Linux进程实践(3) --进程终止与exec函数族
进程的几种终止方式
(1)正常退出
从main函数返回[return]
调用exit
调用_exit/_Exit
(2)异常退出
调用abort 产生SIGABOUT信号
由信号终止 Ctrl+C [SIGINT]
...(并不完全, 如return/pthread_exit等)
测试[exit/_exit]
- //尝试查看该程序的打印输出
- int main()
- {
- cout << "In main, pid = " << getpid();
- //去掉了endl;
- //原理:与终端关联,stdout为行缓冲,在文件中,为全缓冲;
- //详细信息请参考《UNIX环境高级编程》(第三版)8.5节, P188
- //exit(0);为C库函数,详细解释如下
- _exit(0);
- }

由图可知,系统调用_exit直接陷入内核,而C语言库函数是经过一系列的系统清理工作,再调用Linux内核的;
- int main()
- {
- cout << "In main, pid = " << getpid();
- fflush(stdout); //增加了刷新缓冲区工作
- _exit(0);
- }
小结:exit与_exit区别
1)_exit是一个系统调用,exit是一个c库函数
2)exit会执行清除I/O缓存
3)exit会执行调用终止处理程序 //终止处理程序如下
终止处理程序:atexit
- #include <stdlib.h>
- int atexit(void (*function)(void));
- //测试
- void exitHandler1(void)
- {
- cout << "If exit with exit, the function exitHandler will be called1" << endl;
- }
- void exitHandler2(void)
- {
- cout << "If exit with exit, the function exitHandler will be called2" << endl;
- }
- int main()
- {
- cout << "In main, pid = " << getpid() << endl;
- atexit(exitHandler1); //注意,先注册的后执行
- atexit(exitHandler2);
- exit(0);
- }

异常终止
- int main()
- {
- cout << "In main, pid = " << getpid() << endl;
- atexit(exitHandler1);
- atexit(exitHandler2);
- abort();
- //exit(0);
- }

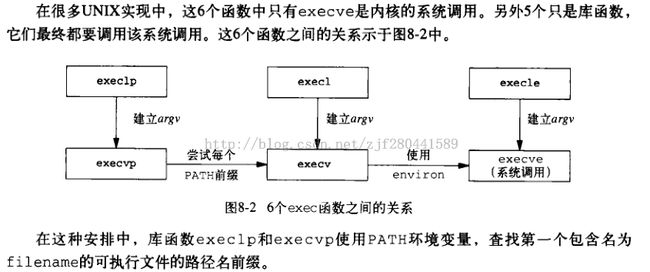
exec函数族
exec替换进程印象
在进程的创建上,Unix采用了一个独特的方法,它将进程创建与加载一个新进程映象分离。这样的好处是有更多的余地对两种操作进行管理。
当我们创建了一个进程之后,通常将子进程替换成新的进程映象,这可以用exec系列的函数来进行。当然,exec系列的函数也可以将当前进程替换掉。
exec只是用磁盘上的一个新程序替换了当前进程的正文段, 数据段, 堆段和栈段.
函数族信息
- #include <unistd.h>
- int execve(const char *filename, char *const argv[],
- char *const envp[]);
- #include <unistd.h>
- extern char **environ;
- int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...);
- int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...);
- int execle(const char *path, const char *arg,
- ..., char * const envp[]);
- int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
- int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
- int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[],
- char *const envp[]);
说明:
execl,execlp,execle(都带“l”, 代表list)的参数个数是可变的,参数以必须一个空指针结束。
execv和execvp的第二个参数是一个字符串数组(“v”代表“vector”,字符串数组必须以NULL结尾),新程序在启动时会把在argv数组中给定的参数传递到main。
名字最后一个字母是“p”的函数会搜索PATH环境变量去查找新程序的可执行文件。如果可执行文件不在PATH定义的路径上,就必须把包括子目录在内的绝对文件名做为一个参数传递给这些函数;
/*总结:l代表可变参数列表,p代表在path环境变量中搜索file文件。envp代表环境变量*/
- //示例execlp
- int main()
- {
- pid_t pid = fork();
- if (pid == 0)
- {
- if (execlp("/bin/pwd", "pwd", NULL) == -1)
- err_exit("execlp pwd error");
- }
- wait(NULL);
- pid = fork();
- if (pid == 0)
- {
- if (execlp("/bin/ls", "ls", "-l", NULL) == -1)
- err_exit("execlp ls -l error");
- }
- wait(NULL);
- cout << "After execlp" << endl;
- }
- //示例execve
- int main()
- {
- char *const args[] =
- {
- (char *)"/bin/date",
- (char *)"+%F",
- NULL
- };
- execve("/bin/date",args,NULL);
- cout << "After fork..." << endl;
- return 0;
- }
- //示例execle
- //1:main.cpp
- int main()
- {
- cout << "In main, pid = " << getpid() << endl;
- char *const environ[] =
- {
- "AA=11",
- "BB=22",
- "CC=33",
- NULL
- };
- execle("./hello","./hello",NULL,environ); //当environ填为NULL时,则什么都不传递
- cout << "After fork..." << endl;
- return 0;
- }
- extern char **environ;
- int main()
- {
- cout << "In hello, pid = " << getpid() << endl;
- cout << "environ:" << endl;
- for (int i = 0; environ[i] != NULL; ++i)
- {
- cout << "\t" << environ[i] << endl;
- }
- }
- /*
- In main, pid = 3572 //PID保持不变
- In hello, pid = 3572
- environ:
- AA=11
- BB=22
- CC=33
- */
- //示例: execve 与 execlp
- int main()
- {
- pid_t pid = fork();
- if (pid == -1)
- err_exit("fork error");
- else if (pid == 0)
- {
- //示例execve
- char *const args[] =
- {
- "echoall",
- "myarg1",
- "MY ARG2",
- NULL
- };
- char *const env[] =
- {
- "USER=unknown",
- "PATH=/tmp",
- NULL
- };
- execve("./echoall",args,env);
- }
- wait(NULL);
- pid = fork();
- if (pid == -1)
- err_exit("fork error");
- else if (pid == 0)
- {
- //示例execlp
- execlp("./echoall", "echoall", "only one arg", NULL);
- }
- wait(NULL);
- return 0;
- }
- //echoall
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- for (int i = 0; i < argc; ++i)
- printf("argv[%d]: %s\t", i , argv[i]);
- printf("\n");
- for (char **ptr = environ; *ptr != NULL; ++ ptr)
- printf("%s\n", *ptr);
- exit(0);
- }
System系统调用
system()函数调用“/bin/sh -c command”执行特定的命令,阻塞当前进程直到command命令执行完毕,system函数执行时,会调用fork、execve、waitpid等函数。
原型:
- int system(const char *command);
返回值:
如果无法启动shell运行命令,system将返回127;出现不能执行system调用的其他错误时返回-1。如果system能够顺利执行,返回那个命令的退出码。
- //示例
- int main()
- {
- system("ls -la");
- return 0;
- }
自己动手写system
- int mySystem(const char *command)
- {
- if (command == NULL)
- {
- errno = EAGAIN;
- return -1;
- }
- pid_t pid = fork();
- if (pid == -1)
- {
- perror("fork");
- exit(-1);
- }
- else if (pid == 0)
- {
- execl("/bin/sh","sh","-c",command,NULL);
- exit(127);
- }
- int status;
- waitpid(pid,&status,0);
- //wait(&status);
- return WEXITSTATUS(status);
- }
- int main()
- {
- mySystem("ls -la");
- return 0;
- }