css笔记
CSS 概述
- CSS 指层叠样式表 (Cascading Style Sheets)
- 样式定义如何显示 HTML 元素
- 样式通常存储在样式表中
- 把样式添加到 HTML 4.0 中,是为了解决内容与表现分离的问题
- 外部样式表可以极大提高工作效率
- 外部样式表通常存储在 CSS 文件中
- 多个样式定义可层叠为一
层叠次序
当同一个 HTML 元素被不止一个样式定义时,会使用哪个样式呢?
一般而言,所有的样式会根据下面的规则层叠于一个新的虚拟样式表中,其中数字 4 拥有最高的优先权。
- 浏览器缺省设置
- 外部样式表
- 内部样式表(位于 <head> 标签内部)
- 内联样式(在 HTML 元素内部)
因此,内联样式(在 HTML 元素内部)拥有最高的优先权,这意味着它将优先于以下的样式声明:<head> 标签中的样式声明,外部样式表中的样式声明,或者浏览器中的样式声明(缺省值)。
下面这行代码的作用是将 h1 元素内的文字颜色定义为红色,同时将字体大小设置为 14 像素。
在这个例子中,h1 是选择器,color 和 font-size 是属性,red 和 14px 是值。
h1 {color:red; font-size:14px;}
下面的示意图为您展示了上面这段代码的结构:

提示:请使用花括号来包围声明。
记得写引号
提示:如果值为若干单词,则要给值加引号:
p {font-family: "sans serif";}
多重声明:
提示:如果要定义不止一个声明,则需要用分号将每个声明分开。下面的例子展示出如何定义一个红色文字的居中段落。最后一条规则是不需要加分号的,因为分号在英语中是一个分隔符号,不是结束符号。然而,大多数有经验的设计师会在每条声明的末尾都加上分号,这么做的好处是,当你从现有的规则中增减声明时,会尽可能地减少出错的可能性。就像这样:
p {text-align:center; color:red;}
你应该在每行只描述一个属性,这样可以增强样式定义的可读性,就像这样:
p {
text-align: center;
color: black;
font-family: arial;
}
在 CSS 中,类选择器以一个点号显示:
.center {text-align: center}在上面的例子中,所有拥有 center 类的 HTML 元素均为居中。
在下面的 HTML 代码中,h1 和 p 元素都有 center 类。这意味着两者都将遵守 ".center" 选择器中的规则。
<h1class="center"> This heading will be center-aligned </h1> <pclass="center"> This paragraph will also be center-aligned. </p>
注意:类名的第一个字符不能使用数字!它无法在 Mozilla 或 Firefox 中起作用。
设置表单的样式
属性选择器在为不带有 class 或 id 的表单设置样式时特别有用:
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<style>
input[type="text"]
{
width:150px;
display:block;
margin-bottom:10px;
background-color:yellow;
font-family: Verdana, Arial;
}
input[type="button"]
{
width:120px;
margin-left:35px;
display:block;
font-family: Verdana, Arial;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<form name="input" action="" method="get">
<input type="text" name="Name" value="Bill" size="20">
<input type="text" name="Name" value="Gates" size="20">
<input type="button" value="Example Button">
</form>
</body>
</html>
背景图像
要把图像放入背景,需要使用 background-image 属性。background-image 属性的默认值是 none,表示背景上没有放置任何图像。
如果需要设置一个背景图像,必须为这个属性设置一个 URL 值:
背景定位
可以利用 background-position 属性改变图像在背景中的位置。
下面的例子在 body 元素中将一个背景图像居中放置:
body
{
background-image:url('/i/eg_bg_03.gif');
background-repeat:no-repeat;
background-position:center;
}
为 background-position 属性提供值有很多方法。首先,可以使用一些关键字:top、bottom、left、right 和 center。通常,这些关键字会成对出现,不过也不总是这样。还可以使用长度值,如 100px 或 5cm,最后也可以使用百分数值。不同类型的值对于背景图像的放置稍有差异。
下面是等价的位置关键字:
| 单一关键字 | 等价的关键字 |
|---|---|
| center | center center |
| top | top center 或 center top |
| bottom | bottom center 或 center bottom |
| right | right center 或 center right |
| left | left center 或 center left |
CSS 背景属性
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| background | 简写属性,作用是将背景属性设置在一个声明中。 |
| background-attachment | 背景图像是否固定或者随着页面的其余部分滚动。 |
| background-color | 设置元素的背景颜色。 |
| background-image | 把图像设置为背景。 |
| background-position | 设置背景图像的起始位置。 |
| background-repeat | 设置背景图像是否及如何重复。 |
CSS 文本属性
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| color | 设置文本颜色 |
| direction | 设置文本方向。 |
| line-height | 设置行高。 |
| letter-spacing | 设置字符间距。 |
| text-align | 对齐元素中的文本。 |
