H.264解码过程剖析-4
x264开源工程实现H.264的视频编码,但没有提供对应的解码器。ffmpeg开源多媒体编解码集合汇集了市面上几乎所有媒体格式的编解码的源代码。其中的H264.c就是一个能正常解码x264编码码流的独立的源文件,其使用步骤也与上述的编码或解码CODEC应用案例基本相同。这一节通过自顶向下的方式,讲述H264.c如何实现H.264视频解码过程。
H264.c源文件有几千行,代码量庞大,很不便于浏览、分析和移植。同时该文件还依赖其他源文件,组织结构较复杂,实现平台由于不是基于Windows的VC++,对编译、跟踪等带来了很多不便。光盘中“chapter7\ffmpeg_h264”目录给出了一个从ffmpeg抽取的C语言实现H.264视频解码的项目案例“ffmpeg_h264”。“ffmpeg_h264”的文件功能分类明确,在VC++2005平台下编译,且剔除了MMX的支持,纯C语言工程便于嵌入式平台的移植。下面从main主函数入手,逐步深入分析实现H.264视频解码的过程。
ffmpeg_h264工程
1 解码主程序
函数main实现H.264视频解码的控制台应用,包括了解码工作的所有过程。其函数调用关系如图所示。
上述应用中,拓扑结构流程与前述的MPEG-1视频解码过程基本相同,包括了avcodec_init、avcodec_register_all、avcodec_find_decoder、avcodec_all_context、avcodec_open、avcodec_all_frame、avcodec_decode_video、avcodec_close等ffmpeg的几大公共模块,其中avcodec_decode_video是解码器的核心,在图中做了标注。main函数的代码实现如下:
int main(){ FILE * inp_file; FILE * out_file; int i; int nalLen; /*NAL 长度*/ unsigned char* Buf; /*H.264码流*/ int got_picture; /*是否解码一帧图像*/ int consumed_bytes; /*解码器消耗的码流长度*/ int cnt=0; AVCodec *codec; /* 编解码CODEC*/ AVCodecContext *c; /* 编解码CODEC context*/ AVFrame *picture; /* 解码后的图像*/ /*输出和输出的文件*/ inp_file = fopen("e:\\bitavc\\busn_dsp.264", "rb"); out_file = fopen("e:\\bitavc\\dsp_dec.yuv", "wb"); nalLen = 0; /*分配内存,并初始化为0*/ Buf = (unsigned char*)calloc ( 500*1024, sizeof(char)); /*CODEC的初始化,初始化一些常量表*/ avcodec_init(); /*注册CODEC*/ avcodec_register_all(); /*查找 H264 CODEC*/ codec = avcodec_find_decoder(CODEC_ID_H264); if (!codec) return 0; /*初始化CODEC的默认参数*/ c = avcodec_alloc_context(); if(!c) return 0; /*1. 打开CODEC,这里初始化H.264解码器,调用decode_init本地函数*/ if (avcodec_open(c, codec) < 0) return 0; /*为AVFrame申请空间,并清零*/ picture = avcodec_alloc_frame(); if(!picture) return 0; /*循环解码*/ while(!feof(inp_file)) { /*从码流中获得一个NAL包*/ nalLen = getNextNal(inp_file, Buf); /*2. NAL解码,调用decode_frame本地函数*/ consumed_bytes= avcodec_decode_video(c, picture, &got_picture, Buf, nalLen); cnt++; /*输出当前的解码信息*/ printf("No:=%4d, length=%4d\n",cnt,consumed_bytes); /*返回<0 表示解码数据头,返回>0,表示解码一帧图像*/ if(consumed_bytes > 0) { /*从二维空间中提取解码后的图像*/ for(i=0; i<c->height; i++) fwrite(picture->data[0] + i * picture->linesize[0], 1, c->width, out_file); for(i=0; i<c->height/2; i++) fwrite(picture->data[1] + i * picture->linesize[1], 1, c->width/2, out_file); for(i=0; i<c->height/2; i++) fwrite(picture->data[2] + i * picture->linesize[2], 1, c->width/2, out_file); } } /*关闭文件*/ if(inp_file) fclose(inp_file); if(out_file) fclose(out_file); /*3. 关闭CODEC,释放资源,调用decode_end本地函数*/ if(c) { avcodec_close(c); av_free(c); c = NULL; } /*释放AVFrame空间*/ if(picture) { av_free(picture); picture = NULL; } /*释放内存*/ if(Buf) { free(Buf); Buf = NULL; } return 0; } 上述过程中,步骤1~8为ffmpeg在编码或解码等工作时的基本步骤。分析函数名称的特点会发现,CODEC的处理函数均以“avcodec_”为前缀。为了使用H.264解码器CODEC,首先需要定义CODEC,如下所示:
AVCodec h264_decoder = {
"h264", //解码器名称
CODEC_TYPE_VIDEO, //解码器类型,视频
CODEC_ID_H264, //解码器ID
sizeof(H264Context), //解码器上下文大小
decode_init, //解码器初始化
NULL, //编码器,禁用
decode_end, //销毁解码器
decode_frame, //解码
0, //CODEC兼容性,禁用
};因此,实际的解码处理模块采用decode_init、decode_frame、decode_end三个本地函数来实现。而main函数中使用公共的函数接口访问这里的函数。实例如注册CODEC。
/** * simple call to register all the codecs. */
void avcodec_register_all(void)
{
static int inited = 0;
if (inited != 0)
return;
inited = 1;
register_avcodec(&h264_decoder);
//av_register_codec_parser(&h264_parser);
}所以,CODEC解码器实际调用H264.c中的三个子函数来完成解码任务。
2 配置解码器
上述是注册和定义解码器,其中ffmpeg的avcodec_open模块打开CODEC,并实际调用decode_init本地函数创建、配置H.264解码器。
int avcodec_open(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVCodec *codec)
{
int ret;
if(avctx->codec) return -1; /*CODEC指针有效*/
avctx->codec = codec; /*指向codec*/
avctx->codec_id = codec->id; /*CODEC 名称*/
avctx->frame_number = 0;
#if 1
if (codec->priv_data_size > 0) {/*CODEC的结构体不为0*/
/*为CODEC申请空间*/
avctx->priv_data = av_mallocz(codec->priv_data_size);
if (!avctx->priv_data)
return -ENOMEM;
} else {
avctx->priv_data = NULL;
}
#endif
/*CODEC的初始化*/
ret = avctx->codec->init(avctx);
/*若失败,则释放context结构体*/
if (ret < 0) {
av_freep(&avctx->priv_data);
return ret;
}
return 0;
}上述实现解码器的初始化,包括设置默认的解码参数、图像宽度和高度、I帧预测函数的初始化等;然后是像素格式为I420的平面模式;最后为可变长度编码VLC表的初始化。
3 H.264视频解码
视频解码模块由ffmpeg的avcodec_decode_video()来完成。由于H.264码流是经过了NAL打包,所以在调用解码器之前,需要调用getNextNal()模块以从码流文件中读取分析一个NAL包,即寻找NAL的头标识0x00 00 00 01,然后将两个头标识之间的数据传给VCL解码器avcodec_decode_video()实现解码:
/** * decode a frame. * @param buf bitstream buffer, must be FF_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE larger then the actual read bytes * because some optimized bitstream readers read 32 or 64 bit at once and could read over the end * @param buf_size the size of the buffer in bytes * @param got_picture_ptr zero if no frame could be decompressed, Otherwise, it is non zero * @return -1 if error, otherwise return the number of * bytes used. */
int avcodec_decode_video(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *picture,
int *got_picture_ptr,
uint8_t *buf, int buf_size)
{
int ret;
/*当前没有解码的标识*/
*got_picture_ptr= 0;
/*H.264解码*/
ret = avctx->codec->decode(avctx, //解码器上下文
picture, //解码的图像
got_picture_ptr, //图像解码标识
buf, //待解码的码流
buf_size); //码流长度
/*如果使用了MMX等指令,需要调用该函数*/
emms_c();
/*解码的是图像,不是头数据*/
if (*got_picture_ptr)
avctx->frame_number++;
return ret;
}
上述的VCL解码器根据传入的码流及长度调用ffmpeg的公共函数接口decode,即实际的解码函数decode_frame实现H.264的VCL解码。若解码过程中使用了MMX指令且退出后又要使用float/double类型,则需要使用emms指令(Empty mmx state)清空MMX状态,以恢复以前的CPU状态。实际的解码函数decode_frame实现VCL的真正解码工作,该模块的拓扑结构如图所示。
图中的decode_frame解码视频编码层VCL数据,模块核心是decode_nal_units。
static int decode_frame(AVCodecContext *avctx, /*解码器上下文*/
void *data, /*解码图像的结构*/
int *data_size, /*结构大小*/
uint8_t *buf, /*码流空间*/
int buf_size) /*码流长度*/
{
H264Context *h = avctx->priv_data; /*解码器上下文*/
MpegEncContext *s = &h->s; /*MpegEncContext指针*/
AVFrame *pict = data; /*图像空间*/
int buf_index; /*当前的码流位置*/
s->flags= avctx->flags; /*CODEC的标志*/
s->flags2= avctx->flags2; /*CODEC的标志2*/
if (buf_size == 0) { /*码流不为空*/
return 0;
}
/*截断的码流解码*/
if(s->flags&CODEC_FLAG_TRUNCATED){
int next= find_frame_end(&s->parse_context, buf, buf_size);
if( ff_combine_frame(&s->parse_context, next, &buf, &buf_size) < 0 )
return buf_size;
}
/*码流中特别数据的解码*/
if(s->avctx->extradata_size && s->picture_number==0){
if(0 < decode_nal_units(h, s->avctx->extradata, s->avctx->extradata_size) )
return -1;
}
/*正常的解码*/
buf_index=decode_nal_units(h, buf, buf_size);
if(buf_index < 0)
return -1;
#if 0 /*B帧*/
if(s->pict_type==B_TYPE || s->low_delay){
*pict= *(AVFrame*)&s->current_picture;
} else {
*pict= *(AVFrame*)&s->last_picture;
}
#endif
/*没有解码输出图像,解码头数据*/
if(!s->current_picture_ptr){
av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "error, NO frame\n");
return -1;
}
/*有解码图像输出*/
*pict= *(AVFrame*)&s->current_picture;
assert(pict->data[0]); /*表明解码输出*/ *data_size = sizeof(AVFrame); /*返回当前消耗的码流*/ return get_consumed_bytes(s, buf_index, buf_size); } 上述解码过程中,首先如果是截断的码流,则将解码后的码流与一帧图像组合;判断码流中是否有特殊的数据如Huffman表等;然后正常解码NAL;最后输出解码图像及消耗的码流长度。其中核心是NAL解码decode_nal_units。
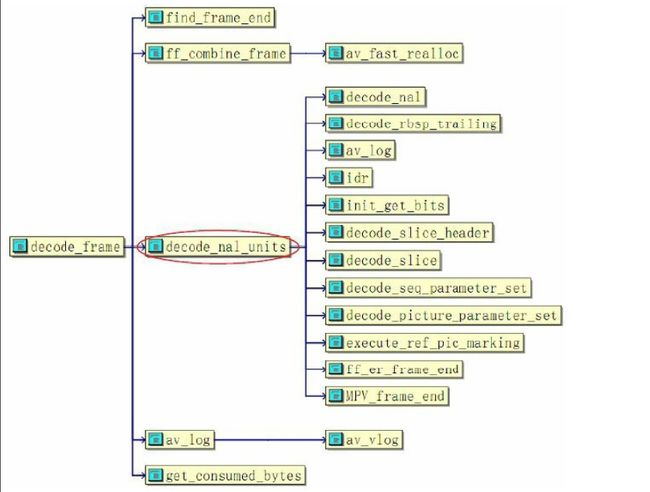
4 NAL包解码
H.264码流中的基本单位表现为各个独立的NAL包,因此解码的处理函数
decode_nal_units()实现解码NAL包。该模块的拓扑结构如图所示:
上图中的NAL解码主要包括序列参数集SPS、图像参数集PPS、即时解码刷新片IDR、图像片头Slice_header、图像片Slice等结构的解码decode_nal_units实现过程如下:
/*NAL单元解码*/
static int decode_nal_units(H264Context *h, //解码器句柄
uint8_t *buf, //码流空间
int buf_size){ //码流长度
MpegEncContext * const s = &h->s;
AVCodecContext * const avctx= s->avctx;
int buf_index=0;
/*循环解码*/
for(;;){
int consumed; //消耗的长度
int dst_length; //目标长度
int bit_length; //比特长度
uint8_t *ptr; //临时指针
/*搜索前缀开始码:0x 00 00 01*/
for(; buf_index + 3 < buf_size; buf_index++){
/*在第一次搜索时,必须成功,否则认为码流出错*/
if(buf[buf_index] == 0 && buf[buf_index+1] == 0 && buf[buf_index+2] == 1)
break;
}
/*后续仍然有数据*/
if(buf_index+3 >= buf_size) break;
/*索引后移*/
buf_index+=3;
/*网络抽象层NAL解包*/
ptr= decode_nal(h, buf + buf_index, &dst_length, &consumed, buf_size - buf_index);
if(ptr[dst_length - 1] == 0) dst_length--;
/*确定码流的精确的结束位置*/
bit_length= 8*dst_length - decode_rbsp_trailing(ptr + dst_length - 1);
if(s->avctx->debug&FF_DEBUG_STARTCODE){
av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "NAL %d at %d length %d\n", h->nal_unit_type, buf_index, dst_length);
}
/*索引后移*/
buf_index += consumed;
if( s->hurry_up == 1 && h->nal_ref_idc == 0 )
continue;
switch(h->nal_unit_type){ /*根据NAL类型执行解码*/
case NAL_IDR_SLICE: //IDR片
idr(h); //
case NAL_SLICE: //图像片SLICE解码
/*初始化码流指针*/
init_get_bits(&s->gb, ptr, bit_length);
h->intra_gb_ptr=
h->inter_gb_ptr= &s->gb;
s->data_partitioning = 0;
/*解码图像片的头*/
if(decode_slice_header(h) < 0) return -1;
if(h->redundant_pic_count==0 && s->hurry_up < 5 )
/*****************图像片数据解码*/
decode_slice(h);
/*****************图像片数据解码*/
break;
case NAL_DPA: //数据分区A
init_get_bits(&s->gb, ptr, bit_length);
h->intra_gb_ptr=
h->inter_gb_ptr= NULL;
