Android包含三种动画:View Animation、 Drawable Animation、Property Animation(Android3.0新引入)。
View Animation :
简介:
基于View的渐变动画,她只改变了View的绘制效果,而实际属性值未变。比如动画移动一个按钮位置,但按钮点击的实际位置仍未改变。在代码中定义动画,可以参考AnimationSet类和Animation的子类;而如果使用XML,可以在res/anim/文件夹中定义XML文件。
View animation系统可以用来执行View上的Tween animation和Frame animation。
Tween animation可以在View对象上执行一系列的简单变换,比如位置、尺寸、旋转、透明度等。
animation package 包中包含了tween animation所有的类。
一系列的动画命令定义了一个完整的tween animation,可以用代码定义也可以用XML资源文件定义。
用法详解:
XML资源文件的使用可以见:Animation Resources。
XML文件放在项目的res/anim/目录下。文件必须有一个唯一的根节点。
这个根节点可以是:<alpha>, <scale>, <translate>, <rotate>, interpolator element, 或者是<set>。
默认情况下,所有的动画都是并行进行的,要想使得它们顺寻发生,你必须指定startOffset属性。
有一些值,可以指定是相对于View本身还是相对于父类容器的。
比如pivotX,要表示相对于自身的50%,要用50%;要表示相对于父类容器的50%,则直接写50。
XML文件存储为:res/anim/hyperspace_jump.xml:
<span style="color:#333333;"><set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:shareInterpolator="false">
<scale
android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_decelerate_interpolator"
android:fromXScale="1.0"
android:toXScale="1.4"
android:fromYScale="1.0"
android:toYScale="0.6"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:fillAfter="false"
android:duration="700" />
<set
android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"
android:startOffset="700">
<scale
android:fromXScale="1.4"
android:toXScale="0.0"
android:fromYScale="0.6"
android:toYScale="0.0"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:duration="400" />
<rotate
android:fromDegrees="0"
android:toDegrees="-45"
android:toYScale="0.0"
android:pivotX="50%"
android:pivotY="50%"
android:duration="400" />
</set>
</set></span>
ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image);
Animation hyperspaceJump = AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(this, R.anim.hyperspace_jump);
image.startAnimation(hyperspaceJump);
除了调用 startAnimation() ,另一种处理方式是通过Animation.setStartTime()方法定义一个开始时间,然后通过View.setAnimation()方法把这个动画赋给控件即可。
Drawable Animation
简介:
加载一系列Drawable资源来创建动画,这种传统动画某种程度上就是创建不同图片序列,顺序播放,就像电影胶片。在代码中定义动画帧,使用AnimationDrawable类;XML文件能更简单的组成动画帧,在res/drawable文件夹,使用<animation-list>采用<item>来定义不同的帧。感觉只能设置的属性是动画间隔时间。
用法详解:
在Andrio的中,可以使用多幅图片实现动画效果。
首先定义一个以 <animation-list>为根节点的xml文件,命名为 anim.xml 放在 res/drawable/目录下。
- <animation-list xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:oneshot="true">
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/image1" android:duration="200" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/image2" android:duration="200" />
- <item android:drawable="@drawable/image3" android:duration="200" />
- </animation-list>
然后,在控件中使用此资源文件
- ImageView image = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.rocket_image);
- image.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.rocket_thrust);
- AnimationDrawable animation = (AnimationDrawable) image.getBackground();
最后,在需要的时候启动动画即可。
Property Animation
简介:
动画的对象除了传统的View对象,还可以是Object对象,动画之后,Object对象的属性值被实实在在的改变了。Property animation能够通过改变View对象的实际属性来实现View动画。任何时候View属性的改变,View能自动调用invalidate()来试试刷新。
View实施Property animation时的新属性:
- translationX 、translationY: 左上坐标的改变值
- rotation、 rotationX、 rotationY
- scaleX 、 scaleY: 横纵向的缩放比例,如:1.2f、0.8f
- pivotX 、 pivotY: 缩放和旋转时横纵向中心点,默认情况下是View的中心,如果想以View的左上坐标为中心进行旋转或者缩放,应该将其值都设置为0
- alpha:透明度. 默认为1,0代表全透明,即不可见
用法详解:
1、相关API
Property Animation故名思议就是通过动画的方式改变对象的属性了,我们首先需要了解几个属性:
Duration动画的持续时间,默认300ms。
Time interpolation:时间差值,定义动画的变化率。
Repeat count and behavior:重复次数、以及重复模式;可以定义重复多少次;重复时从头开始,还是反向。
Animator sets: 动画集合,你可以定义一组动画,一起执行或者顺序执行。
Frame refresh delay:帧刷新延迟,对于你的动画,多久刷新一次帧;默认为10ms,但最终依赖系统的当前状态;基本不用管。
相关的类
ObjectAnimator 动画的执行类,后面详细介绍
ValueAnimator 动画的执行类,后面详细介绍
AnimatorSet 用于控制一组动画的执行:线性,一起,每个动画的先后执行等。
AnimatorInflater 用户加载属性动画的xml文件
TypeEvaluator 类型估值,主要用于设置动画操作属性的值。
TimeInterpolator 时间插值,上面已经介绍。
总的来说,属性动画就是,动画的执行类来设置动画操作的对象的属性、持续时间,开始和结束的属性值,时间差值等,然后系统会根据设置的参数动态的变化对象的属性。
2.ObjectAnimator实现动画
一行代码,秒秒钟实现动画,
布局文件:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/id_container" >
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/id_ball"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:src="@drawable/mv"
android:scaleType="centerCrop"
android:onClick="rotateyAnimRun"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
很简单,就一张妹子图片~
Activity代码:
- package com.example.zhy_property_animation;
- import android.animation.ObjectAnimator;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.View;
-
- public class ObjectAnimActivity extends Activity
- {
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
- {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.xml_for_anim);
- }
-
- public void rotateyAnimRun(View view)
- {
- ObjectAnimator
- .ofFloat(view, "rotationX", 0.0F, 360.0F)
- .setDuration(500)
- .start();
- }
-
- }
效果:
是不是一行代码就能实现简单的动画~~
对于ObjectAnimator
1、提供了ofInt、ofFloat、ofObject,这几个方法都是设置动画作用的元素、作用的属性、动画开始、结束、以及中间的任意个属性值。
当对于属性值,只设置一个的时候,会认为当然对象该属性的值为开始(getPropName反射获取),然后设置的值为终点。如果设置两个,则一个为开始、一个为结束~~~
动画更新的过程中,会不断调用setPropName更新元素的属性,所有使用ObjectAnimator更新某个属性,必须得有getter(设置一个属性值的时候)和setter方法~
2、如果你操作对象的该属性方法里面,比如上例的setRotationX如果内部没有调用view的重绘,则你需要自己按照下面方式手动调用。
- anim.addUpdateListener(new AnimatorUpdateListener()
- {
- @Override
- public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation)
- {
-
-
- }
- });
3、看了上面的例子,因为设置的操作的属性只有一个,那么如果我希望一个动画能够让View既可以缩小、又能够淡出(3个属性scaleX,scaleY,alpha),只使用ObjectAnimator咋弄?
