AdaBoost装袋提升算法
参开资料:http://blog.csdn.net/haidao2009/article/details/7514787
更多挖掘算法:https://github.com/linyiqun/DataMiningAlgorithm
介绍
在介绍AdaBoost算法之前,需要了解一个类似的算法,装袋算法(bagging),bagging是一种提高分类准确率的算法,通过给定组合投票的方式,获得最优解。比如你生病了,去n个医院看了n个医生,每个医生给你开了药方,最后的结果中,哪个药方的出现的次数多,那就说明这个药方就越有可能性是最由解,这个很好理解。而bagging算法就是这个思想。
算法原理
而AdaBoost算法的核心思想还是基于bagging算法,但是他又一点点的改进,上面的每个医生的投票结果都是一样的,说明地位平等,如果在这里加上一个权重,大城市的医生权重高点,小县城的医生权重低,这样通过最终计算权重和的方式,会更加的合理,这就是AdaBoost算法。AdaBoost算法是一种迭代算法,只有最终分类误差率小于阈值算法才能停止,针对同一训练集数据训练不同的分类器,我们称弱分类器,最后按照权重和的形式组合起来,构成一个组合分类器,就是一个强分类器了。算法的只要过程:
1、对D训练集数据训练处一个分类器Ci
2、通过分类器Ci对数据进行分类,计算此时误差率
3、把上步骤中的分错的数据的权重提高,分对的权重降低,以此凸显了分错的数据。为什么这么做呢,后面会做出解释。
完整的adaboost算法如下
最后的sign函数是符号函数,如果最后的值为正,则分为+1类,否则即使-1类。
我们举个例子代入上面的过程,这样能够更好的理解。
adaboost的实现过程:
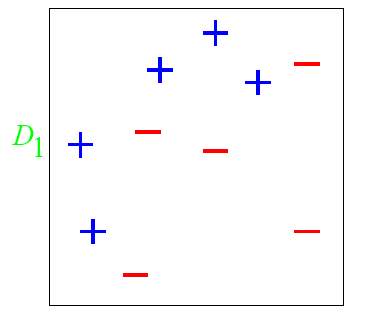
图中,“+”和“-”分别表示两种类别,在这个过程中,我们使用水平或者垂直的直线作为分类器,来进行分类。
第一步:
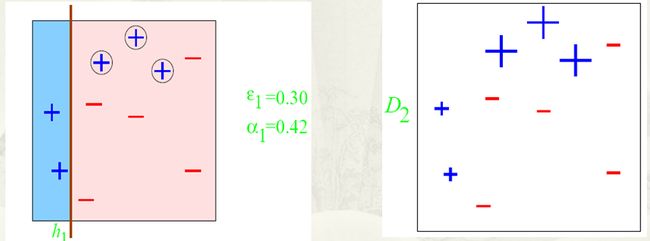
根据分类的正确率,得到一个新的样本分布D2,一个子分类器h1
其中划圈的样本表示被分错的。在右边的途中,比较大的“+”表示对该样本做了加权。
算法最开始给了一个均匀分布 D 。所以h1 里的每个点的值是0.1。ok,当划分后,有三个点划分错了,根据算法误差表达式![]() 得到 误差为分错了的三个点的值之和,所以ɛ1=(0.1+0.1+0.1)=0.3,而ɑ1 根据表达式
得到 误差为分错了的三个点的值之和,所以ɛ1=(0.1+0.1+0.1)=0.3,而ɑ1 根据表达式 的可以算出来为0.42. 然后就根据算法 把分错的点权值变大。如此迭代,最终完成adaboost算法。
第二步:
根据分类的正确率,得到一个新的样本分布D3,一个子分类器h2
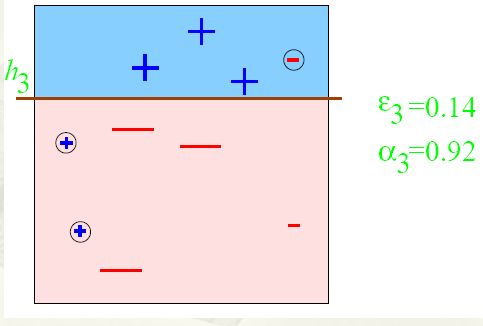
第三步:
得到一个子分类器h3
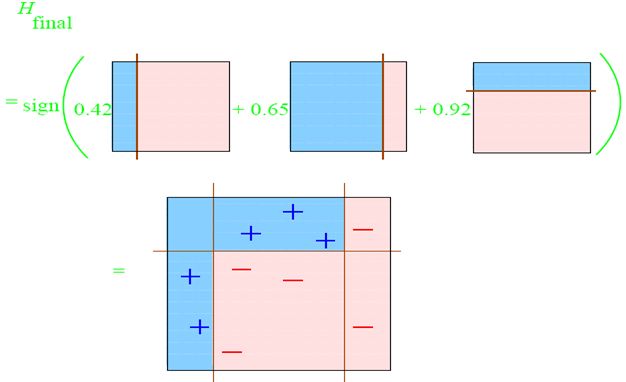
整合所有子分类器:
因此可以得到整合的结果,从结果中看,及时简单的分类器,组合起来也能获得很好的分类效果,在例子中所有的。后面的代码实现时,举出的也是这个例子,可以做对比,这里有一点比较重要,就是点的权重经过大小变化之后,需要进行归一化,确保总和为1.0,这个容易遗忘。
算法的代码实现
输入测试数据,与上图的例子相对应(数据格式:x坐标 y坐标 已分类结果):
- 1 5 1
- 2 3 1
- 3 1 -1
- 4 5 -1
- 5 6 1
- 6 4 -1
- 6 7 1
- 7 6 1
- 8 7 -1
- 8 2 -1
Point.java
- package DataMining_AdaBoost;
- /**
- * 坐标点类
- *
- * @author lyq
- *
- */
- public class Point {
- // 坐标点x坐标
- private int x;
- // 坐标点y坐标
- private int y;
- // 坐标点的分类类别
- private int classType;
- //如果此节点被划错,他的误差率,不能用个数除以总数,因为不同坐标点的权重不一定相等
- private double probably;
- public Point(int x, int y, int classType){
- this.x = x;
- this.y = y;
- this.classType = classType;
- }
- public Point(String x, String y, String classType){
- this.x = Integer.parseInt(x);
- this.y = Integer.parseInt(y);
- this.classType = Integer.parseInt(classType);
- }
- public int getX() {
- return x;
- }
- public void setX(int x) {
- this.x = x;
- }
- public int getY() {
- return y;
- }
- public void setY(int y) {
- this.y = y;
- }
- public int getClassType() {
- return classType;
- }
- public void setClassType(int classType) {
- this.classType = classType;
- }
- public double getProbably() {
- return probably;
- }
- public void setProbably(double probably) {
- this.probably = probably;