s->data_partitioning = 1;
/*解码图像片的头*/
if(decode_slice_header(h) < 0) return -1;
break;
case NAL_DPB: //数据分区B
init_get_bits(&h->intra_gb, ptr, bit_length);
h->intra_gb_ptr= &h->intra_gb;
break;
case NAL_DPC: //数据分区C
init_get_bits(&h->inter_gb, ptr, bit_length);
h->inter_gb_ptr= &h->inter_gb;
if(h->redundant_pic_count==0 && h->intra_gb_ptr && s->data_partitioning && s->hurry_up < 5 )
decode_slice(h);
break;
case NAL_SEI: //补充增强信息
break;
case NAL_SPS: //序列参数集SPS
/*初始化码流*/
init_get_bits(&s->gb, ptr, bit_length);
/*SPS解码*/
decode_seq_parameter_set(h);
if(s->flags& CODEC_FLAG_LOW_DELAY)
s->low_delay=1;
avctx->has_b_frames= !s->low_delay;
printf("decode SPS\n");
break;
case NAL_PPS: //图像参数集PPS
/*初始化码流*/
init_get_bits(&s->gb, ptr, bit_length);
/*PPS解码*/
decode_picture_parameter_set(h);
printf("decode PPS\n");
break;
case NAL_PICTURE_DELIMITER:
break;
case NAL_FILTER_DATA:
break;
default:
av_log(avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Unknown NAL code: %d\n", h->nal_unit_type);
}
/*图像帧类型*/
s->current_picture.pict_type= s->pict_type;
/*关键帧类型初始化*/
s->current_picture.key_frame= s->pict_type == I_TYPE;
}
/*没有解码输出图像*/
if(!s->current_picture_ptr) return buf_index; //no frame
/*修改图像序列POC*/
h->prev_frame_num_offset= h->frame_num_offset;
h->prev_frame_num= h->frame_num;
if(s->current_picture_ptr->reference){
h->prev_poc_msb= h->poc_msb;
h->prev_poc_lsb= h->poc_lsb;
}
/*标记参考帧*/
if(s->current_picture_ptr->reference)
execute_ref_pic_marking(h, h->mmco, h->mmco_index);
else
assert(h->mmco_index==0);
/*码流容错结束*/
ff_er_frame_end(s);
/*解码一帧完毕,扩展图像*/
MPV_frame_end(s);
return buf_index;
}
上述过程首先解析得到NAL的前缀码0x 00 00 01,然后函数decode_nal()实现NAL解包,根据解析到的NAL类型执行不同的解码:SPS、PPS、IDR、Slice_header、Slice等,解码结束后,标记参考帧、码流容错结束,最后扩展解码图像的边界。NAL解码的核心是函数decode_slice()。
5 图像片解码
H.264的编码是以片Slice为单位的,片的类型又分为I_TYPE、P_TYPE和B_TYPE等。ffmpeg的H.264解码器在这一级的图像片解码中是不分片类型的,即统一处理。因为H.264的熵编码分为CABAC和CAVLC两种,故对应的熵解码也区别处理。模块decode_slice()实现图像片的解码功能,该函数的拓扑结构如图所示。
上图中图像片解码分为算术熵解码CABAC和Huffman熵解码CAVLC两大类型,每种又主要包括熵解码、反量化和反变换、运动补偿等功能。decode_slice()模块的实现过程如下:
/*解码图像片*/
static int decode_slice(H264Context *h){
MpegEncContext * const s = &h->s;
const int part_mask= s->partitioned_frame ? (AC_END|AC_ERROR) : 0x7F;
s->mb_skip_run= -1;
/*CABAC解码*/
if( h->pps.cabac ) {
int i;
/* 规整码流 */
align_get_bits( &s->gb );
/* 初始化CABAC 的状态*/
ff_init_cabac_states( &h->cabac, ff_h264_lps_range, ff_h264_mps_state, ff_h264_lps_state, 64 );
/*填充码流解码结构*/
ff_init_cabac_decoder( &h->cabac,
s->gb.buffer + get_bits_count(&s->gb)/8,
( s->gb.size_in_bits - get_bits_count(&s->gb) + 7)/8);
/* 计算固定400的初始状态 */
for( i= 0; i < 399; i++ ) {
int pre;
if( h->slice_type == I_TYPE )
pre = clip( ((cabac_context_init_I[i][0] * s->qscale) >>4 ) + cabac_context_init_I[i][1], 1, 126 );
else
pre = clip( ((cabac_context_init_PB[h->cabac_init_idc][i][0] * s->qscale) >>4 ) + cabac_context_init_PB[h->cabac_init_idc][i][1], 1, 126 );
if( pre <= 63 )
h->cabac_state[i] = 2 * ( 63 - pre ) + 0;
else
h->cabac_state[i] = 2 * ( pre - 64 ) + 1;
}
for(;;){
/*CABAC 宏块熵解码、反量化*/
int ret = decode_mb_cabac(h);
/*返回片的结尾标记*/
int eos = get_cabac_terminate( &h->cabac ); /* End of Slice flag */
/*反变换、运动补偿等*/
hl_decode_mb(h);
/* 帧或场自适应切换 */
if( ret >= 0 && h->sps.mb_aff ) { //FIXME optimal? or let mb_decode decode 16x32 ?
s->mb_y++;
ret = decode_mb_cabac(h);
eos = get_cabac_terminate( &h->cabac );
hl_decode_mb(h);
s->mb_y--;
}
/*解码出错或已经解码到结尾*/
if( ret < 0 || h->cabac.bytestream > h->cabac.bytestream_end + 1) {
av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "error while decoding MB %d %d\n", s->mb_x, s->mb_y);
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x, s->mb_y, (AC_ERROR|DC_ERROR|MV_ERROR)&part_mask);
return -1;
}
/*一行宏块解码结束,为提高Cache效率,保留水平方向内容*/
if( ++s->mb_x >= s->mb_width ) {
s->mb_x = 0;
ff_draw_horiz_band(s, 16*s->mb_y, 16);
/*根据宏块数目,解码结束*/
if( ++s->mb_y >= s->mb_height ) {
tprintf("slice end %d %d\n", get_bits_count(&s->gb), s->gb.size_in_bits);
}
}
/*解码完毕,添加图像片*/
if( eos || s->mb_y >= s->mb_height ) {
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x-1, s->mb_y, (AC_END|DC_END|MV_END)&part_mask);
return 0;
}
}
}
else{
/*CAVLC解码*/
for(;;){
/*一个宏块熵解码、反量化*/
int ret = decode_mb_cavlc(h);
/*反变换、运动补偿等*/
hl_decode_mb(h);
/*宏块自适应帧、场编码*/
if(ret>=0 && h->sps.mb_aff){ //FIXME optimal? or let mb_decode decode 16x32 ?
