滑动删除listview的demo的分析
今天做一个滑动删除listview的demo的分析
先来看一张效果图
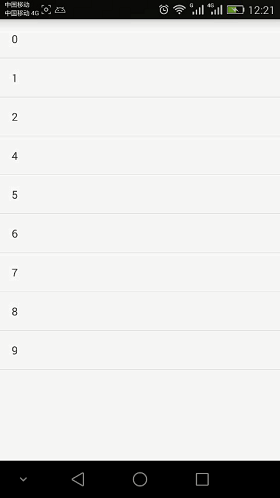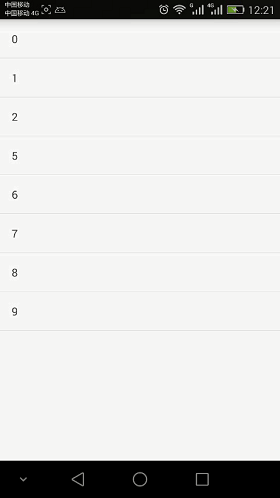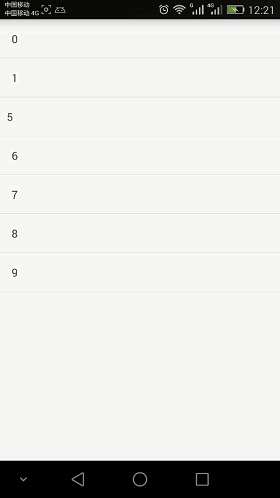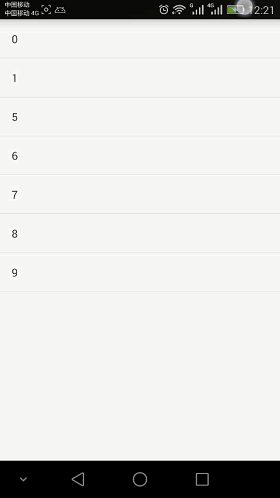
只需要demo的童鞋直接点击下面链接下载就好了, 下面我们来做这个demo的分析
demo下载链接
我们先来看看代码是怎么用的
listview = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listview);
listview.setAdapter(adapter);
touchListener = new SwipeDismissListViewTouchListener(listview, new DismissCallbacks() {
@Override
public void onDismiss(ListView listView, int[] reverseSortedPositions) {
for (int position : reverseSortedPositions) {
adapter.remove(position);
}
}
@Override
public boolean canDismiss(int position) {
return true;
}
});
listview.setOnTouchListener(touchListener);
listview.setOnScrollListener(touchListener.makeScro`
lListener());ok 用完了
其中listview是系统的listview, adapter是baseadapter的实现,和普通listview的区别是setOnTouchListener了一个监听器 同时也setOnScrollListener了一个滑动监听器.
以下是SwipeDismissListViewTouchListener的实现,好大一堆
public class SwipeDismissListViewTouchListener implements View.OnTouchListener {
// Cached ViewConfiguration and system-wide constant values
private int mSlop;
private int mMinFlingVelocity;
private int mMaxFlingVelocity;
private long mAnimationTime;
// Fixed properties
private ListView mListView;
private DismissCallbacks mCallbacks;
private int mViewWidth = 1; // 1 and not 0 to prevent dividing by zero
// Transient properties
private List<PendingDismissData> mPendingDismisses = new ArrayList<PendingDismissData>();
private int mDismissAnimationRefCount = 0;
private float mDownX;
private float mDownY;
private boolean mSwiping;
private int mSwipingSlop;
private VelocityTracker mVelocityTracker;
private int mDownPosition;
private View mDownView;
private boolean mPaused;
/** * The callback interface used by {@link SwipeDismissListViewTouchListener} to inform its client * about a successful dismissal of one or more list item positions. */
public interface DismissCallbacks {
/** * Called to determine whether the given position can be dismissed. */
boolean canDismiss(int position);
/** * Called when the user has indicated they she would like to dismiss one or more list item * positions. * * @param listView The originating {@link ListView}. * @param reverseSortedPositions An array of positions to dismiss, sorted in descending * order for convenience. */
void onDismiss(ListView listView, int[] reverseSortedPositions);
}
/** * Constructs a new swipe-to-dismiss touch listener for the given list view. * * @param listView The list view whose items should be dismissable. * @param callbacks The callback to trigger when the user has indicated that she would like to * dismiss one or more list items. */
public SwipeDismissListViewTouchListener(ListView listView, DismissCallbacks callbacks) {
ViewConfiguration vc = ViewConfiguration.get(listView.getContext());
mSlop = vc.getScaledTouchSlop();
mMinFlingVelocity = vc.getScaledMinimumFlingVelocity() * 16;
mMaxFlingVelocity = vc.getScaledMaximumFlingVelocity();
mAnimationTime = listView.getContext().getResources().getInteger(
android.R.integer.config_shortAnimTime);
mListView = listView;
mCallbacks = callbacks;
}
/** * Enables or disables (pauses or resumes) watching for swipe-to-dismiss gestures. * * @param enabled Whether or not to watch for gestures. */
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
mPaused = !enabled;
}
/** * Returns an {@link AbsListView.OnScrollListener} to be added to the {@link * ListView} using {@link ListView#setOnScrollListener(AbsListView.OnScrollListener)}. * If a scroll listener is already assigned, the caller should still pass scroll changes through * to this listener. This will ensure that this {@link SwipeDismissListViewTouchListener} is * paused during list view scrolling.</p> * * @see SwipeDismissListViewTouchListener */
public AbsListView.OnScrollListener makeScrollListener() {
