SpringMVC 源代码深度解析(扫描和注册的注解Bean)
我们在SpringMVC开发项目中,有的用注解和XML配置Bean,这两种都各有自己的优势,数据源配置比较经常用XML配置,控制层依赖的service比较经常用注解等(在部署时比较不会改变的),我们经常比较常用的注解有@Component是通用标注,@Controller标注web控制器,@Service标注Servicec层的服务,@Respository标注DAO层的数据访问。SpringMVC启动时怎么被自动扫描然后解析并注册到Bean工厂中去(放到DefaultListableBeanFactory中的Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap中 以BeanName为key)?我们今天带着这些问题来了解分析这实现的过程,我们在分析之前先了解一下这些注解。
@Controller标注web控制器,@Service标注Service层的服务,@Respository标注DAO层的数据访问。@Component是通用标注,只是定义为一个类为Bean,SpringMVC会把所有添加@Component注解的类作为使用自动扫描注入配置路径下的备选对象。@Controller、@Service\@Respository只是更加的细化,都是被@Component标注,所以我们比较不推荐使用@Component。源代码如下:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Service {
String value() default "";
}
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Controller {
String value() default "";
}
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Repository {
String value() default "";
}
都是有标示@Component
我们在配置文件中,标示配置需要扫描哪些包下,也可以配置对某个包下不扫描,代码如下:
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.test"> <context:exclude-filter type="regex" expression="cn.test.*.*.controller"/> <context:exclude-filter type="regex" expression="cn.test.*.*.controller2"/> </context:component-scan>
说明:
<context:exclude-filter>指定的不扫描包,<context:exclude-filter>指定的扫描包
SpringMVC先读取配置文件,然后根据context:component-scan中属性base-package去扫描指定包下的class和jar文件,把标示@Controller标注web控制器,@Service标注Servicec层的服务,@Respository标注DAO层的数据访问等注解的都获取,并注册为Bean类放到Bean工厂,我们接下来要分析的这个过程。我们平时项目开发都是这样的注解,实现MVC模式,代码如下:
例如:
//控制层
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value="/test")
public class TestController2 {
@Autowired
private TestService testService;
@RequestMapping(value="/index")
public String getIndex(Model model){
return "";
}
}
//服务层
@Service("testService")
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService{
}
我们今天的入口点就在这,因为解析注解的到注册,也是先读取配置文件并解析,在解析时扫描对应包下的JAVA类,里面有DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader这个类,doRegisterBeanDefinitions这个方法实现解析配置文件的Bean,这边已经读取进来形成Document 形式存储,然后开始解析Bean,是由BeanDefinitionParserDelegate类实现的,BeanDefinitionParserDelegate完成具体Bean的解析(例如:bean标签、import标签等)这个在上一篇SpringMVC 源代码深度解析 IOC容器(Bean 解析、注册)里有解析,今天注解属于扩展的标签,是由NamespaceHandler和BeanDefinitionParser来解析。源代码如下:
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBd) {
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
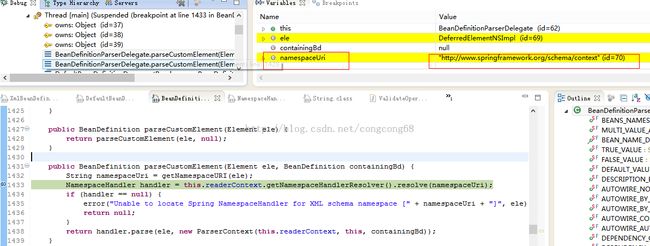
NamespaceHandler这边这边起到了什么作用,根据不同的Namespace获取不同的NamespaceHandler,因为我们在Beans标签配置了命名空间,然后就可以配置对应的标签,解析标签时,比较有自己的所实现的NamespaceHandler来解析,如图所示:

NamespaceHandler中的parse方法是它的子类类NamespaceHandlerSupport实现的,获取通过findParserForElement方法获取BeanDefinitionParser 对象,这个对象在工程初始化时就直接实例化放在缓存中Map<String, BeanDefinitionParser>,然后通过localName获取,源代码如下:
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
return findParserForElement(element, parserContext).parse(element, parserContext);
}
private BeanDefinitionParser findParserForElement(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
String localName = parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(element);
BeanDefinitionParser parser = this.parsers.get(localName);
if (parser == null) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().fatal(
"Cannot locate BeanDefinitionParser for element [" + localName + "]", element);
}
return parser;
}
为什么要获取BeanDefinitionParser ,因为BeanDefinitionParser 类是解析配置文件中的<context:component-scan>,<aop:config>等标签,但是不同的标签是由不同的BeanDefinitionParser来进行解析的,如图所示:

接下来我们开始解析这个标签, <context:component-scan>标签的解析是由ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser类解析的,接下来我们要分析它怎么解析注解的Bean,并把Bean注册到Bean工厂,源代码如下:
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
//获取context:component-scan 配置的属性base-package的值
String[] basePackages = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(element.getAttribute(BASE_PACKAGE_ATTRIBUTE),
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
//创建扫描对应包下的class文件的对象
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = configureScanner(parserContext, element);
//扫描对应包下的class文件并有注解的Bean包装成BeanDefinition
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = scanner.doScan(basePackages);
registerComponents(parserContext.getReaderContext(), beanDefinitions, element);
return null;
}
说明:
(1)获取context:component-scan 配置的属性base-package的值,然后放到数组。
(2)创建扫描对应包下的class和jar文件的对象ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner ,由这个类来实现扫描包下的class和jar文件并把注解的Bean包装成BeanDefinition。
(3)BeanDefinition注册到Bean工厂。
第一:扫描是由ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser的doScan方法来实现的,源代码如下:
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
//新建队列来保存BeanDefinitionHolder
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>();
//循环需要扫描的包
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
//进行扫描注解并包装成BeanDefinition
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
//对BeanDefinition进行注册
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
进行扫描注解并包装成BeanDefinition是ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser由父类ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider的方法findCandidateComponents实现的,源代码如下:
public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinition>();
try {
//base-package中的值替换为classpath*:cn/test/**/*.class
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + "/" + this.resourcePattern;
//获取所以base-package下的资源
Resource[] resources = this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Scanning " + resource);
}
if (resource.isReadable()) {
try {
MetadataReader metadataReader = this.metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(resource);
//对context:exclude-filter进行过滤
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
//包装BeanDefinition
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setResource(resource);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource);
}
candidates.add(sbd);
}
else {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource);
}
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource);
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
return candidates;
}
说明:
(1)先根据context:component-scan 中属性的base-package="cn.test"配置转换为classpath*:cn/test/**/*.class,并扫描对应下的class和jar文件并获取类对应的路径,返回Resources
(2)根据<context:exclude-filter>指定的不扫描包,<context:exclude-filter>指定的扫描包配置进行过滤不包含的包对应下的class和jar。
(3)封装成BeanDefinition放到队列里。
1)怎么根据packageSearchPath获取包对应下的class路径,是通过PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver类,findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));获取配置包下的class路径并封装成Resource,实现也是getClassLoader().getResources(path);实现的。源代码如下:
<span style="font-size:18px;">public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null");
if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX)) {
// a class path resource (multiple resources for same name possible)
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()))) {
// a class path resource pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// all class path resources with the given name
return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
}
else {
// Only look for a pattern after a prefix here
// (to not get fooled by a pattern symbol in a strange prefix).
