Studying note of GCC-3.4.6 source (117)
5.12.4.1.1.2.1.3. Lookup in current scope
Arriving here, no scope is specified, the name should be looked up within current binding scope. Here current scope can be class scope, namespace, function scope, local scope (FOR loop, WHILE loop etc.).
cp_parser_lookup_name (continue)
13832 else
13833 {
13834 decl = lookup_name_real (name, is_type, /*nonclass=*/ 0,
13835 is_namespace, flags);
13836 parser->qualifying_scope = NULL_TREE;
13837 parser->object_scope = NULL_TREE;
13838 }
Notice that argument nonclass is passed with value 0, which means we will look for the parameter name in class scope; while namespaces_only is passed from cp_parser_class_name with value of is_namespace .
3912 tree
3913 lookup_name_real (tree name, int prefer_type, int nonclass, in name-lookup.c
3914 int namespaces_only, int flags)
3915 {
3916 cxx_binding *iter;
3917 tree val = NULL_TREE;
3918
3919 timevar_push (TV_NAME_LOOKUP);
3920 /* Conversion operators are handled specially because ordinary
3921 unqualified name lookup will not find template conversion
3922 operators. */
3923 if (IDENTIFIER_TYPENAME_P (name))
3924 {
3925 struct cp_binding_level *level;
3926
3927 for (level = current_binding_level ;
3928 level && level->kind != sk_namespace;
3929 level = level->level_chain)
3930 {
3931 tree class_type;
3932 tree operators;
3933
3934 /* A conversion operator can only be declared in a class
3935 scope. */
3936 if (level->kind != sk_class)
3937 continue ;
3938
3939 /* Lookup the conversion operator in the class. */
3940 class_type = level->this_entity;
3941 operators = lookup_fnfields (class_type, name, /*protect=*/ 0);
3942 if (operators)
3943 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, operators);
3944 }
3945
3946 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, NULL_TREE);
3947 }
Here first handling conversion operator. Its reason is explained by above comment, as template conversion operator isn’t candidate of ordinary unqualified name lookup (Remember, template, unless instantation, won’t be bound with scope, so oridnary unqualified name lookup unable to find it out).
5.12.4.1.1.2.1.3.1. Conversion operator
At line 3923, IDENTIFIER_TYPENAME_P returns true if the name names a type-conversion operator. Conversion operator must be defined within class. So the searching is confined within classes and from the innermost class up (seeing that level_chain field tells the enclosing class for the nested class, and name not found within nested class should be searched follows level_chain ).
1387 tree
1388 lookup_fnfields (tree xbasetype, tree name, int protect) in search.c
1389 {
1390 tree rval = lookup_member (xbasetype, name, protect, /*want_type=*/ false);
1391
1392 /* Ignore non-functions. */
1393 if (rval && !BASELINK_P (rval))
1394 return NULL_TREE;
1395
1396 return rval;
1397 }
Its implement in fact is the same as searching in specified class.
5.12.4.1.1.2.1.3.2. Other names
If name does not specifiy conversion operator, it begins with lookup_flags to setup flags used for followed searching.
3562 static int
3563 lookup_flags (int prefer_type, int namespaces_only) in name-lookup.c
3564 {
3565 if (namespaces_only)
3566 return LOOKUP_PREFER_NAMESPACES;
3567 if (prefer_type > 1)
3568 return LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES;
3569 if (prefer_type > 0)
3570 return LOOKUP_PREFER_BOTH;
3571 return 0;
3572 }
Above LOOKUP_PREFER_NAMESPACES means not to accept objects, and possibly namespaces; LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES means not to accept objects, and possibly types; LOOKUP_PREFER_BOTH means class-or-namespace-name.
lookup_name_real (continue)
3949 flags |= lookup_flags (prefer_type, namespaces_only);
3650
3951 /* First, look in non-namespace scopes. */
3952
3953 if (current_class_type == NULL_TREE)
3954 nonclass = 1;
3955
3956 for (iter = IDENTIFIER_BINDING (name); iter; iter = iter->previous)
3957 {
3958 tree binding;
3959
3960 if (!LOCAL_BINDING_P (iter) && nonclass)
3961 /* We're not looking for class-scoped bindings, so keep going. */
3962 continue ;
3963
3964 /* If this is the kind of thing we're looking for, we're done. */
3965 if (qualify_lookup (iter->value, flags))
3966 binding = iter->value;
3967 else if ((flags & LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES)
3968 && qualify_lookup (iter->type, flags))
3969 binding = iter->type;
3970 else
3971 binding = NULL_TREE;
3972
3973 if (binding)
3974 {
3975 val = binding;
3976 break ;
3977 }
3978 }
The binding slot of lang_identifier refers to the list of binding scopes, which contains nodes of cxx_binding of non-namespace scopes (refer to figure nodes of builtin types as example). IDNEITIFIER_BINDING accesses the binding field, and visits the list via the previous slot of each node. Remember that list records the identifier defined within different binding scopes as far. And value field of each node of cxx_binding records the non-type entity this name is bound to (usually the TYPE_DECL or NAMESPACE_DECL), while type slot records the type entity this name is bound to.
