泛洪法与SMC算法的综合使用
前言
本文是继承自之前的种子点生长系列文章和网格生成算法系列文章,主要介绍一种综合两类算法的思路的方法,实现了对种子生长区域的较为快速的网格生成,算法中大量使用查找表来实现代码的简化和运行效率的提高。本文介绍的方法采用了泛洪法结合SMC算法来实现对单联通区域的网格生成。这两种方法的结合具有一定的代表性。
单联通区域的网格生成
根据之前的文章介绍可以知道,种子点生长算法通过指定种子点,在三维图像中向四周按一定条件扩散形成一片连通的区域。这个区域是在很多应用当中需要被提取的内容,往往会对其再进行表面网格的提取。而网格生成算法是对三维图像实点和虚点的边界进行网格的抽取。也就是说,在一般的思路下,为这样的单联通区域生成网格,应该是如下的步骤:
- 使用种子点生长算法,首先将区域生长出来。
- 将生长出的区域的所有点设为实点,其它部分的点设为虚点。
- 针对这样一个具有虚实点的三维图像执行SMC算法,得到网格。
实际上,由于种子点生长算法在执行过程中,会发现虚实点的边界。所以通过记录边界的信息,可以让SMC算法只处理边界体元(边界体元即是包含等值面的体元,详细请见MC算法的那一篇),因而省去了对很多空体元的访问的代价。所以本文介绍一种基于这样的思路实现的种子生长区域网格生成算法。
泛洪法和边界处理
根据之前的博文,泛洪法的过程如下面的过程所述:
1 FloodFill(Seed,Process) 2 创建一个容器,将Seed置入其中 3 创建位图标记表,将Seed的位置标记为true 4 Procee(Seed) 5 While(当容器不为空) 6 从容器中取出一个点P 7 获取P的邻域点集 8 对P的邻域点集的每一点T 9 若T未越界并且T的位置未被标记并且T的值符合被纳入条件 10 将T加入容器 11 对T的位置标记为true 12 Procees(T) 13 结束循环 14 结束循环 15 结束函数
在这样的过程中,没有对边界的信息进行记录。但在循环之中确实是访问到了边界,即在发现有未被标记的且不符合纳入条件的点时,就等于是找到了一个实点和虚点的交界。
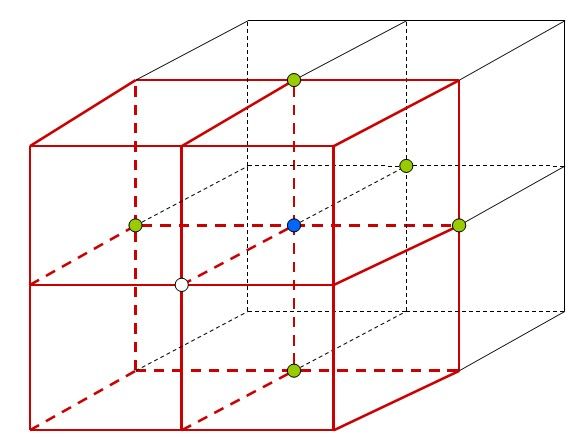
在SMC算法的那部分我们知道,网格生成时的基本单位是体元,其中以同时包含实点和虚点的边界体元最为重要。那么这时候思路就自然而然的形成了:在泛洪法执行过程中,每当遇到边界的时候把与其相关的体元进行标记和存储。这样最后将这些体元集合使用SMC算法抽取三角片就可以生成区域表面的网格。下图示意了发现一个实点和虚点之后,在他们连线上的四个体元均是边界体元,会被记录下来。其中蓝色点表示冲队列中弹出的点,绿色表示其邻域点中的实点,而白色则表示虚点。
下面的伪代码是这个算法的主逻辑,其中从体元中抽取三角形的过程在SMC算法中有详细讲述,这里不再展开。
1 GenerateMesh(Seed) 2 创建一个空的Mesh 3 创建一个容器,将Seed置入其中 4 创建位图标记表,将Seed的位置标记为true 5 While(当容器不为空) 6 从容器中取出一个点P 7 获取P的邻域点集 8 对P的邻域点集的每一点T 9 若T未越界并且T的位置未被标记并且T的值符合被纳入条件 10 将T加入容器 11 对T的位置标记为true 12 否则 13 若T位置未被标记且未越界则说明T为虚点,此时找到对应四个相关体元,存入哈希表。 14 结束循环 15 结束循环 16 对每个标记了的体元C 17 抽取C中的三角形 18 将三角形加入Mesh 19 结束函数
编号与查找表的建立
从上诉伪代码描述的过程以及示意图可以看出,一个体元很可能被重复标记,如下图所示的情况。点P(蓝色表示)的邻域点中有两个虚点T(白色表示),这样一个结构中一共就有6个体元需要被标记(红色框出),这样对于这两个T点来说其实就有两个共同的体元需要进行标记。由此我们容易想到,由于一个点P其6邻域的虚实情况是可以枚举的,一共是2的6次方即64种情况,这样可以将这所有64种情况所要标记的体元做成一个查找表,这样就可以根据查找表来方便的获得需要标记的体元。而这64种情况可以仿照MC算法中体元配置的方式进行存储。为此我们特地对一个点的6邻域进行编号,然后把他们的虚实情况对应着一个字节的各个位,如下图表所示:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 示意图 | 表说明 |
同时我们为那八个体元进行编号。在MC算法介绍里我们使用基准体素来对应一个体元的位置,这样在这里的模型中,八个体元的基准体素的位置用红色标注了出来,这样我们就可以使用一张表来表示基准体素相对P的位置。
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| 示意图 | 表说明 |
算法的实现
通过编号和建立查找表,算法的相关伪代码变成了如下的形式:
1 GenerateMesh(Seed) 2 创建一个空的Mesh 3 创建一个容器,将Seed置入其中 4 创建位图标记表,将Seed的位置标记为true 5 While(当容器不为空) 6 创建一个为0的Config值 7 从容器中取出一个点P 8 获取P的邻域点集 9 对P的邻域点集的每一点T 10 若T未越界 11 若T的位置未被标记 12 若T的值符合被纳入条件 13 将T加入容器 14 对T的位置标记为true 15 将Config中T对应的位填为1 16 否则 17 将Config中T对应的位填为1 18 结束循环 19 使用Config值查找需要标记的体元编号 20 根据体元编号找到体元的坐标,将其标记在哈希表中 21 结束循环 22 对哈希表中每个标记了的体元C 23 抽取C中的三角形 24 将三角形加入Mesh 25 结束函数
采用c#语言实现的算法代码如下。
首先定义一系列查找表:
static class Tables { public const byte ZeroFilled = 1 << 0; public const byte OneFilled = 1 << 1; public const byte TwoFilled = 1 << 2; public const byte ThreeFilled = 1 << 3; public const byte FourFilled = 1 << 4; public const byte FiveFilled = 1 << 5; public static byte[] Adj6IndexToFilledState = new byte[6] { ZeroFilled,OneFilled,TwoFilled,ThreeFilled,FourFilled,FiveFilled, };//邻域索引到其对应的位标记 public static int[][] AdjStateToQuadrantIndices = new int[64][] { new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 5, 6 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 3, 4, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 3, 5, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7 }, new int[] { 2, 4, 6, 7 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 5, 6, 7, 8 }, new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 }, new int[] { }, };//邻域配置到对应的标记体元的索引 public static Int16Triple[] QuadrantIndexToCellIndices = new Int16Triple[9] { new Int16Triple(int.MaxValue, int.MaxValue, int.MaxValue), new Int16Triple(-1, 0, -1), new Int16Triple(0, 0, -1), new Int16Triple(-1, 0, 0), new Int16Triple(0, 0, 0), new Int16Triple(-1, -1, -1), new Int16Triple(0, -1, -1), new Int16Triple(0, -1, 0), new Int16Triple(-1, -1, 0), };//体元索引到其坐标偏移(注意是从1开始的) public static byte VULF = 1 << 0; public static byte VULB = 1 << 1; public static byte VLLB = 1 << 2; public static byte VLLF = 1 << 3; public static byte VURF = 1 << 4; public static byte VURB = 1 << 5; public static byte VLRB = 1 << 6; public static byte VLRF = 1 << 7; //以上为体素为实点的位标记 public static Int16Triple[] PointIndexToPointDelta = new Int16Triple[8] { new Int16Triple(0, 1, 1 ), new Int16Triple(0, 1, 0 ), new Int16Triple(0, 0, 0 ), new Int16Triple(0, 0, 1 ), new Int16Triple(1, 1, 1 ), new Int16Triple(1, 1, 0 ), new Int16Triple(1, 0, 0 ), new Int16Triple(1, 0, 1 ) };//体元内每个体素相对基准体素坐标的偏移 public static byte[] PointIndexToFlag = new byte[8] { VULF, VULB, VLLB, VLLF, VURF, VURB, VLRB, VLRF };//每个体素对应的位标记 #region TableFat public static int[,] TableFat = new int[256, 16]; //三角形表 省略
然后是算法主体:
class Method { public static void InitAdj6(ref Int16Triple[] adjPoints6, ref Int16Triple p) { adjPoints6[0].X = p.X; adjPoints6[0].Y = p.Y + 1; adjPoints6[0].Z = p.Z; adjPoints6[1].X = p.X; adjPoints6[1].Y = p.Y - 1; adjPoints6[1].Z = p.Z; adjPoints6[2].X = p.X + 1; adjPoints6[2].Y = p.Y; adjPoints6[2].Z = p.Z; adjPoints6[3].X = p.X - 1; adjPoints6[3].Y = p.Y; adjPoints6[3].Z = p.Z; adjPoints6[4].X = p.X; adjPoints6[4].Y = p.Y; adjPoints6[4].Z = p.Z + 1; adjPoints6[5].X = p.X; adjPoints6[5].Y = p.Y; adjPoints6[5].Z = p.Z - 1; } public static Mesh ExcuteMethod(BitMap3d bmp, Int16Triple seed) { #region FloodFill int width=bmp.width; int height=bmp.height; int depth=bmp.depth; byte[] data=bmp.data; MeshBuilder_IntegerVertex mb = new MeshBuilder_IntegerVertex(bmp.width + 2, bmp.height + 2, bmp.depth + 2); HashTable_Double2dArray<bool> CellhashMap = new HashTable_Double2dArray<bool>(bmp.width + 2, bmp.height + 2, bmp.depth + 2); BitArray flagsMap = new BitArray(width * height * depth, false); Queue<Int16Triple> queue = new Queue<Int16Triple>(); Int16Triple[] adjPoints6 = new Int16Triple[6]; bool temp=false; int stindex = seed.Z * width * height + seed.Y * width + seed.X; flagsMap[stindex] = true; queue.Enqueue(seed); while (queue.Count != 0) { byte adjState = 0; Int16Triple p = queue.Dequeue(); InitAdj6(ref adjPoints6, ref p); for (int adjIndex = 0; adjIndex < adjPoints6.Length; adjIndex++) { Int16Triple t = adjPoints6[adjIndex]; if (t.X < width && t.X >= 0 && t.Y < height && t.Y >= 0 && t.Z < depth && t.Z >= 0) { int indext = t.Z * width * height + t.Y * width + t.X; if (!flagsMap[indext]) { if (data[indext]==BitMap3d.WHITE) { flagsMap[indext] = true; adjState |= Tables.Adj6IndexToFilledState[adjIndex]; queue.Enqueue(t); } } else { adjState |= Tables.Adj6IndexToFilledState[adjIndex]; } } } if (adjState != 63) { int[] qIndex = Tables.AdjStateToQuadrantIndices[adjState]; for (int j = 0; j < qIndex.Length; j++) { Int16Triple delta = Tables.QuadrantIndexToCellIndices[qIndex[j]]; int cellX = delta.X + p.X ; int cellY = delta.Y + p.Y; int cellZ = delta.Z + p.Z; if (cellX >= 0 && cellY >= 0 && cellZ >= 0) { bool innerIndex = CellhashMap.GetHashValue(cellX, cellY, cellZ, ref temp); if (!innerIndex) { CellhashMap.SetHashValue(cellX, cellY, cellZ, true); } } } } } #endregion #region SMC List<Int16TripleWithTValue<bool>> cubesList = CellhashMap.GetAllKeyValues(); Int16Triple[] tempSet = new Int16Triple[8]; for (int i = 0; i < cubesList.Count; i++) { int indexInWidth = cubesList[i].X; int indexInHeight = cubesList[i].Y; int indexInDepth = cubesList[i].Z; byte value = 0; for (int pi = 0; pi < 8; pi++) { tempSet[pi].X = indexInWidth + Tables.PointIndexToPointDelta[pi].X; tempSet[pi].Y = indexInHeight + Tables.PointIndexToPointDelta[pi].Y; tempSet[pi].Z = indexInDepth + Tables.PointIndexToPointDelta[pi].Z; if (tempSet[pi].X>=0&&tempSet[pi].X<width&&tempSet[pi].Y>=0&&tempSet[pi].Y<height&&tempSet[pi].Z>=0&&tempSet[pi].Z<depth &&flagsMap[tempSet[pi].X + tempSet[pi].Y * width + tempSet[pi].Z * height * width]) { value |= Tables.PointIndexToFlag[pi]; } } if (Tables.TableFat[value, 0] != -1) { int index = 0; while (Tables.TableFat[value, index] != -1) { Int16Triple t0 = tempSet[Tables.TableFat[value, index]]; Int16Triple t1 = tempSet[Tables.TableFat[value, index + 1]]; Int16Triple t2 = tempSet[Tables.TableFat[value, index + 2]]; mb.AddTriangle(t0, t1, t2); index += 3; } } } return mb.GetMesh(); #endregion } }
算法实验
算法采用Lobster、Engine、BackPack数据进行对比实验,使用单独的泛洪法与SMC算法与本文结合的算法进行效率上的比较。可以看出结合后的算法更具时间效率。
| 数据预览 |  |
||
| 数据描述 | Lobster.raw 301×324×56 |
Engine.raw 256×256×128 |
Backpack.raw 512×512×373 |
| 单独使用泛洪法与SMC算法时间 | 1124ms | 2052ms | 20616ms |
| 结合使用的算法时间 | 260ms | 770ms | 4064ms |
本文的代码可从https://github.com/chnhideyoshi/SeededGrow2d下载