python + opencv: kalman 跟踪
运动模型的建立:
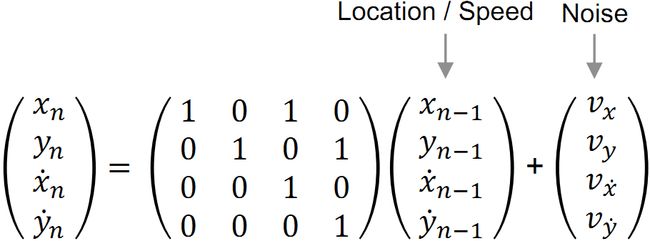
在进入kalman跟踪之前,首先要建立鼠标运动的模型,至少有两个状态变量:鼠标位置x,y,也可以是四个状态变量:位置x,y和速度vx,vy。两个测量变量:鼠标位置x,y。由于鼠标的运动是个随机运动,并没有一个精确复杂的数学模型。在粒子滤波博文中,也做过图像跟踪,跟那里程序类似的是,鼠标的位置主要通过上一时刻的位置再叠加一个随机噪声来预测。
opencv kalman代码:
例程主要分为两部分,第一部分是针对目标跟踪而封装好的的一个kalman滤波器类,方便以后扩展到其他程序中。第二部分是使用之前封装好的kalman目标跟踪类进行鼠标跟踪。
第一部分:封装好的用于目标跟踪的滤波器类
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
kalman2d - 2D Kalman filter using OpenCV
Based on http://jayrambhia.wordpress.com/2012/07/26/kalman-filter/
Copyright (C) 2014 Simon D. Levy
This code is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as
published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the
License, or (at your option) any later version.
This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
along with this code. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
'''
from cv2 import cv
class Kalman2D(object):
'''
A class for 2D Kalman filtering
'''
def __init__(self, processNoiseCovariance=1e-4, measurementNoiseCovariance=1e-1, errorCovariancePost=0.1):
'''
Constructs a new Kalman2D object.
For explanation of the error covariances see
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kalman_filter
'''
# 状态空间:位置--2d,速度--2d
self.kalman = cv.CreateKalman(4, 2, 0)
self.kalman_state = cv.CreateMat(4, 1, cv.CV_32FC1)
self.kalman_process_noise = cv.CreateMat(4, 1, cv.CV_32FC1)
self.kalman_measurement = cv.CreateMat(2, 1, cv.CV_32FC1)
for j in range(4):
for k in range(4):
self.kalman.transition_matrix[j,k] = 0
self.kalman.transition_matrix[j,j] = 1
#加入速度 x = x + vx, y = y + vy
# 1,0,1,0, 0,1,0,1, 0,0,1,0, 0,0,0,1
#如果把下面两句注释掉,那么位置跟踪kalman滤波器的状态模型就是没有使用速度信息
# self.kalman.transition_matrix[0, 2]=1
# self.kalman.transition_matrix[1, 3]=1
cv.SetIdentity(self.kalman.measurement_matrix)
#初始化带尺度的单位矩阵
cv.SetIdentity(self.kalman.process_noise_cov, cv.RealScalar(processNoiseCovariance))
cv.SetIdentity(self.kalman.measurement_noise_cov, cv.RealScalar(measurementNoiseCovariance))
cv.SetIdentity(self.kalman.error_cov_post, cv.RealScalar(errorCovariancePost))
self.predicted = None
self.esitmated = None
def update(self, x, y):
'''
Updates the filter with a new X,Y measurement
'''
self.kalman_measurement[0, 0] = x
self.kalman_measurement[1, 0] = y
self.predicted = cv.KalmanPredict(self.kalman)
self.corrected = cv.KalmanCorrect(self.kalman, self.kalman_measurement)
def getEstimate(self):
'''
Returns the current X,Y estimate.
'''
return self.corrected[0,0], self.corrected[1,0]
def getPrediction(self):
'''
Returns the current X,Y prediction.
