div id="div_0">
<div id="div_4">这是一个div中的文字4</div>
<div id="div_5">这是一个div中的文字5</div>
<div id="div_6">这是一个div中的文字6</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
4、CSS布局——图文混排、图像签名
例:
<html>
<head>
<title>img.html</title>
<style type="text/css">
#imgSign{
border:#09f solid 1px;
width:600px;
position:absolute;
top:100px;
left:600px;
}
/*#imgSign、img1、img之间一定要有空格*/
#imgSign #img1 img{
float:right;
height:300;
width:400;
}
#imgSign #text1{
font-family:"隶书";
color:#ff0;
font-size:18px;
position:relative;
top:240px;
left:240px;
}
#imgText{
border:#09f solid 1px;
width:600px;
}
#imgText #img2{
float:right;
}
#imgText #text2{
font-family:"隶书";
color:#f60;
font-size:18px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>2015级新生军训动员大会</h1>
<div id="imgSign">
<div id="img1"><img alt="" src="2.jpg" /></div>
<div id="text1">军训动员现场</div>
</div>
<hr/>
<div id="imgText">
<div id="img2"><img alt="" src="2.jpg" height=200 width=300/></div>
<div id="text2">
9 月 17 日 上午,我校2015级新生军训动员大会在田径场隆重举行。副校长汤放华、丁亮中、国防科技大学指挥学院副指导员李旺军以及学校武装部、宣传部、学生工作部、资产处相关负责人,各学院总支副书记、新生辅导员、全体承训官兵和2015级4000名参训新生参加大会。
大会在庄严的升旗仪式中拉开序幕。丁亮中在会上作了军训动员报告。
2015级新生军训按专业分为55个连队,参训学生4000人。在为期12天的军训中,参训新生将参加队列训练、法制安全教育、消防知识教育、内务整理、实弹射击、军训阅兵活动等。
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>