android bluetooth 移植相关注意事项
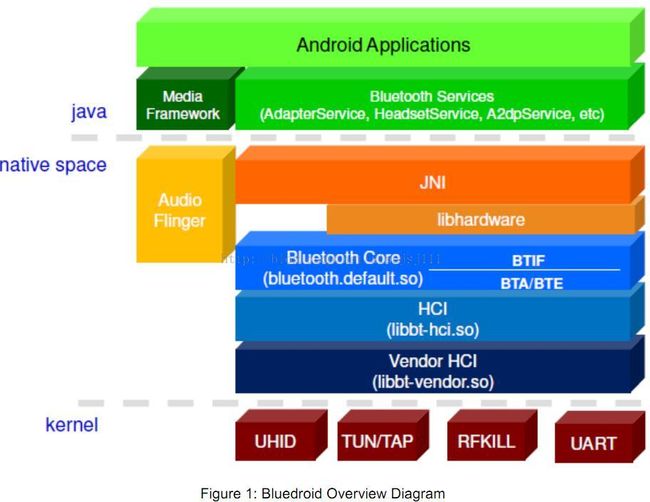
bluedroid的通用架构框图:
由上图可知,bluedroid包含如下的核心组件:
Bluetooth core stack library
HCI library
Vendor Specific HCI library
UART, RFKILL,TUN/TAP and UHID device drivers
移植过程
基于android上bluedroid上的蓝牙移植涉及到文件有:
bluetooth.apk
bludroid协议栈涉及到的库:
bluetooth.default.so
libbt-hci.so
libbt-utils.so
libbt-vendor.so
audio.a2dp.default.so
android.hardware.bluetooth.xml:该文件用于控制是否显示蓝牙的设置界面,位于/etc/permissions/目录下
bluetooth.default.so依赖于libbt-hci.so、libbt-utils.so、libbt-vendor.so等动态库,该库是蓝牙bluedroid协议栈的核心,该库的核心文件bluetooth.c实现了蓝牙的HAL层。
该硬件抽象层对应的接口定义如下(hardware/include/hardware/bluetooth.h):
- /** NOTE: By default, no profiles are initialized at the time of init/enable.
- * Whenever the application invokes the 'init' API of a profile, then one of
- * the following shall occur:
- *
- * 1.) If Bluetooth is not enabled, then the Bluetooth core shall mark the
- * profile as enabled. Subsequently, when the application invokes the
- * Bluetooth 'enable', as part of the enable sequence the profile that were
- * marked shall be enabled by calling appropriate stack APIs. The
- * 'adapter_properties_cb' shall return the list of UUIDs of the
- * enabled profiles.
- *
- * 2.) If Bluetooth is enabled, then the Bluetooth core shall invoke the stack
- * profile API to initialize the profile and trigger a
- * 'adapter_properties_cb' with the current list of UUIDs including the
- * newly added profile's UUID.
- *
- * The reverse shall occur whenever the profile 'cleanup' APIs are invoked
- */
- /** Represents the standard Bluetooth DM interface. */
- typedef struct {
- /** set to sizeof(bt_interface_t) */
- size_t size;
- /**
- * Opens the interface and provides the callback routines
- * to the implemenation of this interface.
- */
- int (*init)(bt_callbacks_t* callbacks );
- /** Enable Bluetooth. */
- int (*enable)(void);
- /** Disable Bluetooth. */
- int (*disable)(void);
- /** This ensures the chip is Powered ON to support other radios in the combo chip.
- * If the chip is OFF it set the chip to ON, if it is already ON it just increases the radio ref count
- * to keep track when to Power OFF */
- int (*enableRadio)(void);
- /** This decreases radio ref count and ensures that chip is Powered OFF
- * when the radio ref count becomes zero. */
- int (*disableRadio)(void);
- /** Closes the interface. */
- void (*cleanup)(void);
- /** Get all Bluetooth Adapter properties at init */
- int (*get_adapter_properties)(void);
- /** Get Bluetooth Adapter property of 'type' */
- int (*get_adapter_property)(bt_property_type_t type);
- /** Set Bluetooth Adapter property of 'type' */
- /* Based on the type, val shall be one of
- * bt_bdaddr_t or bt_bdname_t or bt_scanmode_t etc
- */
- int (*set_adapter_property)(const bt_property_t *property);
- /** Get all Remote Device properties */
- int (*get_remote_device_properties)(bt_bdaddr_t *remote_addr);
- /** Get Remote Device property of 'type' */
- int (*get_remote_device_property)(bt_bdaddr_t *remote_addr,
- bt_property_type_t type);
- /** Set Remote Device property of 'type' */
- int (*set_remote_device_property)(bt_bdaddr_t *remote_addr,
- const bt_property_t *property);
- /** Get Remote Device's service record for the given UUID */
- int (*get_remote_service_record)(bt_bdaddr_t *remote_addr,
- bt_uuid_t *uuid);
- /** Start SDP to get remote services */
- int (*get_remote_services)(bt_bdaddr_t *remote_addr);
- /** Start Discovery */
- int (*start_discovery)(void);
- /** Cancel Discovery */
- int (*cancel_discovery)(void);
- /** Create Bluetooth Bonding */
- int (*create_bond)(const bt_bdaddr_t *bd_addr);
- /** Remove Bond */
- int (*remove_bond)(const bt_bdaddr_t *bd_addr);
- /** Cancel Bond */
- int (*cancel_bond)(const bt_bdaddr_t *bd_addr);
- /** BT Legacy PinKey Reply */
- /** If accept==FALSE, then pin_len and pin_code shall be 0x0 */
- int (*pin_reply)(const bt_bdaddr_t *bd_addr, uint8_t accept,
- uint8_t pin_len, bt_pin_code_t *pin_code);
- /** BT SSP Reply - Just Works, Numeric Comparison and Passkey
- * passkey shall be zero for BT_SSP_VARIANT_PASSKEY_COMPARISON &
- * BT_SSP_VARIANT_CONSENT
- * For BT_SSP_VARIANT_PASSKEY_ENTRY, if accept==FALSE, then passkey
- * shall be zero */
- int (*ssp_reply)(const bt_bdaddr_t *bd_addr, bt_ssp_variant_t variant,
- uint8_t accept, uint32_t passkey);
- /** Get Bluetooth profile interface */
- const void* (*get_profile_interface) (const char *profile_id);
- /** Bluetooth Test Mode APIs - Bluetooth must be enabled for these APIs */
- /* Configure DUT Mode - Use this mode to enter/exit DUT mode */
- int (*dut_mode_configure)(uint8_t enable);
- /* Send any test HCI (vendor-specific) command to the controller. Must be in DUT Mode */
- int (*dut_mode_send)(uint16_t opcode, uint8_t *buf, uint8_t len);
- /* Send service level Authorization response */
- int (*authorize_response)(const bt_bdaddr_t *bd_addr, bt_service_id_t service_id,
- uint8_t authorize, uint8_t save_settings);
- /** Get FM module interface */
- const void* (*get_fm_interface) ();
- /** BLE Test Mode APIs */
- /* opcode MUST be one of: LE_Receiver_Test, LE_Transmitter_Test, LE_Test_End */
- int (*le_test_mode)(uint16_t opcode, uint8_t *buf, uint8_t len);
- } bt_interface_t;
而bluetooth services和bluetooth JNI编译出来的结果就是bluetooth.apk, bluetooth services透过bluetooth JNI,bluetooth JNI透过硬件抽象层,直接调用到bluedroid的核心协议栈,而核心协议栈通过uart driver,rfkill driver,UHID,TUN等vfs文件接口直接调用到内核空间的驱动。
audio.a2dp.default.so文件是音频模块针对ad2p的硬件抽象层的实现,供音频模块来控制a2dp的通路切换,声音和音量的控制。注意该模块跟BT_PROFILE_ADVANCED_AUDIO_ID模块的关系。
libbt-vendor.so是需要根据特定的蓝牙芯片去客制化实现的。
具体该移植库(libbt-vendor.so),需要实现如下的通用接口(external/bluetooth/bluedroid/hci/include/bt_vendor_lib.h):
- /*
- * Bluetooth Host/Controller VENDOR Interface
- */
- typedef struct {
- /** Set to sizeof(bt_vndor_interface_t) */
- size_t size;
- /*
- * Functions need to be implemented in Vendor libray (libbt-vendor.so).
- */
- /**
- * Caller will open the interface and pass in the callback routines
- * to the implemenation of this interface.