s->mb_y++;
ret = decode_mb_cavlc(h);
hl_decode_mb(h);
s->mb_y--;
}
/*解码出错*/
if(ret<0){
av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "error while decoding MB %d %d\n", s->mb_x, s->mb_y);
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x, s->mb_y, (AC_ERROR|DC_ERROR|MV_ERROR)&part_mask);
return -1;
}
/*一行宏块解码结束,为提高Cache效率,保留水平区*/
if(++s->mb_x >= s->mb_width){
s->mb_x=0;
ff_draw_horiz_band(s, 16*s->mb_y, 16);
/*根据宏块数目,解码完毕,添加图像片*/
if(++s->mb_y >= s->mb_height){
tprintf("slice end %d %d\n", get_bits_count(&s->gb), s->gb.size_in_bits);
if(get_bits_count(&s->gb) == s->gb.size_in_bits ) {
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x-1, s->mb_y, (AC_END|DC_END|MV_END)&part_mask);
return 0;
}else{
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x, s->mb_y, (AC_END|DC_END|MV_END)&part_mask);
return -1;
}
}
}
/*码流消耗完毕,添加图像片*/
if(get_bits_count(&s->gb) >= s->gb.size_in_bits && s->mb_skip_run<=0){
if(get_bits_count(&s->gb) == s->gb.size_in_bits ){
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x-1, s->mb_y, (AC_END|DC_END|MV_END)&part_mask);
return 0;
}else{
ff_er_add_slice(s, s->resync_mb_x, s->resync_mb_y, s->mb_x, s->mb_y, (AC_ERROR|DC_ERROR|MV_ERROR)&part_mask);
return -1;
}
}
}
}
return -1; //正常情况下不会达到这里
}
上述的图像片解码中,熵解码包含了反量化处理,预测、反变换和运动补偿在模块hl_decode_mb()中实现。解码中以宏块为循环单位,根据宏块递增量以及码流消耗的情况决定解码结束,记录解码中的出错状态,填充图像块,正常或报错返回。
6 宏块熵解码
熵编码是完全可逆的无损编码,H.264码流首先经过熵解码、反量化形成DCT变换的系数。在H.264编码中熵编码包括上下文自适应的可变长度编码CAVLC、上下文自适应的二进制算术编码CABAC。相对应的熵解码也包括decode_mb_cavlc和decode_mb_cabac两种,这两个模块的执行过程非常类似,限于篇幅,这里只介绍CAVLC的解码decode_mb_ cavlc,该函数的拓扑结构如图所示。
在实施熵解码前,需要首先确定宏块的预测模式Mode或运动向量MV,以及块编码模式CBP,然后再分别对亮度和色度执行熵解码。宏块的CAVLC模块的运行过程如下。在介绍实现过程中,省略了部分无关紧要的代码,重点从功能上详细说明实现步骤。具体内容详见光盘中的“ffmpeg_h264\cavlc.c”文件。
/** * decodes a macroblock * @returns 0 if ok, AC_ERROR / DC_ERROR / MV_ERROR if an error is noticed */ int decode_mb_cavlc(H264Context *h){ MpegEncContext * const s = &h->s; const int mb_xy= s->mb_x + s->mb_y*s->mb_stride; int mb_type, partition_count, cbp; s->dsp.clear_blocks(h->mb); //FIXME avoid if allready clear (move after skip handlong? tprintf("pic:%d mb:%d/%d\n", h->frame_num, s->mb_x, s->mb_y); cbp = 0; /* avoid warning. FIXME: find a solution without slowing down the code */ if(h->slice_type != I_TYPE && h->slice_type != SI_TYPE){ if(s->mb_skip_run==-1) s->mb_skip_run= get_ue_golomb(&s->gb); if (s->mb_skip_run--) { int mx, my; /* skip mb */ //FIXME b frame mb_type= MB_TYPE_16x16|MB_TYPE_P0L0|MB_TYPE_P1L0; memset(h->non_zero_count[mb_xy], 0, 16); memset(h->non_zero_count_cache + 8, 0, 8*5); //FIXME ugly, remove pfui if(h->sps.mb_aff && s->mb_skip_run==0 && (s->mb_y&1)==0){ h->mb_field_decoding_flag= get_bits1(&s->gb); } if(h->mb_field_decoding_flag) mb_type|= MB_TYPE_INTERLACED; fill_caches(h, mb_type); //FIXME check what is needed and what not ... pred_pskip_motion(h, &mx, &my); fill_rectangle(&h->ref_cache[0][scan8[0]], 4, 4, 8, 0, 1); fill_rectangle( h->mv_cache[0][scan8[0]], 4, 4, 8, pack16to32(mx,my), 4); write_back_motion(h, mb_type); s->current_picture.mb_type[mb_xy]= mb_type; //FIXME SKIP type s->current_picture.qscale_table[mb_xy]= s->qscale; h->slice_table[ mb_xy ]= h->slice_num; h->prev_mb_skiped= 1; return 0; } } if(h->sps.mb_aff /* && !field pic FIXME needed? */){ if((s->mb_y&1)==0) h->mb_field_decoding_flag = get_bits1(&s->gb); }else h->mb_field_decoding_flag=0; //FIXME som ed note ?! h->prev_mb_skiped= 0; mb_type= get_ue_golomb(&s->gb); if(h->slice_type == B_TYPE){ if(mb_type < 23){ partition_count= b_mb_type_info[mb_type].partition_count; mb_type= b_mb_type_info[mb_type].type; }else{ mb_type -= 23; goto decode_intra_mb; } }else if(h->slice_type == P_TYPE /*|| h->slice_type == SP_TYPE */){ if(mb_type < 5){ partition_count= p_mb_type_info[mb_type].partition_count; mb_type= p_mb_type_info[mb_type].type; }else{ mb_type -= 5; goto decode_intra_mb; } }else{ assert(h->slice_type == I_TYPE); decode_intra_mb: if(mb_type > 25){ av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "mb_type %d in %c slice to large at %d %d\n", mb_type, av_get_pict_type_char(h->slice_type), s->mb_x, s->mb_y); return -1; } partition_count=0; cbp= i_mb_type_info[mb_type].cbp; h->intra16x16_pred_mode= i_mb_type_info[mb_type].pred_mode; mb_type= i_mb_type_info[mb_type].type; } if(h->mb_field_decoding_flag) mb_type |= MB_TYPE_INTERLACED; s->current_picture.mb_type[mb_xy]= mb_type; h->slice_table[ mb_xy ]= h->slice_num; if(IS_INTRA_PCM(mb_type)){ const uint8_t *ptr; int x, y; // we assume these blocks are very rare so we dont optimize it align_get_bits(&s->gb); ptr= s->gb.buffer + get_bits_count(&s->gb); for(y=0; y<16; y++){ const int index= 