GCC-3.4.6源代码学习笔记(37)
4.1.3.1.2.2. 读入普通文件
回到should_stack_file,对于普通文件,整个文件内容将被放入cpp_reader的buffer内。
should_stack_file (continue)
584 if (!read_file (pfile, file))
585 return false;
586
587 /* Now we've read the file's contents, we can stack it if there
588 are no once-only files. */
589 if (!pfile->seen_once_only)
590 return true;
对于普通文件,其内容的读入直接而简单。
523 static bool
524 read_file (cpp_reader *pfile, _cpp_file *file) in cppfiles.c
525 {
526 /* If we already have its contents in memory, succeed immediately. */
527 if (file->buffer_valid)
528 return true;
529
530 /* If an earlier read failed for some reason don't try again. */
531 if (file->dont_read || file->err_no)
532 return false;
533
534 if (file->fd == -1 && !open_file (file))
535 {
536 open_file_failed (pfile, file, 0);
537 return false;
538 }
539
540 file->dont_read = !read_file_guts (pfile, file);
541 close (file->fd);
542 file->fd = -1;
543
544 return !file->dont_read;
545 }
上面cpp_reader的dont_read域,如果非0,表示文件读入已发生错误。对这样的文件不要再尝试做任何读入。
450 static bool
451 read_file_guts (cpp_reader *pfile, _cpp_file *file) in cppfiles.c
452 {
453 ssize_t size, total, count;
454 uchar *buf;
455 bool regular;
456
457 if (S_ISBLK (file->st.st_mode))
458 {
459 cpp_error (pfile, CPP_DL_ERROR, "%s is a block device", file->path);
460 return false;
461 }
462
463 regular = S_ISREG (file->st.st_mode);
464 if (regular)
465 {
466 /* off_t might have a wider range than ssize_t - in other words,
467 the max size of a file might be bigger than the address
468 space. We can't handle a file that large. (Anyone with
469 a single source file bigger than 2GB needs to rethink
470 their coding style.) Some systems (e.g. AIX 4.1) define
471 SSIZE_MAX to be much smaller than the actual range of the
472 type. Use INTTYPE_MAXIMUM unconditionally to ensure this
473 does not bite us. */
474 if (file->st.st_size > INTTYPE_MAXIMUM (ssize_t))
475 {
476 cpp_error (pfile, CPP_DL_ERROR, "%s is too large", file->path);
477 return false;
478 }
479
480 size = file->st.st_size;
481 }
482 else
483 /* 8 kilobytes is a sensible starting size. It ought to be bigger
484 than the kernel pipe buffer, and it's definitely bigger than
485 the majority of C source files. */
486 size = 8 * 1024;
487
488 buf = xmalloc (size + 1);
489 total = 0;
490 while ((count = read (file->fd, buf + total, size - total)) > 0)
491 {
492 total += count;
493
494 if (total == size)
495 {
496 if (regular)
497 break;
498 size *= 2;
499 buf = xrealloc (buf, size + 1);
500 }
501 }
502
503 if (count < 0)
504 {
505 cpp_errno (pfile, CPP_DL_ERROR, file->path);
506 return false;
507 }
508
509 if (regular && total != size && STAT_SIZE_RELIABLE (file->st))
510 cpp_error (pfile, CPP_DL_WARNING,
511 "%s is shorter than expected", file->path);
512
513 file->buffer = _cpp_convert_input (pfile, CPP_OPTION (pfile, input_charset),
514 buf, size, total, &file->st.st_size);
515 file->buffer_valid = true;
516
517 return true;
518 }
上面的_cpp_convert_input通过系统调用iconv,转换使用UTF-8或UTF-EBCDIC字符集以外的文件的内容。其中细节,请参考源文件cppcharset.c,strcasecmp.c。
如果文件不是通过#pragma once或者#import来包含的,那么读入其内容后,在should_stack_file的590行退出。否则,需要确保其内容只存在一份拷贝。