Pay attention to the order and parameters of the invocation of qualify_lookup above; the function checks whether the found is the object or not.
3577 static tree
3578 qualify_lookup (tree val, int flags)
3579 {
3580 if (val == NULL_TREE)
3581 return val;
3582 if ((flags & LOOKUP_PREFER_NAMESPACES) && TREE_CODE (val) == NAMESPACE_DECL)
3583 return val;
3584 if ((flags & LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES)
3585 && (TREE_CODE (val) == TYPE_DECL || TREE_CODE (val) == TEMPLATE_DECL))
3586 return val;
3587 if (flags & (LOOKUP_PREFER_NAMESPACES | LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES))
3588 return NULL_TREE;
3589 return val;
3590 }
Above (LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES | LOOKUP_PREFER_NAMESPACES) is the definition of LOOKUP_PREFER_BOTH. And notice that if flags is zero, it accepts everything (no filter is done).
lookup_name_real (continue)
3980 /* Now lookup in namespace scopes. */
3981 if (!val)
3982 {
3983 tree t = unqualified_namespace_lookup (name, flags);
3984 if (t)
3985 val = t;
3986 }
3987
3988 if (val)
3989 {
3990 /* If we have a single function from a using decl, pull it out. */
3991 if (TREE_CODE (val) == OVERLOAD && ! really_overloaded_fn (val))
3992 val = OVL_FUNCTION (val);
3993 }
3994
3995 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, val);
3996 }
If we can’t find out the name in this quick way, the identifier must be declared within some namespaces or even those introduced by using statement. We have to do the search along those namespaces.
3706 static tree
3707 unqualified_namespace_lookup (tree name, int flags) in name-lookup.c
3708 {
3709 tree initial = current_decl_namespace ();
3710 tree scope = initial;
3711 tree siter;
3712 struct cp_binding_level *level;
3713 tree val = NULL_TREE;
3714 cxx_binding binding;
3715
3716 timevar_push (TV_NAME_LOOKUP);
3717 cxx_binding_clear (&binding);
First, current_decl_namespace helps to find out the innermost enclosing namespace. Below, if decl_namespace_list is non-null, it saves enclosing namespaces in order of the inner the closer to the head. So the closest namespace can be fetched from the header.
3039 tree
3040 current_decl_namespace (void) in name-lookup.c
3041 {
3042 tree result;
3043 /* If we have been pushed into a different namespace, use it. */
3044 if (decl_namespace_list )
3045 return TREE_PURPOSE (decl_namespace_list );
3046
3047 if (current_class_type )
3048 result = decl_namespace_context (current_class_type );
3049 else if (current_function_decl )
3050 result = decl_namespace_context (current_function_decl );
3051 else
3052 result = current_namespace ;
3053 return result;
3054 }
Otherwise, decl_namespace_context steps into the context of declaration till finding out scope of namespace. Notice that the namespace can always be found, as on top there is always global_namespace , for which case NULL_TREE will be returned.