| text-decoration | 向文本添加修饰。 |
| text-indent | 缩进元素中文本的首行。 |
| text-shadow | 设置文本阴影。CSS2 包含该属性,但是 CSS2.1 没有保留该属性。 |
| text-transform | 控制元素中的字母。 |
| unicode-bidi | 设置文本方向。 |
| white-space | 设置元素中空白的处理方式。 |
| word-spacing | 设置字间距。 |
CSS 字体属性
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| font | 简写属性。作用是把所有针对字体的属性设置在一个声明中。 |
| font-family | 设置字体系列。 |
| font-size | 设置字体的尺寸。 |
| font-size-adjust | 当首选字体不可用时,对替换字体进行智能缩放。(CSS2.1 已删除该属性。) |
| font-stretch | 对字体进行水平拉伸。(CSS2.1 已删除该属性。) |
| font-style | 设置字体风格。 |
| font-variant | 以小型大写字体或者正常字体显示文本。 |
| font-weight | 设置字体的粗细。 |
设置链接的样式
能够设置链接样式的 CSS 属性有很多种(例如 color, font-family, background 等等)。
链接的特殊性在于能够根据它们所处的状态来设置它们的样式。
链接的四种状态:
- a:link - 普通的、未被访问的链接
- a:visited - 用户已访问的链接
- a:hover - 鼠标指针位于链接的上方
- a:active - 链接被点击的时刻
实例
a:link {color:#FF0000;} /* 未被访问的链接 */
a:visited {color:#00FF00;} /* 已被访问的链接 */
a:hover {color:#FF00FF;} /* 鼠标指针移动到链接上 */
a:active {color:#0000FF;} /* 正在被点击的链接 */
亲自试一试
当为链接的不同状态设置样式时,请按照以下次序规则:
- a:hover 必须位于 a:link 和 a:visited 之后
- a:active
必须位于 a:hover 之后
<html>
<head>
<style type="text/css">
body {background-image:url(/i/eg_bg_04.gif);}
p.flower {background-image: url(/i/eg_bg_03.gif); padding: 20px;}
a.radio {background-image: url(/i/eg_bg_07.gif); padding: 20px;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="flower">我是一个有花纹背景的段落。<a href="#" class="radio">我是一个有放射性背景的链接。</a></p>
<p><b>注释:</b>为了清晰地显示出段落和链接的背景图像,我们为它们设置了少许内边距。</p>
</body>
</html>
非常漂亮的表格
<html>
<head>
<style type="text/css">
#customers
{
font-family:"Trebuchet MS", Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;
width:100%;
border-collapse:collapse;
}
#customers td, #customers th
{
font-size:1em;
border:1px solid #98bf21;
padding:3px 7px 2px 7px;
}
#customers th
{
font-size:1.1em;
text-align:left;
padding-top:5px;
padding-bottom:4px;
background-color:#A7C942;
color:#ffffff;
}
#customers tr.alt td
{
color:#000000;
background-color:#EAF2D3;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table id="customers">
<tr>
<th>Company</th>
<th>Contact</th>
<th>Country</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Apple</td>
<td>Steven Jobs</td>
<td>USA</td>
</tr>
<tr class="alt">
<td>Baidu</td>
<td>Li YanHong</td>
<td>China</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Google</td>
<td>Larry Page</td>
<td>USA</td>
</tr>
<tr class="alt">
<td>Lenovo</td>
<td>Liu Chuanzhi</td>
<td>China</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Microsoft</td>
<td>Bill Gates</td>
<td>USA</td>
</tr>
<tr class="alt">
<td>Nokia</td>
<td>Stephen Elop</td>
<td>Finland</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
- 在元素周围画线
- 本例演示使用outline属性在元素周围画一条线。
-
<html> <head> <style type="text/css"> p { border:red solid thin; outline:#00ff00 dotted thick; } </style> </head> <body> <p><b>注释:</b>只有在规定了 !DOCTYPE时,Internet Explore 8才支持outline属性。</p> </body> </html>
- 设置轮廓的样式
- 本例演示如何设置轮廓的样式。
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<style type="text/css">
p
{
border: red solid thin;
}
p.dotted {outline-style: dotted}
p.dashed {outline-style: dashed}