4*(y&3) + 64*(y>>2); for(x=0; x<16; x++){ h->mb[index + (x&3) + 16*(x>>2)]= *(ptr++); } } for(y=0; y<8; y++){ const int index= 256 + 4*(y&3) + 32*(y>>2); for(x=0; x<8; x++){ h->mb[index + (x&3) + 16*(x>>2)]= *(ptr++); } } for(y=0; y<8; y++){ const int index= 256 + 64 + 4*(y&3) + 32*(y>>2); for(x=0; x<8; x++){ h->mb[index + (x&3) + 16*(x>>2)]= *(ptr++); } } skip_bits(&s->gb, 384); //FIXME check /fix the bitstream readers //FIXME deblock filter, non_zero_count_cache init ... memset(h->non_zero_count[mb_xy], 16, 16); s->current_picture.qscale_table[mb_xy]= s->qscale; return 0; } fill_caches(h, mb_type); //mb_pred if(IS_INTRA(mb_type)){ if(IS_INTRA4x4(mb_type)){ int i; for(i=0; i<16; i++){ const int mode_coded= !get_bits1(&s->gb); const int predicted_mode= pred_intra_mode(h, i); int mode; if(mode_coded){ const int rem_mode= get_bits(&s->gb, 3); if(rem_mode<predicted_mode) mode= rem_mode; else mode= rem_mode + 1; }else{ mode= predicted_mode; } h->intra4x4_pred_mode_cache[ scan8[i] ] = mode; } write_back_intra_pred_mode(h); if( check_intra4x4_pred_mode(h) < 0) return -1; }else{ h->intra16x16_pred_mode= check_intra_pred_mode(h, h->intra16x16_pred_mode); if(h->intra16x16_pred_mode < 0) return -1; } h->chroma_pred_mode= get_ue_golomb(&s->gb); h->chroma_pred_mode= check_intra_pred_mode(h, h->chroma_pred_mode); if(h->chroma_pred_mode < 0) return -1; }else if(partition_count==4){ int i, j, sub_partition_count[4], list, ref[2][4]; if(h->slice_type == B_TYPE){ for(i=0; i<4; i++){ h->sub_mb_type[i]= get_ue_golomb(&s->gb); if(h->sub_mb_type[i] >=13){ av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "B sub_mb_type %d out of range at %d %d\n", h->sub_mb_type[i], s->mb_x, s->mb_y); return -1; } sub_partition_count[i]= b_sub_mb_type_info[ h->sub_mb_type[i] ].partition_count; h->sub_mb_type[i]= b_sub_mb_type_info[ h->sub_mb_type[i] ].type; } }else{ assert(h->slice_type == P_TYPE || h->slice_type == SP_TYPE); //FIXME SP correct ? for(i=0; i<4; i++){ h->sub_mb_type[i]= get_ue_golomb(&s->gb); if(h->sub_mb_type[i] >=4){ av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "P sub_mb_type %d out of range at %d %d\n", h->sub_mb_type[i], s->mb_x, s->mb_y); return -1; } sub_partition_count[i]= p_sub_mb_type_info[ h->sub_mb_type[i] ].partition_count; h->sub_mb_type[i]= p_sub_mb_type_info[ h->sub_mb_type[i] ].type; } } for(list=0; list<2; list++){ const int ref_count= IS_REF0(mb_type) ? 1 : h->ref_count[list]; if(ref_count == 0) continue; for(i=0; i<4; i++){ if(IS_DIR(h->sub_mb_type[i], 0, list) && !IS_DIRECT(h->sub_mb_type[i])){ ref[list][i] = get_te0_golomb(&s->gb, ref_count); //FIXME init to 0 before and skip? }else{ //FIXME ref[list][i] = -1; } } } for(list=0; list<2; list++){ const int ref_count= IS_REF0(mb_type) ? 1 : h->ref_count[list]; if(ref_count == 0) continue; for(i=0; i<4; i++){ h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i] ]=h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i]+1 ]= h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i]+8 ]=h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[4*i]+9 ]= ref[list][i]; if(IS_DIR(h->sub_mb_type[i], 0, list) && !IS_DIRECT(h->sub_mb_type[i])){ const int sub_mb_type= h->sub_mb_type[i]; const int block_width= (sub_mb_type & (MB_TYPE_16x16|MB_TYPE_16x8)) ? 2 : 1; for(j=0; j<sub_partition_count[i]; j++){ int mx, my; const int index= 4*i + block_width*j; int16_t (* mv_cache)[2]= &h->mv_cache[list][ scan8[index] ]; pred_motion(h, index, block_width, list, h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[index] ], &mx, &my); mx += get_se_golomb(&s->gb); my += get_se_golomb(&s->gb); tprintf("final mv:%d %d\n", mx, my); if(IS_SUB_8X8(sub_mb_type)){ mv_cache[ 0 ][0]= mv_cache[ 1 ][0]= mv_cache[ 8 ][0]= mv_cache[ 9 ][0]= mx; mv_cache[ 0 ][1]= mv_cache[ 1 ][1]= mv_cache[ 8 ][1]= mv_cache[ 9 ][1]= my; }else if(IS_SUB_8X4(sub_mb_type)){ mv_cache[ 0 ][0]= mv_cache[ 1 ][0]= mx; mv_cache[ 0 ][1]= mv_cache[ 1 ][1]= my; }else if(IS_SUB_4X8(sub_mb_type)){ mv_cache[ 0 ][0]= mv_cache[ 8 ][0]= mx; mv_cache[ 0 ][1]= mv_cache[ 8 ][1]= my; }else{ assert(IS_SUB_4X4(sub_mb_type)); mv_cache[ 0 ][0]= mx; mv_cache[ 0 ][1]= my; } } }else{ uint32_t *p= (uint32_t *)&h->mv_cache[list][ scan8[4*i] ][0]; p[0] = p[1]= p[8] = p[9]= 0; } } } }else if(!IS_DIRECT(mb_type)){ int list, mx, my, i; //FIXME we should set ref_idx_l? to 0 if we use that later ... if(IS_16X16(mb_type)){ for(list=0; list<2; list++){ if(h->ref_count[0]>0){ if(IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, list)){ const int val= get_te0_golomb(&s->gb, h->ref_count[list]); fill_rectangle(&h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[0] ], 4, 4, 8, val, 1); } } } for(list=0; list<2; list++){ if(IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, list)){ pred_motion(h, 0, 4, list, h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[0] ], &mx, &my); mx += get_se_golomb(&s->gb); my += get_se_golomb(&s->gb); tprintf("final mv:%d %d\n", mx, my); fill_rectangle(h->mv_cache[list][ scan8[0] ], 4, 4, 8, pack16to32(mx,my), 4); } } } else if(IS_16X8(mb_type)){ for(list=0; list<2; list++){ if(h->ref_count[list]>0){ for(i=0; i<2; i++){ if(IS_DIR(mb_type, i, list)){ const int val= get_te0_golomb(&s->gb, h->ref_count[list]); fill_rectangle(&h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[0] + 16*i ], 4, 2, 8, val, 1); } } } } for(list=0; list<2; list++){ for(i=0; i<2; i++){ if(IS_DIR(mb_type, i, list)){ pred_16x8_motion(h, 8*i, list, h->ref_cache[list][scan8[0] + 16*i], &mx, &my); mx += get_se_golomb(&s->gb); my += get_se_golomb(&s->gb); tprintf("final mv:%d %d\n", mx, my); fill_rectangle(h->mv_cache[list][ scan8[0] + 16*i ], 4, 2, 8, pack16to32(mx,my), 4); } } } }else{ assert(IS_8X16(mb_type)); for(list=0; list<2; list++){ if(h->ref_count[list]>0){ for(i=0; i<2; i++){ if(IS_DIR(mb_type, i, list)){ //FIXME optimize const int val= get_te0_golomb(&s->gb, h->ref_count[list]); fill_rectangle(&h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[0] + 2*i ], 2, 4, 8, val, 1); } } } } for(list=0; list<2; list++){ for(i=0; i<2; i++){ if(IS_DIR(mb_type, i, list)){ pred_8x16_motion(h, i*4, list, h->ref_cache[list][ scan8[0] + 2*i ], &mx, &my); mx += get_se_golomb(&s->gb); my += get_se_golomb(&s->gb); tprintf("final mv:%d %d\n", mx, my); fill_rectangle(h->mv_cache[list][ scan8[0] + 2*i ], 2, 4, 8, pack16to32(mx,my), 4); } } } } } if(IS_INTER(mb_type)) write_back_motion(h, mb_type); if(!IS_INTRA16x16(mb_type)){ cbp= get_ue_golomb(&s->gb); if(cbp > 47){ av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "cbp too large (%d) at %d %d\n", cbp, s->mb_x, s->mb_y); return -1; } if(IS_INTRA4x4(mb_type)) cbp= golomb_to_intra4x4_cbp[cbp]; else cbp= golomb_to_inter_cbp[cbp]; } if(cbp || IS_INTRA16x16(mb_type)){ int i8x8, i4x4, chroma_idx; int chroma_qp, dquant; GetBitContext *gb= IS_INTRA(mb_type) ? h->intra_gb_ptr : h->inter_gb_ptr; const uint8_t *scan, *dc_scan; // fill_non_zero_count_cache(h); if(IS_INTERLACED(mb_type)){ scan= field_scan; dc_scan= luma_dc_field_scan; }else{ scan= zigzag_scan; dc_scan= luma_dc_zigzag_scan; } dquant= get_se_golomb(&s->gb); if( dquant > 25 || dquant < -26 ){ av_log(h->s.avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "dquant out of range (%d) at %d %d\n", dquant, s->mb_x, s->mb_y); return -1; } s->qscale += dquant; if(((unsigned)s->qscale) > 51){ if(s->qscale<0) s->qscale+= 52; else s->qscale-= 52; } h->chroma_qp= chroma_qp= get_chroma_qp(h, s->qscale); if(IS_INTRA16x16(mb_type)){ if( decode_residual(h, h->intra_gb_ptr, h->mb, LUMA_DC_BLOCK_INDEX, dc_scan, s->qscale, 16) < 0){ return -1; //FIXME continue if partotioned and other retirn -1 too } assert((cbp&15) == 0 || (cbp&15) == 15); if(cbp&15){ for(i8x8=0; i8x8<4; i8x8++){ for(i4x4=0; i4x4<4; i4x4++){ const int index= i4x4 + 4*i8x8; if( decode_residual(h, h->intra_gb_ptr, h->mb + 16*index, index, scan + 1, s->qscale, 15) < 0 ){ return -1; } } } }else{ fill_rectangle(&h->non_zero_count_cache[scan8[0]], 4, 4, 8, 0, 1); } }else{ for(i8x8=0; i8x8<4; i8x8++){ if(cbp & (1<<i8x8)){ for(i4x4=0; i4x4<4; i4x4++){ const int index= i4x4 + 4*i8x8; if( decode_residual(h, gb, h->mb + 16*index, index, scan, s->qscale, 16) <0 ){ return -1; } } }else{ uint8_t * const nnz= &h->non_zero_count_cache[ scan8[4*i8x8] ]; nnz[0] = nnz[1] = nnz[8] = nnz[9] = 0; } } } if(cbp&0x30){ for(chroma_idx=0; chroma_idx<2; chroma_idx++) if( decode_residual(h, gb, h->mb + 256 + 16*4*chroma_idx, CHROMA_DC_BLOCK_INDEX, chroma_dc_scan, chroma_qp, 4) < 0){ return -1; } } if(cbp&0x20){ for(chroma_idx=0; chroma_idx<2; chroma_idx++){ for(i4x4=0; i4x4<4; i4x4++){ const int index= 16 + 4*chroma_idx + i4x4; if( decode_residual(h, gb, h->mb + 16*index, index, scan + 1, chroma_qp, 15) < 0){ return -1; } } } }else{ uint8_t * const nnz= &h->non_zero_count_cache[0]; nnz[ scan8[16]+0 ] = nnz[ scan8[16]+1 ] =nnz[ scan8[16]+8 ] =nnz[ scan8[16]+9 ] = nnz[ scan8[20]+0 ] = nnz[ scan8[20]+1 ] =nnz[ scan8[20]+8 ] =nnz[ scan8[20]+9 ] = 0; } }else{ uint8_t * const nnz= &h->non_zero_count_cache[0]; fill_rectangle(&nnz[scan8[0]], 4, 4, 8, 0, 1); nnz[ scan8[16]+0 ] = nnz[ scan8[16]+1 ] =nnz[ scan8[16]+8 ] =nnz[ scan8[16]+9 ] = nnz[ scan8[20]+0 ] = nnz[ scan8[20]+1 ] =nnz[ scan8[20]+8 ] =nnz[ scan8[20]+9 ] = 0; } s->current_picture.qscale_table[mb_xy]= s->qscale; write_back_non_zero_count(h); return 0; } 上述过程中,首先判断宏块是否被编码,如果未被编码则跳过解码,并返回。若已被编码,从码流中读取宏块类型,并根据帧类型(I/P/B)修改宏块模式mb_type等信息。若该宏块为PCM模式编码,则直接从码流中读取Y/U/V分量的像素值,然后返回。接下来的过程主要分为预测模式和熵解码。宏块预测模式包括Intra块的Mode预测、Inter块的MV预测。Intra块的Mode预测又分为:4×4的Intra亮度宏块预测、16×16的Intra亮度宏块预测、色度预测。Inter块的4个子块MV预测又分为:8×8、8×4、4×8、4×4的MV预测。Inter块的非直接的MV预测又分为:16×16、16×8、8×16块的预测。模式及运动向量预测完毕后,从码流中读取并计算CBP。若CBP非零,首先是宏块的亮度分量的熵解码,包括Intra16×16块熵解码、其他块模式的熵解码,然后是宏块的色度分量的熵解码。若CBP为零,非零数目缓存清空。实际上,在熵解decode_mb_cavlc中还包括了反量化操作,所以经过该步骤后得到图像数据(本身或残差)的DCT系数,接下来就是反变换和运动补偿处理。