return new AbsListView.OnScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView absListView, int scrollState) {
setEnabled(scrollState != AbsListView.OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_TOUCH_SCROLL);
}
@Override
public void onScroll(AbsListView absListView, int i, int i1, int i2) {
}
};
}
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View view, MotionEvent motionEvent) {
if (mViewWidth < 2) {
mViewWidth = mListView.getWidth();
}
switch (motionEvent.getActionMasked()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: {
if (mPaused) {
return false;
}
// TODO: ensure this is a finger, and set a flag
// Find the child view that was touched (perform a hit test)
Rect rect = new Rect();
int childCount = mListView.getChildCount();
int[] listViewCoords = new int[2];
mListView.getLocationOnScreen(listViewCoords);
int x = (int) motionEvent.getRawX() - listViewCoords[0];
int y = (int) motionEvent.getRawY() - listViewCoords[1];
View child;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
child = mListView.getChildAt(i);
child.getHitRect(rect);
if (rect.contains(x, y)) {
mDownView = child;
break;
}
}
if (mDownView != null) {
mDownX = motionEvent.getRawX();
mDownY = motionEvent.getRawY();
mDownPosition = mListView.getPositionForView(mDownView);
if (mCallbacks.canDismiss(mDownPosition)) {
mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(motionEvent);
} else {
mDownView = null;
}
}
return false;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: {
if (mVelocityTracker == null) {
break;
}
if (mDownView != null && mSwiping) {
// cancel
mDownView.animate()
.translationX(0)
.alpha(1)
.setDuration(mAnimationTime)
.setListener(null);
}
mVelocityTracker.recycle();
mVelocityTracker = null;
mDownX = 0;
mDownY = 0;
mDownView = null;
mDownPosition = ListView.INVALID_POSITION;
mSwiping = false;
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: {
if (mVelocityTracker == null) {
break;
}
float deltaX = motionEvent.getRawX() - mDownX;
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(motionEvent);
mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
float velocityX = mVelocityTracker.getXVelocity();
float absVelocityX = Math.abs(velocityX);
float absVelocityY = Math.abs(mVelocityTracker.getYVelocity());
boolean dismiss = false;
boolean dismissRight = false;
if (Math.abs(deltaX) > mViewWidth / 2 && mSwiping) {
dismiss = true;
dismissRight = deltaX > 0;
} else if (mMinFlingVelocity <= absVelocityX && absVelocityX <= mMaxFlingVelocity
&& absVelocityY < absVelocityX && mSwiping) {
// dismiss only if flinging in the same direction as dragging
dismiss = (velocityX < 0) == (deltaX < 0);
dismissRight = mVelocityTracker.getXVelocity() > 0;
}
if (dismiss && mDownPosition != ListView.INVALID_POSITION) {
// dismiss
final View downView = mDownView; // mDownView gets null'd before animation ends
final int downPosition = mDownPosition;
++mDismissAnimationRefCount;
mDownView.animate()
.translationX(dismissRight ? mViewWidth : -mViewWidth)
.alpha(0)
.setDuration(mAnimationTime)
.setListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
performDismiss(downView, downPosition);
}
});
} else {
// cancel
mDownView.animate()
.translationX(0)
.alpha(1)
.setDuration(mAnimationTime)
.setListener(null);
}
mVelocityTracker.recycle();
mVelocityTracker = null;
mDownX = 0;
mDownY = 0;
mDownView = null;
mDownPosition = ListView.INVALID_POSITION;
mSwiping = false;
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: {
if (mVelocityTracker == null || mPaused) {
break;
}
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(motionEvent);
float deltaX = motionEvent.getRawX() - mDownX;
float deltaY = motionEvent.getRawY() - mDownY;
if (Math.abs(deltaX) > mSlop && Math.abs(deltaY) < Math.abs(deltaX) / 2) {
mSwiping = true;
mSwipingSlop = (deltaX > 0 ? mSlop : -mSlop);