'''
return self.predicted[0,0], self.predicted[1,0]
代码详细解读:
这部分程序中,最主要的kalman滤波器的创建和使用。
self.kalman = cv.CreateKalman(4, 2, 0)该句命令为创建kalman滤波器,使用方法如下:
CreateKalman(dynam_params, measure_params, control_params=0)
它有3个输入参数,dynam_params:状态空间的维数;measure_param:测量值的维数;control_params:控制向量的维数,默认为0。由于这里该模型中并没有控制变量,因此也为0。
cv.SetIdentity(self.kalman.process_noise_cov, cv.RealScalar(processNoiseCovariance)) cv.SetIdentity(self.kalman.measurement_noise_cov, cv.RealScalar(measurementNoiseCovariance)) cv.SetIdentity(self.kalman.error_cov_post, cv.RealScalar(errorCovariancePost))
代码中这三句为设定过程噪声协方差矩阵、测量噪声协方差矩阵、以及初始化后验误差协方差矩阵。
创建完成以后,就只等待在主函数中调用,进行预测和更新了。
注意:在使用过程中,为达到好的跟踪效果主要调节下示参数中的前两个参数processNosieCovariance和measurementNoiseCovariance
__init__(self, processNoiseCovariance=1e-2, measurementNoiseCovariance=1e-1, errorCovariancePost=0.1)
第二部分:鼠标跟踪主程序
#!/usr/bin/env python
'''
kalman_mousetracker.py - OpenCV mouse-tracking demo using 2D Kalman filter
Adapted from
http://www.morethantechnical.com/2011/06/17/simple-kalman-filter-for-tracking-using-opencv-2-2-w-code/
Copyright (C) 2014 Simon D. Levy
This code is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as
published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the
License, or (at your option) any later version.
This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY without even the implied warranty of
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
along with this code. If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
'''
# This delay will affect the Kalman update rate
DELAY_MSEC = 20
# Arbitrary display params
WINDOW_NAME = 'Kalman Mousetracker [ESC to quit]'
WINDOW_SIZE = 500
import cv2
import numpy as np
from sys import exit
from kalman2d import Kalman2D
class MouseInfo(object):
'''
A class to store X,Y points
'''
def __init__(self):
self.x, self.y = -1, -1
def __str__(self):
return '%4d %4d' % (self.x, self.y)
def mouseCallback(event, x, y, flags, mouse_info):
'''
Callback to update a MouseInfo object with new X,Y coordinates
'''
mouse_info.x = x
mouse_info.y = y
def drawCross(img, center, r, g, b):
'''
Draws a cross a the specified X,Y coordinates with color RGB
'''
d = 5
t = 2
color = (r, g, b)
ctrx = center[0]
ctry = center[1]
cv2.line(img, (ctrx - d, ctry - d), (ctrx + d, ctry + d), color, t, cv2.CV_AA)
cv2.line(img, (ctrx + d, ctry - d), (ctrx - d, ctry + d), color, t, cv2.CV_AA)
def drawLines(img, points, r, g, b):
'''
Draws lines
'''
cv2.polylines(img, [np.int32(points)], isClosed=False, color=(r, g, b))
def newImage():
'''
Returns a new image
'''
return np.zeros((500,500,3), np.uint8)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Create a new image in a named window
img = newImage()
cv2.namedWindow(WINDOW_NAME)
# Create an X,Y mouse info object and set the window's mouse callback to modify it
mouse_info = MouseInfo()
cv2.setMouseCallback(WINDOW_NAME, mouseCallback, mouse_info)
# Loop until mouse inside window
while True:
if mouse_info.x > 0 and mouse_info.y > 0:
break
cv2.imshow(WINDOW_NAME, img)
if cv2.waitKey(1) == 27:
exit(0)
# These will get the trajectories for mouse location and Kalman estiamte
measured_points = []
kalman_points = []
# Create a new Kalman2D filter and initialize it with starting mouse location
kalman2d = Kalman2D()
# Loop till user hits escape
while True:
# Serve up a fresh image
img = newImage()
# Grab current mouse position and add it to the trajectory
measured = (mouse_info.x, mouse_info.y)
measured_points.append(measured)
# Update the Kalman filter with the mouse point
kalman2d.update(mouse_info.x, mouse_info.y)
# Get the current Kalman estimate and add it to the trajectory
estimated = [int (c) for c in kalman2d.getEstimate()]
kalman_points.append(estimated)
# Display the trajectories and current points
drawLines(img, kalman_points, 0, 255, 0)
drawCross(img, estimated, 255, 255, 255)
drawLines(img, measured_points, 255, 255, 0)
drawCross(img, measured, 0, 0, 255)
# Delay for specified interval, quitting on ESC
cv2.imshow(WINDOW_NAME, img)
if cv2.waitKey(DELAY_MSEC) == 27:
break运行程序就能看到效果。
值得一提的是:状态模型中使不使用速度变量,效果是不一样的。
状态模型中加入速度变量:
不加入速度变量:
调节之前提到的参数,得到最好的效果。
最后,读者可以将本文中的程序稍作修改实现粒子滤波博文中视频跟踪穿红衣女子,视频可以在粒子滤波博文代码材料中找到,祝好运。
(转载请注明作者和出处:http://blog.csdn.net/heyijia0327 未经允许请勿用于商业用途)
reference:
1.鼠标跟踪C++例程原出处
2.Simon D. Levy将上述例程修改为python代码
3.目标跟踪模型
4.opencv官方资料1
5.opencv官方资料2:该官方链接中有一个跟踪旋转点的c例程