should_stack_file (continue)
592 /* We may have read the file under a different name. Look
593 for likely candidates and compare file contents to be sure. */
594 for (f = pfile->all_files; f; f = f->next_file)
595 {
596 if (f == file)
597 continue;
598
599 if ((import || f->once_only)
600 && f->err_no == 0
601 && f->st.st_mtime == file->st.st_mtime
602 && f->st.st_size == file->st.st_size)
603 {
604 _cpp_file *ref_file;
605 bool same_file_p = false;
606
607 if (f->buffer && !f->buffer_valid)
608 {
609 /* We already have a buffer but it is not valid, because
610 the file is still stacked. Make a new one. */
611 ref_file = make_cpp_file (pfile, f->dir, f->name);
612 ref_file->path = f->path;
613 }
614 else
615 /* The file is not stacked anymore. We can reuse it. */
616 ref_file = f;
617
618 same_file_p = read_file (pfile, ref_file)
619 /* Size might have changed in read_file(). */
620 && ref_file->st.st_size == file->st.st_size
621 && !memcmp (ref_file->buffer,
622 file->buffer,
623 file->st.st_size);
624
625 if (f->buffer && !f->buffer_valid)
626 {
627 ref_file->path = 0;
628 destroy_cpp_file (ref_file);
629 }
630
631 if (same_file_p)
632 break;
633 }
634 }
635
636 return f == NULL;
637 }
上面594行,cpp_reader的all_files域保存了所有已读入的属于当前编译单元的文件,而在622行的file即是刚读入的文件。在636行,如果f为NULL,表明file未出现在cpp_reader的all_files中,需要被堆叠(stacked)。
4.1.3.1.2.3. 堆叠文件(PCH文件除外)
如果should_stack_file返回true,该文件需要被堆叠(注意PCH文件促使该函数返回false,它不会被堆叠)。在下面的672和673行,mi_valid及mi_cmacro用于多次包含优化(multiple include optimization),这个技术的细节由【5】给出如下。
| 头文件通常有如下形式 #ifndef FOO #define FOO ... #endif 来防止编译器多次处理这些语句。预处理器注意到这样的头文件,因此如果头文件出现在一个#include指示序列中,而且FOO被定义,那么这个头文件被忽略不作预处理,甚至于不尝试第二次打开文件。这被称为多次包含优化(multiple include optimization)。 在什么环境下这个优化是有效的?如果文件被第二次包含,它可以被优化掉,仅如果这个被优化掉的包含不会返回任何符号,也不会处理任何相关的指示。因此,当前的实现有如下的要求及宽限: 在`#if'-`#endif'控制对外,不能有符号,但允许空格和注释。 在控制指示对外不能有任何指示,但允许“空指示”(只包含单个#和空格的行)。 引导的(opening)指示必须是以下形式 #ifndef FOO 或 #if !defined FOO [等同于#if !defined(FOO)] 在上面的第二个形式,构成#if表达式的符号必须直接来自源文件——不能掺合宏展开。这是因为宏定义可以改变,而跟踪是否有相关的改变,其实现代价超出了所能得的好处。 在外层的条件块,可以没有#else或#elif指示,因为它们可能包含一些随后的遍(subsequent pass)感兴趣的东西。 首先,当把一个新文件压入缓存栈时,_stack_include_file设置控制宏mi_cmacro为NULL,并设置mi_valid为true。这表示预处理器还没碰到任何会使多次包含优化失效的东西。如接下来的章节所描述的,这2个具有这些值的变量有效地表明了文件的开头(top-of-file)。 当准备返回一个不是指示的一部分的符号,_cpp_lex_token将mi_valid设为false。这就强制了限制:控制条件块外的符号使得优化无效。 函数do_if,在正常时,及函数do_ifndef把控制宏传递给函数push_conditional。Cpplib维护着一个嵌套的条件块的栈,在处理完每个打开的条件后, push_conditional往栈中压入一个if_stack结构。在这个结构中,记录了这个块的控制宏,只要有这样的宏及我们在文件的开头(如上所述)。如果遇到了一个#elif或#else的指示,那么该块的控制宏就被清为NULL。否则直到块结尾的#endif, do_endif才设置mi_valid为true,并保存这个控制宏进mi_cmacro。 当处理已打开的条件(opening conditional)及空指示以外的指示时,_cpp_handle_directive清除mi_valid。这样,连同要求文件头(top-of-file)记录控制宏,并且没有对应的#else或#elif存在,从而被do_endif拷贝入mi_cmacro,我们强制优化的打开必须是主控制块外没有指示。 注意到当处于条件块内,mi_valid也可能被重置为false,但这不是问题,因为正常情况下结尾的#endif会将其恢复为true。 最后,因为遇到EOF(行尾)_cpp_lex_direct会将文件从缓存栈弹出而不返回符号,如果#endif指示后面没跟有符号,则mi_valid是true,而_cpp_pop_file_buffer记着这个文件的控制宏。随后的_stack_include_file调用会导致没有缓存压入,如果控制宏定义了,从而实现优化。 简而言之,处理语句 #if !defined FOO 时,_cpp_parse_expr和parse_defined 按步骤查看,在一个#if表达式中,是否依次为!, defined-expression和end-of-directive。如果如此,它们把这个宏通过变量mi_ind_cmacro返回给do_if,否则将mi_ind_cmacro设为NULL。而enter_macro_context把mi_valid设置为false,因此如果在解析这个表达式时展开一个宏,那么在push_conditional的文件头测试(top-of-file test)就会失败,从而关闭优化。 |