int prefixEnd = locationPattern.indexOf(":") + 1;
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) {
// a file pattern
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// a single resource with the given name
return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
}
protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException {
String path = location;
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = getClassLoader().getResources(path);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16);
while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement();
result.add(convertClassLoaderURL(url));
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
</span>
说明:getClassLoader().getResources获取classpath*:cn/test/**/*.class下的cn/test包下的class的路径信息。并返回了URL。这里能把对应class路径获取到了,就能获取里面的信息。
2)isCandidateComponent实现的标签是里配置的<context:exclude-filter>指定的不扫描包,<context:exclude-filter>指定的扫描包的过滤,源代码如下:
<span style="font-size:18px;">protected boolean isCandidateComponent(MetadataReader metadataReader) throws IOException {
for (TypeFilter tf : this.excludeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
return false;
}
}
for (TypeFilter tf : this.includeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
AnnotationMetadata metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
if (!metadata.isAnnotated(Profile.class.getName())) {
return true;
}
AnnotationAttributes profile = MetadataUtils.attributesFor(metadata, Profile.class);
return this.environment.acceptsProfiles(profile.getStringArray("value"));
}
}
return false;
}</span>
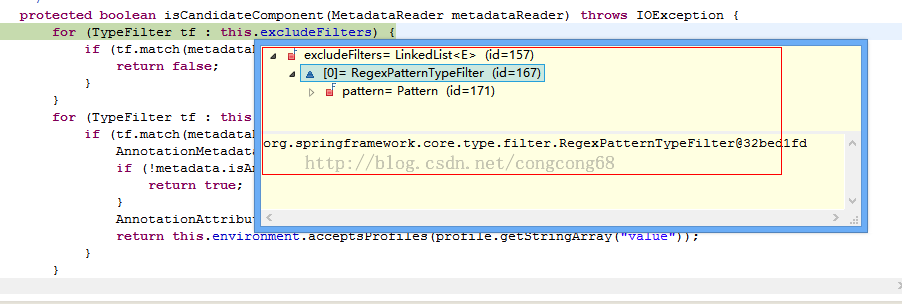
说明: this.excludeFilters有pattern属性,值是就是<context:exclude-filter type="regex" expression="cn.test.*.*.controller"/>的cn.test.*.*.controller值this.pattern.matcher(metadata.getClassName()).matches();通过这个去匹配,如果是就返回false。如图所示:
我们到这边已经把对应的通过在XML配置把注解扫描解析并封装成BeanDefinition。
接下来我们来分析一下注册到Bean工厂,大家还记得ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser的doScan方法,然后到工厂的是由registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);实现的,源代码如下:
protected void registerBeanDefinition(BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, registry);
}
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String aliase : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, aliase);
}
}
}
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
Object oldBeanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (oldBeanDefinition != null) {
if (!this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +
"': There is already [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] bound.");
}
else {
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"': replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
}
else {
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
说明:DefaultListableBeanFactory要实现的保存到Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap中 以BeanName为key,如果有,就不用保存了。DefaultListableBeanFactory我们在上一篇SpringMVC 源代码深度解析 IOC容器(Bean 解析、注册)有介绍过了,DefaultListableBeanFactory继承了BeanFactory。
总结:
(1)因为解析注解的到注册,也是先读取配置文件并解析,在解析时扫描对应包下的JAVA类,里面有DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader这个类,doRegisterBeanDefinitions这个方法实现解析配置文件的Bean,这边已经读取进来形成Document 形式存储。然后注解属于扩展的标签,是由NamespaceHandler和BeanDefinitionParser来解析。
(2)根据context:component-scan中属性base-package去扫描指定包下的class和jar文件,获取对应的路径信息,然后根据配置<context:exclude-filter>指定的扫描包配置进行过滤不包含的包对应下的class和jar路径的Resources。
(3)把标示@Controller标注web控制器,@Service标注Servicec层的服务,@Respository标注DAO层的数据访问等注解路径都获取包装成BeanDefinition,并注册为Bean类放到Bean工厂,也就是DefaultListableBeanFactoryMap<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap中以BeanName为key。