7 宏块解码
模块hl_decode_mb包括I帧的预测、DCT反变换、P帧的运动补偿及反变换、环路滤波等。该函数的拓扑结构如图所示。
由于I帧的预测为函数指针数组,所以在上述的结构中没有体现出来。该函数的代码实现过程如下:
/*宏块解码*/
static void hl_decode_mb(H264Context *h){
MpegEncContext * const s = &h->s;
const int mb_x= s->mb_x; //宏块宽度
const int mb_y= s->mb_y; //宏块高度
const int mb_xy= mb_x + mb_y*s->mb_stride; //宏块序号
const int mb_type= s->current_picture.mb_type[mb_xy];//宏块模式
uint8_t *dest_y, *dest_cb, *dest_cr;
int linesize, uvlinesize /*dct_offset*/;
int i;
if(!s->decode)
return;
/*指向当前的图像空间,以保存解码图像*/
dest_y = s->current_picture.data[0] + (mb_y * 16* s->linesize ) + mb_x * 16;
dest_cb = s->current_picture.data[1] + (mb_y * 8 * s->uvlinesize) + mb_x * 8;
dest_cr = s->current_picture.data[2] + (mb_y * 8 * s->uvlinesize) + mb_x * 8;
/*图像场解码*/
if (h->mb_field_decoding_flag) { /*交织编码标志*/
linesize = s->linesize * 2;
uvlinesize = s->uvlinesize * 2;
if(mb_y&1){
dest_y -= s->linesize*15;
dest_cb-= s->linesize*7;
dest_cr-= s->linesize*7;
}
} else {
linesize = s->linesize;
uvlinesize = s->uvlinesize;
}
/************************************ Intra块 *********************************/
if(IS_INTRA(mb_type)){
/*环路滤波启用,改变宏块的边界*/
if(h->deblocking_filter)
xchg_mb_border(h, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, linesize, uvlinesize, 1);
if(!(s->flags&CODEC_FLAG_GRAY)){ /*不是灰度图像*/
/*两个色度分量预测*/
h->pred8x8[ h->chroma_pred_mode ](dest_cb, uvlinesize);
h->pred8x8[ h->chroma_pred_mode ](dest_cr, uvlinesize);
}
/*4x4的intra模式*/
if(IS_INTRA4x4(mb_type)){
if(!s->encoding){
for(i=0; i<16; i++){
uint8_t * const ptr= dest_y + h->block_offset[i];
uint8_t *topright= ptr + 4 - linesize;
const int topright_avail= (h->topright_samples_available<<i)&0x8000;
const int dir= h->intra4x4_pred_mode_cache[ scan8[i] ];
int tr;
/*右上块*/
if(!topright_avail){
tr= ptr[3 - linesize]*0x01010101;
topright= (uint8_t*) &tr;
}else if(i==5 && h->deblocking_filter){
tr= *(uint32_t*)h->top_border[mb_x+1];
topright= (uint8_t*) &tr;
}
/*4x4预测*/
h->pred4x4[ dir ](ptr, topright, linesize);
/*具有非零系数*/
if(h->non_zero_count_cache[ scan8[i] ]){
/*反DCT变换,并补偿*/
if(s->codec_id == CODEC_ID_H264)
h264_add_idct_c(ptr, h->mb + i*16, linesize);
else
;//svq3_add_idct_c(ptr, h->mb + i*16, linesize, s->qscale, 0);
}
}
}
}else{/*非4x4模式,16x16模式*/
/*16x16的亮度预测*/
h->pred16x16[ h->intra16x16_pred_mode ](dest_y , linesize);
/*16个直流分量DC反变换、反量化*/
if(s->codec_id == CODEC_ID_H264)
h264_luma_dc_dequant_idct_c(h->mb, s->qscale);
else
;//svq3_luma_dc_dequant_idct_c(h->mb, s->qscale);
}
/*存在deblock,处理块边界*/
if(h->deblocking_filter)
xchg_mb_border(h, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, linesize, uvlinesize, 0);
}else {
/*************************** Inter块运动补偿***************************/
hl_motion(h, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr,
s->dsp.put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab, s->dsp.put_h264_chroma_pixels_tab,
s->dsp.avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab, s->dsp.avg_h264_chroma_pixels_tab);
}
if(!IS_INTRA4x4(mb_type)){/*非4x4 的Intra模式*/
for(i=0; i<16; i++){
if(h->non_zero_count_cache[ scan8[i] ] || h->mb[i*16]){ //FIXME benchmark weird rule, & below
uint8_t * const ptr= dest_y + h->block_offset[i];
/*反变换,并补偿*/
h264_add_idct_c(ptr, h->mb + i*16, linesize);
}
}
}
/*色度IDCT、IQUANT*/
if(!(s->flags&CODEC_FLAG_GRAY)){ /*不是灰度图像*/
/*色度的直流分量IDCT/IQUANT*/
chroma_dc_dequant_idct_c(h->mb + 16*16, h->chroma_qp);
chroma_dc_dequant_idct_c(h->mb + 16*16+4*16, h->chroma_qp);
/*色度的交流分量IDCT*/
if(s->codec_id == CODEC_ID_H264){
/*色度U的反变换,并补偿*/
for(i=16; i<16+4; i++){
if(h->non_zero_count_cache[ scan8[i] ] || h->mb[i*16]){
uint8_t * const ptr= dest_cb + h->block_offset[i];
h264_add_idct_c(ptr, h->mb + i*16, uvlinesize);
}
}
/*色度V的反变换,并补偿*/
for(i=20; i<20+4; i++){
if(h->non_zero_count_cache[ scan8[i] ] || h->mb[i*16]){
uint8_t * const ptr= dest_cr + h->block_offset[i];
h264_add_idct_c(ptr, h->mb + i*16, uvlinesize);
}
}
}else{
}
}
/*deblock 的后处理,备份宏块的边界*/
if(h->deblocking_filter) {
backup_mb_border(h, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, linesize, uvlinesize);
/*环路滤波*/
filter_mb(h, mb_x, mb_y, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr);