- */
- int (*init)(const bt_vendor_callbacks_t* p_cb, unsigned char *local_bdaddr);
- /** Vendor specific operations */
- int (*op)(bt_vendor_opcode_t opcode, void *param);
- /** Closes the interface */
- void (*cleanup)(void);
- } bt_vendor_interface_t;
在以上结构体中,其中大部份的工作是由int (*op)(bt_vendor_opcode_t opcode, void *param);函数实现,该函数更具OPCODE操作码的不同,一般通过switch语句来实现。
各个OPCODE操作码对应的功能说明如下:(external/bluetooth/bluedroid/hci/include/bt_vendor_lib.h)
- /** Vendor specific operations OPCODE */
- typedef enum {
- /* [operation]
- * Power on or off the BT Controller.
- * [input param]
- * A pointer to int type with content of bt_vendor_power_state_t.
- * Typecasting conversion: (int *) param.
- * [return]
- * 0 - default, don't care.
- * [callback]
- * None.
- */
- BT_VND_OP_POWER_CTRL,
- /* [operation]
- * Perform any vendor specific initialization or configuration
- * on the BT Controller. This is called before stack initialization.
- * [input param]
- * None.
- * [return]
- * 0 - default, don't care.
- * [callback]
- * Must call fwcfg_cb to notify the stack of the completion of vendor
- * specific initialization once it has been done.
- */
- BT_VND_OP_FW_CFG,
- /* [operation]
- * Perform any vendor specific SCO/PCM configuration on the BT Controller.
- * This is called after stack initialization.
- * [input param]
- * None.
- * [return]
- * 0 - default, don't care.
- * [callback]
- * Must call scocfg_cb to notify the stack of the completion of vendor
- * specific SCO configuration once it has been done.
- */
- BT_VND_OP_SCO_CFG,
- /* [operation]
- * Open UART port on where the BT Controller is attached.
- * This is called before stack initialization.
- * [input param]
- * A pointer to int array type for open file descriptors.
- * The mapping of HCI channel to fd slot in the int array is given in
- * bt_vendor_hci_channels_t.
- * And, it requires the vendor lib to fill up the content before returning
- * the call.
- * Typecasting conversion: (int (*)[]) param.
- * [return]
- * Numbers of opened file descriptors.
- * Valid number:
- * 1 - CMD/EVT/ACL-In/ACL-Out via the same fd (e.g. UART)
- * 2 - CMD/EVT on one fd, and ACL-In/ACL-Out on the other fd
- * 4 - CMD, EVT, ACL-In, ACL-Out are on their individual fd
- * [callback]
- * None.
- */
- BT_VND_OP_USERIAL_OPEN,
- /* [operation]
- * Close the previously opened UART port.
- * [input param]
- * None.
- * [return]
- * 0 - default, don't care.
- * [callback]
- * None.
- */
- BT_VND_OP_USERIAL_CLOSE,
- /* [operation]
- * Get the LPM idle timeout in milliseconds.
- * The stack uses this information to launch a timer delay before it
- * attempts to de-assert LPM WAKE signal once downstream HCI packet
- * has been delivered.
- * [input param]
- * A pointer to uint32_t type which is passed in by the stack. And, it
- * requires the vendor lib to fill up the content before returning
- * the call.
- * Typecasting conversion: (uint32_t *) param.
- * [return]
- * 0 - default, don't care.
- * [callback]
- * None.
- */
- BT_VND_OP_GET_LPM_IDLE_TIMEOUT,
- /* [operation]
- * Enable or disable LPM mode on BT Controller.
- * [input param]
- * A pointer to uint8_t type with content of bt_vendor_lpm_mode_t.
- * Typecasting conversion: (uint8_t *) param.
- * [return]
- * 0 - default, don't care.
- * [callback]
- * Must call lpm_cb to notify the stack of the completion of LPM
- * disable/enable process once it has been done.
- */
- BT_VND_OP_LPM_SET_MODE,
- /* [operation]
- * Assert or Deassert LPM WAKE on BT Controller.
- * [input param]
- * A pointer to uint8_t type with content of bt_vendor_lpm_wake_state_t.
- * Typecasting conversion: (uint8_t *) param.
- * [return]
- * 0 - default, don't care.
