Programming Exercise 8:Anomaly Detection and Recommender Systems第一部分
大家好,我是Mac Jiang,今天和大家分享Coursera-Stanford University-Machine Learning-Programming Exercise 8:Anomaly Detection and Recommender System的第一部分:Anomaly Detection。第二部分Recommender System的代码我将会在接下来的博客中给出。我的代码虽然是通过了系统的测试,但不一定是最好的,如果博友有更好的想法,请留言联系,谢谢!希望我的博客可以为您带来一些学习上的帮助!
这部分的主要内容是Anomaly Detection,即异常点检测。异常点检测的作用是找出那些明显偏离的样本,在生产中他能帮助找到不合格的产品,在生活中他可以帮助检测用户的银行卡是否被盗刷,在机器学习中有着广泛的应用。异常点检测的一般算法是利用高斯分布函数实现的,利用已有样本训练适合的高斯分布函数(可高维),并设定阈值epsilon,如果样本p(x)小于epsilon则认为它是异常点。
由于正常点的样本占绝大多数,只有极少数的异常样本,所以这是一个偏斜类。对于偏斜类好坏的评价,我们采用F1 score,因此我们利用F1 score决定到底选取那个epsilon。
这次实验是对一个二维数据集进行异常检测。具体过程为:
1.首先输入二维数据,建立高斯分布函数拟合这些样本。
2.由于我们不知道具体阈值epsilon的最优取值,我们取多个epsilon的值,分别计算他的F1 score并比较,取最大的F1 score对应的epsilon为最优阈值。
3.根据得到的epsilon,标出样本中p(x)小于epsilon的点,即为异常点。
1.数据集和文件说明
数据集:ex8data1.mat---即上面所述的二位数据集合,二位数据可以可视化
ex8data2.mat----用于异常检测的多维数据集合,实际上它的维度为11维,不可以可视化
文件:ex8.m---控制异常检测进行的过程的控制文件
multivariateGuassian.mat---利用已有的均值mu和方差sigma2建立多位高斯分布函数
estimateGusssian.m---对于输入的样本X,分别对每一维计算均值mu和方差sigma2,保存在向量中,需要完善代码!
selectThreshold.m---对于多个输入epsilon分别计算F1 score,去最大F1 score对应的epsilon为最优解,需要完善代码!
2.ex8.m过程说明
%% Initialization
clear ; close all; clc
%% ================== Part 1: Load Example Dataset ===================
% We start this exercise by using a small dataset that is easy to
% visualize.
%
% Our example case consists of 2 network server statistics across
% several machines: the latency and throughput of each machine.
% This exercise will help us find possibly faulty (or very fast) machines.
%
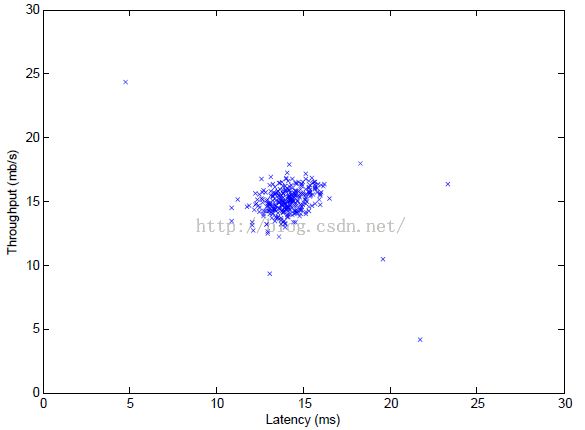
fprintf('Visualizing example dataset for outlier detection.\n\n');
% The following command loads the dataset. You should now have the
% variables X, Xval, yval in your environment
load('ex8data1.mat');
% Visualize the example dataset
plot(X(:, 1), X(:, 2), 'bx');
axis([0 30 0 30]);
xlabel('Latency (ms)');
ylabel('Throughput (mb/s)');
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause
%% ================== Part 2: Estimate the dataset statistics ===================
% For this exercise, we assume a Gaussian distribution for the dataset.
%
% We first estimate the parameters of our assumed Gaussian distribution,
% then compute the probabilities for each of the points and then visualize
% both the overall distribution and where each of the points falls in
% terms of that distribution.
%
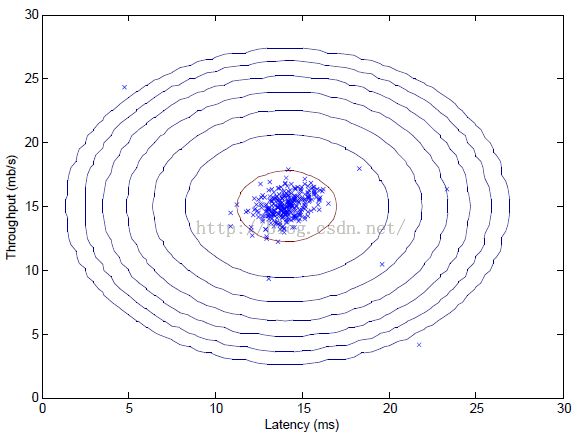
fprintf('Visualizing Gaussian fit.\n\n');
% Estimate my and sigma2
[mu sigma2] = estimateGaussian(X);
% Returns the density of the multivariate normal at each data point (row)
% of X
p = multivariateGaussian(X, mu, sigma2);
% Visualize the fit
visualizeFit(X, mu, sigma2);
xlabel('Latency (ms)');
ylabel('Throughput (mb/s)');
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ================== Part 3: Find Outliers ===================
% Now you will find a good epsilon threshold using a cross-validation set
% probabilities given the estimated Gaussian distribution
%
pval = multivariateGaussian(Xval, mu, sigma2);
[epsilon F1] = selectThreshold(yval, pval);
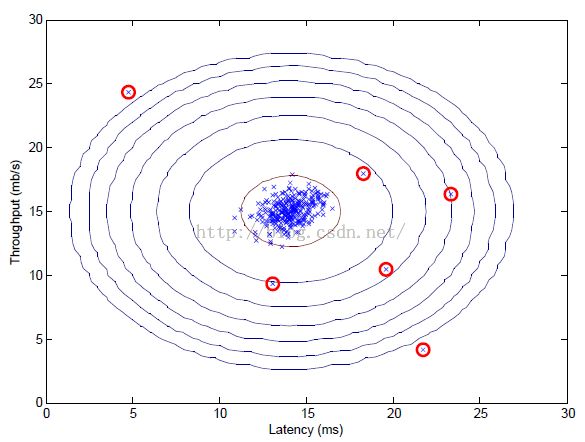
fprintf('Best epsilon found using cross-validation: %e\n', epsilon);
fprintf('Best F1 on Cross Validation Set: %f\n', F1);
fprintf(' (you should see a value epsilon of about 8.99e-05)\n\n');
% Find the outliers in the training set and plot the
outliers = find(p < epsilon);
% Draw a red circle around those outliers
hold on
plot(X(outliers, 1), X(outliers, 2), 'ro', 'LineWidth', 2, 'MarkerSize', 10);
hold off
fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
%% ================== Part 4: Multidimensional Outliers ===================
% We will now use the code from the previous part and apply it to a
% harder problem in which more features describe each datapoint and only
% some features indicate whether a point is an outlier.