mListView.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true);
// Cancel ListView's touch (un-highlighting the item)
MotionEvent cancelEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(motionEvent);
cancelEvent.setAction(MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL |
(motionEvent.getActionIndex()
<< MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_SHIFT));
mListView.onTouchEvent(cancelEvent);
cancelEvent.recycle();
}
if (mSwiping) {
mDownView.setTranslationX(deltaX - mSwipingSlop);
mDownView.setAlpha(Math.max(0f, Math.min(1f,
1f - 2f * Math.abs(deltaX) / mViewWidth)));
return true;
}
break;
}
}
return false;
}
class PendingDismissData implements Comparable<PendingDismissData> {
public int position;
public View view;
public PendingDismissData(int position, View view) {
this.position = position;
this.view = view;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(PendingDismissData other) {
// Sort by descending position
return other.position - position;
}
}
private void performDismiss(final View dismissView, final int dismissPosition) {
// Animate the dismissed list item to zero-height and fire the dismiss callback when
// all dismissed list item animations have completed. This triggers layout on each animation
// frame; in the future we may want to do something smarter and more performant.
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = dismissView.getLayoutParams();
final int originalHeight = dismissView.getHeight();
ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofInt(originalHeight, 1).setDuration(mAnimationTime);
animator.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
--mDismissAnimationRefCount;
if (mDismissAnimationRefCount == 0) {
// No active animations, process all pending dismisses.
// Sort by descending position
Collections.sort(mPendingDismisses);
int[] dismissPositions = new int[mPendingDismisses.size()];
for (int i = mPendingDismisses.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
dismissPositions[i] = mPendingDismisses.get(i).position;
}
mCallbacks.onDismiss(mListView, dismissPositions);
// Reset mDownPosition to avoid MotionEvent.ACTION_UP trying to start a dismiss
// animation with a stale position
mDownPosition = ListView.INVALID_POSITION;
ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp;
for (PendingDismissData pendingDismiss : mPendingDismisses) {
// Reset view presentation
pendingDismiss.view.setAlpha(1f);
pendingDismiss.view.setTranslationX(0);
lp = pendingDismiss.view.getLayoutParams();
lp.height = originalHeight;
pendingDismiss.view.setLayoutParams(lp);
}
// Send a cancel event
long time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
MotionEvent cancelEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(time, time,
MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL, 0, 0, 0);
mListView.dispatchTouchEvent(cancelEvent);
mPendingDismisses.clear();
}
}
});
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
lp.height = (Integer) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
dismissView.setLayoutParams(lp);
}
});
mPendingDismisses.add(new PendingDismissData(dismissPosition, dismissView));
animator.start();
}
}
这么大一堆代码,看了也是一头雾水,不过我们先挑重点的来看:
不管它多么复杂,首先它是一个OnTouchListener那就肯定需要实现onTouch方法,那我们一一步步的来看:
先来看ACTION_DOWN的时候它做了什么
Rect rect = new Rect();
int childCount = mListView.getChildCount();
int[] listViewCoords = new int[2];
// 找到listview在屏幕上的起始位置
mListView.getLocationOnScreen(listViewCoords);
// 计算出相对于listview的位置
int x = (int) motionEvent.getRawX() - listViewCoords[0];
int y = (int) motionEvent.getRawY() - listViewCoords[1];
View child;
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
// 这个子布局的矩形
child = mListView.getChildAt(i);
child.getHitRect(rect);
if (rect.contains(x, y)) { // 这个点是否在矩形内?
mDownView = child; // 是的的话就找到了,直接beak
break;
}
}这部分代码是找到event事件在哪个item上,把这个item揪出来,
这么麻烦吧这个item找出来而那为什么不是直接在item上设置ontouch不是更简单一些?
