Opencv2.4.9源码分析——HoughLinesP
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaocj/article/details/40047397
标准霍夫变换本质上是把图像映射到它的参数空间上,它需要计算所有的M个边缘点,这样它的运算量和所需内存空间都会很大。如果在输入图像中只是处理m(m<M)个边缘点,则这m个边缘点的选取是具有一定概率性的,因此该方法被称为概率霍夫变换(Probabilistic Hough Transform)。该方法还有一个重要的特点就是能够检测出线端,即能够检测出图像中直线的两个端点,确切地定位图像中的直线。
HoughLinesP函数就是利用概率霍夫变换来检测直线的。它的一般步骤为:
1、随机抽取图像中的一个特征点,即边缘点,如果该点已经被标定为是某一条直线上的点,则继续在剩下的边缘点中随机抽取一个边缘点,直到所有边缘点都抽取完了为止;
2、对该点进行霍夫变换,并进行累加和计算;
3、选取在霍夫空间内值最大的点,如果该点大于阈值的,则进行步骤4,否则回到步骤1;
4、根据霍夫变换得到的最大值,从该点出发,沿着直线的方向位移,从而找到直线的两个端点;
5、计算直线的长度,如果大于某个阈值,则被认为是好的直线输出,回到步骤1。
HoughLinesP函数的原型为:
void HoughLinesP(InputArray image,OutputArray lines, double rho, double theta, int threshold, double minLineLength=0,double maxLineGap=0 )
image为输入图像,要求是8位单通道图像
lines为输出的直线向量,每条线用4个元素表示,即直线的两个端点的4个坐标值
rho和theta分别为距离和角度的分辨率
threshold为阈值,即步骤3中的阈值
minLineLength为最小直线长度,在步骤5中要用到,即如果小于该值,则不被认为是一条直线
maxLineGap为最大直线间隙,在步骤4中要用到,即如果有两条线段是在一条直线上,但它们之间因为有间隙,所以被认为是两个线段,如果这个间隙大于该值,则被认为是两条线段,否则是一条。
HoughLinesP函数是在sources/modules/imgproc/src/hough.cpp文件中被定义的:
- void cv::HoughLinesP( InputArray _image, OutputArray _lines,
- double rho, double theta, int threshold,
- double minLineLength, double maxGap )
- {
- Ptr<CvMemStorage> storage = cvCreateMemStorage(STORAGE_SIZE);
- Mat image = _image.getMat();
- CvMat c_image = image;
- CvSeq* seq = cvHoughLines2( &c_image, storage, CV_HOUGH_PROBABILISTIC,
- rho, theta, threshold, minLineLength, maxGap );
- seqToMat(seq, _lines);
- }
- static void
- icvHoughLinesProbabilistic( CvMat* image,
- float rho, float theta, int threshold,
- int lineLength, int lineGap,
- CvSeq *lines, int linesMax )
- {
- //accum为累加器矩阵,mask为掩码矩阵
- cv::Mat accum, mask;
- cv::vector<float> trigtab; //用于存储事先计算好的正弦和余弦值
- //开辟一段内存空间
- cv::MemStorage storage(cvCreateMemStorage(0));
- //用于存储特征点坐标,即边缘像素的位置
- CvSeq* seq;
- CvSeqWriter writer;
- int width, height; //图像的宽和高
- int numangle, numrho; //角度和距离的离散数量
- float ang;
- int r, n, count;
- CvPoint pt;
- float irho = 1 / rho; //距离分辨率的倒数
- CvRNG rng = cvRNG(-1); //随机数
- const float* ttab; //向量trigtab的地址指针
- uchar* mdata0; //矩阵mask的地址指针
- //确保输入图像的正确性
- CV_Assert( CV_IS_MAT(image) && CV_MAT_TYPE(image->type) == CV_8UC1 );
- width = image->cols; //提取出输入图像的宽
- height = image->rows; //提取出输入图像的高
- //由角度和距离分辨率,得到角度和距离的离散数量
- numangle = cvRound(CV_PI / theta);
- numrho = cvRound(((width + height) * 2 + 1) / rho);
- //创建累加器矩阵,即霍夫空间
- accum.create( numangle, numrho, CV_32SC1 );
- //创建掩码矩阵,大小与输入图像相同
- mask.create( height, width, CV_8UC1 );
- //定义trigtab的大小,因为要存储正弦和余弦值,所以长度为角度离散数的2倍
- trigtab.resize(numangle*2);
- //累加器矩阵清零
- accum = cv::Scalar(0);
- //避免重复计算,事先计算好所需的所有正弦和余弦值
- for( ang = 0, n = 0; n < numangle; ang += theta, n++ )
- {
- trigtab[n*2] = (float)(cos(ang) * irho);
- trigtab[n*2+1] = (float)(sin(ang) * irho);
- }
- //赋值首地址
- ttab = &trigtab[0];
- mdata0 = mask.data;
- //开始写入序列
- cvStartWriteSeq( CV_32SC2, sizeof(CvSeq), sizeof(CvPoint), storage, &writer );
- // stage 1. collect non-zero image points
