Studying note of GCC-3.4.6 source (36)
4.1.3.1.2.1.4.4.3. The expansion body
In macro expansion body, hash ‘#’ only can immediately precede the macro parameter to stringify it. Otherwise it only can appear freely in assembler language as comment. CLK_ASM at line 1431 will be set with switch –lang-asm which indicates the compiler to processing the assemble.
create_iso_definition (continue)
1408 if (macro->fun_like)
1409 token = lex_expansion_token (pfile, macro);
1410 else
1411 {
1412 token = alloc_expansion_token (pfile, macro);
1413 *token = *ctoken;
1414 }
1415
1416 for (;;)
1417 {
1418 /* Check the stringifying # constraint 6.10.3.2.1 of
1419 function-like macros when lexing the subsequent token. */
1420 if (macro->count > 1 && token[-1].type == CPP_HASH && macro->fun_like)
1421 {
1422 if (token->type == CPP_MACRO_ARG)
1423 {
1424 token->flags &= ~PREV_WHITE;
1425 token->flags |= STRINGIFY_ARG;
1426 token->flags |= token[-1].flags & PREV_WHITE;
1427 token[-1] = token[0];
1428 macro->count--;
1429 }
1430 /* Let assembler get away with murder. */
1431 else if (CPP_OPTION (pfile, lang) != CLK_ASM)
1432 {
1433 cpp_error (pfile, CPP_DL_ERROR,
1434 "'#' is not followed by a macro parameter");
1435 return false;
1436 }
1437 }
1438
1439 if (token->type == CPP_EOF)
1440 break;
1441
1442 /* Paste operator constraint 6.10.3.3.1. */
1443 if (token->type == CPP_PASTE)
1444 {
1445 /* Token-paste ##, can appear in both object-like and
1446 function-like macros, but not at the ends. */
1447 if (--macro->count > 0)
1448 token = lex_expansion_token (pfile, macro);
1449
1450 if (macro->count == 0 || token->type == CPP_EOF)
1451 {
1452 cpp_error (pfile, CPP_DL_ERROR,
1453 "'##' cannot appear at either end of a macro expansion");
1454 return false;
1455 }
1456
1457 token[-1].flags |= PASTE_LEFT;
1458 }
1459
1460 token = lex_expansion_token (pfile, macro);
1461 }
1462
1463 macro->exp.tokens = (cpp_token *) BUFF_FRONT (pfile->a_buff);
1464
1465 /* Don't count the CPP_EOF. */
1466 macro->count--;
1467
1468 /* Clear whitespace on first token for warn_of_redefinition(). */
1469 if (macro->count)
1470 macro->exp.tokens[0].flags &= ~PREV_WHITE;
1471
1472 /* Commit the memory. */
1473 BUFF_FRONT (pfile->a_buff) = (uchar *) ¯o->exp.tokens[macro->count];
1474
1475 return true;
1476 }
Pay attention to line 1463 and 1473, macro->exp.tokens points to the the beginning of the buffer for the tokens, and macro->exp.tokens[macro->count] points to the end.
Before back to _cpp_create_definition, we’d better first see what buffers now contains with above example (this buffer is referred by pfile->base_run).
Figure 11 buffers after parse_params
Note that for directive of #define, tokens between pfile->cur_run and saved_cur_token will be: #, define (type of CPP_NAME). And for directive of #include, tokens will be: #, include, filename (type of CPP_NAME) for quoted filename, or: #, include, <, filename, > (type of CPP_GREATER) for bracketed filename.
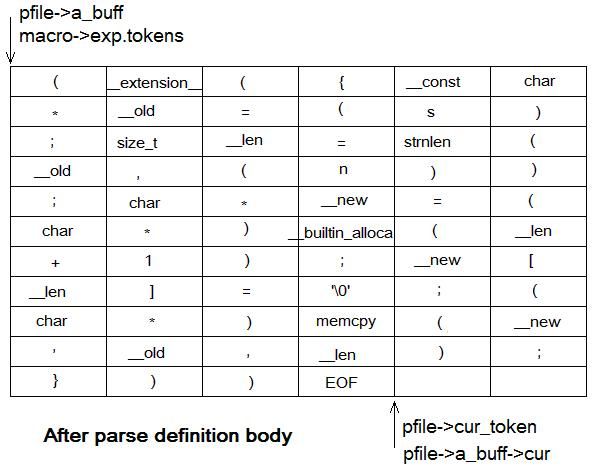
Figure 8 buffers after create_iso_definition
During parsing the expansion body, pfile offers buffer for tokens from a_buff, and these tokens are also referred by macro->exp.tokens.
