通过AOP方式实现Service计算结果的缓存
AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming, 面向切面的编程。意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。
Spring框架的AOP基础知识详见:
Spring实现AOP的4种方式
Spring AOP 详解
AOP的应用场景很多。可以作为日志系统的记录拦截,也可以用于缓存的拦截。
以下用我自己的框架项目 springMVC 中实现的Ehcache对Service层计算结果缓存的实现为例子。介绍一下。
Service缓存实现
主要实现思路通过AOP拦截的方式插入缓存层的操作。
参考:Spring AOP+ehCache简单缓存系统解决方案
简单的配置以及实现效果
Ehcache配置
ehcache的配置文件默认在 classpath:ehcache.xml MAVEN工程对应 src/main/resources 。定义了缓存的配置信息,* 必须有一个 默认缓存defaultCache *。在管理器找不到缓存的时候,就会用默认缓存。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- Ehcache2.x的变化(取自https://github.com/springside/springside4/wiki/Ehcache) -->
<!-- 1)最好在ehcache.xml中声明不进行updateCheck -->
<!-- 2)为了配合BigMemory和Size Limit,原来的属性最好改名 -->
<!-- maxElementsInMemory->maxEntriesLocalHeap -->
<!-- maxElementsOnDisk->maxEntriesLocalDisk -->
<ehcache mlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd">
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir" />
<defaultCache maxElementsInMemory="1000" eternal="false" timeToIdleSeconds="120" timeToLiveSeconds="120" overflowToDisk="false" />
<cache name="myCache" maxElementsOnDisk="20000" maxElementsInMemory="2000" eternal="true" overflowToDisk="true" diskPersistent="true" />
</ehcache>
<!-- <diskStore>==========当内存缓存中对象数量超过maxElementsInMemory时,将缓存对象写到磁盘缓存中(需对象实现序列化接口) <diskStore path="">==用来配置磁盘缓存使用的物理路径,Ehcache磁盘缓存使用的文件后缀名是*.data和*.index name=================缓存名称,cache的唯一标识(ehcache会把这个cache放到HashMap里) maxElementsOnDisk====磁盘缓存中最多可以存放的元素数量,0表示无穷大 maxElementsInMemory==内存缓存中最多可以存放的元素数量,若放入Cache中的元素超过这个数值,则有以下两种情况 1)若overflowToDisk=true,则会将Cache中多出的元素放入磁盘文件中 2)若overflowToDisk=false,则根据memoryStoreEvictionPolicy策略替换Cache中原有的元素 eternal==============缓存中对象是否永久有效,即是否永驻内存,true时将忽略timeToIdleSeconds和timeToLiveSeconds timeToIdleSeconds====缓存数据在失效前的允许闲置时间(单位:秒),仅当eternal=false时使用,默认值是0表示可闲置时间无穷大,此为可选属性 即访问这个cache中元素的最大间隔时间,若超过这个时间没有访问此Cache中的某个元素,那么此元素将被从Cache中清除 timeToLiveSeconds====缓存数据在失效前的允许存活时间(单位:秒),仅当eternal=false时使用,默认值是0表示可存活时间无穷大 即Cache中的某元素从创建到清楚的生存时间,也就是说从创建开始计时,当超过这个时间时,此元素将从Cache中清除 overflowToDisk=======内存不足时,是否启用磁盘缓存(即内存中对象数量达到maxElementsInMemory时,Ehcache会将对象写到磁盘中) 会根据标签中path值查找对应的属性值,写入磁盘的文件会放在path文件夹下,文件的名称是cache的名称,后缀名是data diskPersistent=======是否持久化磁盘缓存,当这个属性的值为true时,系统在初始化时会在磁盘中查找文件名为cache名称,后缀名为index的文件 这个文件中存放了已经持久化在磁盘中的cache的index,找到后会把cache加载到内存 要想把cache真正持久化到磁盘,写程序时注意执行net.sf.ehcache.Cache.put(Element element)后要调用flush()方法 diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds==磁盘缓存的清理线程运行间隔,默认是120秒 diskSpoolBufferSizeMB============设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小,默认是30MB memoryStoreEvictionPolicy========内存存储与释放策略,即达到maxElementsInMemory限制时,Ehcache会根据指定策略清理内存 共有三种策略,分别为LRU(最近最少使用)、LFU(最常用的)、FIFO(先进先出) -->
AOP拦截
拦截器编写
- 取缓存
MethodCacheInterceptor
package org.company.core.common.interceptor;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.List;
import net.sf.ehcache.Cache;
import net.sf.ehcache.Element;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInterceptor;
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
public class MethodCacheInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor, InitializingBean {
private Cache cache;
/** * 设置缓存名 */
public void setCache(Cache cache) {
this.cache = cache;
}
/** * 检查是否提供必要参数。 */
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
Assert.notNull(cache,
"A cache is required. Use setCache(Cache) to provide one.");
}
/** * 主方法 如果某方法可被缓存就缓存其结果 方法结果必须是可序列化的(serializable) */
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// String methodName = invocation.getMethod().getName();
// if(methodName.contains("find")){
// return get(invocation);
// } else {
// return remove(invocation);
// }
String targetName = invocation.getThis().getClass().getName();