- //收集图像中的所有非零点,因为输入图像是边缘图像,所以非零点就是边缘点
- for( pt.y = 0, count = 0; pt.y < height; pt.y++ )
- {
- //提取出输入图像和掩码矩阵的每行地址指针
- const uchar* data = image->data.ptr + pt.y*image->step;
- uchar* mdata = mdata0 + pt.y*width;
- for( pt.x = 0; pt.x < width; pt.x++ )
- {
- if( data[pt.x] ) //是边缘点
- {
- mdata[pt.x] = (uchar)1; //掩码的相应位置置1
- CV_WRITE_SEQ_ELEM( pt, writer ); 把该坐标位置写入序列
- }
- else //不是边缘点
- mdata[pt.x] = 0; //掩码的相应位置清0
- }
- }
- //终止写序列,seq为所有边缘点坐标位置的序列
- seq = cvEndWriteSeq( &writer );
- count = seq->total; //得到边缘点的数量
- // stage 2. process all the points in random order
- //随机处理所有的边缘点
- for( ; count > 0; count-- )
- {
- // choose random point out of the remaining ones
- //步骤1,在剩下的边缘点中随机选择一个点,idx为不大于count的随机数
- int idx = cvRandInt(&rng) % count;
- //max_val为累加器的最大值,max_n为最大值所对应的角度
- int max_val = threshold-1, max_n = 0;
- //由随机数idx在序列中提取出所对应的坐标点
- CvPoint* point = (CvPoint*)cvGetSeqElem( seq, idx );
- //定义直线的两个端点
- CvPoint line_end[2] = {{0,0}, {0,0}};
- float a, b;
- //累加器的地址指针,也就是霍夫空间的地址指针
- int* adata = (int*)accum.data;
- int i, j, k, x0, y0, dx0, dy0, xflag;
- int good_line;
- const int shift = 16;
- //提取出坐标点的横、纵坐标
- i = point->y;
- j = point->x;
- // "remove" it by overriding it with the last element
- //用序列中的最后一个元素覆盖掉刚才提取出来的随机坐标点
- *point = *(CvPoint*)cvGetSeqElem( seq, count-1 );
- // check if it has been excluded already (i.e. belongs to some other line)
- //检测这个坐标点是否已经计算过,也就是它已经属于其他直线
- //因为计算过的坐标点会在掩码矩阵mask的相对应位置清零
- if( !mdata0[i*width + j] ) //该坐标点被处理过
- continue; //不做任何处理,继续主循环
- // update accumulator, find the most probable line
- //步骤2,更新累加器矩阵,找到最有可能的直线
- for( n = 0; n < numangle; n++, adata += numrho )
- {
- //由角度计算距离
- r = cvRound( j * ttab[n*2] + i * ttab[n*2+1] );
- r += (numrho - 1) / 2;
- //在累加器矩阵的相应位置上数值加1,并赋值给val
- int val = ++adata[r];
- //更新最大值,并得到它的角度
- if( max_val < val )
- {
- max_val = val;
- max_n = n;
- }
- }
- // if it is too "weak" candidate, continue with another point
- //步骤3,如果上面得到的最大值小于阈值,则放弃该点,继续下一个点的计算
- if( max_val < threshold )
- continue;
- // from the current point walk in each direction
- // along the found line and extract the line segment
- //步骤4,从当前点出发,沿着它所在直线的方向前进,直到达到端点为止
- a = -ttab[max_n*2+1]; //a=-sinθ
- b = ttab[max_n*2]; //b=cosθ
- //当前点的横、纵坐标值
- x0 = j;
- y0 = i;
- //确定当前点所在直线的角度是在45度~135度之间,还是在0~45或135度~180度之间
- if( fabs(a) > fabs(b) ) //在45度~135度之间
- {
- xflag = 1; //置标识位,标识直线的粗略方向
- //确定横、纵坐标的位移量
- dx0 = a > 0 ? 1 : -1;
- dy0 = cvRound( b*(1 << shift)/fabs(a) );
- //确定纵坐标
- y0 = (y0 << shift) + (1 << (shift-1));
- }
- else //在0~45或135度~180度之间
- {
- xflag = 0; //清标识位
- //确定横、纵坐标的位移量
- dy0 = b > 0 ? 1 : -1;
- dx0 = cvRound( a*(1 << shift)/fabs(b) );
- //确定横坐标
- x0 = (x0 << shift) + (1 << (shift-1));
- }
- //搜索直线的两个端点
- for( k = 0; k < 2; k++ )
- {
- //gap表示两条直线的间隙,x和y为搜索位置,dx和dy为位移量
- int gap = 0, x = x0, y = y0, dx = dx0, dy = dy0;
- //搜索第二个端点的时候,反方向位移
- if( k > 0 )
- dx = -dx, dy = -dy;
- // walk along the line using fixed-point arithmetics,
- // stop at the image border or in case of too big gap