p.solid {outline-style: solid}
p.double {outline-style: double}
p.groove {outline-style: groove}
p.ridge {outline-style: ridge}
p.inset {outline-style: inset}
p.outset {outline-style: outset}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p class="dotted">A dotted outline</p>
<p class="dashed">A dashed outline</p>
<p class="solid">A solid outline</p>
<p class="double">A double outline</p>
<p class="groove">A groove outline</p>
<p class="ridge">A ridge outline</p>
<p class="inset">An inset outline</p>
<p class="outset">An outset outline</p>
<p><b>注释:</b>只有在规定了 !DOCTYPE 时,Internet Explorer 8 (以及更高版本) 才支持 outline-style 属性。</p>
</body>
</html>
CSS 框模型概述
CSS 框模型 (Box Model) 规定了元素框处理元素内容、内边距、边框 和外边距 的方式。CSS 框模型概述
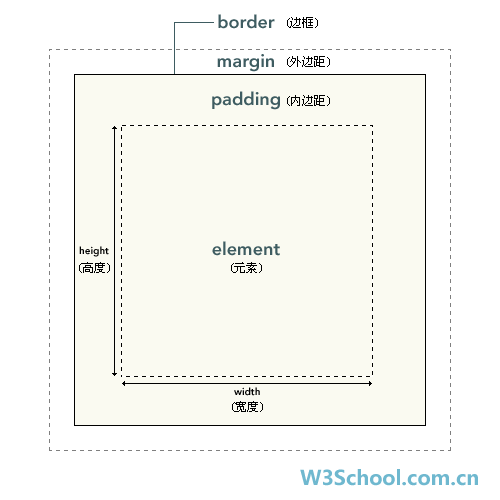
提示:背景应用于由内容和内边距、边框组成的区域。
提示:内边距、边框和外边距可以应用于一个元素的所有边,也可以应用于单独的边。
提示:外边距可以是负值,而且在很多情况下都要使用负值的外边距。
元素的边框 (border) 是围绕元素内容和内边距的一条或多条线。CSS 边框属性
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| border | 简写属性,用于把针对四个边的属性设置在一个声明。 |
| border-style | 用于设置元素所有边框的样式,或者单独地为各边设置边框样式。 |
| border-width | 简写属性,用于为元素的所有边框设置宽度,或者单独地为各边边框设置宽度。 |
| border-color | 简写属性,设置元素的所有边框中可见部分的颜色,或为 4 个边分别设置颜色。 |
| border-bottom | 简写属性,用于把下边框的所有属性设置到一个声明中。 |
| border-bottom-color | 设置元素的下边框的颜色。 |
| border-bottom-style | 设置元素的下边框的样式。 |
| border-bottom-width | 设置元素的下边框的宽度。 |
| border-left | 简写属性,用于把左边框的所有属性设置到一个声明中。 |
| border-left-color | 设置元素的左边框的颜色。 |
| border-left-style | 设置元素的左边框的样式。 |
| border-left-width | 设置元素的左边框的宽度。 |
| border-right | 简写属性,用于把右边框的所有属性设置到一个声明中。 |
| border-right-color | 设置元素的右边框的颜色。 |
| border-right-style | 设置元素的右边框的样式。 |
| border-right-width | 设置元素的右边框的宽度。 |
| border-top | 简写属性,用于把上边框的所有属性设置到一个声明中。 |
| border-top-color | 设置元素的上边框的颜色。 |
| border-top-style | 设置元素的上边框的样式。 |
| border-top-width | 设置元素的上边框的宽度。 |
CSS 外边距
设置外边距的最简单的方法就是使用 margin 属性,这个属性接受任何长度单位、百分数值甚至负值。提示和注释
提示:Netscape 和 IE 对 body 标签定义的默认边距(margin)值是 8px。而 Opera 不是这样。相反地,Opera 将内部填充(padding)的默认值定义为 8px,因此如果希望对整个网站的边缘部分进行调整,并将之正确显示于 Opera 中,那么必须对 body 的 padding 进行自定义。
注释:只有普通文档流中块框的垂直外边距才会发生外边距合并。行内框、浮动框或绝对定位之间的外边距不会合并
CSS 外边距属性
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| margin | 简写属性。在一个声明中设置所有外边距属性。 |
| margin-bottom | 设置元素的下外边距。 |
| margin-left | 设置元素的左外边距。 |
| margin-right | 设置元素的右外边距。 |
| margin-top | 设置元素的上外边距。 |
CSS 定位属性
CSS 定位属性允许你对元素进行定位。
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| position | 把元素放置到一个静态的、相对的、绝对的、或固定的位置中。 |
| top | 定义了一个定位元素的上外边距边界与其包含块上边界之间的偏移。 |
| right | 定义了定位元素右外边距边界与其包含块右边界之间的偏移。 |
| bottom | 定义了定位元素下外边距边界与其包含块下边界之间的偏移。 |
| left | 定义了定位元素左外边距边界与其包含块左边界之间的偏移。 |
| overflow | 设置当元素的内容溢出其区域时发生的事情。 |
| clip | 设置元素的形状。元素被剪入这个形状之中,然后显示出来。 |
| vertical-align | 设置元素的垂直对齐方式。 |
| z-index | 设置元素的堆叠顺序。 |
CSS 相对定位
相对定位是一个非常容易掌握的概念。如果对一个元素进行相对定位,它将出现在它所在的位置上。然后,可以通过设置垂直或水平位置,让这个元素“相对于”它的起点进行移动。
如果将 top 设置为 20px,那么框将在原位置顶部下面 20 像素的地方。如果 left 设置为 30 像素,那么会在元素左边创建 30 像素的空间,也就是将元素向右移动。
#box_relative {
position: relative;
left: 30px;
top: 20px;
}
设置为绝对定位的元素框从文档流完全删除,并相对于其包含块定位,包含块可能是文档中的另一个元素或者是初始包含块。元素原先在正常文档流中所占的空间会关闭,就好像该元素原来不存在一样。元素定位后生成一个块级框,而不论原来它在正常流中生成何种类型的框。