Figure 9 buffers after restore lexer position
Then after restoring lexer position, see that pfile->cur_token goes back to pfile->base_run again, and tokens after and including strndupa will be abandoned. And the token before current token is marked as end of line. However, though tokens of macro name and parameters are thrown away, its name has been saved by corresponding hashnode in ident_hash, and its expanded body is saved in buffer of a_buff in cpp_reader with parameters marked.
4.1.3.1.2.1.4.4.3. Finish
In view from syntax, as long as passing the macro expansion body, macro arguments are out of its effective scope, and variables covered are visible again. Thus it needs restore these objects cached by _cpp_save_parameter before.
_cpp_create_definition (continue)
1518 /* Clear the fast argument lookup indices. */
1519 for (i = macro->paramc; i-- > 0; )
1520 {
1521 struct cpp_hashnode *node = macro->params[i];
1522 node->flags &= ~ NODE_MACRO_ARG;
1523 node->value = ((union _cpp_hashnode_value *) pfile->macro_buffer)[i];
1524 }
1525
1526 if (!ok)
1527 return ok;
1528
1529 if (node->type == NT_MACRO)
1530 {
1531 if (CPP_OPTION (pfile, warn_unused_macros))
1532 _cpp_warn_if_unused_macro (pfile, node, NULL);
1533
1534 if (warn_of_redefinition (pfile, node, macro))
1535 {
1536 cpp_error_with_line (pfile, CPP_DL_PEDWARN, pfile->directive_line, 0,
1537 "/"%s/" redefined", NODE_NAME (node));
1538
1539 if (node->type == NT_MACRO && !(node->flags & NODE_BUILTIN))
1540 cpp_error_with_line (pfile, CPP_DL_PEDWARN,
1541 node->value.macro->line, 0,
1542 "this is the location of the previous definition");
1543 }
1544 }
1545
1546 if (node->type != NT_VOID)
1547 _cpp_free_definition (node);
1548
1549 /* Enter definition in hash table. */
1550 node->type = NT_MACRO;
1551 node->value.macro = macro;
1552 if (! ustrncmp (NODE_NAME (node), DSC ("__STDC_")))
1553 node->flags |= NODE_WARN;
1554
1555 return ok;
1556 }
Note that node at line 1529 is a parameter of the function, and in current scenario it is other syntax ingredence of the same name. In this GCC preprocessor implementation, except in the definition, the macro name appears in other place in the source will be replaced with the macro expansion body immediately. Thus, if there already exists macro of the name (condition at lien 1529), gives out warning appropriately.
74 int
75 _cpp_warn_if_unused_macro (cpp_reader *pfile, cpp_hashnode *node, in cppmacro.c
76 void *v ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED)
77 {
78 if (node->type == NT_MACRO && !(node->flags & NODE_BUILTIN))
79 {
80 cpp_macro *macro = node->value.macro;
81
82 if (!macro->used
83 && MAIN_FILE_P (linemap_lookup (&pfile->line_maps, macro->line)))
84 cpp_error_with_line (pfile, CPP_DL_WARNING, macro->line, 0,
85 "macro /"%s/" is not used", NODE_NAME (node));
86 }
87
88 return 1;
89 }
According to [3] the C++ standard, if old and new definitions are the same, it is not an error.
1185 static bool
1186 warn_of_redefinition (cpp_reader *pfile, const cpp_hashnode *node, in cppmacro.c
1187 const cpp_macro *macro2)
1188 {
1189 const cpp_macro *macro1;
1190 unsigned int i;
1191
1192 /* Some redefinitions need to be warned about regardless. */
1193 if (node->flags & NODE_WARN)
1194 return true;
1195
1196 /* Redefinition of a macro is allowed if and only if the old and new
1197 definitions are the same. (6.10.3 paragraph 2). */
1198 macro1 = node->value.macro;
1199
1200 /* Don't check count here as it can be different in valid
1201 traditional redefinitions with just whitespace differences. */
1202 if (macro1->paramc != macro2->paramc
1203 || macro1->fun_like != macro2->fun_like
1204 || macro1->variadic != macro2->variadic)
1205 return true;
1206
1207 /* Check parameter spellings. */
1208 for (i = 0; i < macro1->paramc; i++)
1209 if (macro1->params[i] != macro2->params[i])
1210 return true;
1211
1212 /* Check the replacement text or tokens. */
1213 if (CPP_OPTION (pfile, traditional))
1214 return _cpp_expansions_different_trad (macro1, macro2);
1215
1216 if (macro1->count != macro2->count)
1217 return true;
1218
1219 for (i = 0; i < macro1->count; i++)
1220 if (!_cpp_equiv_tokens (¯o1->exp.tokens[i], ¯o2->exp.tokens[i]))
1221 return true;
1222
1223 return false;
1224 }
If the macro parameters’ name are same, _cpp_equiv_tokens comes to check tokens in the expansion body.
1274 int
1275 _cpp_equiv_tokens (const cpp_token *a, const cpp_token *b) in cpplex.c
1276 {
1277 if (a->type == b->type && a->flags == b->flags)
1278 switch (TOKEN_SPELL (a))
1279 {
1280 default: /* Keep compiler happy. */
1281 case SPELL_OPERATOR:
1282 return 1;
1283 case SPELL_NONE:
1284 return (a->type != CPP_MACRO_ARG || a->val.arg_no == b->val.arg_no);
1285 case SPELL_IDENT:
1286 return a->val.node == b->val.node;
1287 case SPELL_LITERAL:
1288 return (a->val.str.len == b->val.str.len
1289 && !memcmp (a->val.str.text, b->val.str.text,
1290 a->val.str.len));
1291 }
1292
1293 return 0;
1294 }
To better understand above code, considers following examples given in [3].
Following sequence is valid.
#define OBJ_LIKE (1-1)
#define OBJ_LIKE /* white space */ (1-1) /* other */
#define FTN_LIKE(a) ( a )
#define FTN_LIKE(a) ( /* note the white space */ /
a /* other stuff on this line
*/ )
But the following redefinitions are invalid (tegother with above definitions):
#define OBJ_LIKE (0) /* different token sequence */
#define OBJ_LIKE (1 – 1) /* different white space */
#define FTN_LIKE(b) ( a ) /* different parameter usage */
#define FTN_LIKE(b) ( b ) /* different parameter spelling */
4.1.3.1.2.1.1. Finish read in
For PCH file, cpp_buffer object is allocated for every macro definition within it. With finishing the macro parsing, it can free this object now.
1949 void
1950 _cpp_pop_buffer (cpp_reader *pfile) in cpplib.c
1951 {
1952 cpp_buffer *buffer = pfile->buffer;
1953 struct _cpp_file *inc = buffer->file;
1954 struct if_stack *ifs;
1955
1956 /* Walk back up the conditional stack till we reach its level at
1957 entry to this file, issuing error messages. */
1958 for (ifs = buffer->if_stack; ifs; ifs = ifs->next)
1959 cpp_error_with_line (pfile, CPP_DL_ERROR, ifs->line, 0,
1960 "unterminated #%s", dtable[ifs->type].name);
1961
1962 /* In case of a missing #endif. */
1963 pfile->state.skipping = 0;
1964
1965 /* _cpp_do_file_change expects pfile->buffer to be the new one. */
1966 pfile->buffer = buffer->prev;
1967
1968 free (buffer->notes);
1969
1970 /* Free the buffer object now; we may want to push a new buffer
1971 in _cpp_push_next_include_file. */
1972 obstack_free (&pfile->buffer_ob, buffer);
1973
1974 if (inc)
1975 {
1976 _cpp_pop_file_buffer (pfile, inc);
1977
1978 _cpp_do_file_change (pfile, LC_LEAVE, 0, 0, 0);
1979 }
1980 }
if_stack is a stack of conditionals currently in progress including both successful and failing conditionals.
38 struct if_stack in cpplib.c
39 {
40 struct if_stack *next;
41 unsigned int line; /* Line where condition started. */
42 const cpp_hashnode *mi_cmacro;/* macro name for #ifndef around entire file */
43 bool skip_elses; /* Can future #else / #elif be skipped? */
44 bool was_skipping; /* If were skipping on entry. */
45 int type; /* Most recent conditional for diagnostics. */
46 };
When reaching end of buffer (for common include file the buffer will hold the whole file content. While for PCH file, the buffer only holds the definition of the single macro but for the case not directive will be seen, so no if_stack will be created), if there is still existing if_stack, it means certain conditonal directive is not enclosed; then gives out error at line 1960 above.
1059 void
1060 _cpp_pop_file_buffer (cpp_reader *pfile, _cpp_file *file) in cppfiles.c
1061 {
1062 /* Record the inclusion-preventing macro, which could be NULL
1063 meaning no controlling macro. */
1064 if (pfile->mi_valid && file->cmacro == NULL)
1065 file->cmacro = pfile->mi_cmacro;
1066
1067 /* Invalidate control macros in the #including file. */
1068 pfile->mi_valid = false;
1069
1070 if (file->buffer)
1071 {
1072 free ((void *) file->buffer);
1073 file->buffer = NULL;
1074 file->buffer_valid = false;
1075 }
1076 }
For PCH file reading, _cpp_do_file_change is trivial.
