大话设计模式-外观模式
本文转载自点击打开链接
需求
实现股民炒股。
实现
级别1
public class Stock1
{
public void sell()
{
System.out.println("股票1卖出");
}
public void buy()
{
System.out.println("股票1买入");
}
}
public class Stock2
{
public void sell()
{
System.out.println("股票2卖出");
}
public void buy()
{
System.out.println("股票2买入");
}
}
public class Stock3
{
public void sell()
{
System.out.println("股票3卖出");
}
public void buy()
{
System.out.println("股票3买入");
}
}
public class Realty1
{
public void sell()
{
System.out.println("房地产1卖出");
}
public void buy()
{
System.out.println("房地产1买入");
}
}
public class NationalDebt1
{
public void sell()
{
System.out.println("国债1卖出");
}
public void buy()
{
System.out.println("国债1买入");
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Stock1 gu1 = new Stock1();
Stock2 gu2 = new Stock2();
Stock3 gu3 = new Stock3();
NationalDebt1 nd1 = new NationalDebt1();
Realty1 rt1 = new Realty1();
gu1.buy();
gu2.buy();
gu3.buy();
nd1.buy();
rt1.buy();
gu1.sell();
gu2.sell();
gu3.sell();
nd1.sell();
rt1.sell();
}
}
这样的代码,用户需要了解股票、国债、房产情况,需要参与这些项目的具体买和卖。耦合性很高。
级别2
public class Fund
{
Stock1 gu1;
Stock2 gu2;
Stock3 gu3;
NationalDebt1 nd1;
Realty1 rt1;
public Fund()
{
gu1 = new Stock1();
gu2 = new Stock2();
gu3 = new Stock3();
nd1 = new NationalDebt1();
rt1 = new Realty1();
}
public void buyFund()
{
gu1.buy();
gu2.buy();
gu3.buy();
nd1.buy();
rt1.buy();
}
public void sellFund()
{
gu1.sell();
gu2.sell();
gu3.sell();
nd1.sell();
rt1.sell();
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Fund jijin = new Fund();
jijin.buyFund();
jijin.sellFund();
}
} 外观模式,为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,此模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。
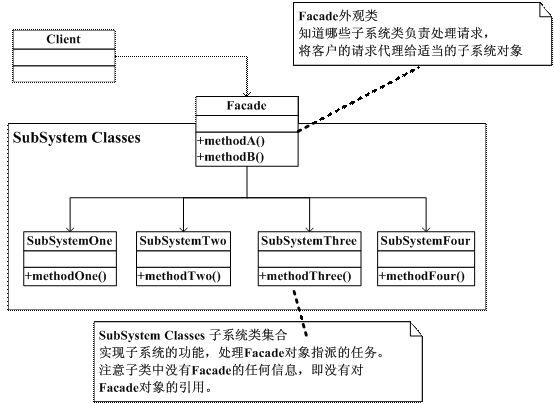
//四个子系统的类
public class SubSystemOne
{
public void methodOne()
{
System.out.println("子系统方法1");
}
}
public class SubSystemTwo
{
public void methodTwo()
{
System.out.println("子系统方法2");
}
}
public class SubSystemThree
{
public void methodThree()
{
System.out.println("子系统方法3");
}
}
public class SubSystemFour
{
public void methodFour()
{
System.out.println("子系统方法4");
}
}
//外观类
public class Facade
{
SubSystemOne one;
SubSystemTwo two;
SubSystemThree three;
SubSystemFour four;
public Facade()
{
one = new SubSystemOne();
two = new SubSystemTwo();
three = new SubSystemThree();
four = new SubSystemFour();
}
public void methodA()
{
System.out.println("方法组A");
one.methodOne();
two.methodTwo();
four.methodFour();
}
public void methodB()
{
System.out.println("方法组B");
two.methodTwo();
three.methodThree();
}
}
//客户端代码
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Facade facade = new Facade();
facade.methodA();
facade.methodB();
}
}