- }
- }
- package DataMining_AdaBoost;
- import java.io.BufferedReader;
- import java.io.File;
- import java.io.FileReader;
- import java.io.IOException;
- import java.text.MessageFormat;
- import java.util.ArrayList;
- import java.util.HashMap;
- import java.util.Map;
- /**
- * AdaBoost提升算法工具类
- *
- * @author lyq
- *
- */
- public class AdaBoostTool {
- // 分类的类别,程序默认为正类1和负类-1
- public static final int CLASS_POSITIVE = 1;
- public static final int CLASS_NEGTIVE = -1;
- // 事先假设的3个分类器(理论上应该重新对数据集进行训练得到)
- public static final String CLASSIFICATION1 = "X=2.5";
- public static final String CLASSIFICATION2 = "X=7.5";
- public static final String CLASSIFICATION3 = "Y=5.5";
- // 分类器组
- public static final String[] ClASSIFICATION = new String[] {
- CLASSIFICATION1, CLASSIFICATION2, CLASSIFICATION3 };
- // 分类权重组
- private double[] CLASSIFICATION_WEIGHT;
- // 测试数据文件地址
- private String filePath;
- // 误差率阈值
- private double errorValue;
- // 所有的数据点
- private ArrayList<Point> totalPoint;
- public AdaBoostTool(String filePath, double errorValue) {
- this.filePath = filePath;
- this.errorValue = errorValue;
- readDataFile();
- }
- /**
- * 从文件中读取数据
- */
- private void readDataFile() {
- File file = new File(filePath);
- ArrayList<String[]> dataArray = new ArrayList<String[]>();
- try {
- BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
- String str;
- String[] tempArray;
- while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
- tempArray = str.split(" ");
- dataArray.add(tempArray);
- }
- in.close();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.getStackTrace();
- }
- Point temp;
- totalPoint = new ArrayList<>();
- for (String[] array : dataArray) {
- temp = new Point(array[0], array[1], array[2]);
- temp.setProbably(1.0 / dataArray.size());
- totalPoint.add(temp);
- }
- }
- /**
- * 根据当前的误差值算出所得的权重
- *
- * @param errorValue
- * 当前划分的坐标点误差率
- * @return
- */
- private double calculateWeight(double errorValue) {
- double alpha = 0;
- double temp = 0;
- temp = (1 - errorValue) / errorValue;
- alpha = 0.5 * Math.log(temp);
- return alpha;
- }
- /**
- * 计算当前划分的误差率
- *
- * @param pointMap
- * 划分之后的点集
- * @param weight
- * 本次划分得到的分类器权重
- * @return
- */
- private double calculateErrorValue(
- HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Point>> pointMap) {
- double resultValue = 0;
- double temp = 0;
- double weight = 0;
- int tempClassType;
- ArrayList<Point> pList;
- for (Map.Entry entry : pointMap.entrySet()) {
- tempClassType = (int) entry.getKey();
- pList = (ArrayList<Point>) entry.getValue();