当然,作者这个搞是很有目的的,先不急,先来看看下面代码都干嘛了?稍后再来思考这个问题
if (mDownView != null) {
mDownX = motionEvent.getRawX();
mDownY = motionEvent.getRawY();
mDownPosition = mListView.getPositionForView(mDownView); // 找出点击的item的position
if (mCallbacks.canDismiss(mDownPosition)) {
// 速度跟踪
mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(motionEvent);
} else {
mDownView = null;
}
}
return false;看代码最后直接返回 false 了
也就是说没有做任何事件拦截
ok 我们再来看看move里面做了什么
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: {
// 根据上面的代码,我们知道如果mVelocityTracker为空那么肯定没有找到点击的那个item到时是哪个item就谈不上滑动删除了,所以如果mVelocityTracker为空就break, mPaused先不管
if (mVelocityTracker == null || mPaused) {
break;
}
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(motionEvent);
float deltaX = motionEvent.getRawX() - mDownX;
float deltaY = motionEvent.getRawY() - mDownY;
// mSlop 表示手指触摸引起滑动的像素值
// 下面表示 : 如果 移动的x轴像素 > 引起滑动的像素值 并且 Y轴的距离小于X轴的二分之一
// 简单来说就是 if(是横向滑动)
if (Math.abs(deltaX) > mSlop && Math.abs(deltaY) < Math.abs(deltaX) / 2) {
mSwiping = true;
mSwipingSlop = (deltaX > 0 ? mSlop : -mSlop);
// 请求listview不要把此事件向child分发传递了,因为横向滑动就表示该删除了
mListView.requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true);
// Cancel ListView's touch (un-highlighting the item)
// 翻译上面注释: 给listview设置一个cancel事件,取消掉item的高亮状态
// 分析:因为前面down的时候并没有截获事件,而listview开始的时候也不会截获事件,item是会接受到touch,并高亮的
MotionEvent cancelEvent = MotionEvent.obtain(motionEvent);
cancelEvent.setAction(MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL |
(motionEvent.getActionIndex()
<< MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_SHIFT));
mListView.onTouchEvent(cancelEvent);
cancelEvent.recycle();
}
// 刚开看到 如果是横向滑动就会 mSwiping = true; 那么mSwiping 的意思就是如果是滑动删除状态
if (mSwiping) {
// 设置item的X的移动距离
mDownView.setTranslationX(deltaX - mSwipingSlop);
// 同时设置item的透明度
mDownView.setAlpha(Math.max(0f, Math.min(1f,
1f - 2f * Math.abs(deltaX) / mViewWidth)));
return true; // 这个是重点,如果在滑动,那么就直接返回true把事件截获了
}
break;
}上面说了如果在滑动,那么直接返回true
此时大家想想,这时候如果用户在不抬起手指的情况下上下滑动, listview 是不会滚动了,
========= 这里有必要讲下事件分发的相关逻辑, 不需要看的童鞋直接跳过 ===========
listview继承关系:
view中dispatch中有这么一段:

如果listview有自己的ontouch 并且 返回 true 就直接返回了,
如果ontouchListener返回false就会执行view本身的ontouch
而listivew中重写的ontouch方法:
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (!isEnabled()) {
// A disabled view that is clickable still consumes the touch
// events, it just doesn't respond to them.
return isClickable() || isLongClickable();
}
if (mPositionScroller != null) {
mPositionScroller.stop();
}
if (!isAttachedToWindow()) {
// Something isn't right.
// Since we rely on being attached to get data set change notifications,
// don't risk doing anything where we might try to resync and find things
// in a bogus state.