- //沿着直线的方向位移,直到到达图像的边界或大的间隙为止
- for( ;; x += dx, y += dy )
- {
- uchar* mdata;
- int i1, j1;
- //确定新的位移后的坐标位置
- if( xflag )
- {
- j1 = x;
- i1 = y >> shift;
- }
- else
- {
- j1 = x >> shift;
- i1 = y;
- }
- //如果到达了图像的边界,停止位移,退出循环
- if( j1 < 0 || j1 >= width || i1 < 0 || i1 >= height )
- break;
- //定位位移后掩码矩阵位置
- mdata = mdata0 + i1*width + j1;
- // for each non-zero point:
- // update line end,
- // clear the mask element
- // reset the gap
- //该掩码不为0,说明该点可能是在直线上
- if( *mdata )
- {
- gap = 0; //设置间隙为0
- //更新直线的端点位置
- line_end[k].y = i1;
- line_end[k].x = j1;
- }
- //掩码为0,说明不是直线,但仍继续位移,直到间隙大于所设置的阈值为止
- else if( ++gap > lineGap ) //间隙加1
- break;
- }
- }
- //步骤5,由检测到的直线的两个端点粗略计算直线的长度
- //当直线长度大于所设置的阈值时,good_line为1,否则为0
- good_line = abs(line_end[1].x - line_end[0].x) >= lineLength ||
- abs(line_end[1].y - line_end[0].y) >= lineLength;
- //再次搜索端点,目的是更新累加器矩阵和更新掩码矩阵,以备下一次循环使用
- for( k = 0; k < 2; k++ )
- {
- int x = x0, y = y0, dx = dx0, dy = dy0;
- if( k > 0 )
- dx = -dx, dy = -dy;
- // walk along the line using fixed-point arithmetics,
- // stop at the image border or in case of too big gap
- for( ;; x += dx, y += dy )
- {
- uchar* mdata;
- int i1, j1;
- if( xflag )
- {
- j1 = x;
- i1 = y >> shift;
- }
- else
- {
- j1 = x >> shift;
- i1 = y;
- }
- mdata = mdata0 + i1*width + j1;
- // for each non-zero point:
- // update line end,
- // clear the mask element
- // reset the gap
- if( *mdata )
- {
- //if语句的作用是清除那些已经判定是好的直线上的点对应的累加器的值,避免再次利用这些累加值
- if( good_line ) //在第一次搜索中已经确定是好的直线
- {
- //得到累加器矩阵地址指针
- adata = (int*)accum.data;
- for( n = 0; n < numangle; n++, adata += numrho )
- {
- r = cvRound( j1 * ttab[n*2] + i1 * ttab[n*2+1] );
- r += (numrho - 1) / 2;
- adata[r]--; //相应的累加器减1
- }
- }
- //搜索过的位置,不管是好的直线,还是坏的直线,掩码相应位置都清0,这样下次就不会再重复搜索这些位置了,从而达到减小计算边缘点的目的
- *mdata = 0;
- }
- //如果已经到达了直线的端点,则退出循环
- if( i1 == line_end[k].y && j1 == line_end[k].x )
- break;
- }
- }
- //如果是好的直线
- if( good_line )
- {
- CvRect lr = { line_end[0].x, line_end[0].y, line_end[1].x, line_end[1].y };
- //把两个端点压入序列中
- cvSeqPush( lines, &lr );
- //如果检测到的直线数量大于阈值,则退出该函数
- if( lines->total >= linesMax )
- return;
- }
- }
- }
- #include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
- #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
- #include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace cv;
- using namespace std;
- int main( int argc, char** argv )
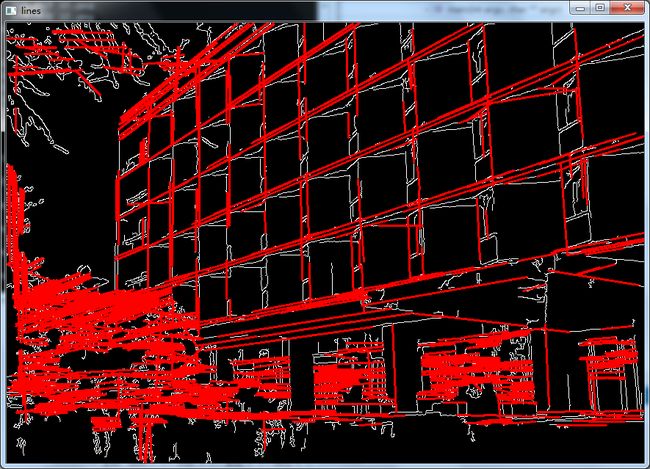
- {
- Mat src, edge,color_edge;
- src=imread("building.jpg");
- if( !src.data )
- return -1;
- Canny(src,edge,50,200,3);
- cvtColor( edge, color_edge, CV_GRAY2BGR );
- vector<Vec4i> lines;
- HoughLinesP(edge, lines, 1, CV_PI/180, 80, 30, 10 );
- for( size_t i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++ )
- {
- Vec4i l = lines[i];
- line( color_edge, Point(l[0], l[1]), Point(l[2], l[3]), Scalar(0,0,255), 2);
- }
- namedWindow( "lines", CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
- imshow( "lines", color_edge );
- waitKey(0);
- return 0;
- }