Android群英传第五章笔记·Android Scroll分析
发生滑动效果的原因
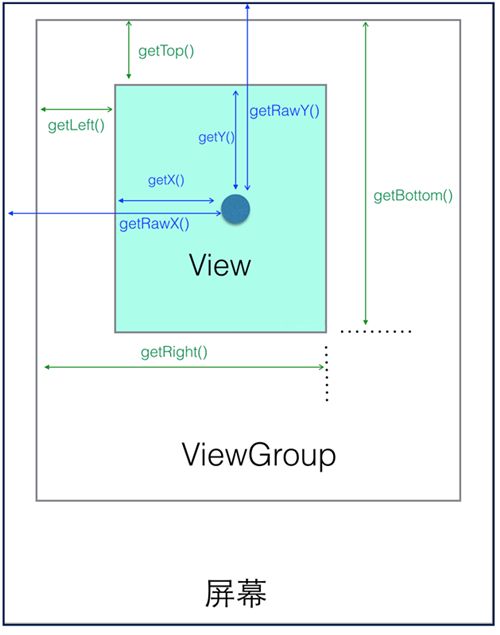
Android坐标系
View view = (View) findViewById(R.id.view);
int []location=new int[2];
view.getLocationOnScreen(location);
int x=location[0];//获取当前位置的横坐标
int y=location[1];//获取当前位置的纵坐标
触控事件使用getRawX(),getRawY()获得也是Android坐标系的坐标。
视图坐标系
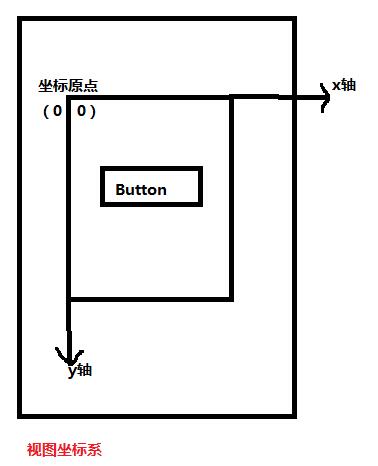
获取view相对父view的坐标(以父view左上角为坐标原点)
View view = (View) findViewById(R.id.view);
int []location=new int[2];
view.getLocationInWindow(location);
int x=location[0];//获取当前位置的横坐标
int y=location[1];//获取当前位置的纵坐标
触控事件中getX(),getY()获得坐标是视图坐标系中的坐标。
View坐标、距离API总结
实现滑动的七种方法
实现思路:触摸view时,记下当前触摸点坐标和移动后的触摸点坐标,从而获取到偏移量,并通过偏移量来修改View的坐标,从而实现滑动过程。
layout
view在绘制之前,会调用onLayout方法设置显示的位置。那么可以改变view的left,top,bottom,right值来改变view的位置。
//视图坐标方式
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int x = (int) event.getX();
int y = (int) event.getY();
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
// 记录触摸点坐标
lastX = x;
lastY = y;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
// 计算偏移量
int offsetX = x - lastX;
int offsetY = y - lastY;
// 在当前left、top、right、bottom的基础上加上偏移量
layout(getLeft() + offsetX,
getTop() + offsetY,
getRight() + offsetX,
getBottom() + offsetY);
// offsetLeftAndRight(offsetX);
// offsetTopAndBottom(offsetY);
break;
}
return true;
}
// 绝对坐标方式
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
int rawX = (int) (event.getRawX());
int rawY = (int) (event.getRawY());
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
// 记录触摸点坐标
lastX = rawX;
lastY = rawY;
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
// 计算偏移量
int offsetX = rawX - lastX;
int offsetY = rawY - lastY;
// 在当前left、top、right、bottom的基础上加上偏移量
layout(getLeft() + offsetX,
getTop() + offsetY,
getRight() + offsetX,
getBottom() + offsetY);
// 重新设置初始坐标
lastX = rawX;
lastY = rawY;
break;
}
return true;
}
offsetLeftAndRight和offsetTopAndBottom
这个方法相当于系统提供的一个左右、上下移动的API封装。只需要把计算出的偏移量传入即可完成view的移动。偏移量计算与上一个方法相同。
//同时对left和right进行偏移
offsetLeftAndRight(offsetX);
//同时对top和bottom进行偏移
offsetTopAndBottom(offsetY);
LayoutParams
LayoutParams保存了一个view的布局参数。通过改变LayoutParams的参数来改变view的位置。
// ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams layoutParams = (ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
LinearLayout.LayoutParams layoutParams = (LinearLayout.LayoutParams) getLayoutParams();
layoutParams.leftMargin = getLeft() + offsetX;
layoutParams.topMargin = getTop() + offsetY;
setLayoutParams(layoutParams);
要注意的是,通过getLayoutParams获取LayoutParams时,要根据view的父view的类型设置不同的类型。例如父布局是LinearLayout时,就可以使用LinearLayout.LayoutParams。而且,前提是要有一个父布局,不然无法获取LayoutParams。
另外一种方法是使用ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams,不需要考虑父布局的类型。
scrollTo与scrollBy
srcollTo表示将移动到一个具体的坐标点,scrollBy表示移动偏移量。
但是,scrollTo和scrollBy移动的是view的content(ViewGroup的content是子view,textview的content是文本,imageview的content是drawable对象)。所以要移动一个view时,应该使用父view的scrollTo和scrollBy方法。
另外一个问题是,父view和子view的移动方向是相反的。例如子view想要实现向右移动的效果,偏移量为10。如果调用父view的scrollBy(10,0),子view实际上是向左偏移10单位。原因是父view和子view的相对位置是相反的:父view向右时,子view相对父view是向左的。
((View) getParent()).scrollBy(-offsetX, -offsetY);
Note:书上读到这儿有点困惑:一边说scrollBy移动的是viewGroup的内容(即view),一边又说移动的是ViewGroup本身(所以才有相对位移)。
Scroller
前面提到的方法都是在触摸移动过程中不断修改view的坐标来实现移动,因此移动过程看上去是平滑的。如果要实现这样一种效果:点击一个按钮,让一个view移动。那么这个移动过程将是瞬间完成的。要使这样一个移动过程也变得平滑,就要使用Scroller类。
步骤:
1. 初始化Scroller
mScroller = new Scroller(context);
2. 重写computeScroll()方法,实现模拟滑动
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
