TensorFlow实战— —K-Means聚类
TensorFlow是Google最近开源的人工智能库。
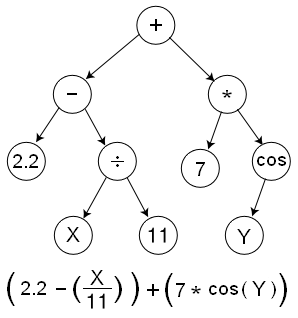
TensorFlow使用了data-flow graphs(DFG),如下图
从图中可以看出,DFG是表示计算表达式的一种树形结构图。每个节点代表一个运算,非叶子节点是运算符,叶子节点是直接的值(确定的值或者不确定的值),箭头方向表示了不同节点间的依赖关系。
TensorFlow目前提供两种API,Python和C++,目前只有Linux和MacOS的安装方法,暂时没有Windows版本。官方还推荐用虚拟环境如Docker,VirtualEnv。官方给出了相应的使用说明,一般的程序猿可以参考阅读官方文档。但假如你是个菜鸟,可以安装下面的步骤慢慢学习~(貌似网站被墙了。。。)
安装
阅读官方的栗子,知道TensorFlow的代码是怎么写的,有个大概印象
阅读关于基本组件的官方解释
阅读这个使用TensorFlow解决一个普通机器学习问题的详细栗子
基本了解之后,就可以去看一下Python API或者C++ API
下面给出一段使用TensorFlow写的K-Means聚类的方法
import tensorflow as tf
from random import choice, shuffle
from numpy import array
def TFKMeansCluster(vectors, noofclusters):
""" K-Means Clustering using TensorFlow. 'vectors' should be a n*k 2-D NumPy array, where n is the number of vectors of dimensionality k. 'noofclusters' should be an integer. """
noofclusters = int(noofclusters)
assert noofclusters < len(vectors)
#Find out the dimensionality
dim = len(vectors[0])
#Will help select random centroids from among the available vectors
vector_indices = list(range(len(vectors)))
shuffle(vector_indices)
#GRAPH OF COMPUTATION
#We initialize a new graph and set it as the default during each run
#of this algorithm. This ensures that as this function is called
#multiple times, the default graph doesn't keep getting crowded with
#unused ops and Variables from previous function calls.
graph = tf.Graph()
with graph.as_default():
#SESSION OF COMPUTATION
sess = tf.Session()
##CONSTRUCTING THE ELEMENTS OF COMPUTATION
##First lets ensure we have a Variable vector for each centroid,
##initialized to one of the vectors from the available data points
centroids = [tf.Variable((vectors[vector_indices[i]]))
for i in range(noofclusters)]
##These nodes will assign the centroid Variables the appropriate
##values
centroid_value = tf.placeholder("float64", [dim])
cent_assigns = []
for centroid in centroids:
cent_assigns.append(tf.assign(centroid, centroid_value))
##Variables for cluster assignments of individual vectors(initialized
##to 0 at first)
assignments = [tf.Variable(0) for i in range(len(vectors))]
##These nodes will assign an assignment Variable the appropriate
##value
assignment_value = tf.placeholder("int32")
cluster_assigns = []
for assignment in assignments:
cluster_assigns.append(tf.assign(assignment,
assignment_value))
##Now lets construct the node that will compute the mean
#The placeholder for the input
mean_input = tf.placeholder("float", [None, dim])
#The Node/op takes the input and computes a mean along the 0th
#dimension, i.e. the list of input vectors
mean_op = tf.reduce_mean(mean_input, 0)
##Node for computing Euclidean distances
#Placeholders for input
v1 = tf.placeholder("float", [dim])
v2 = tf.placeholder("float", [dim])
euclid_dist = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.pow(tf.sub(
v1, v2), 2)))
##This node will figure out which cluster to assign a vector to,
##based on Euclidean distances of the vector from the centroids.
#Placeholder for input
centroid_distances = tf.placeholder("float", [noofclusters])
cluster_assignment = tf.argmin(centroid_distances, 0)
##INITIALIZING STATE VARIABLES
##This will help initialization of all Variables defined with respect
##to the graph. The Variable-initializer should be defined after
##all the Variables have been constructed, so that each of them
##will be included in the initialization.
init_op = tf.initialize_all_variables()
#Initialize all variables
sess.run(init_op)
##CLUSTERING ITERATIONS
#Now perform the Expectation-Maximization steps of K-Means clustering
#iterations. To keep things simple, we will only do a set number of
#iterations, instead of using a Stopping Criterion.
noofiterations = 100
for iteration_n in range(noofiterations):
##EXPECTATION STEP
##Based on the centroid locations till last iteration, compute
##the _expected_ centroid assignments.
#Iterate over each vector
for vector_n in range(len(vectors)):
vect = vectors[vector_n]
#Compute Euclidean distance between this vector and each
#centroid. Remember that this list cannot be named
#'centroid_distances', since that is the input to the
#cluster assignment node.
distances = [sess.run(euclid_dist, feed_dict={
v1: vect, v2: sess.run(centroid)})
for centroid in centroids]
#Now use the cluster assignment node, with the distances
#as the input
assignment = sess.run(cluster_assignment, feed_dict = {
centroid_distances: distances})
#Now assign the value to the appropriate state variable
sess.run(cluster_assigns[vector_n], feed_dict={
assignment_value: assignment})
##MAXIMIZATION STEP
#Based on the expected state computed from the Expectation Step,
#compute the locations of the centroids so as to maximize the
#overall objective of minimizing within-cluster Sum-of-Squares
for cluster_n in range(noofclusters):
#Collect all the vectors assigned to this cluster
assigned_vects = [vectors[i] for i in range(len(vectors))
if sess.run(assignments[i]) == cluster_n]
#Compute new centroid location
new_location = sess.run(mean_op, feed_dict={
mean_input: array(assigned_vects)})
#Assign value to appropriate variable
sess.run(cent_assigns[cluster_n], feed_dict={
centroid_value: new_location})
#Return centroids and assignments
centroids = sess.run(centroids)
assignments = sess.run(assignments)
return centroids, assignments