- for (Point p : pList) {
- temp = p.getProbably();
- // 如果划分类型不相等,代表划错了
- if (tempClassType != p.getClassType()) {
- resultValue += temp;
- }
- }
- }
- weight = calculateWeight(resultValue);
- for (Map.Entry entry : pointMap.entrySet()) {
- tempClassType = (int) entry.getKey();
- pList = (ArrayList<Point>) entry.getValue();
- for (Point p : pList) {
- temp = p.getProbably();
- // 如果划分类型不相等,代表划错了
- if (tempClassType != p.getClassType()) {
- // 划错的点的权重比例变大
- temp *= Math.exp(weight);
- p.setProbably(temp);
- } else {
- // 划对的点的权重比减小
- temp *= Math.exp(-weight);
- p.setProbably(temp);
- }
- }
- }
- // 如果误差率没有小于阈值,继续处理
- dataNormalized();
- return resultValue;
- }
- /**
- * 概率做归一化处理
- */
- private void dataNormalized() {
- double sumProbably = 0;
- double temp = 0;
- for (Point p : totalPoint) {
- sumProbably += p.getProbably();
- }
- // 归一化处理
- for (Point p : totalPoint) {
- temp = p.getProbably();
- p.setProbably(temp / sumProbably);
- }
- }
- /**
- * 用AdaBoost算法得到的组合分类器对数据进行分类
- *
- */
- public void adaBoostClassify() {
- double value = 0;
- Point p;
- calculateWeightArray();
- for (int i = 0; i < ClASSIFICATION.length; i++) {
- System.out.println(MessageFormat.format("分类器{0}权重为:{1}", (i+1), CLASSIFICATION_WEIGHT[i]));
- }
- for (int j = 0; j < totalPoint.size(); j++) {
- p = totalPoint.get(j);
- value = 0;
- for (int i = 0; i < ClASSIFICATION.length; i++) {
- value += 1.0 * classifyData(ClASSIFICATION[i], p)
- * CLASSIFICATION_WEIGHT[i];
- }
- //进行符号判断
- if (value > 0) {
- System.out
- .println(MessageFormat.format(
- "点({0}, {1})的组合分类结果为:1,该点的实际分类为{2}", p.getX(), p.getY(),
- p.getClassType()));
- } else {
- System.out.println(MessageFormat.format(
- "点({0}, {1})的组合分类结果为:-1,该点的实际分类为{2}", p.getX(), p.getY(),
- p.getClassType()));
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- * 计算分类器权重数组
- */
- private void calculateWeightArray() {
- int tempClassType = 0;
- double errorValue = 0;
- ArrayList<Point> posPointList;
- ArrayList<Point> negPointList;
- HashMap<Integer, ArrayList<Point>> mapList;
- CLASSIFICATION_WEIGHT = new double[ClASSIFICATION.length];
- for (int i = 0; i < CLASSIFICATION_WEIGHT.length; i++) {
- mapList = new HashMap<>();
- posPointList = new ArrayList<>();
- negPointList = new ArrayList<>();
- for (Point p : totalPoint) {
- tempClassType = classifyData(ClASSIFICATION[i], p);
- if (tempClassType == CLASS_POSITIVE) {
- posPointList.add(p);
- } else {
- negPointList.add(p);
- }
- }
- mapList.put(CLASS_POSITIVE, posPointList);
- mapList.put(CLASS_NEGTIVE, negPointList);
- if (i == 0) {
- // 最开始的各个点的权重一样,所以传入0,使得e的0次方等于1