super.computeScroll();
// 判断Scroller是否执行完毕
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
((View) getParent()).scrollTo(
mScroller.getCurrX(),
mScroller.getCurrY());
// 通过重绘来不断调用computeScroll
invalidate();
}
}
invalidate()方法的作用是循环调用computeScroll。执行流程为:invalidate()–> draw()–> computeScroll()。从而实现不断调用scrollTo移动一小段距离,实现模拟滑动的效果。当滑动完成后,循环结束。
3. startScroll开启模拟过程
使用以下两个重载方法:
public void startScroll(int startX,int startY,int dx,int dy,int duration);
public void startScroll(int startX,int startY,int dx,int dy);
在需要开始移动的方法里写入以下代码:
View viewGroup = ((View) getParent());
mScroller.startScroll(
viewGroup.getScrollX(),
viewGroup.getScrollY(),
-viewGroup.getScrollX(),
-viewGroup.getScrollY());//偏移量仍为相反数
invalidate();
属性动画
一个功能强大的类:ViewDragHelper。通过它可以实现各种不同的滑动、拖放需求。以下以实现滑动展开侧边菜单栏效果为例说明ViewDragHelper的使用。整个布局分为mMenuView和mMainView。功能为监听mMainView的触摸事件实现拖动,拖动完成后根据拖动距离使mMenuView滑动。
1. 初始化ViewDragHelper
mViewDragHelper = ViewDragHelper.create(this, callback);
第一个参数是要监听的view,通常需要时一个ViewGroup。第二个参数是一个callback回调。
2. 拦截事件
要重写事件拦截方法,将事件传递给ViewDragHelper进行处理。
@Override
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
return mViewDragHelper.shouldInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//将触摸事件传递给ViewDragHelper,此操作必不可少
mViewDragHelper.processTouchEvent(event);
return true;
}
3. 处理computeScroll()
ViewDragHelper也是使用Scroller来实现平滑移动的。因此也需要重写computeScroll方法。
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
if (mViewDragHelper.continueSettling(true)) {
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(this);
}
}
4. 处理回调callback
private ViewDragHelper.Callback callback =
new ViewDragHelper.Callback() {
// 何时开始检测触摸事件
@Override
public boolean tryCaptureView(View child, int pointerId) {
//如果当前触摸的child是mMainView时开始检测,即只有mMainView是可以被拖动的
return mMainView == child;
}
// 触摸到View后回调
@Override
public void onViewCaptured(View capturedChild,
int activePointerId) {
super.onViewCaptured(capturedChild, activePointerId);
}
// 当拖拽状态改变,比如idle,dragging
@Override
public void onViewDragStateChanged(int state) {
super.onViewDragStateChanged(state);
}
// 当位置改变的时候调用,常用与滑动时更改scale等
@Override
public void onViewPositionChanged(View changedView,
int left, int top, int dx, int dy) {
super.onViewPositionChanged(changedView, left, top, dx, dy);
}
// 处理垂直滑动
@Override
public int clampViewPositionVertical(View child, int top, int dy) {
return 0;
}
// 处理水平滑动
@Override
public int clampViewPositionHorizontal(View child, int left, int dx) {
return left;
}
// 拖动结束后调用
@Override
public void onViewReleased(View releasedChild, float xvel, float yvel) {
super.onViewReleased(releasedChild, xvel, yvel);
//手指抬起后缓慢移动到指定位置
if (mMainView.getLeft() < 500) {
//关闭菜单
//相当于Scroller的startScroll方法
mViewDragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mMainView, 0, 0);
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(DragViewGroup.this);
} else {
//打开菜单
mViewDragHelper.smoothSlideViewTo(mMainView, 300, 0);
ViewCompat.postInvalidateOnAnimation(DragViewGroup.this);
}
}
};
- clampViewPositionVertical和clampViewPositionHorizontal方法分别对应垂直和水平方向上的滑动。这两个类必须重写。因为它们默认返回0,即不滑动。clampViewPositionVertical中的参数top,代表在垂直方向上child移动的距离,dy表示比较前一次的增量。通常情况下,只需要返回top和left即可。需要更加精确的时候,才对top和left进行一些处理。
- onViewReleased在拖动结束后,即手指抬起后的处理。这里实现的是view的移动(继续展开或者撤回),实现原理和Scroller一样。
- ViewDragHelper其他回调事件举例:
- onViewCaptured():触摸到View后回调
- onViewDragStateChanged():拖曳状态改变时回调,如idle,dragging等状态
- onViewPositinChanged():位置改变时回调,常用于滑动时更改scale进行缩放等效果。
ViewDragHelper使用完整代码