_cpp_stack_file (continue)
652 sysp = MAX ((pfile->map ? pfile->map->sysp : 0),
653 (file->dir ? file->dir->sysp : 0));
654
655 /* Add the file to the dependencies on its first inclusion. */
656 if (CPP_OPTION (pfile, deps.style) > !!sysp && !file->stack_count)
657 {
658 if (!file->main_file || !CPP_OPTION (pfile, deps.ignore_main_file))
659 deps_add_dep (pfile->deps, file->path);
660 }
661
662 /* Clear buffer_valid since _cpp_clean_line messes it up. */
663 file->buffer_valid = false;
664 file->stack_count++;
665
666 /* Stack the buffer. */
667 buffer = cpp_push_buffer (pfile, file->buffer, file->st.st_size,
668 CPP_OPTION (pfile, preprocessed));
669 buffer->file = file;
670
671 /* Initialize controlling macro state. */
672 pfile->mi_valid = true;
673 pfile->mi_cmacro = 0;
674
675 /* Generate the call back. */
676 _cpp_do_file_change (pfile, LC_ENTER, file->path, 1, sysp);
677
678 return true;
679 }
4.1.3.1.2.3.1. 更换文件
当把文件(非PCH文件)读入缓存后,词法分析器(lexer,它还提供预处理操作,如宏展开等),随后是解析器(parser)对此进行预处理后结果进行语法分析。不过在切换处理缓存之前,仍需要一些处理。
906 void
907 _cpp_do_file_change (cpp_reader *pfile, enum lc_reason reason, in cpplib.c
908 const char *to_file, unsigned int file_line,
909 unsigned int sysp)
910 {
911 pfile->map = linemap_add (&pfile->line_maps, reason, sysp,
912 pfile->line, to_file, file_line);
913
914 if (pfile->cb.file_change)
915 pfile->cb.file_change (pfile, pfile->map);
916 }
注意上面的pfile中的line记录了文件当前位置的行号,而linemap_add的参数set则引用pfile中的line_maps。并且其参数to_file和to_line提及被包含的文件(如果文件由#include引入)或者源文件本身。在这里,因为我们第一次打开感兴趣的文件,to_line是1。在line_maps中的used表示在这个文件上下文中(the file context)有多少文件已经被行映射,并且域depth表示了其在包含链中的位置。
76 const struct line_map *
77 linemap_add (struct line_maps *set, enum lc_reason reason, in line-map.c
78 unsigned int sysp, source_location from_line,
79 const char *to_file, unsigned int to_line)
80 {
81 struct line_map *map;
82
83 if (set->used && from_line < set->maps[set->used - 1].from_line)
84 abort ();
85
86 if (set->used == set->allocated)
87 {
88 set->allocated = 2 * set->allocated + 256;
89 set->maps = xrealloc (set->maps, set->allocated * sizeof (struct line_map));
90 }
91
92 map = &set->maps[set->used++];
93
94 if (to_file && *to_file == '/0')
95 to_file = "<stdin>";
96
97 /* If we don't keep our line maps consistent, we can easily
98 segfault. Don't rely on the client to do it for us. */
99 if (set->depth == 0)
100 reason = LC_ENTER;
101 else if (reason == LC_LEAVE)
102 {
103 struct line_map *from;
104 bool error;
105
106 if (MAIN_FILE_P (map - 1))
107 {
108 if (to_file == NULL)
109 {
110 set->depth--;
111 set->used--;
112 return NULL;
113 }
114 error = true;
115 reason = LC_RENAME;
116 from = map - 1;
117 }
118 else
119 {
120 from = INCLUDED_FROM (set, map - 1);
121 error = to_file && strcmp (from->to_file, to_file);
122 }
123
124 /* Depending upon whether we are handling preprocessed input or
125 not, this can be a user error or an ICE. */
126 if (error)