%
% Loads the second dataset. You should now have the
% variables X, Xval, yval in your environment
load('ex8data2.mat');
% Apply the same steps to the larger dataset
[mu sigma2] = estimateGaussian(X);
% Training set
p = multivariateGaussian(X, mu, sigma2);
% Cross-validation set
pval = multivariateGaussian(Xval, mu, sigma2);
% Find the best threshold
[epsilon F1] = selectThreshold(yval, pval);
fprintf('Best epsilon found using cross-validation: %e\n', epsilon);
fprintf('Best F1 on Cross Validation Set: %f\n', F1);
fprintf('# Outliers found: %d\n', sum(p < epsilon));
fprintf(' (you should see a value epsilon of about 1.38e-18)\n\n');
pause
Part1:Load Example Dataset---导入数据并可视化
Part2:Esitimate the dataset statistics---调用estimateGuassian.m对每一维度分别计算均值mu(i),方差sigma2(i),之后利用得到数据建立多位高斯分布,并调用selectThreshold.m计算最有epsilon
Part3:Find Outliers---利用上面训练得到的高斯分布和epsilon值找到那些异常点
Part4:Multidimensional Outliers---调用ex8data2.mat中的数据,这是11维的数据,对这个数据进行异常检测,得到异常点。注意:11维的数据不能可视化
2.estimateGaussian.m实现过程
function [mu sigma2] = estimateGaussian(X)
%ESTIMATEGAUSSIAN This function estimates the parameters of a
%Gaussian distribution using the data in X
% [mu sigma2] = estimateGaussian(X),
% The input X is the dataset with each n-dimensional data point in one row
% The output is an n-dimensional vector mu, the mean of the data set
% and the variances sigma^2, an n x 1 vector
%
% Useful variables
[m, n] = size(X);
% You should return these values correctly
mu = zeros(n, 1);
sigma2 = zeros(n, 1);
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the mean of the data and the variances
% In particular, mu(i) should contain the mean of
% the data for the i-th feature and sigma2(i)
% should contain variance of the i-th feature.
%
%这里当然也可以采取for循环的方式计算,但是向量法的计算速度快一些
mu = sum(X)' / m; %sum是对X按列求和的意思
temp = X' - repmat(mu,1,m); %repmat(A,m,n),把矩阵A复制m*n份,行为m,列为n
%这里也可用temp = bsxfun(@minus, X', mu)
sigma2 = sum(temp.^2,2) / m; %sum(A,2)对矩阵按列求和
注意:可能有些同学会用for循环的方法编写代码,但是一般来说利用向量的方法会比循环的方法快很多,所以如果能利用向量方法的最好利用向量
3.selectThreshold.m实现过程
function [bestEpsilon bestF1] = selectThreshold(yval, pval)
%SELECTTHRESHOLD Find the best threshold (epsilon) to use for selecting
%outliers
% [bestEpsilon bestF1] = SELECTTHRESHOLD(yval, pval) finds the best
% threshold to use for selecting outliers based on the results from a
% validation set (pval) and the ground truth (yval).
%
bestEpsilon = 0;
bestF1 = 0;
F1 = 0;
stepsize = (max(pval) - min(pval)) / 1000;
for epsilon = min(pval):stepsize:max(pval)
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the F1 score of choosing epsilon as the
% threshold and place the value in F1. The code at the
% end of the loop will compare the F1 score for this
% choice of epsilon and set it to be the best epsilon if
% it is better than the current choice of epsilon.
%
% Note: You can use predictions = (pval < epsilon) to get a binary vector
% of 0's and 1's of the outlier predictions
%yval表示的是它是不是异常点,是为1不是为0。
%pval表示的是利用已经训练出的系统对xval计算p(x)的值,若小于ipsilon我们就认为它是异常点
%tp:true possitive,即它实际为1我们又预测它为1的样本数
%fp:false possitive即他实际为0我们预测他为1的样本数
%fn:false negative,即它实际为1我们预测他为0的样本数
%prec = tp/(tp+fn)查准率;rec = tp/(tp+fn)回收率;F1 srcore = 2*prec*rec/(prec+rec)
cvPrediction = pval < epsilon; %yval小于ipsilon则置1否则置0
tp = sum((cvPrediction == 1) & (yval == 1)); %cvPrediction为我们的预测值,yval为实际值
fp = sum((cvPrediction == 1) & (yval == 0));
fn = sum((cvPrediction == 0) & (yval == 1));
prec = tp / (tp + fp);
rec = tp / (tp + fn);
F1 = 2 * prec * rec / (prec + rec);
% =============================================================
if F1 > bestF1
bestF1 = F1;
bestEpsilon = epsilon;
end
end
end
From:http://blog.csdn.net/a1015553840/article/details/50913824