- * [callback]
- * None.
- */
- BT_VND_OP_LPM_WAKE_SET_STATE,
- } bt_vendor_opcode_t;
另外还有就是蓝协议栈的配置选项,分为两种:
一种是编译时的配置选项
一种是运行时的配置选项
涉及蓝牙相关的通用配置选项有(具体配置格式的组织是 vendor specific的):
1:uart的端口号,如/dev/ttyS1, /dev/ttS2,/dev/ttyO1等等
2: uart的boadrate,如921600,460800,3000000等
3: 蓝牙固件的名字和路径
4: 是否使能LPM mode(低功耗管理模式)
5: PCM的配置
6: 如果是cob(chip on board)的蓝牙芯片,还需要指定蓝牙mac地址,如果是模块的一般直接可有从模块里读出来,则不需要该项
调试过程
硬件方面有如下的check点:
1:蓝牙的power_enable是否正常
2:蓝牙的32Khz是否正常,并且是否足够接近32768HZ
3:蓝牙的26MHZ是否正常
4:蓝牙的硬件流控双方是否支持,如果不支持,需要硬件上进行欺骗:譬如brcm的蓝牙芯片是必须需要硬件流控,而我们uart 主控的硬件流控却有问题,因此我们将brcm的蓝牙端的cts pin硬件拉地(low active),这样就是相当于告诉拨通的蓝牙芯片,我们的uart controller始终都是准备好可以接收数据的。从而实现无硬件流控也可以实现互通讯
5:uart是否需要电平转换,像我们的AP 输出的都是3.3v的电平,而拨通的蓝牙则则只能输出1.8v的电平,这样的话,就需要在拨通的rts和tx pin上接电平转换,将拨通的1.8v提升到3.3v,这样可以让我们AP能够正确检测到高电平。
6:蓝牙芯片的工作电压是否正常
软件方面的调试:
1:通过控制台命令:echo 1/0 > /sys/class/rfkill/rfill0/state再结合示波器来检测power enabe pin和32KHZ的输出/关闭是否正常
2:通过配置文件/etc/bluetooth/bt_stack.conf文件,我们可以来用来控制调试信息的显示,和蓝牙封包的保存,他能够将hci层的cmd,data,event包都保存到btsnoop_hci.log文件中,然后可以通过frontline公司的capture file viewer工具来查看封包的格式和含义。
bt_stack.conf的格式如下:
- /system/etc/bluetooth #
- /system/etc/bluetooth # cat bt_stack.conf
- # Set the phone BT device name
- #Name=Bluetooth Phone
- # Set the phone BT device COD (Class of Device)
- #Class={0x5A, 0x02, 0x0C}
- # Enable BtSnoop logging function
- # valid value : true, false
- BtSnoopLogOutput=false
- # BtSnoop log output file
- BtSnoopFileName=/sdcard/btsnoop_hci.log
- # Enable trace level reconfiguration function
- # Must be present before any TRC_ trace level settings
- TraceConf=true
- # Trace level configuration
- # BT_TRACE_LEVEL_NONE 0 ( No trace messages to be generated )
- # BT_TRACE_LEVEL_ERROR 1 ( Error condition trace messages )
- # BT_TRACE_LEVEL_WARNING 2 ( Warning condition trace messages )
- # BT_TRACE_LEVEL_API 3 ( API traces )
- # BT_TRACE_LEVEL_EVENT 4 ( Debug messages for events )
- # BT_TRACE_LEVEL_DEBUG 5 ( Full debug messages )
- # BT_TRACE_LEVEL_VERBOSE 6 ( Verbose messages ) - Currently supported for TRC_BTAPP only.