想法是不是很不错,可能会说使用AnimatorSet啊,这一看就是一堆动画塞一起执行,但是我偏偏要用一个ObjectAnimator实例实现呢~下面看代码:
- public void rotateyAnimRun(final View view)
- {
- ObjectAnimator anim = ObjectAnimator
- .ofFloat(view, "zhy", 1.0F, 0.0F)
- .setDuration(500);
- anim.start();
- anim.addUpdateListener(new AnimatorUpdateListener()
- {
- @Override
- public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation)
- {
- float cVal = (Float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
- view.setAlpha(cVal);
- view.setScaleX(cVal);
- view.setScaleY(cVal);
- }
- });
- }
把设置属性的那个字符串,随便写一个该对象没有的属性,就是不管~~咱们只需要它按照时间插值和持续时间计算的那个值,我们自己手动调用~
效果:
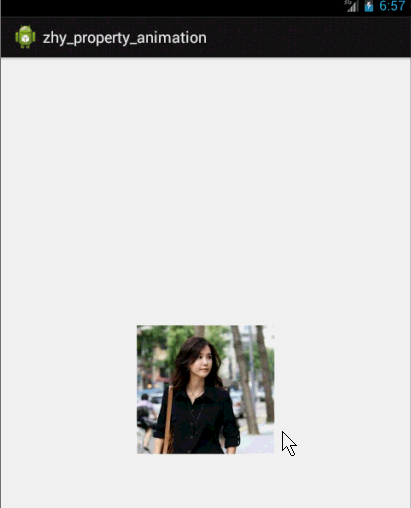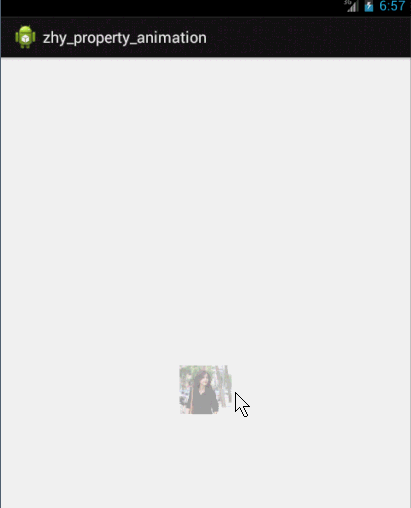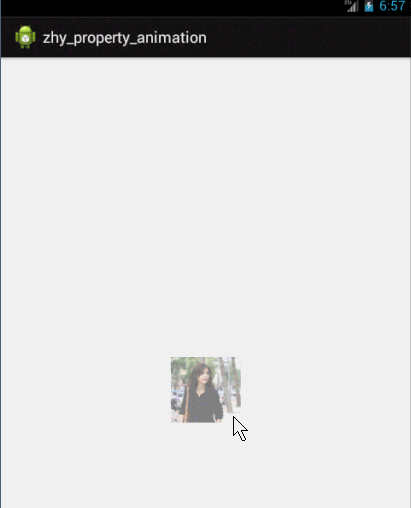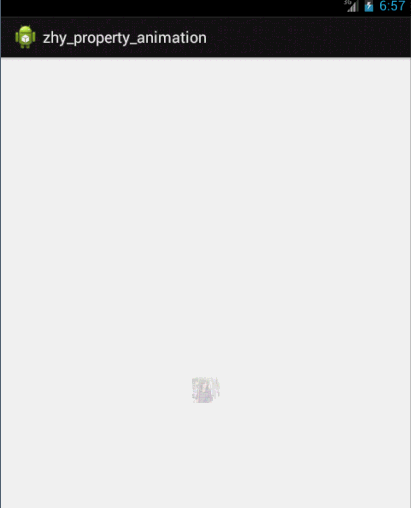
这个例子就是想说明一下,有时候换个思路不要被API所约束,利用部分API提供的功能也能实现好玩的效果~~~
比如:你想实现抛物线的效果,水平方向100px/s,垂直方向加速度200px/s*s ,咋实现呢~~可以自己用ObjectAnimator试试~
4、其实还有更简单的方式,实现一个动画更改多个效果:使用propertyValuesHolder
- public void propertyValuesHolder(View view)
- {
- PropertyValuesHolder pvhX = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("alpha", 1f,
- 0f, 1f);
- PropertyValuesHolder pvhY = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("scaleX", 1f,
- 0, 1f);
- PropertyValuesHolder pvhZ = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("scaleY", 1f,
- 0, 1f);
- ObjectAnimator.ofPropertyValuesHolder(view, pvhX, pvhY,pvhZ).setDuration(1000).start();
- }
3.ValueAnimator实现动画
和ObjectAnimator用法很类似,简单看一下用view垂直移动的动画代码:
- public void verticalRun(View view)
- {
- ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0, mScreenHeight
- - mBlueBall.getHeight());
- animator.setTarget(mBlueBall);
- animator.setDuration(1000).start();
- }
给你的感觉是不是,坑爹啊,这和ValueAnimator有毛线区别~但是仔细看,你看会发现,没有设置操作的属性~~也就是说,上述代码是没有任何效果的,没有指定属性~
这就是和ValueAnimator的区别之处:ValueAnimator并没有在属性上做操作,你可能会问这样有啥好处?我岂不是还得手动设置?