String methodName = invocation.getMethod().getName();
Object[] arguments = invocation.getArguments();
Object result;
String cacheKey = getCacheKey(targetName, methodName, arguments);
System.out.println("getting from cache...");
Element element = cache.get(cacheKey);
System.out.println("cache Key:" + cacheKey);
if (element == null) {
System.out.println("miss");
result = invocation.proceed();
element = new Element(cacheKey, (Serializable) result);
cache.put(element);
return element.getValue();
} else {
System.out.println("hit");
return element.getValue();
}
}
// }
/** * creates cache key: targetName.methodName.argument0.argument1... */
private String getCacheKey(String targetName, String methodName,
Object[] arguments) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append(targetName).append(".").append(methodName);
if ((arguments != null) && (arguments.length != 0)) {
for (int i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
sb.append(".").append(arguments[i]);
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
- 删除缓存
package org.company.core.common.interceptor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.List;
import net.sf.ehcache.Cache;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
public class MethodCacheAfterAdvice implements AfterReturningAdvice, InitializingBean {
private Cache cache;
public void setCache(Cache cache) {
this.cache = cache;
}
public MethodCacheAfterAdvice() {
super();
}
@Transactional
public void afterReturning(Object arg0, Method arg1, Object[] arg2, Object arg3) throws Throwable {
String className = arg3.getClass().getName();
List list = cache.getKeys();
System.out.println("invoking...");
System.out.println("removing cache key:"+className+".*");
for(int i = 0;i<list.size();i++){
String cacheKey = String.valueOf(list.get(i));
if(cacheKey.startsWith(className)){
System.out.println("remving key:"+cacheKey);
cache.remove(cacheKey);
}
}
}
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
Assert.notNull(cache, "Need a cache. Please use setCache(Cache) create it.");
}
}
配置文件
配置详见 applicationContext-ehcache.xml
注册拦截器类
声明了拦截器的BEAN
<!-- find/create cache拦截器 -->
<bean id="methodCacheInterceptor" class="org.company.frame.interceptor.MethodCacheInterceptor">
<property name="cache">
<ref local="demoCache" />
</property>
</bean>
<!-- flush cache拦截器 -->
<bean id="methodCacheAfterAdvice" class="org.company.frame.interceptor.MethodCacheAfterAdvice">
<property name="cache">
<ref local="demoCache" />
</property>
</bean>
切入点声明
将拦截器BEAN与方法匹配。
<!-- find/get cache拦截器方法匹配 -->
<bean id="methodCachePointCut" class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="advice">
<ref local="methodCacheInterceptor" />
</property>
<property name="patterns">
<list>
<value>org.company.core.*.service.*find.*</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- flush 拦截器方法匹配 -->
<bean id="methodCachePointCutAdvice" class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="advice">
<ref local="methodCacheAfterAdvice"/>
</property>
<property name="patterns">
<list>
<value>org.company.core.*.service.*create.*</value>
<value>org.company.core.*.service.*update.*</value>
<value>org.company.core.*.service.*delete.*</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
AOP的最终声明
绑定服务BEAN与拦截器切入点。
<!-- AOP 的最终配置 -->
<!-- BEAN与find/get 拦截器关联 -->
<bean id="myService" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="target">
<ref local="testTableServiceBean" />
</property>
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>methodCachePointCut</value>
<value>methodCachePointCutAdvice</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 拦截BEAN -->
<bean id="testTableServiceBean" class="org.company.core.moduel.service.TestTableServiceImpl">
</bean>
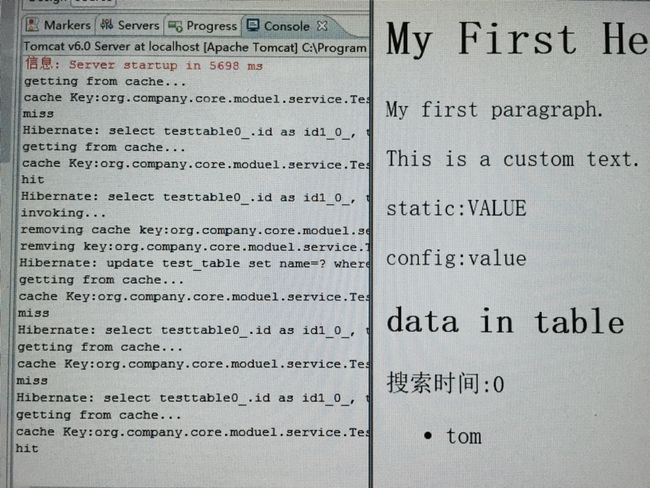
缓存的最终实现效果如图: