SimpleAdapter源码和VIewBinder浅析
先看下SimpleAdapter的简单用法
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private ListView list;
private SimpleAdapter adapter;
private List<Map<String, String>> dataList;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
init();
}
private void init() {
list = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.list);
intitData();
adapter = new SimpleAdapter(MainActivity.this,
dataList, R.layout.list_item,
new String[]{"tv", "btn"}, new int[]{R.id.tv, R.id.btn});
list.setAdapter(adapter);
}
private void intitData() {
dataList = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("tv", "data"+i);
map.put("btn", "btn"+i);
dataList.add(map);
}
}
}
布局:
activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/list"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello_world" />
</RelativeLayout> list_item.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="asdd"
android:textSize="22sp"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="btn"
/>
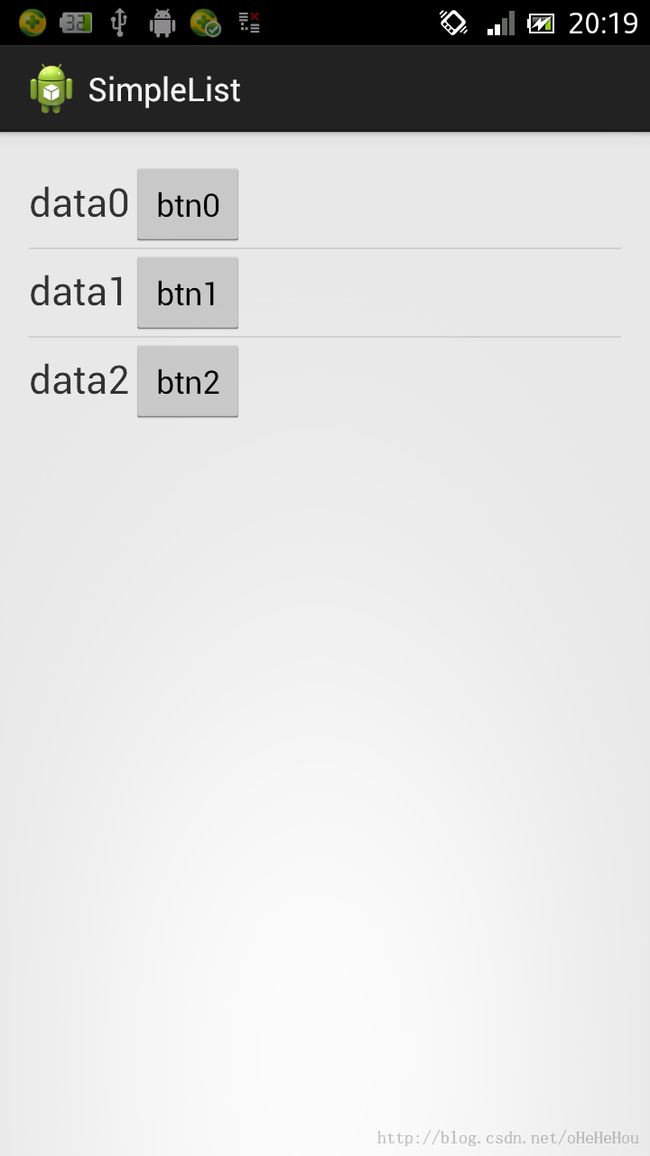
</LinearLayout> 效果:
下面来分析一下SimpleAdapter中关键的代码
getView(),返回listview每行的视图
private View createViewFromResource(int position, View convertView,
ViewGroup parent, int resource) {
View v;
if (convertView == null) {
v = mInflater.inflate(resource, parent, false);
} else {
v = convertView;
}
bindView(position, v);
return v;
}
if (convertView == null)不用每次都加载view,提升加载效率bindView(position, v);负责每行中所有view控件的显示
bindView()方法:
private void bindView(int position, View view) {
final Map dataSet = mData.get(position);
if (dataSet == null) {
return;
}
final ViewBinder binder = mViewBinder;
final String[] from = mFrom;
final int[] to = mTo;
final int count = to.length;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//遍历item中的每个view对象
final View v = view.findViewById(to[i]);
if (v != null) {
/*根据传入的String数组包含的key,去map里取值,toString()返回一个字符串,这个字符串在下面调用setViewValue时当做第三个参数传入
setViewValue的第三个参数在API中的描述为:
a safe String representation of the supplied data: it is either the result of data.toString()
or an empty String but it is never null
*/
final Object data = dataSet.get(from[i]);
String text = data == null ? "" : data.toString();
if (text == null) {
text = "";
}
/*bound 这个变量很关键,它依赖于ViewBinder的实例binder.setViewValue的返回值,item中每个view对象如何渲染取决于bound的值
setViewValue返回true,即bound为true的话,表明item中每个view对象的渲染已经在setViewValue方法中处理完毕了,
如果setViewValue返回false,则使用默认的渲染方法
*/
boolean bound = false;
if (binder != null) {
bound = binder.setViewValue(v, data, text);
}
//setViewValue返回false,使用默认的渲染方法
if (!bound) {
//如果类型是CheckBox,RadioButton, ToggleButton等或者是实现了Checkable接口的文本控件,根据map中的值设置选中状态
if (v instanceof Checkable) {
if (data instanceof Boolean) {
((Checkable) v).setChecked((Boolean) data);
} else if (v instanceof TextView) {
// Note: keep the instanceof TextView check at the bottom of these
// ifs since a lot of views are TextViews (e.g. CheckBoxes).
setViewText((TextView) v, text);
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException(v.getClass().getName() +
" should be bound to a Boolean, not a " +
(data == null ? "<unknown type>" : data.getClass()));
}
}
//如果是TextView
else if (v instanceof TextView) {
// Note: keep the instanceof TextView check at the bottom of these
// ifs since a lot of views are TextViews (e.g. CheckBoxes).
setViewText((TextView) v, text);
}
//如果是图片
else if (v instanceof ImageView) {
if (data instanceof Integer) {
setViewImage((ImageView) v, (Integer) data);
} else {
setViewImage((ImageView) v, text);
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException(v.getClass().getName() + " is not a " +
" view that can be bounds by this SimpleAdapter");
}
}
}
}
}
可以看出,SimpleAdapter只能处理简单的view控件的内容的显示,如果要对在item上的button等进行事件监听的话,可以使用ViewBinder,这就是他在存在SimpleAdapter中存在的意义,ViewBinder可以在程序中为listview的item中的控件绑定数据或者事件。
设置ViewBinder:
public void setViewBinder(ViewBinder viewBinder) {
mViewBinder = viewBinder;
}
下面的例子是如何实现自己的ViewBinder,并且在SimpleAdapter中设置以达到自己想要的效果。
给item上的button增加点击事件
改动以上的代码,
1.让MainActivity实现ViewBinder接口
2.重写setViewValue方法
改进后的完整代码:
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements ViewBinder{
private ListView list;
private SimpleAdapter adapter;
private List<Map<String, String>> dataList;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
init();
}
private void init() {
list = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.list);
intitData();
adapter = new SimpleAdapter(MainActivity.this,
dataList, R.layout.list_item,
new String[]{"tv", "btn"}, new int[]{R.id.tv, R.id.btn});
//设置ViewBinder
adapter.setViewBinder(this);
list.setAdapter(adapter);
}
private void intitData() {
dataList = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("tv", "data"+i);
map.put("btn", "btn"+i);
dataList.add(map);
}
}
//重写setViewValue方法,设置按钮点击事件
@Override
public boolean setViewValue(View view, Object data,
String textRepresentation) {
if (view instanceof Button) {
((Button)view).setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "点击", 3000).show();
}
});
}
//返回值为true
return true;
}
}
再次查看效果,发现点击按钮弹出toast。
SimpleAdapter中的ViewBinder还是比较简单的,通过继承BaseAdapter和实现自己的ViewBinder可以实现功能更加强大,更灵活的listview的数据绑定