好处:不需要操作的对象的属性一定要有getter和setter方法,你可以自己根据当前动画的计算值,来操作任何属性,记得上例的那个【我希望一个动画能够让View既可以缩小、又能够淡出(3个属性scaleX,scaleY,alpha)】吗?其实就是这么个用法~
实例:
布局文件:
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- android:id="@+id/id_container"
-
- >
-
- <ImageView
- android:id="@+id/id_ball"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/bol_blue" />
-
- <LinearLayout
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
- android:orientation="horizontal" >
-
- <Button
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:onClick="verticalRun"
- android:text="垂直" />
-
- <Button
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:onClick="paowuxian"
- android:text="抛物线" />
-
- </LinearLayout>
-
- </RelativeLayout>
左上角一个小球,底部两个按钮~我们先看一个自由落体的代码:
-
-
-
-
- public void verticalRun( View view)
- {
- ValueAnimator animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0, mScreenHeight
- - mBlueBall.getHeight());
- animator.setTarget(mBlueBall);
- animator.setDuration(1000).start();
-
- animator.addUpdateListener(new AnimatorUpdateListener()
- {
- @Override
- public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation)
- {
- mBlueBall.setTranslationY((Float) animation.getAnimatedValue());
- }
- });
- }
与ObjectAnimator不同的就是我们自己设置元素属性的更新~虽然多了几行代码,但是貌似提高灵活性~
下面再来一个例子,如果我希望小球抛物线运动【实现抛物线的效果,水平方向100px/s,垂直方向加速度200px/s*s 】,分析一下,貌似只和时间有关系,但是根据时间的变化,横向和纵向的移动速率是不同的,我们该咋实现呢?此时就要重写TypeValue的时候了,因为我们在时间变化的同时,需要返回给对象两个值,x当前位置,y当前位置:
代码:
-
-
-
-
- public void paowuxian(View view)
- {
-
- ValueAnimator valueAnimator = new ValueAnimator();
- valueAnimator.setDuration(3000);
- valueAnimator.setObjectValues(new PointF(0, 0));
- valueAnimator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
- valueAnimator.setEvaluator(new TypeEvaluator<PointF>()
- {
-
- @Override
- public PointF evaluate(float fraction, PointF startValue,
- PointF endValue)
- {
- Log.e(TAG, fraction * 3 + "");
-
- PointF point = new PointF();
- point.x = 200 * fraction * 3;
- point.y = 0.5f * 200 * (fraction * 3) * (fraction * 3);
- return point;
- }
- });
-
- valueAnimator.start();
- valueAnimator.addUpdateListener(new AnimatorUpdateListener()
- {
- @Override
- public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation)
- {
- PointF point = (PointF) animation.getAnimatedValue();
- mBlueBall.setX(point.x);
- mBlueBall.setY(point.y);
-
- }
- });
- }
可以看到,因为ofInt,ofFloat等无法使用,我们自定义了一个TypeValue,每次根据当前时间返回一个PointF对象,(PointF和Point的区别就是x,y的单位一个是float,一个是int;RectF,Rect也是)PointF中包含了x,y的当前位置~然后我们在监听器中获取,动态设置属性:
效果图:
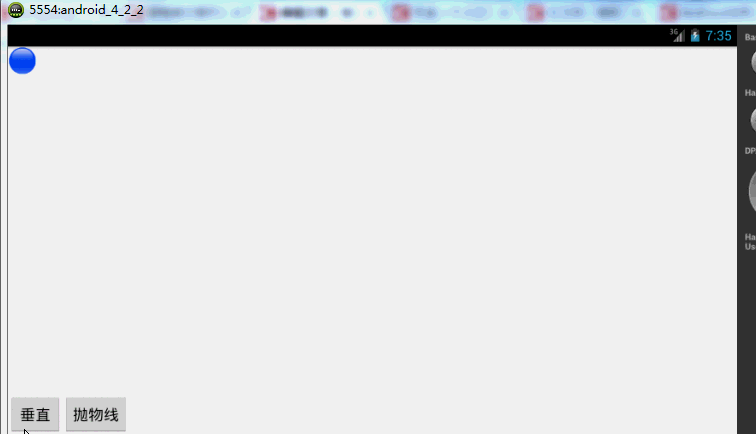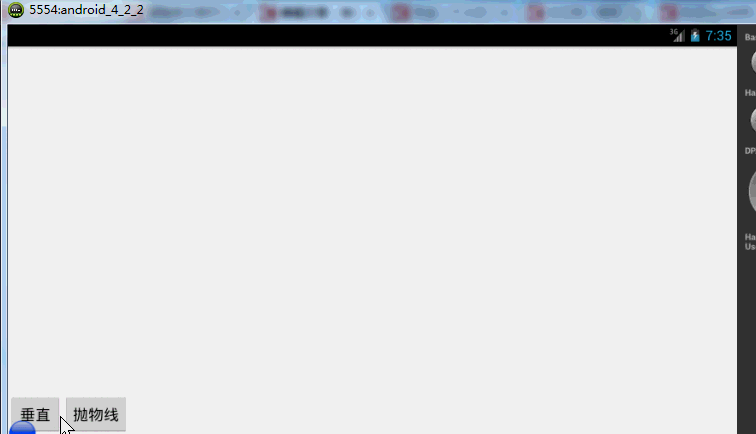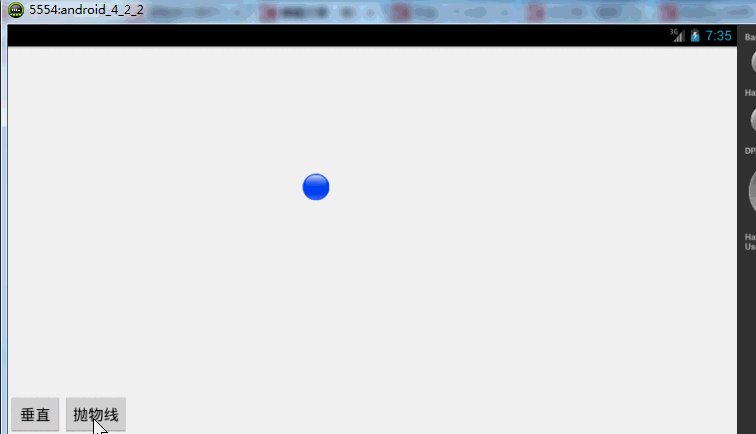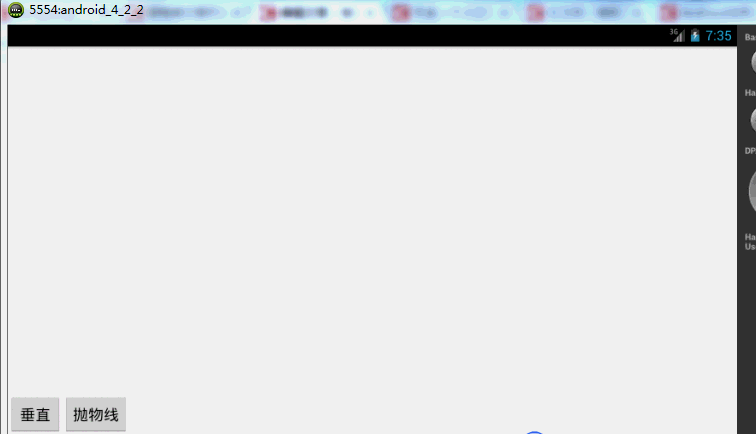
有木有两个铁球同时落地的感觉~~对,我应该搞两个球~~ps:物理公式要是错了,就当没看见哈
自定义TypeEvaluator传入的泛型可以根据自己的需求,自己设计个Bean。
