OpenCV2.4.10之samples_cpp_tutorial-code_learn-----ImgTrans(Hough变换)
本系列学习笔记参考自OpenCV2.4.10之
opencv\sources\samples\cpp\tutorial_code和
http://www.opencv.org.cn/opencvdoc/2.3.2/html/genindex.html
在图像中我们往往需要检测出一定形状的图形,比如圆等。霍夫变换就是用来检测图像中特定形状的变换,本文将介绍霍夫变换进行检测员和霍夫变换检测线的应用。
1.HoughCircle_Demo.cpp(霍夫圆变换)
示意demo源码及注释如下:
#include "stdafx.h" //预编译头文件
/**
霍夫圆变换demo
*/
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
namespace
{
// 滑动条命名
const std::string windowName = "Hough Circle Detection Demo";
const std::string cannyThresholdTrackbarName = "Canny threshold";
const std::string accumulatorThresholdTrackbarName = "Accumulator Threshold";
const std::string usage = "Usage : tutorial_HoughCircle_Demo <path_to_input_image>\n";
// 初始值和最大值
const int cannyThresholdInitialValue = 200;
const int accumulatorThresholdInitialValue = 50;
const int maxAccumulatorThreshold = 200;
const int maxCannyThreshold = 255;
//霍夫圆检测主函数
void HoughDetection(const Mat& src_gray, const Mat& src_display, int cannyThreshold, int accumulatorThreshold)
{
// 存储检测到的圆
std::vector<Vec3f> circles;
// 霍夫圆检测函数
HoughCircles( src_gray, circles, CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, src_gray.rows/8, cannyThreshold, accumulatorThreshold, 0, 0 );
// 显示
Mat display = src_display.clone();
for( size_t i = 0; i < circles.size(); i++ )
{
Point center(cvRound(circles[i][0]), cvRound(circles[i][1]));
int radius = cvRound(circles[i][2]);
// 圆中心
circle( display, center, 3, Scalar(0,255,0), -1, 8, 0 );
// 圆周线
circle( display, center, radius, Scalar(0,0,255), 3, 8, 0 );
}
// 显示检测结果
imshow( windowName, display);
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
Mat src, src_gray;
// 读入图像
src = imread("D:\\opencv\\lena.png", 1 );
if( !src.data )
{
std::cerr<<"Invalid input image\n";
std::cout<<usage;
return -1;
}
// 转换成灰度图
cvtColor( src, src_gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY );
// 减少图像噪声以避免错误的检测
GaussianBlur( src_gray, src_gray, Size(9, 9), 2, 2 );
//初始化
int cannyThreshold = cannyThresholdInitialValue;
int accumulatorThreshold = accumulatorThresholdInitialValue;
// 创建窗口和滑动条
namedWindow( windowName, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
createTrackbar(cannyThresholdTrackbarName, windowName, &cannyThreshold,maxCannyThreshold);
createTrackbar(accumulatorThresholdTrackbarName, windowName, &accumulatorThreshold, maxAccumulatorThreshold);
// 无限循环显示
// 更新检测图像直到输入q或者Q
int key = 0;
while(key != 'q' && key != 'Q')
{
//确保这些参数不为0
cannyThreshold = std::max(cannyThreshold, 1);
accumulatorThreshold = std::max(accumulatorThreshold, 1);
//检测与显示
HoughDetection(src_gray, src, cannyThreshold, accumulatorThreshold);
key = waitKey(10);
}
return 0;
}
运行截图:

核心函数为HouguCircles,该函数用于使用霍夫曼变换在灰度图中检测圆,函数原型为:
C++:
void HoughCircles (
InputArray
image
, OutputArray
circles
, int
method
, double
dp
, double
minDist
, double
param1
=100, double
param2
=100, int
minRadius
=0, int
maxRadius
=0 )
第一个参数image为待检测的8位单通道灰度图,
第二个参数circles为检测到的圆,该参数为一个向量,其中向量每个元素为一个三个元素的向量(x,y,radius),x和y代表圆心坐标,radius代表半径。method为检测方式,当前的检测方式为CV_HOUGH_GRADIENT,即梯度检测。第三个参数dp为分辨率比率,一般为1。我的感觉是该值越大,检测到的圆越多。第四个参数minDist为检测到的圆的圆心之间的最小距离,该值太大会导致检测多个相邻的圆被错误的检测成一个。如果该值过大,会发生漏检情况。param1为canny边缘检测阈值,param2为蓄能器阈值,param3和param4为检测圆的最小半径和最大半径。
1.