- errorValue = calculateErrorValue(mapList);
- } else {
- // 每次把上次计算所得的权重代入,进行概率的扩大或缩小
- errorValue = calculateErrorValue(mapList);
- }
- // 计算当前分类器的所得权重
- CLASSIFICATION_WEIGHT[i] = calculateWeight(errorValue);
- }
- }
- /**
- * 用各个子分类器进行分类
- *
- * @param classification
- * 分类器名称
- * @param p
- * 待划分坐标点
- * @return
- */
- private int classifyData(String classification, Point p) {
- // 分割线所属坐标轴
- String position;
- // 分割线的值
- double value = 0;
- double posProbably = 0;
- double negProbably = 0;
- // 划分是否是大于一边的划分
- boolean isLarger = false;
- String[] array;
- ArrayList<Point> pList = new ArrayList<>();
- array = classification.split("=");
- position = array[0];
- value = Double.parseDouble(array[1]);
- if (position.equals("X")) {
- if (p.getX() > value) {
- isLarger = true;
- }
- // 将训练数据中所有属于这边的点加入
- for (Point point : totalPoint) {
- if (isLarger && point.getX() > value) {
- pList.add(point);
- } else if (!isLarger && point.getX() < value) {
- pList.add(point);
- }
- }
- } else if (position.equals("Y")) {
- if (p.getY() > value) {
- isLarger = true;
- }
- // 将训练数据中所有属于这边的点加入
- for (Point point : totalPoint) {
- if (isLarger && point.getY() > value) {
- pList.add(point);
- } else if (!isLarger && point.getY() < value) {
- pList.add(point);
- }
- }
- }
- for (Point p2 : pList) {
- if (p2.getClassType() == CLASS_POSITIVE) {
- posProbably++;
- } else {
- negProbably++;
- }
- }
- //分类按正负类数量进行划分
- if (posProbably > negProbably) {
- return CLASS_POSITIVE;
- } else {
- return CLASS_NEGTIVE;
- }
- }
- }
- /**
- * AdaBoost提升算法调用类
- * @author lyq
- *
- */
- public class Client {
- public static void main(String[] agrs){
- String filePath = "C:\\Users\\lyq\\Desktop\\icon\\input.txt";
- //误差率阈值
- double errorValue = 0.2;
- AdaBoostTool tool = new AdaBoostTool(filePath, errorValue);
- tool.adaBoostClassify();
- }
- }
输出结果:
- 分类器1权重为:0.424
- 分类器2权重为:0.65
- 分类器3权重为:0.923
- 点(1, 5)的组合分类结果为:1,该点的实际分类为1
- 点(2, 3)的组合分类结果为:1,该点的实际分类为1
- 点(3, 1)的组合分类结果为:-1,该点的实际分类为-1
- 点(4, 5)的组合分类结果为:-1,该点的实际分类为-1
- 点(5, 6)的组合分类结果为:1,该点的实际分类为1
- 点(6, 4)的组合分类结果为:-1,该点的实际分类为-1
- 点(6, 7)的组合分类结果为:1,该点的实际分类为1
- 点(7, 6)的组合分类结果为:1,该点的实际分类为1
- 点(8, 7)的组合分类结果为:-1,该点的实际分类为-1
- 点(8, 2)的组合分类结果为:-1,该点的实际分类为-1
我们可以看到,如果3个分类单独分类,都没有百分百分对,而尽管组合结果之后,全部分类正确。
我对AdaBoost算法的理解
到了算法的末尾,有必要解释一下每次分类自后需要把错的点的权重增大,正确的减少的理由了,加入上次分类之后,(1,5)已经分错了,如果这次又分错,由于上次的权重已经提升,所以误差率更大,则代入公式ln(1-误差率/误差率)所得的权重越小,也就是说,如果同个数据,你分类的次数越多,你的权重越小,所以这就造成整体好的分类器的权重会越大,内部就会同时有各种权重的分类器,形成了一种互补的结果,如果好的分类器结果分错 ,可以由若干弱一点的分类器进行弥补。
AdaBoost算法的应用
可以运用在诸如特征识别,二分类的一些应用上,与单个模型相比,组合的形式能显著的提高准确率。