127 fprintf (stderr, "line-map.c: file /"%s/" left but not entered/n",
128 to_file);
129
130 /* A TO_FILE of NULL is special - we use the natural values. */
131 if (error || to_file == NULL)
132 {
133 to_file = from->to_file;
134 to_line = LAST_SOURCE_LINE (from) + 1;
135 sysp = from->sysp;
136 }
137 }
138
139 map->reason = reason;
140 map->sysp = sysp;
141 map->from_line = from_line;
142 map->to_file = to_file;
143 map->to_line = to_line;
144
145 if (reason == LC_ENTER)
146 {
147 map->included_from = set->depth == 0 ? -1 : (int) (set->used - 2);
148 set->depth++;
149 if (set->trace_includes)
150 trace_include (set, map);
151 }
152 else if (reason == LC_RENAME)
153 map->included_from = map[-1].included_from;
154 else if (reason == LC_LEAVE)
155 {
156 set->depth--;
157 map->included_from = INCLUDED_FROM (set, map - 1)->included_from;
158 }
159
160 return map;
161 }
看到上面的106行,(map-1)被用作MAIN_FILE_P的参数。
120 #define MAIN_FILE_P(MAP) ((MAP)->included_from < 0) in line-map.h
而在120行INCLUDED_FROM被定义为:
117 #define INCLUDED_FROM(SET, MAP) (&(SET)->maps[(MAP)->included_from])
为了展示line_maps和linemap_add任何工作,假设我们有如下文件栈:
当前文件 ß 包含文件1 ß 包含文件2 ß 包含文件3
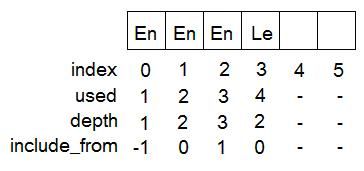
当我们处理文件3时,我们有line_maps如下图。
图14:linemap_add,步骤1
然后如果我们离开文件3回到文件2,我们则有如下line_maps。
图15:linemap_add,步骤2
再回到文件1。
图16:linemap_add,步骤3
若进一步离开当前文件。注意到对于这个情形,NULL将被返回,在索引5的元素将被下一个“主文件”所重用,而之前的5个元素跟踪了所有相关文件到预处理输出的映射关系。
图17:linemap_add,步骤4
在_cpp_do_file_change的914行,如果前端在文件切换之际,也有话要说,则需要设置cpp_reader的cb结构中file_change钩子。C++前端用如下函数绑定这个钩子。
1500 static void
1501 cb_file_change (cpp_reader *pfile ATTRIBUTE_UNUSED, in c-opts.c
1502 const struct line_map *new_map)c
1503 {
1504 if (flag_preprocess_only)
1505 pp_file_change (new_map);
1506 else
1507 fe_file_change (new_map);
1508
1509 if (new_map == 0 || (new_map->reason == LC_LEAVE && MAIN_FILE_P (new_map)))
1510 push_command_line_include ();
1511 }
下面的宏NO_IMPLICIT_EXTERN_C被定义,如果系统头文件同时支持C++和C。这个宏禁止在通常在C++中使用系统头文件的方法,这些方法假定文件的内容包括在extern "C" {...}内。在Linux中这个宏被定义。下面的input_filename和input_line分别访问input_location的line和file域。
203 void
204 fe_file_change (const struct line_map *new_map) in c-lex.c
205 {
206 if (new_map == NULL)
207 {
208 map = NULL;
209 return;
210 }
211
212 if (new_map->reason == LC_ENTER)
213 {
214 /* Don't stack the main buffer on the input stack;
215 we already did in compile_file. */
216 if (map != NULL)
217 {
218 int included_at = SOURCE_LINE (new_map - 1, new_map->from_line - 1);
219
220 input_line = included_at;
221 push_srcloc (new_map->to_file, 1);
222 (*debug_hooks->start_source_file) (included_at, new_map->to_file);
223 #ifndef NO_IMPLICIT_EXTERN_C
…
231 #endif
232 }
233 }
234 else if (new_map->reason == LC_LEAVE)
235 {
236 #ifndef NO_IMPLICIT_EXTERN_C
…
243 #endif
244 pop_srcloc ();
245
246 (*debug_hooks->end_source_file) (new_map->to_line);
247 }
248
249 update_header_times (new_map->to_file);
250 in_system_header = new_map->sysp != 0;
251 input_filename = new_map->to_file;
252 input_line = new_map->to_line;
253 map = new_map;
254
255 /* Hook for C++. */
256 extract_interface_info ();
257 }
对于包含头文件,push_srcloc,pop_srcloc,start_source_file及end_source_file用于调试诊断的目的。