CSS 绝对定位
绝对定位使元素的位置与文档流无关,因此不占据空间。这一点与相对定位不同,相对定位实际上被看作普通流定位模型的一部分,因为元素的位置相对于它在普通流中的位置。
普通流中其它元素的布局就像绝对定位的元素不存在一样:
#box_relative {
position: absolute;
left: 30px;
top: 20px;
}
提示:请同时看一看我们完整样式的导航栏实例。
注释:请始终规定垂直导航栏中 <a> 元素的宽度。如果省略宽度,IE6 会产生意想不到的结果。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
ul
{
list-style-type:none;
margin:0;
padding:0;
}
a:link,a:visited
{
display:block;
font-weight:bold;
color:#FFFFFF;
background-color:#bebebe;
width:120px;
text-align:center;
padding:4px;
text-decoration:none;
text-transform:uppercase;
}
a:hover,a:active
{
background-color:#cc0000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li><a href="#home">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#news">News</a></li>
<li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li>
<li><a href="#about">About</a></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
水平导航示例,非常精致的导航。
例子解释:
- float:left - 使用 float 来把块元素滑向彼此。
- display:block - 把链接显示为块元素可使整个链接区域可点击(不仅仅是文本),同时也允许我们规定宽度。
- width:60px - 由于块元素默认占用全部可用宽度,链接无法滑动至彼此相邻。我们需要规定 60 像素的宽度。
提示:请看一下我们完整样式的水平导航栏实例。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
ul
{
list-style-type:none;
margin:0;
padding:0;
overflow:hidden;
}
li
{
float:left;
}
a:link,a:visited
{
display:block;
width:120px;
font-weight:bold;
color:#FFFFFF;
background-color:#bebebe;
text-align:center;
padding:4px;
text-decoration:none;
text-transform:uppercase;
}
a:hover,a:active
{
background-color:#cc0000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li><a href="#home">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#news">News</a></li>
<li><a href="#contact">Contact</a></li>
<li><a href="#about">About</a></li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
图片库
下面的图片库是由 CSS 创建的:
实例
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div.img
{
margin:3px;
border:1px solid #bebebe;
height:auto;
width:auto;
float:left;
text-align:center;
}
div.img img
{
display:inline;
margin:3px;
border:1px solid #bebebe;
}
div.img a:hover img
{
border:1px solid #333333;
}
div.desc
{
text-align:center;
font-weight:normal;
width:150px;
font-size:12px;
margin:10px 5px 10px 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="img">
<a target="_blank" href="/i/tulip_ballade.jpg">
<img src="/i/tulip_ballade_s.jpg" alt="Ballade" width="160" height="160">
</a>
<div class="desc">在此处添加对图像的描述</div>
</div>
<div class="img">
<a target="_blank" href="/i/tulip_flaming_club.jpg">
<img src="/i/tulip_flaming_club_s.jpg" alt="Ballade" width="160" height="160">
</a>
<div class="desc">在此处添加对图像的描述</div>
</div>
<div class="img">
<a target="_blank" href="/i/tulip_fringed_family.jpg">
<img src="/i/tulip_fringed_family_s.jpg" alt="Ballade" width="160" height="160">
</a>
<div class="desc">在此处添加对图像的描述</div>
</div>
<div class="img">
<a target="_blank" href="/i/tulip_peach_blossom.jpg">
<img src="/i/tulip_peach_blossom_s.jpg" alt="Ballade" width="160" height="160">
</a>
<div class="desc">在此处添加对图像的描述</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>