好了,我们已经分别讲解了ValueAnimator和ObjectAnimator实现动画;二者区别;如何利用部分API,自己更新属性实现效果;自定义TypeEvaluator实现我们的需求;但是我们并没有讲如何设计插值,其实我觉得把,这个插值默认的那一串实现类够用了~~很少,会自己去设计个超级变态的~嗯~所以:略
4、监听动画的事件
对于动画,一般都是一些辅助效果,比如我要删除个元素,我可能希望是个淡出的效果,但是最终还是要删掉,并不是你透明度没有了,还占着位置,所以我们需要知道动画如何结束。
所以我们可以添加一个动画的监听:
- public void fadeOut(View view)
- {
- ObjectAnimator anim = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mBlueBall, "alpha", 0.5f);
-
- anim.addListener(new AnimatorListener()
- {
-
- @Override
- public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation)
- {
- Log.e(TAG, "onAnimationStart");
- }
-
- @Override
- public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation)
- {
-
- Log.e(TAG, "onAnimationRepeat");
- }
-
- @Override
- public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation)
- {
- Log.e(TAG, "onAnimationEnd");
- ViewGroup parent = (ViewGroup) mBlueBall.getParent();
- if (parent != null)
- parent.removeView(mBlueBall);
- }
-
- @Override
- public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation)
- {
-
- Log.e(TAG, "onAnimationCancel");
- }
- });
- anim.start();
- }
这样就可以监听动画的开始、结束、被取消、重复等事件~但是有时候会觉得,我只要知道结束就行了,这么长的代码我不能接收,那你可以使用AnimatorListenerAdapter
- anim.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter()
- {
- @Override
- public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation)
- {
- Log.e(TAG, "onAnimationEnd");
- ViewGroup parent = (ViewGroup) mBlueBall.getParent();
- if (parent != null)
- parent.removeView(mBlueBall);
- }
- });
AnimatorListenerAdapter继承了AnimatorListener接口,然后空实现了所有的方法~
效果图:
animator还有cancel()和end()方法:cancel动画立即停止,停在当前的位置;end动画直接到最终状态。
5、AnimatorSet的使用
实例:
布局文件:
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- android:id="@+id/id_container"
-
- >
-
- <ImageView
- android:id="@+id/id_ball"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_centerInParent="true"
- android:src="@drawable/bol_blue" />
-
- <LinearLayout
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
- android:orientation="horizontal" >
-
- <Button
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:onClick="togetherRun"
- android:text="简单的多动画Together" />
-
- <Button
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:onClick="playWithAfter"
- android:text="多动画按次序执行" />
-
-
- </LinearLayout>
-
- </RelativeLayout>
继续玩球~
代码:
- package com.example.zhy_property_animation;
-
- import android.animation.AnimatorSet;
- import android.animation.ObjectAnimator;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.view.animation.LinearInterpolator;
- import android.widget.ImageView;
-
- public class AnimatorSetActivity extends Activity
- {
- private ImageView mBlueBall;
-
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
- {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.anim_set);
-
- mBlueBall = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.id_ball);
