怎么样递增的注册成对的点云
这次我们将使用Iterative Closest Point algorithm来递增的注册一系列的点云。
这个主意来自于把所有的点云转换成第一个点云的框架,通过找到每个连续点云间最好的装换,并且计算整个点云的转换。
你的数据集应该由重新排列的,在一个相同的框架里面重叠的点云构成。
/* * Software License Agreement (BSD License) * * Copyright (c) 2010, Willow Garage, Inc. * All rights reserved. * * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions * are met: * * * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. * * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above * copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following * disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided * with the distribution. * * Neither the name of Willow Garage, Inc. nor the names of its * contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived * from this software without specific prior written permission. * * THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS * "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT * LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS * FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE * COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, * INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, * BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; * LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER * CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT * LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN * ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE * POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. * * $Id$ * */ /* \author Radu Bogdan Rusu * adaptation Raphael Favier*/ #include <boost/make_shared.hpp> #include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/point_cloud.h> #include <pcl/point_representation.h> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h> #include <pcl/filters/filter.h> #include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h> #include <pcl/registration/icp.h> #include <pcl/registration/icp_nl.h> #include <pcl/registration/transforms.h> #include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField; using pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom; //convenient typedefs typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT; typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointT> PointCloud; typedef pcl::PointNormal PointNormalT; typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointNormalT> PointCloudWithNormals; // This is a tutorial so we can afford having global variables //our visualizer pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer *p; //its left and right viewports int vp_1, vp_2; //convenient structure to handle our pointclouds struct PCD { PointCloud::Ptr cloud; std::string f_name; PCD() : cloud (new PointCloud) {}; }; struct PCDComparator { bool operator () (const PCD& p1, const PCD& p2) { return (p1.f_name < p2.f_name); } }; // Define a new point representation for < x, y, z, curvature > class MyPointRepresentation : public pcl::PointRepresentation <PointNormalT> { using pcl::PointRepresentation<PointNormalT>::nr_dimensions_; public: MyPointRepresentation () { // Define the number of dimensions nr_dimensions_ = 4; } // Override the copyToFloatArray method to define our feature vector virtual void copyToFloatArray (const PointNormalT &p, float * out) const { // < x, y, z, curvature > out[0] = p.x; out[1] = p.y; out[2] = p.z; out[3] = p.curvature; } }; //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// /** \brief Display source and target on the first viewport of the visualizer * */ void showCloudsLeft(const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_target, const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_source) { p->removePointCloud ("vp1_target"); p->removePointCloud ("vp1_source"); PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> tgt_h (cloud_target, 0, 255, 0); PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> src_h (cloud_source, 255, 0, 0); p->addPointCloud (cloud_target, tgt_h, "vp1_target", vp_1); p->addPointCloud (cloud_source, src_h, "vp1_source", vp_1); PCL_INFO ("Press q to begin the registration.\n"); p-> spin(); } //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// /** \brief Display source and target on the second viewport of the visualizer * */ void showCloudsRight(const PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr cloud_target, const PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr cloud_source) { p->removePointCloud ("source"); p->removePointCloud ("target"); PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<PointNormalT> tgt_color_handler (cloud_target, "curvature"); if (!tgt_color_handler.isCapable ()) PCL_WARN ("Cannot create curvature color handler!"); PointCloudColorHandlerGenericField<PointNormalT> src_color_handler (cloud_source, "curvature"); if (!src_color_handler.isCapable ()) PCL_WARN ("Cannot create curvature color handler!"); p->addPointCloud (cloud_target, tgt_color_handler, "target", vp_2); p->addPointCloud (cloud_source, src_color_handler, "source", vp_2); p->spinOnce(); } //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// /** \brief Load a set of PCD files that we want to register together * \param argc the number of arguments (pass from main ()) * \param argv the actual command line arguments (pass from main ()) * \param models the resultant vector of point cloud datasets */ void loadData (int argc, char **argv, std::vector<PCD, Eigen::aligned_allocator<PCD> > &models) { std::string extension (".pcd"); // Suppose the first argument is the actual test model for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) { std::string fname = std::string (argv[i]); // Needs to be at least 5: .plot if (fname.size () <= extension.size ()) continue; std::transform (fname.begin (), fname.end (), fname.begin (), (int(*)(int))tolower); //check that the argument is a pcd file if (fname.compare (fname.size () - extension.size (), extension.size (), extension) == 0) { // Load the cloud and saves it into the global list of models PCD m; m.f_name = argv[i]; pcl::io::loadPCDFile (argv[i], *m.cloud); //remove NAN points from the cloud std::vector<int> indices; pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*m.cloud,*m.cloud, indices); models.push_back (m); } } } //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// /** \brief Align a pair of PointCloud datasets and return the result * \param cloud_src the source PointCloud * \param cloud_tgt the target PointCloud * \param output the resultant aligned source PointCloud * \param final_transform the resultant transform between source and target */ void pairAlign (const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_src, const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_tgt, PointCloud::Ptr output, Eigen::Matrix4f &final_transform, bool downsample = false) { // // Downsample for consistency and speed // \note enable this for large datasets PointCloud::Ptr src (new PointCloud); PointCloud::Ptr tgt (new PointCloud); pcl::VoxelGrid<PointT> grid; if (downsample) { grid.setLeafSize (0.05, 0.05, 0.05); grid.setInputCloud (cloud_src); grid.filter (*src); grid.setInputCloud (cloud_tgt); grid.filter (*tgt); } else { src = cloud_src; tgt = cloud_tgt; } // Compute surface normals and curvature PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_src (new PointCloudWithNormals); PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr points_with_normals_tgt (new PointCloudWithNormals); pcl::NormalEstimation<PointT, PointNormalT> norm_est; pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree (new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ> ()); norm_est.setSearchMethod (tree); norm_est.setKSearch (30); norm_est.setInputCloud (src); norm_est.compute (*points_with_normals_src); pcl::copyPointCloud (*src, *points_with_normals_src); norm_est.setInputCloud (tgt); norm_est.compute (*points_with_normals_tgt); pcl::copyPointCloud (*tgt, *points_with_normals_tgt); // // Instantiate our custom point representation (defined above) ... MyPointRepresentation point_representation; // ... and weight the 'curvature' dimension so that it is balanced against x, y, and z float alpha[4] = {1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0}; point_representation.setRescaleValues (alpha); // // Align pcl::IterativeClosestPointNonLinear<PointNormalT, PointNormalT> reg; reg.setTransformationEpsilon (1e-6); // Set the maximum distance between two correspondences (src<->tgt) to 10cm // Note: adjust this based on the size of your datasets reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance (0.1); // Set the point representation reg.setPointRepresentation (boost::make_shared<const MyPointRepresentation> (point_representation)); reg.setInputSource (points_with_normals_src); reg.setInputTarget (points_with_normals_tgt); // // Run the same optimization in a loop and visualize the results Eigen::Matrix4f Ti = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity (), prev, targetToSource; PointCloudWithNormals::Ptr reg_result = points_with_normals_src; reg.setMaximumIterations (2); for (int i = 0; i < 30; ++i) { PCL_INFO ("Iteration Nr. %d.\n", i); // save cloud for visualization purpose points_with_normals_src = reg_result; // Estimate reg.setInputSource (points_with_normals_src); reg.align (*reg_result); //accumulate transformation between each Iteration Ti = reg.getFinalTransformation () * Ti; //if the difference between this transformation and the previous one //is smaller than the threshold, refine the process by reducing //the maximal correspondence distance if (fabs ((reg.getLastIncrementalTransformation () - prev).sum ()) < reg.getTransformationEpsilon ()) reg.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance (reg.getMaxCorrespondenceDistance () - 0.001); prev = reg.getLastIncrementalTransformation (); // visualize current state showCloudsRight(points_with_normals_tgt, points_with_normals_src); } // // Get the transformation from target to source targetToSource = Ti.inverse(); // // Transform target back in source frame pcl::transformPointCloud (*cloud_tgt, *output, targetToSource); p->removePointCloud ("source"); p->removePointCloud ("target"); PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_tgt_h (output, 0, 255, 0); PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointT> cloud_src_h (cloud_src, 255, 0, 0); p->addPointCloud (output, cloud_tgt_h, "target", vp_2); p->addPointCloud (cloud_src, cloud_src_h, "source", vp_2); PCL_INFO ("Press q to continue the registration.