1426 tree
1427 decl_namespace_context (tree decl) in tree.c
1428 {
1429 while (1)
1430 {
1431 if (TREE_CODE (decl) == NAMESPACE_DECL)
1432 return decl;
1433 else if (TYPE_P (decl))
1434 decl = CP_DECL_CONTEXT (TYPE_MAIN_DECL (decl));
1435 else
1436 decl = CP_DECL_CONTEXT (decl);
1437 }
1438 }
Assuming now we have following definitions:
namespace C {
namespace B {
void func1() { … } // block scope A
void func2 () { // block scope D
using namespace Y;
using namespace X;
W w;
}
}
}
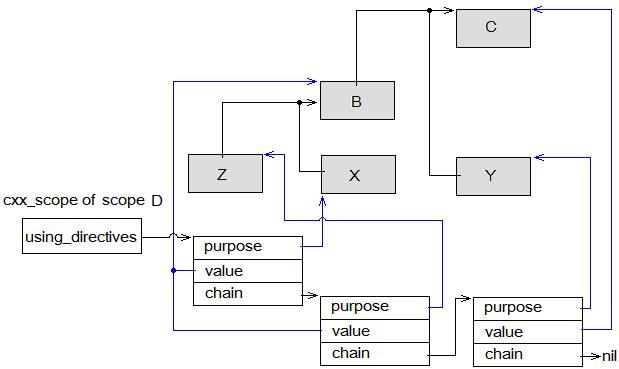
Compiler is going to lookup name of W. The hierarch of scopes can be shown in below figure:
Figure 100 : example for unqualified_namespace_lookup
For these statements, current_decl_namespace will return NAMESPACE_DECL of B as result. Then in the outer FOR loop at line 3719, the function will visit the namespaces along the hierarch till arriving global namespace if the definition not found.
unqualified_namespace_lookup (continue)
3719 for (; !val; scope = CP_DECL_CONTEXT (scope))
3720 {
3721 cxx_binding *b =
3722 cxx_scope_find_binding_for_name (NAMESPACE_LEVEL (scope), name);
3723
3724 if (b)
3725 {
3726 if (b->value && DECL_P (b->value)
3727 && DECL_LANG_SPECIFIC (b->value)
3728 && DECL_ANTICIPATED (b->value))
3729 /* Ignore anticipated built-in functions. */
3730 ;
3731 else
3732 binding.value = b->value;
3733 binding.type = b->type;
3734 }
3735
3736 /* Add all _DECLs seen through local using-directives. */
3737 for (level = current_binding_level ;
3738 level->kind != sk_namespace;
3739 level = level->level_chain)
3740 if (!lookup_using_namespace (name, &binding, level->using_directives,
3741 scope, flags))
3742 /* Give up because of error. */
3743 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, error_mark_node);
While in the inner FOR loop at line 3737, current_binding_level will return cxx_scope of scope D (if it is a class scope, as using directive is not allowed in class scope, lookup_using_namespace will exit immediately). As in these non-namespace scope (except class scope), using directives can be used to include namespace, obviously they are part of the visible set, should be searched and have ambiguity checked.
3809 static bool
3810 lookup_using_namespace (tree name, cxx_binding *val, tree usings, in name-lookup.c
3811 tree scope, int flags)
3812 {
3813 tree iter;
3814 timevar_push (TV_NAME_LOOKUP);
3815 /* Iterate over all used namespaces in current, searching for using
3816 directives of scope. */
3817 for (iter = usings; iter; iter = TREE_CHAIN (iter))
3818 if (TREE_VALUE (iter) == scope)
3819 {
3820 tree used = ORIGINAL_NAMESPACE (TREE_PURPOSE (iter));
3821 cxx_binding *val1 =
3822 cxx_scope_find_binding_for_name (NAMESPACE_LEVEL (used), name);
3823 /* Resolve ambiguities. */
3824 if (val1)
3825 val = ambiguous_decl (name, val, val1, flags);
3826 }
3827 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, val->value != error_mark_node);
3828 }
To understand the behavor of lookup_using_namespace , we assume namespace X is enclosed within namespace B, there is “using namespace Z” in X; and namespace Y is enclosed within namespace C:
Figure 101 : example of using_directives
So in using_directives field of the cxx_scope of scope D, the list should have 3 nodes (note that above list has reverse order, but here order doesn’t matter). The first node is added by “using namespace X”; and the second is added by “using namespace Z” in namespace X; then the thrid is added by “using namespace Y”. To every node, its value field is the common ancestor of the context of the included namespace and the context of scope of D, and the purpose field is the included namespace.
Pay attention to line 3818 in lookup_using_namespace , at beginning scope is the innermost enclosing namespace of scope D. This statement strictly mainatins namespaces’ hierarchy, avoids penetrations between namespaces, in the example “using namespace Y” tries to include namespace Y into namespace B, which is prohibited. But if nothing is found in namespace B, scope will go up one level to namespace C. In this time, as “using namespace X” and indirect “using namespace Z” has been handled, they are filtered at line 3818; but “using namespace Y” gets processed.
unqualified_namespace_lookup (continue)
3745 /* Add all _DECLs seen through global using-directives. */
3746 /* XXX local and global using lists should work equally. */
3747 siter = initial;
3748 while (1)
3749 {
3750 if (!lookup_using_namespace (name, &binding,
3751 DECL_NAMESPACE_USING (siter),
3752 scope, flags))
3753 /* Give up because of error. */
3754 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, error_mark_node);
3755 if (siter == scope) break ;
3756 siter = CP_DECL_CONTEXT (siter);
3757 }
3758
3759 val = select_decl (&binding, flags);
3760 if (scope == global_namespace )
3761 break ;
3762 }
3763 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, val);
3764 }
At line 3747, initial is the enclosing namespace found at beiginning. And DECL_NAMESPACE_USING is the list used by namespace to record namespaces included by using directive. Its structure is similar with that of using_directive above. lookup_using_namespace remains firmly keeping namespace hierachy and searching faithfully. In the result found, select_decl selects the most appropriate entity.
3765 static tree
3766 select_decl (cxx_binding *binding, int flags) in name-lookup.c
3767 {
3768 tree val;
3769 val = binding->value;
3770
3771 timevar_push (TV_NAME_LOOKUP);
3772 if (LOOKUP_NAMESPACES_ONLY (flags))
3773 {
3774 /* We are not interested in types. */
3775 if (val && TREE_CODE (val) == NAMESPACE_DECL)
3776 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, val);
3777 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, NULL_TREE);
3778 }
3779
3780 /* If looking for a type, or if there is no non-type binding, select
3781 the value binding. */
3782 if (binding->type && (!val || (flags & LOOKUP_PREFER_TYPES)))
3783 val = binding->type;
3784 /* Don't return non-types if we really prefer types. */
3785 else if (val && LOOKUP_TYPES_ONLY (flags) && TREE_CODE (val) != TYPE_DECL
3786 && (TREE_CODE (val) != TEMPLATE_DECL
3787 || !DECL_CLASS_TEMPLATE_P (val)))
3788 val = NULL_TREE;
3789
3790 POP_TIMEVAR_AND_RETURN (TV_NAME_LOOKUP, val);
3791 }
See that if thing found out is not we expected, select_decl will return null, but binding will not be cleaned, so in next iteration, ambiguous checking can be taken if new definition found.And if valid val returned, we will exit up to cp_parser_lookup_name .
cp_parser_lookup_name (continue)
13840 /* If the lookup failed, let our caller know. */
13841 if (!decl
13842 || decl == error_mark_node
13843 || (TREE_CODE (decl) == FUNCTION_DECL
13844 && DECL_ANTICIPATED (decl)))
13845 return error_mark_node;
13846
13847 /* If it's a TREE_LIST, the result of the lookup was ambiguous. */
13848 if (TREE_CODE (decl) == TREE_LIST)
13849 {
13850 /* The error message we have to print is too complicated for
13851 cp_parser_error, so we incorporate its actions directly. */
13852 if (!cp_parser_simulate_error (parser))
13853 {
13854 error ("reference to `%D' is ambiguous", name);
13855 print_candidates (decl);
13856 }
13857 return error_mark_node;
13858 }
13859
13860 my_friendly_assert (DECL_P (decl)
13861 || TREE_CODE (decl) == OVERLOAD
13862 || TREE_CODE (decl) == SCOPE_REF
13863 || TREE_CODE (decl) == UNBOUND_CLASS_TEMPLATE
13864 || BASELINK_P (decl),
13865 20000619);
13866
13867 /* If we have resolved the name of a member declaration, check to
13868 see if the declaration is accessible. When the name resolves to
13869 set of overloaded functions, accessibility is checked when
13870 overload resolution is done.
13871
13872 During an explicit instantiation, access is not checked at all,
13873 as per [temp.explicit]. */
13874 if (DECL_P (decl))
13875 check_accessibility_of_qualified_id (decl, object_type, parser->scope);
13876
13877 return decl;
13878 }
Remember that for overloaded functions, the nodes returned are those of OVERLOAD, not TREE_LIST which just indicates ambiguous found (though from the path here, ambiguous should be found before entering the function).
If valid declaration is found, it is time to check its accessibility at this point.
1311 void
1312 check_accessibility_of_qualified_id (tree decl, in semantics.c
1313 tree object_type,
1314 tree nested_name_specifier)
1315 {
1316 tree scope;
1317 tree qualifying_type = NULL_TREE;
1318
1319 /* Determine the SCOPE of DECL. */
1320 scope = context_for_name_lookup (decl);
First, we should find out the context that encloses the declaration we find. See that an exception is relate to anonymous union definition, which are considered to have been defined in the scope the union is declared.
600 tree
601 context_for_name_lookup (tree decl)
602 {
603 /* [class.union]
604
605 For the purposes of name lookup, after the anonymous union
606 definition, the members of the anonymous union are considered to
607 have been defined in the scope in which the anonymous union is
608 declared. */
609 tree context = DECL_CONTEXT (decl);
610
611 while (context && TYPE_P (context) && ANON_AGGR_TYPE_P (context))
612 context = TYPE_CONTEXT (context);
613 if (!context)
614 context = global_namespace ;
615
616 return context;
617 }
Notice that TYPE_P returns false for NAMESPACE_DECL. For namespace, it is always accessible.
check_accessibility_of_qualified_id (continue)
1321 /* If the SCOPE is not a type, then DECL is not a member. */
1322 if (!TYPE_P (scope))
1323 return ;
1324 /* Compute the scope through which DECL is being accessed. */
1325 if (object_type
1326 /* OBJECT_TYPE might not be a class type; consider:
1327
1328 class A { typedef int I; };
1329 I *p;
1330 p->A::I::~I();
1331
1332 In this case, we will have "A::I" as the DECL, but "I" as the
1333 OBJECT_TYPE. */
1334 && CLASS_TYPE_P (object_type)
1335 && DERIVED_FROM_P (scope, object_type))
1336 /* If we are processing a `->' or `.' expression, use the type of the
1337 left-hand side. */
1338 qualifying_type = object_type;
1339 else if (nested_name_specifier)
1340 {
1341 /* If the reference is to a non-static member of the
1342 current class, treat it as if it were referenced through
1343 `this'. */
1344 if (DECL_NONSTATIC_MEMBER_P (decl)
1345 && current_class_ptr
1346 && DERIVED_FROM_P (scope, current_class_type ))
1347 qualifying_type = current_class_type ;
1348 /* Otherwise, use the type indicated by the
1349 nested-name-specifier. */
1350 else
1351 qualifying_type = nested_name_specifier;
1352 }
1353 else
1354 /* Otherwise, the name must be from the current class or one of
1355 its bases. */
1356 qualifying_type = currently_open_derived_class (scope);
1357
1358 if (qualifying_type)
1359 perform_or_defer_access_check (TYPE_BINFO (qualifying_type), decl);
1360 }
Above if argument object_type is non-null, we have just seen `x->' or `x.' and object_type is the type of `*x', or `x', respectively. And if the argument decl was named as `A::B' then argument nested_name_specifier is `A'.
Obvious, if object_type or nested_name_specifier is non-null, the accessibilty check should be done according to the type. See that if object_type is not of class type, qualifying_type will stay null. While if these two variables are null, the enclosing scope must be one of currently opened classes. It is found be currently_open_derived_class .
5599 tree
5600 currently_open_derived_class (tree t) in class.c
5601 {
5602 int i;
5603
5604 /* The bases of a dependent type are unknown. */
5605 if (dependent_type_p (t))
5606 return NULL_TREE;
5607
5608 if (!current_class_type )
5609 return NULL_TREE;
5610
5611 if (DERIVED_FROM_P (t, current_class_type ))
5612 return current_class_type ;
5613
5614 for (i = current_class_depth - 1; i > 0; --i)
5615 if (DERIVED_FROM_P (t, current_class_stack [i].type))
5616 return current_class_stack [i].type;
5617
5618 return NULL_TREE;
5619 }
Once the enclosing type is found, the accessible check for the declaration can be done by perform_or_defer_access_check .
Returns back to cp_parser_class_name , for non-template candidate, nothing meaningful for normal case will be done. Then the function returns the found type (as type_p is true in invocation).
5.12.4.1.1.2.2. The result of lookup
Compared with unqualified_namespace_lookup , looking-up qualified-id is nearly the same as that of unqualified-id, except for former one, only specified scope and limited relevant scopes will be searched, but for the rear one, the lookup will climb up to the root till an match found. Here refer to previous sections about parsing the class “SingleThreaded”, we can see that the TEMPLATE_DECL is returned as value field of the corresponding cxx_binding node points to it. Then at line 7835 in cp_parser_type_parameter , check_template_template_default_arg verifies that this default argument is kind of template, and for failure case error_mark_node node is returned. Then the parameter and parameter-list at this point looks like below.
(Click here for open )
Figure 102 : parameter & parameter-list built