-
- }
-
- public void togetherRun(View view)
- {
- ObjectAnimator anim1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mBlueBall, "scaleX",
- 1.0f, 2f);
- ObjectAnimator anim2 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mBlueBall, "scaleY",
- 1.0f, 2f);
- AnimatorSet animSet = new AnimatorSet();
- animSet.setDuration(2000);
- animSet.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator());
-
- animSet.playTogether(anim1, anim2);
- animSet.start();
- }
-
- public void playWithAfter(View view)
- {
- float cx = mBlueBall.getX();
-
- ObjectAnimator anim1 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mBlueBall, "scaleX",
- 1.0f, 2f);
- ObjectAnimator anim2 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mBlueBall, "scaleY",
- 1.0f, 2f);
- ObjectAnimator anim3 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mBlueBall,
- "x", cx , 0f);
- ObjectAnimator anim4 = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(mBlueBall,
- "x", cx);
-
-
-
-
-
- AnimatorSet animSet = new AnimatorSet();
- animSet.play(anim1).with(anim2);
- animSet.play(anim2).with(anim3);
- animSet.play(anim4).after(anim3);
- animSet.setDuration(1000);
- animSet.start();
- }
- }
写了两个效果:
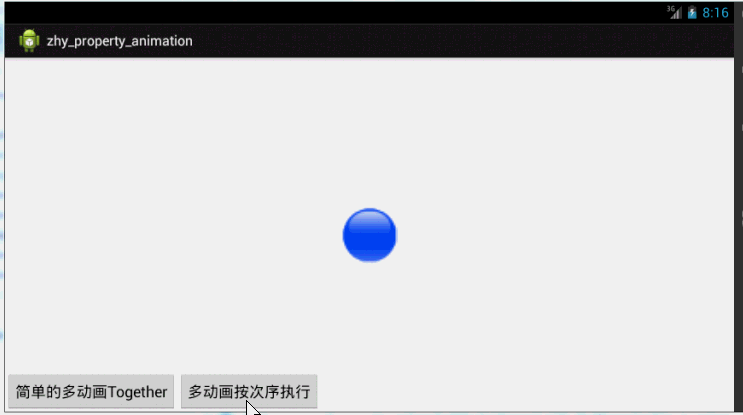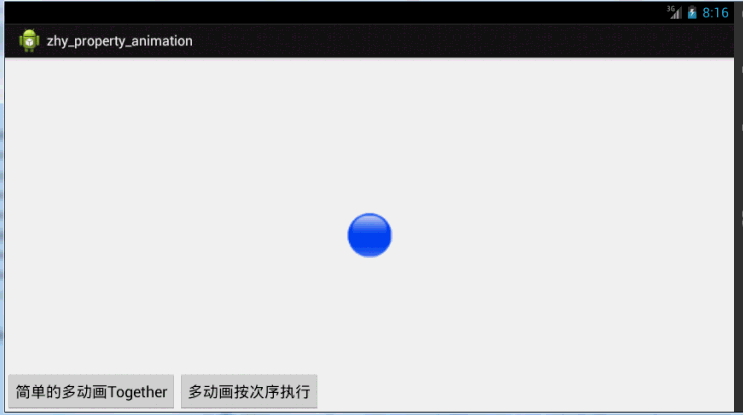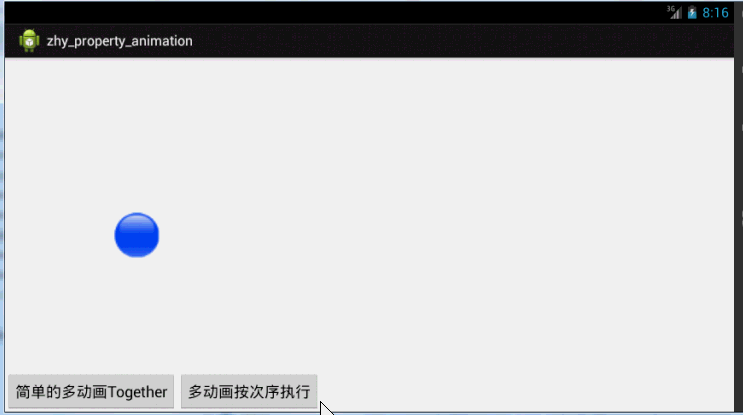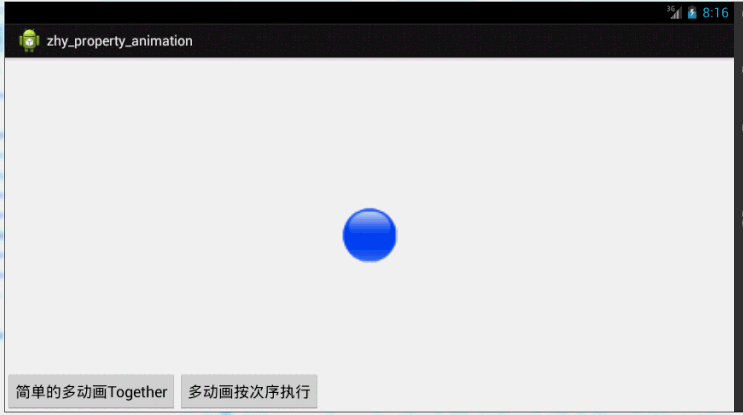
第一:使用playTogether两个动画同时执行,当然还有playSequentially依次执行~~
第二:如果我们有一堆动画,如何使用代码控制顺序,比如1,2同时;3在2后面;4在1之前等~就是效果2了
有一点注意:animSet.play().with();也是支持链式编程的,但是不要想着狂点,比如 animSet.play(anim1).with(anim2).before(anim3).before(anim5); 这样是不行的,系统不会根据你写的这一长串来决定先后的顺序,所以麻烦你按照上面例子的写法,多写几行:
效果图:
6、如何使用xml文件来创建属性动画
大家肯定都清楚,View Animator 、Drawable Animator都可以在anim文件夹下创建动画,然后在程序中使用,甚至在Theme中设置为属性值。当然了,属性动画其实也可以在文件中声明:
首先在res下建立animator文件夹,然后建立res/animator/scalex.xml
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:duration="1000"
- android:propertyName="scaleX"
- android:valueFrom="1.0"
- android:valueTo="2.0"
- android:valueType="floatType" >
- </objectAnimator>
代码:
- public void scaleX(View view)
- {
-
- Animator anim = AnimatorInflater.loadAnimator(this, R.animator.scalex);
- anim.setTarget(mMv);
- anim.start();
- }
使用AnimatorInflater加载动画的资源文件,然后设置目标,就ok~~是不是很简单,这只是单纯横向的放大一倍~
如果我希望纵向与横向同时缩放呢?则可以怎么定义属性文件:
- <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
- <set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:ordering="together" >
-
- <objectAnimator
- android:duration="1000"
- android:propertyName="scaleX"
- android:valueFrom="1"
- android:valueTo="0.5" >
- </objectAnimator>
- <objectAnimator
- android:duration="1000"
- android:propertyName="scaleY"
- android:valueFrom="1"
- android:valueTo="0.5" >
- </objectAnimator>
-
- </set>
使用set标签,有一个orderring属性设置为together,【还有另一个值:sequentially(表示一个接一个执行)】。