return false; // 我们看到只有这一个地方会返回false, 其他地方全部返回true
}
if (mFastScroller != null) {
boolean intercepted = mFastScroller.onTouchEvent(ev);
if (intercepted) {
return true;
}
}
initVelocityTrackerIfNotExists();
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(ev);
final int actionMasked = ev.getActionMasked();
switch (actionMasked) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: {
onTouchDown(ev);
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: {
onTouchMove(ev);
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: {
onTouchUp(ev);
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: {
onTouchCancel();
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP: {
onSecondaryPointerUp(ev);
final int x = mMotionX;
final int y = mMotionY;
final int motionPosition = pointToPosition(x, y);
if (motionPosition >= 0) {
// Remember where the motion event started
final View child = getChildAt(motionPosition - mFirstPosition);
mMotionViewOriginalTop = child.getTop();
mMotionPosition = motionPosition;
}
mLastY = y;
break;
}
case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN: {
// New pointers take over dragging duties
final int index = ev.getActionIndex();
final int id = ev.getPointerId(index);
final int x = (int) ev.getX(index);
final int y = (int) ev.getY(index);
mMotionCorrection = 0;
mActivePointerId = id;
mMotionX = x;
mMotionY = y;
final int motionPosition = pointToPosition(x, y);
if (motionPosition >= 0) {
// Remember where the motion event started
final View child = getChildAt(motionPosition - mFirstPosition);
mMotionViewOriginalTop = child.getTop();
mMotionPosition = motionPosition;
}
mLastY = y;
break;
}
}
return true;也就是说在listview中ontouch是一直都返回true的,而在item中其实也是能在listview的ontouchevent返回true的情况下接受到事件的.
那么我们就不得不接受这么一个事实:
我们知道 view是在dispatchtouch 中进行事件分发,
但是 在listview中却是始终交给 listview的 ontouchevent来执行事件分发!!
不得不吐槽一下, 不过这也解决了在item中设置onclick和ontouch不会影响listview滑动的流畅性了!
========= 这里有必要讲下事件分发的相关逻辑, 不需要看的童鞋直接跳过(完) =========
下面继续来看ACTION_UP:
if (mVelocityTracker == null) {
break;
}
float deltaX = motionEvent.getRawX() - mDownX;
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(motionEvent);
mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000);
float velocityX = mVelocityTracker.getXVelocity();
float absVelocityX = Math.abs(velocityX);
float absVelocityY = Math.abs(mVelocityTracker.getYVelocity());
boolean dismiss = false;
boolean dismissRight = false;
if (Math.abs(deltaX) > mViewWidth / 2 && mSwiping) { //这代码就不难理解了
dismiss = true; // 滑动大于view的二分之一就表示需要滑动删除
dismissRight = deltaX > 0;
} else if (mMinFlingVelocity <= absVelocityX && absVelocityX <= mMaxFlingVelocity
&& absVelocityY < absVelocityX && mSwiping) { // 滑动速度够了,不用滑动那么多也可以删!
// dismiss only if flinging in the same direction as dragging
dismiss = (velocityX < 0) == (deltaX < 0);
dismissRight = mVelocityTracker.getXVelocity() > 0;
}
if (dismiss && mDownPosition != ListView.INVALID_POSITION) {
//如果删除 并且 position有效,执行删除动画, 在动画完成的时候调用删除回调函数
// dismiss
final View downView = mDownView; // mDownView gets null'd before animation ends
final int downPosition = mDownPosition;
++mDismissAnimationRefCount;
mDownView.animate()
.translationX(dismissRight ? mViewWidth : -mViewWidth)
.alpha(0)
.setDuration(mAnimationTime)
.setListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
performDismiss(downView, downPosition);
}
});
} else {
// 取消删除, 直接动画回去
// cancel
mDownView.animate()
.translationX(0)
.alpha(1)
.setDuration(mAnimationTime)
.setListener(null);
}
// 回复初始状态
mVelocityTracker.recycle();
mVelocityTracker = null;
mDownX = 0;
mDownY = 0;
mDownView = null;
mDownPosition = ListView.INVALID_POSITION;
mSwiping = false;ACTION_CANCEL就不看了,就是取消的动画执行一下,然后变量初始化一下就行了
mPaused 再解释一下
public AbsListView.OnScrollListener makeScrollListener() {
return new AbsListView.OnScrollListener() {
@Override
public void onScrollStateChanged(AbsListView absListView, int scrollState) {
setEnabled(scrollState != AbsListView.OnScrollListener.SCROLL_STATE_TOUCH_SCROLL); // 这里!!是给mPaused 的赋值的
}
@Override
public void onScroll(AbsListView absListView, int i, int i1, int i2) {
}
};
}也就是说一但listview滚动了,就不在判断是否能滑动删除了
那么作者为什么不直接给item设置滑动事件的监听? 相信大家已经知道了, 就是是listview的时间分发和普通的Viewgroup不一样,如果给item直接设置时间监听,那么会在滑动一般的时候listview会滚动起来影响滑动效果!