- TRC_BTM=2
- TRC_HCI=2
- TRC_L2CAP=2
- TRC_RFCOMM=2
- TRC_OBEX=2
- TRC_AVCT=2
- TRC_AVDT=2
- TRC_AVRC=2
- TRC_AVDT_SCB=2
- TRC_AVDT_CCB=2
- TRC_A2D=2
- TRC_SDP=2
- TRC_GATT=2
- TRC_SMP=2
- TRC_BTAPP=2
- TRC_PROTOCOL=0
3:上一种方法有一个局限性,那就是只能保存完整的hci包,如果hci包不完整,则不能够通过btsnoop_hci.log文件来查看,这个时候可以在hci_h4.c文件中的hci_h4_send_msg函数和userial.c文件中的userial_read_thread函数中添加array2strings()来将串口上发送和接收的数据都打印出来,这样就可以发现那些不完整的hci包。array2strings实现如下:
- int array2strings(char* header, char * array_buf, int array_len)
- {
- #if BT_DEBUG
- int n,i;
- uint8_t buf_strings[1600];
- //IS_DEBUG_ENABLE_CMD_EVENT;
- memset(buf_strings,0,sizeof(buf_strings));
- char * tmpbuf = (char * )buf_strings;
- array_len = (array_len>32)?32:array_len;
- for(i=0; i<array_len; i++)
- {
- n = sprintf(tmpbuf,"0x%x ",array_buf[i]);
- tmpbuf += n;
- }
- ALOGD("%s:len=%d %s", header, array_len, buf_strings);
- #endif
- return 0;
- }
4:涉及硬件流控的情况下,需要注意的问题:
有些ap的uart cotroller并不支持硬件流控,这样的话在蓝牙芯片初始化过程中,会碰到如下一些问题:
A: 在切换波特率时会出现错误:
原因就是有些蓝牙芯片,如brcm的6330/6476等芯片在蓝牙芯片和uart controller的波特率切换到较高的波特率时,蓝牙芯片端会忙一段时间,在这段时间里,uart controller就不能够给蓝牙芯片段发送命令或数据。
否则会导致命令或数据超时无响应。如果支持硬件流控则不会存在该问题,因为蓝牙芯片端在切换到高波特率时,在忙的时间段,他会自动将芯片的rts脚拉高,uart controller端在检测到cts变高,认为接收端在忙,
从而不会将数据发送出去,而只是将数据缓存在tty xmit buffer中,待cts变低后,再继续从tty xmit buffer取数据通过dma方式发送出去。
B: 会出现应用层已经将数据写到了/dev/ttyS1设备里,但uart controller并未将数据在tx pin上发送出来。
原因是蓝牙芯片的硬件流控极性跟ap中的uart controller定义的硬件流控的极性不一致,导致蓝牙芯片已经通知ap端,蓝牙芯片已经准备好接受数据,但由于极性不一致,所以导致ap段一直以为蓝牙芯片端没有准备好,所以一直未发送数据。出现这个钟情况时,就是第一条hci reset的命令都不能发送出去。蓝牙芯片的rx pin上也未有任何的波形。这个时候可以通过查看 state->port.tty->hw_stopped位是否为1,如果为1,说明正是由于ap的uart controller检测到硬件流控不允许所以才未发送。
uart驱动的调试
譬如在蓝牙串口出错时,我们可以命令:cat /proc/bt_debug来查看串口的如下信息:
a: uart controller的寄存器上下文
b: uart DMA rx buffer中是否还有剩余数据未通过tty_insert_flip_string_fixed_flag函数提交到tty io层会导致bluedroid层收到一个不完整的数据包,但uart controller其实已经收到了一个完整的数据包
c: uart xmit circ_buf中是否还有剩余数据未能及时发送出去
这会导致蓝牙芯片收到一个不完整的hci包,从而导致蓝牙出错
d: 在proc的文件属性中,还可以添加关键的一些变量的值,这样检测出错时,这些是否正确。
譬如打印port.icount.rx,port.icount.tx,port.icount.overrun,port.icount.parity
port.icount.cts,port.tty->hw_stopped,port.tty->stopped等。
该命令可以查看DMA tx buf和DMA rx buf中的数据内容,可以非常的方便检查数据收发是否正确
这个时候,就可以用示波器来测试下ap端的uart的cotroller的tx pin是否有波形发出来,如果有波形发送出来,但蓝牙芯片段的tx pin没有任何回复波形,则基本可以断定是一下几种问题之一:a:蓝牙电路上还有问题(请按上面的硬件check点,逐项检测)b:蓝牙芯片的上电时序还有问题(请严格按芯片的datasheet上电时许规范来配置)如果ap端的uart的cotroller的tx pin没有波形出来。那基本可以肯定,是如下问题之一:
a:硬件流控的问题(详细的见上面有关流控注意事项)
b:uart驱动的问题(不得不说,这个的调试要比其他驱动更具有挑战性)