上篇博客中忽略了一个效果,就是缩放、反转等都有中心点或者轴,默认中心缩放,和中间对称线为反转线,所以我决定这个横向,纵向缩小以左上角为中心点:
代码:
-
- Animator anim = AnimatorInflater.loadAnimator(this, R.animator.scale);
- mMv.setPivotX(0);
- mMv.setPivotY(0);
-
- mMv.invalidate();
- anim.setTarget(mMv);
- anim.start();
很简单,直接给View设置pivotX和pivotY,然后调用一下invalidate,就ok了。
下面看效果图:
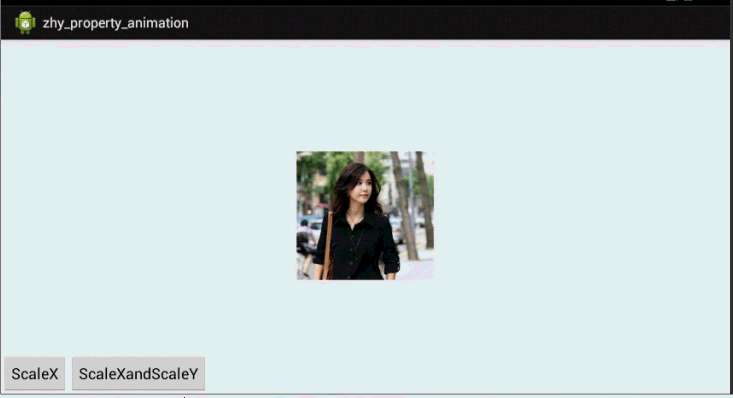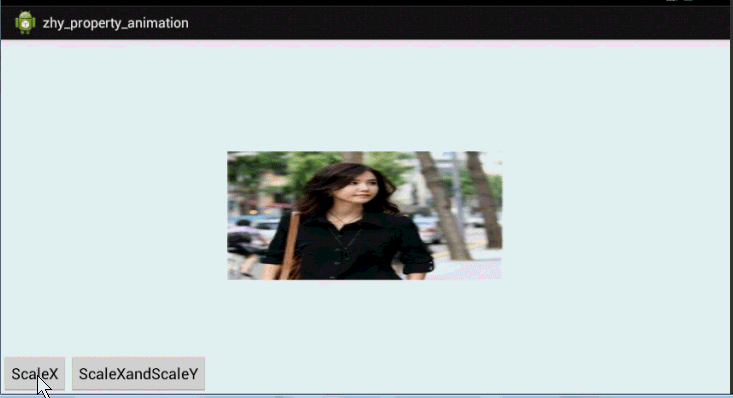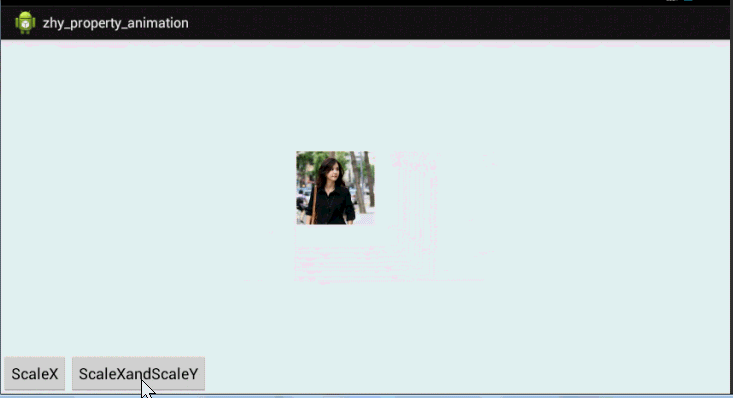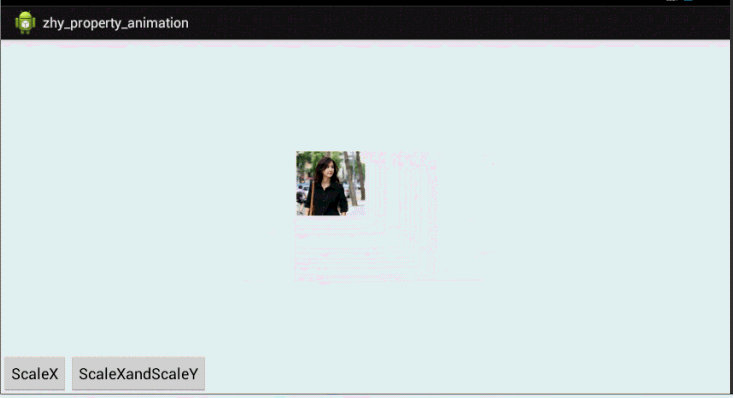
好了,通过写xml声明动画,使用set嵌套set,结合orderring属性,也基本可以实现任何动画~~上面也演示了pivot的设置。
7、布局动画(Layout Animations)
主要使用LayoutTransition为布局的容器设置动画,当容器中的视图层次发生变化时存在过渡的动画效果。
基本代码为:
- LayoutTransition transition = new LayoutTransition();
- transition.setAnimator(LayoutTransition.CHANGE_APPEARING,
- transition.getAnimator(LayoutTransition.CHANGE_APPEARING));
- transition.setAnimator(LayoutTransition.APPEARING,
- null);
- transition.setAnimator(LayoutTransition.DISAPPEARING,
- null);
- transition.setAnimator(LayoutTransition.CHANGE_DISAPPEARING,
- null);
- mGridLayout.setLayoutTransition(transition);
过渡的类型一共有四种:
LayoutTransition.APPEARING 当一个View在ViewGroup中出现时,对此View设置的动画
LayoutTransition.CHANGE_APPEARING 当一个View在ViewGroup中出现时,对此View对其他View位置造成影响,对其他View设置的动画
LayoutTransition.DISAPPEARING 当一个View在ViewGroup中消失时,对此View设置的动画
LayoutTransition.CHANGE_DISAPPEARING 当一个View在ViewGroup中消失时,对此View对其他View位置造成影响,对其他View设置的动画
LayoutTransition.CHANGE 不是由于View出现或消失造成对其他View位置造成影响,然后对其他View设置的动画。
注意动画到底设置在谁身上,此View还是其他View。
好了下面看一个综合的例子:
布局文件:
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:id="@+id/id_container"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical" >
-
- <Button
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:onClick="addBtn"
- android:text="addBtns" />
-
- <CheckBox
- android:id="@+id/id_appear"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:checked="true"
- android:text="APPEARING" />
-
- <CheckBox
- android:id="@+id/id_change_appear"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:checked="true"
- android:text="CHANGE_APPEARING" />
-
- <CheckBox
- android:id="@+id/id_disappear"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:checked="true"
- android:text="DISAPPEARING" />
-
- <CheckBox
- android:id="@+id/id_change_disappear"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:checked="true"
- android:text="CHANGE_DISAPPEARING " />
-
- </LinearLayout>
代码:
- package com.example.zhy_property_animation;
-
- import android.animation.LayoutTransition;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
- import android.view.ViewGroup;
- import android.widget.Button;
- import android.widget.CheckBox;
- import android.widget.CompoundButton;
- import android.widget.CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener;
- import android.widget.GridLayout;