HoughLines_Demo.cpp(霍夫线变换)
实例Demo源码及注释如下:
#include "stdafx.h" //预编译头文件
/**
霍夫线变化Demo
*/
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
/// 全局变量
Mat src, edges;
Mat src_gray;
Mat standard_hough, probabilistic_hough;
int min_threshold = 50;
int max_trackbar = 150;
const char* standard_name = "Standard Hough Lines Demo";
const char* probabilistic_name = "Probabilistic Hough Lines Demo";
int s_trackbar = max_trackbar;
int p_trackbar = max_trackbar;
/// 函数声明
void Standard_Hough( int, void* );
void Probabilistic_Hough( int, void* );
/**
主函数
*/
int main( int, char** argv )
{
///读入图像
src = imread("D:\\opencv\\lena.png", 1 );
///将图像转换为灰度图
cvtColor( src, src_gray, COLOR_RGB2GRAY );
///进行Canny边缘检测
Canny( src_gray, edges, 50, 200, 3 );
///创建阈值滑动条
char thresh_label[50];
sprintf( thresh_label, "Thres: %d + input", min_threshold );
namedWindow( standard_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
createTrackbar( thresh_label, standard_name, &s_trackbar, max_trackbar, Standard_Hough);
namedWindow( probabilistic_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE );
createTrackbar( thresh_label, probabilistic_name, &p_trackbar, max_trackbar, Probabilistic_Hough);
///开始
Standard_Hough(0, 0);
Probabilistic_Hough(0, 0);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
/**
* 标准霍夫变换
*/
void Standard_Hough( int, void* )
{
vector<Vec2f> s_lines;
cvtColor( edges, standard_hough, CV_GRAY2BGR );
/// 标准霍夫变换
HoughLines( edges, s_lines, 1, CV_PI/180, min_threshold + s_trackbar, 0, 0 );
/// 显示
for( size_t i = 0; i < s_lines.size(); i++ )
{
float r = s_lines[i][0], t = s_lines[i][1];
double cos_t = cos(t), sin_t = sin(t);
double x0 = r*cos_t, y0 = r*sin_t;
double alpha = 1000;
Point pt1( cvRound(x0 + alpha*(-sin_t)), cvRound(y0 + alpha*cos_t) );
Point pt2( cvRound(x0 - alpha*(-sin_t)), cvRound(y0 - alpha*cos_t) );
line( standard_hough, pt1, pt2, Scalar(255,0,0), 3, CV_AA);
}
imshow( standard_name, standard_hough );
}
/**
* @概率霍夫变换
*/
void Probabilistic_Hough( int, void* )
{
vector<Vec4i> p_lines;
cvtColor( edges, probabilistic_hough, CV_GRAY2BGR );
/// 概率霍夫变换
HoughLinesP( edges, p_lines, 1, CV_PI/180, min_threshold + p_trackbar, 30, 10 );
///显示
for( size_t i = 0; i < p_lines.size(); i++ )
{
Vec4i l = p_lines[i];
line( probabilistic_hough, Point(l[0], l[1]), Point(l[2], l[3]), Scalar(255,0,0), 3, CV_AA);
}
imshow( probabilistic_name, probabilistic_hough );
}
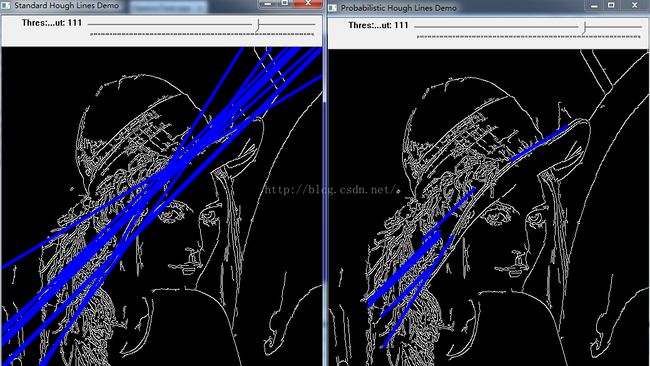
运行结果如下:
HoughLines函数的功能使用标准霍夫变换在一张二值图像中检测直线。
函数原型:
C++:
void HoughLines (
InputArray
image
, OutputArray
lines
, double
rho
, double
theta
, int
threshold
, double
srn
=0, double
stn
=0 )
image表示输入的二值图像,lines为检测到的线向量,向量每个值用 极坐标表示。rho为像素的距离分辨率。theta为像素的角度分辨率,threshold为累加器阈值
HoughLinesP函数的功能使用概率霍夫变换在一张二值图像中检测直线。
函数原型为:C++: void HoughLinesP(InputArray image, OutputArray lines, double rho, double theta, int threshold, double minLineLength=0, doublemaxLineGap=0 )参数说明参照HoughLines。