DesignPattern_Java:Composite Pattern
组合模式 Composite Pattern 合成模式
compose objects into tree structures to represent part-whole hierarchies.Composite lets clients treat individual objects and compositions of objects uniformly.
将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构,使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
抽象构件角色(Component):该角色定义参加组合对象的共有方法和属性,规范一些默认的行为接口。
package com.DesignPattern.Structural.Composite;
//定义抽象构建接口
public interface Component {
public void operation();
}
叶子构件角色(Leaf):该角色是叶子对象,其下没有其他的分支,定义出参加组合的原始对象的行为。
package com.DesignPattern.Structural.Composite;
//定义叶子构件
public class Leaf implements Component {
@Override
public void operation() {
//业务逻辑代码
System.out.println("Leaf operation");
}
}
树枝构件角色(Composite):该角色代表参加组合的、其下的分支的树枝对象,他的作用是将树枝和叶子组合成一个树形结构,并定义出管理子对象的方法,如add()、remove()等。
package com.DesignPattern.Structural.Composite;
import java.util.ArrayList;
//定义树枝构件
public class Composite implements Component {
// 构件容器
private ArrayList<Component> componentList = new ArrayList<Component>();
// 添加构件
public void add(Component component) {
this.componentList.add(component);
}
// 删除构件
public void remove(Component component) {
this.componentList.remove(component);
}
// 获取子构件
public ArrayList<Component> getChild() {
return this.componentList;
}
@Override
public void operation() {
// 业务逻辑代码
System.out.println("Composite operation");
}
}
Client
package com.DesignPattern.Structural.Composite;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个根节点
Composite root = new Composite();
root.operation();
// 创建树枝节点
Composite branch = new Composite();
// 创建叶子节点
Leaf leaf = new Leaf();
// 构件树形结构
root.add(branch);
branch.add(leaf);
display(root);
}
// 遍历树(递归)
public static void display(Composite root) {
for (Component c : root.getChild()) {
if (c instanceof Leaf) { // 如果节点类型是叶子节点
c.operation();
} else { // 树枝节点
c.operation();
display((Composite) c); // 递归调用
}
}
}
}
组合模式的实例
Company.java
package com.DesignPattern.Structural.Composite;
//抽象接口
public interface Company {
//获取信息
public String getInfo();
}
ConcreteCompany.java
package com.DesignPattern.Structural.Composite;
import java.util.ArrayList;
//树枝节点类
public class ConcreteCompany implements Company {
private ArrayList<Company> companyList = new ArrayList<Company>();
private String name;
private String position;
private int salary;
//构造函数
public ConcreteCompany(String name, String position, int salary) {
this.name = name; //姓名
this.position = position; //职位
this.salary = salary; //薪水
}
public void add(Company company){
this.companyList.add(company);
}
public void remove(Company company){
this.companyList.remove(company);
}
public ArrayList<Company> getChild(){
return this.companyList;
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
String info="";
info="名称:"+this.name;
info=info+"\t职位:"+this.position;
info=info+"\t薪水:"+this.salary;
return info;
}
}
Employee.java
package com.DesignPattern.Structural.Composite;
//叶子节点类
public class Employee implements Company {
private String name;
private String position;
private int salary;
public Employee(String name, String position, int salary) {
this.name = name;
this.position = position;
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String getInfo() {
String info="";
info="名称:"+this.name;
info=info+"\t职位:"+this.position;
info=info+"\t薪水:"+this.salary;
return info;
}
}
ClientDemo.java
package com.DesignPattern.Structural.Composite;
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
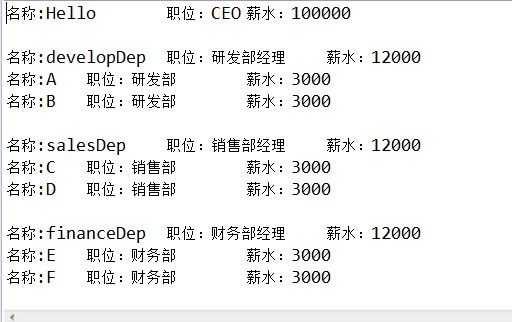
//CEO
ConcreteCompany root=new ConcreteCompany("Hello","CEO",100000);
//部门经理
ConcreteCompany developDep=new ConcreteCompany("developDep","研发部经理",12000);
ConcreteCompany salesDep=new ConcreteCompany("salesDep","销售部经理",12000);
ConcreteCompany financeDep=new ConcreteCompany("financeDep","财务部经理",12000);
//部门员工
Employee e1=new Employee("A","研发部",3000);
Employee e2=new Employee("B","研发部",3000);
Employee e3=new Employee("C","销售部",3000);
Employee e4=new Employee("D","销售部",3000);
Employee e5=new Employee("E","财务部",3000);
Employee e6=new Employee("F","财务部",3000);
//生成树
root.add(developDep);
root.add(salesDep);
root.add(financeDep);
developDep.add(e1);
developDep.add(e2);
salesDep.add(e3);
salesDep.add(e4);
financeDep.add(e5);
financeDep.add(e6);
System.out.println(root.getInfo());
display(root);
}
//遍历树(递归)
public static void display(ConcreteCompany root){
for(Company c:root.getChild()){
if(c instanceof Employee){ //如果节点类型是叶子节点
System.out.println(c.getInfo());
}else{ //树枝节点
System.out.println("\n"+c.getInfo());
display((ConcreteCompany)c); //递归调用
}
}
}
}