}
}
上述的宏块解码包括Intra宏块及Inter宏块的预测、反变换和补偿等。具体包括:两个色度的预测、4×4Intra块预测(预测、反变换、补偿)、16×16Intra块预测(预测、16个DC分量的反变换、反量化);Inter宏块的运动补偿(hl_motion);非Intra4×4的反变换、补偿。色度的IDCT/IQUANT:色度U的DC分量的反变换、反量化;色度V的DC分量的反变换、反量化;色度U的反变换、补偿;色度V的反变换、补偿。最后是环路滤波。Inter块的运动补偿是P帧的解码处理重点,接下来重点介绍模块hl_motion。
8 运动补偿
运动补偿是根据从码流中读取的运动向量信息,定位参考帧的具体位置,然后将从码流中解码得到的残差补偿(加)到参考帧中,获得最后的解码图像。该模块的拓扑结构如图所示。
该模块的拓扑结构较简单,但是从解码器系统的CPU资源占用来说,却是耗时最多的模块。运动补偿的实质是参考帧图像的插值操作,包括一个亮度和两个色度分量的运动补偿。hl_motion模块中由于使用了函数指针变量,所以有部分函数在上述的拓扑结构中未体现出来。
/*Inter块的运动补偿*/
static void hl_motion(H264Context *h, uint8_t *dest_y, uint8_t *dest_cb, uint8_t *dest_cr,
qpel_mc_func (*qpix_put)[16], h264_chroma_mc_func (*chroma_put),
qpel_mc_func (*qpix_avg)[16], h264_chroma_mc_func (*chroma_avg)){
MpegEncContext * const s = &h->s;
const int mb_xy= s->mb_x + s->mb_y*s->mb_stride;
const int mb_type= s->current_picture.mb_type[mb_xy];
assert(IS_INTER(mb_type));
if(IS_16X16(mb_type)){
mc_part(h, 0, 1, 8, 0, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, 0, 0,
qpix_put[0], chroma_put[0], qpix_avg[0], chroma_avg[0],
IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, 1));
}else if(IS_16X8(mb_type)){
mc_part(h, 0, 0, 4, 8, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, 0, 0,
qpix_put[1], chroma_put[0], qpix_avg[1], chroma_avg[0],
IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, 1));
mc_part(h, 8, 0, 4, 8, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, 0, 4,
qpix_put[1], chroma_put[0], qpix_avg[1], chroma_avg[0],
IS_DIR(mb_type, 1, 0), IS_DIR(mb_type, 1, 1));
}else if(IS_8X16(mb_type)){
mc_part(h, 0, 0, 8, 8*s->linesize, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, 0, 0,
qpix_put[1], chroma_put[1], qpix_avg[1], chroma_avg[1],
IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, 1));
mc_part(h, 4, 0, 8, 8*s->linesize, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, 4, 0,
qpix_put[1], chroma_put[1], qpix_avg[1], chroma_avg[1],
IS_DIR(mb_type, 1, 0), IS_DIR(mb_type, 1, 1));
}else{
int i;
assert(IS_8X8(mb_type));
for(i=0; i<4; i++){
const int sub_mb_type= h->sub_mb_type[i];
const int n= 4*i;
int x_offset= (i&1)<<2;
int y_offset= (i&2)<<1;
if(IS_SUB_8X8(sub_mb_type)){
mc_part(h, n, 1, 4, 0, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, x_offset, y_offset,
qpix_put[1], chroma_put[1], qpix_avg[1], chroma_avg[1],
IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 1));
}else if(IS_SUB_8X4(sub_mb_type)){
mc_part(h, n , 0, 2, 4, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, x_offset, y_offset,
qpix_put[2], chroma_put[1], qpix_avg[2], chroma_avg[1],
IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 1));
mc_part(h, n+2, 0, 2, 4, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, x_offset, y_offset+2,
qpix_put[2], chroma_put[1], qpix_avg[2], chroma_avg[1],
IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 1));
}else if(IS_SUB_4X8(sub_mb_type)){
mc_part(h, n , 0, 4, 4*s->linesize, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, x_offset, y_offset,
qpix_put[2], chroma_put[2], qpix_avg[2], chroma_avg[2],
IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 1));
mc_part(h, n+1, 0, 4, 4*s->linesize, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, x_offset+2, y_offset,
qpix_put[2], chroma_put[2], qpix_avg[2], chroma_avg[2],
IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 1));
}else{
int j;
assert(IS_SUB_4X4(sub_mb_type));
for(j=0; j<4; j++){
int sub_x_offset= x_offset + 2*(j&1);
int sub_y_offset= y_offset + (j&2);
mc_part(h, n+j, 1, 2, 0, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, sub_x_offset, sub_y_offset,
qpix_put[2], chroma_put[2], qpix_avg[2], chroma_avg[2],
IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 1));
}
}
}
}
}
上述运动补偿过程中,Inter块以不同的宏块大小16×16、16×8、8×16、8×8、8×4、4×8、4×4等块方式进行运动补偿。补偿函数mc_part模块以不同的参考帧list0和list1而分为两种类型。宏块索引定位当前解码图像的目标位置,运动向量定位参考帧pic->data的准确的补偿位置。应用qpix_op(put_h264_qpel16_mcxx_c,
avg_h264_qpel16_mcxx_c,其中xx表示00、10、20、ƒ、23、33等16种组合情况)函数指针数组的成员实施亮度Y的运动补偿,chroma_op(put_h264_chroma_mc8_c、avg_h264_chroma_mc8_c)函数指针实施U/V的运动补偿。
9 其他模块
H.264解码器除了上述介绍的主要功能模块外,还有其他函数模块,如序列参数集SPS解码decode_seq_parameter_set、图像参数集PPS解码
decode_picture_parameter_set、图像片头解decode_slice_header、块反变换h264_add_idct_c、环路滤波filter_mb等。去除块效应的环路滤波由于解码每一帧图像均调用该函数,所以环路滤波对解码图像的质量、解码器的工作效率有重要的影响。filter_mb模块本身是对图像的独立的像素点进行非规整的处理,难以实现高效的优化。ffmpeg并没有提供filter_mb模块的直接的汇编优化,而实际上,x264工程提供了与处理过程类似的环路滤波功能,且实现了MMX/SSE的汇编优化。有兴趣的读
者可以借鉴或研究x264算法的去除块效应的优化方法。
另外,较为底层的处理模块,如插值运动补偿dsputil文件,实现了MMX汇编语言的优化h264dsp_mmx.c。这些数字信号处理模块通常是对图像数据的规整处理,实现数据打包、单指令多数据SIMD的高效运行。鉴于篇幅,这里不再详细展开介绍,感兴趣的读者请参见ffmpeg主目录下的\libavcodec\x86中的汇编(*.asm)或C文件(嵌入式汇编)。