\n"); p->spin (); p->removePointCloud ("source"); p->removePointCloud ("target"); //add the source to the transformed target *output += *cloud_src; final_transform = targetToSource; } /* ---[ */ int main (int argc, char** argv) { // Load data std::vector<PCD, Eigen::aligned_allocator<PCD> > data; loadData (argc, argv, data); // Check user input if (data.empty ()) { PCL_ERROR ("Syntax is: %s <source.pcd> <target.pcd> [*]", argv[0]); PCL_ERROR ("[*] - multiple files can be added. The registration results of (i, i+1) will be registered against (i+2), etc"); return (-1); } PCL_INFO ("Loaded %d datasets.", (int)data.size ()); // Create a PCLVisualizer object p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer (argc, argv, "Pairwise Incremental Registration example"); p->createViewPort (0.0, 0, 0.5, 1.0, vp_1); p->createViewPort (0.5, 0, 1.0, 1.0, vp_2); PointCloud::Ptr result (new PointCloud), source, target; Eigen::Matrix4f GlobalTransform = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity (), pairTransform; for (size_t i = 1; i < data.size (); ++i) { source = data[i-1].cloud; target = data[i].cloud; // Add visualization data showCloudsLeft(source, target); PointCloud::Ptr temp (new PointCloud); PCL_INFO ("Aligning %s (%d) with %s (%d).\n", data[i-1].f_name.c_str (), source->points.size (), data[i].f_name.c_str (), target->points.size ()); pairAlign (source, target, temp, pairTransform, true); //transform current pair into the global transform pcl::transformPointCloud (*temp, *result, GlobalTransform); //update the global transform GlobalTransform = GlobalTransform * pairTransform; //save aligned pair, transformed into the first cloud's frame std::stringstream ss; ss << i << ".pcd"; pcl::io::savePCDFile (ss.str (), *result, true); } } /* ]--- */
我们这次直接看看核心函数的功能
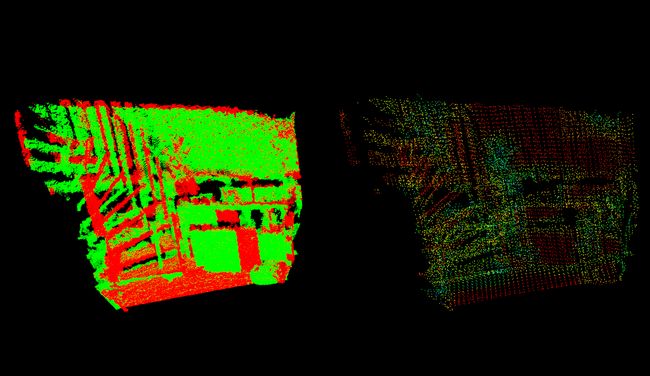
主函数检查用户输入,加载数据通过矢量的形式并且开启了一个匹配注册的过程,在找到一对点云的转换后,这一对点云将转换到第一个点云的框架。全局的转换就会被更新。
int main (int argc, char** argv) { // Load data std::vector<PCD, Eigen::aligned_allocator<PCD> > data; loadData (argc, argv, data); // Check user input if (data.empty ()) { PCL_ERROR ("Syntax is: %s <source.pcd> <target.pcd> [*]", argv[0]); PCL_ERROR ("[*] - multiple files can be added. The registration results of (i, i+1) will be registered against (i+2), etc"); return (-1); } PCL_INFO ("Loaded %d datasets.", (int)data.size ()); // Create a PCLVisualizer object p = new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer (argc, argv, "Pairwise Incremental Registration example"); p->createViewPort (0.0, 0, 0.5, 1.0, vp_1); p->createViewPort (0.5, 0, 1.0, 1.0, vp_2); PointCloud::Ptr result (new PointCloud), source, target; Eigen::Matrix4f GlobalTransform = Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity (), pairTransform; for (size_t i = 1; i < data.size (); ++i) { source = data[i-1].cloud; target = data[i].cloud; // Add visualization data showCloudsLeft(source, target); PointCloud::Ptr temp (new PointCloud); PCL_INFO ("Aligning %s (%d) with %s (%d).\n", data[i-1].f_name.c_str (), source->points.size (), data[i].f_name.c_str (), target->points.size ()); pairAlign (source, target, temp, pairTransform, true); //transform current pair into the global transform pcl::transformPointCloud (*temp, *result, GlobalTransform); //update the global transform GlobalTransform = GlobalTransform * pairTransform; //save aligned pair, transformed into the first cloud's frame std::stringstream ss; ss << i << ".pcd"; pcl::io::savePCDFile (ss.str (), *result, true); } } /* ]--- */
加载数据是很简单的。我们迭代了每个程序的参数。
对于每一个参数,我们检测是否它链接到一个pcd文件。如果是,我们就创造一个PCD对象来添加点云向量。
void loadData (int argc, char **argv, std::vector<PCD, Eigen::aligned_allocator<PCD> > &models) { std::string extension (".pcd"); // Suppose the first argument is the actual test model for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) { std::string fname = std::string (argv[i]); // Needs to be at least 5: .plot if (fname.size () <= extension.size ()) continue; std::transform (fname.begin (), fname.end (), fname.begin (), (int(*)(int))tolower); //check that the argument is a pcd file if (fname.compare (fname.size () - extension.size (), extension.size (), extension) == 0) { // Load the cloud and saves it into the global list of models PCD m; m.f_name = argv[i]; pcl::io::loadPCDFile (argv[i], *m.cloud); //remove NAN points from the cloud std::vector<int> indices; pcl::removeNaNFromPointCloud(*m.cloud,*m.cloud, indices); models.push_back (m); } } }
我们现在实际已经到了点的注册
void pairAlign (const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_src, const PointCloud::Ptr cloud_tgt, PointCloud::Ptr output, Eigen::Matrix4f &final_transform, bool downsample = false)
接下去我们进行对点云的降低采样,然后创建ICP这个对象。
一旦最好的转换找到了,我们将把它进行反转并把它放到目标点云里面。
// // Get the transformation from target to source targetToSource = Ti.inverse(); // // Transform target back in source frame pcl::transformPointCloud (*cloud_tgt, *output, targetToSource); [...] *output += *cloud_tgt; final_transform = targetToSource;
运行
/pairwise_incremental_registration capture000[1-5].pcd
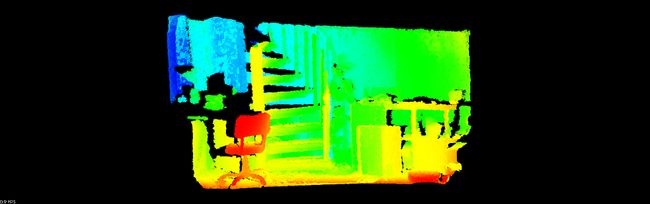
结果
运行最终结果
pcl_viewer 1.pcd 2.pcd 3.pcd 4.pcd