-
- public class LayoutAnimaActivity extends Activity implements
- OnCheckedChangeListener
- {
- private ViewGroup viewGroup;
- private GridLayout mGridLayout;
- private int mVal;
- private LayoutTransition mTransition;
-
- private CheckBox mAppear, mChangeAppear, mDisAppear, mChangeDisAppear;
-
- @Override
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
- {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.layout_animator);
- viewGroup = (ViewGroup) findViewById(R.id.id_container);
-
- mAppear = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.id_appear);
- mChangeAppear = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.id_change_appear);
- mDisAppear = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.id_disappear);
- mChangeDisAppear = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.id_change_disappear);
-
- mAppear.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);
- mChangeAppear.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);
- mDisAppear.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);
- mChangeDisAppear.setOnCheckedChangeListener(this);
-
-
- mGridLayout = new GridLayout(this);
-
- mGridLayout.setColumnCount(5);
-
- viewGroup.addView(mGridLayout);
-
- mTransition = new LayoutTransition();
- mGridLayout.setLayoutTransition(mTransition);
-
- }
-
-
-
-
-
-
- public void addBtn(View view)
- {
- final Button button = new Button(this);
- button.setText((++mVal) + "");
- mGridLayout.addView(button, Math.min(1, mGridLayout.getChildCount()));
- button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
- {
-
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v)
- {
- mGridLayout.removeView(button);
- }
- });
- }
-
- @Override
- public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked)
- {
- mTransition = new LayoutTransition();
- mTransition.setAnimator(
- LayoutTransition.APPEARING,
- (mAppear.isChecked() ? mTransition
- .getAnimator(LayoutTransition.APPEARING) : null));
- mTransition
- .setAnimator(
- LayoutTransition.CHANGE_APPEARING,
- (mChangeAppear.isChecked() ? mTransition
- .getAnimator(LayoutTransition.CHANGE_APPEARING)
- : null));
- mTransition.setAnimator(
- LayoutTransition.DISAPPEARING,
- (mDisAppear.isChecked() ? mTransition
- .getAnimator(LayoutTransition.DISAPPEARING) : null));
- mTransition.setAnimator(
- LayoutTransition.CHANGE_DISAPPEARING,
- (mChangeDisAppear.isChecked() ? mTransition
- .getAnimator(LayoutTransition.CHANGE_DISAPPEARING)
- : null));
- mGridLayout.setLayoutTransition(mTransition);
- }
- }
效果图:
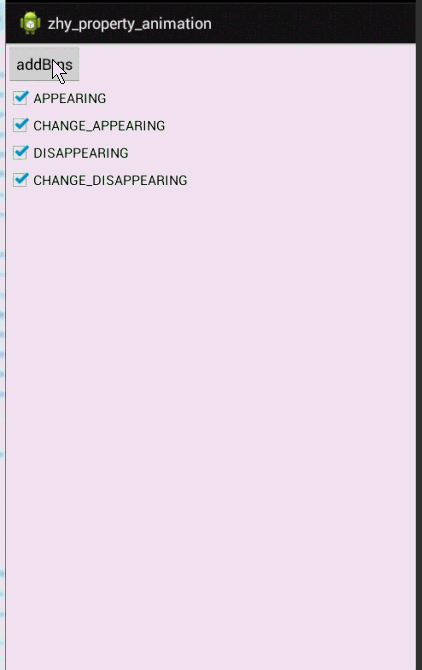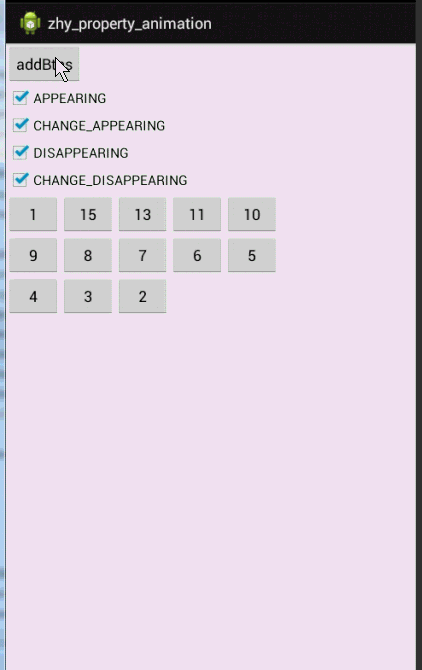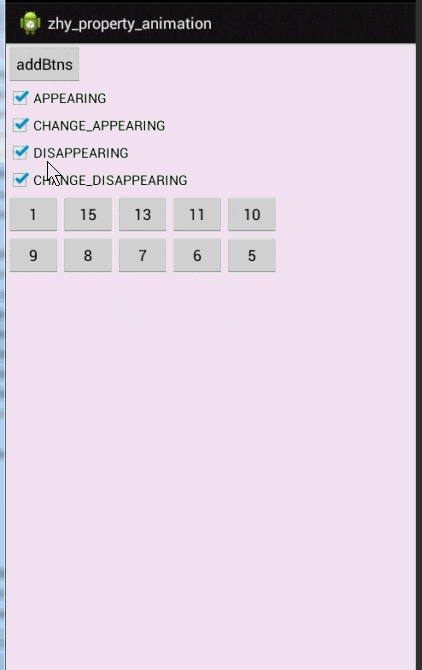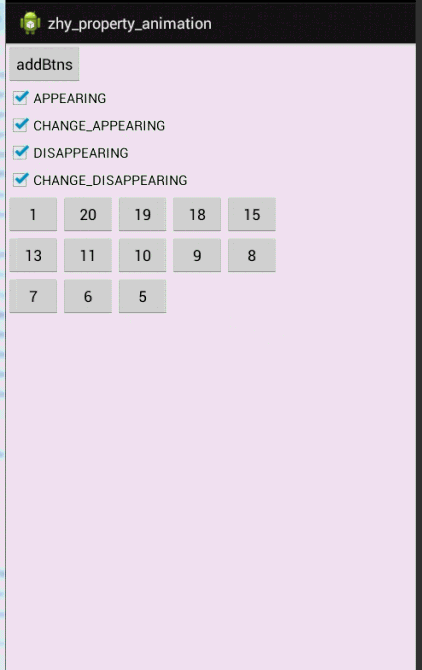
动画有点长,耐心点看,一定要注意,是对当前View还是其他Views设置的动画。
当然了动画支持自定义,还支持设置时间,比如我们修改下,添加的动画为:
- mTransition.setAnimator(LayoutTransition.APPEARING, (mAppear
- .isChecked() ? ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(this, "scaleX", 0, 1)
- : null));
则效果为:

原本的淡入,变成了宽度从中间放大的效果~~是不是还不错~~
3、View的anim方法
在SDK11的时候,给View添加了animate方法,更加方便的实现动画效果。
布局文件:
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- >
-
- <ImageView
- android:id="@+id/id_ball"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:src="@drawable/bol_blue" />
-
- <LinearLayout
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
- android:orientation="horizontal" >
-
- <Button
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:onClick="viewAnim"
- android:text="View Anim" />
-
- <Button
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:onClick="propertyValuesHolder"
- android:text="PropertyValuesHolder " />
-
-
- </LinearLayout>
-
- </RelativeLayout>
代码:
- package com.example.zhy_property_animation;
-
- import android.animation.ObjectAnimator;
- import android.animation.PropertyValuesHolder;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.util.DisplayMetrics;
- import android.util.Log;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.widget.ImageView;
-
- public class ViewAnimateActivity extends Activity
- {
- protected static final String TAG = "ViewAnimateActivity";
-
- private ImageView mBlueBall;
- private float mScreenHeight;
-
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
- {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.view_animator);
-
- DisplayMetrics outMetrics = new DisplayMetrics();
- getWindowManager().getDefaultDisplay().getMetrics(outMetrics);
- mScreenHeight = outMetrics.heightPixels;
- mBlueBall = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.id_ball);
-
- }
-
- public void viewAnim(View view)
- {
-
- mBlueBall.animate()
- .alpha(0)
- .y(mScreenHeight / 2).setDuration(1000)
-
- .withStartAction(new Runnable()
- {
- @Override
- public void run()
- {
- Log.e(TAG, "START");
- }
-
- }).withEndAction(new Runnable()
- {
-
- @Override
- public void run()
- {
- Log.e(TAG, "END");
- runOnUiThread(new Runnable()
- {
- @Override
- public void run()
- {
- mBlueBall.setY(0);
- mBlueBall.setAlpha(1.0f);
- }
- });
- }
- }).start();
- } }
简单的使用mBlueBall.animate().alpha(0).y(mScreenHeight / 2).setDuration(1000).start()就能实现动画~~不过需要SDK11,此后在SDK12,SDK16又分别添加了withStartAction和withEndAction用于在动画前,和动画后执行一些操作。当然也可以.setListener(listener)等操作。
使用ObjectAnimator实现上面的变化,我们可以使用:PropertyValueHolder
- PropertyValuesHolder pvhX = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("alpha", 1f,
- 0f, 1f);
- PropertyValuesHolder pvhY = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("y", 0,
- mScreenHeight / 2, 0);
- ObjectAnimator.ofPropertyValuesHolder(mBlueBall, pvhX, pvhY).setDuration(1000).start();
效果与上面一样。
运行结果:









