YARN源码分析(二)-----ResourceManager中的NM节点管理
前言
继上一篇文章讲述完ApplicationMaster的相关用法,核心主题都是围绕着2个字"应用",当然在RM中还有另外一项比较重要的服务也很重要,他就是节点管理服务,在RM中是如何维系管理多个节点,对于应用管理的话,在RM中已经有了ApplicationMasterService这个服务对象了,那么对应于节点NodeManager来说,难道叫做NodeManagerService吗,听起来非常顺,其实他叫做?ResourceTrackerService,当然名称叫什么都无所谓啦,他扮演的功能就是类似于节点NodeManager大管家的角色了.OK,在这里我们就以NodeManager管理为核心线索,逐步分析RM在此方面的设计思想.
相关涉及类
在分析之前,还是需要了解一下相关类,在阅读本篇文章之前,可以建议大家阅读我的上一篇文章ApplicationMaster文章的分析,因为NM和AM管理许多思想共同,也有共同的父类,比如AbstractService这样的抽象服务类.下面是我归纳出的几个类.
1.NodeManager.java--节点管理类,这个类是yarn-resourcemanager包中的类,不是yarn-nodemanager中的同名类,这个类是本篇文章的核心角色类,
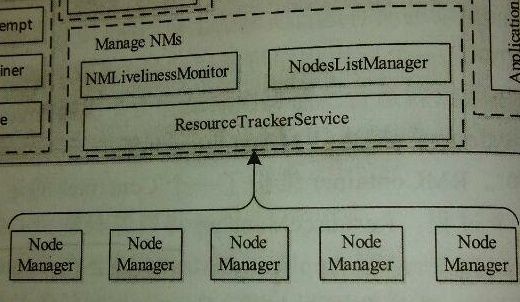
2.NodesListManager--节点列表管理类,这个类中管理了类似黑名单,白名单的节点列表形式。
3.NMLivelinessMonitor--节点存活状态监控线程类,与之前的AMLivelinessMonitor线程的原理类似,最简单的心跳更新检查。
4.ResourceTrackerService--节点服务管理对象,负责与各个NodeManager通信。包括NM在此服务上的注册请求处理,心跳更新操作等等。
下面是一张结构简图帮助大家宏观上理解RM中的NM管理:
NodeManager节点注册
我们从一个比较初始的状态出发,比如说节点注册开始,一步步的贯穿的去分析整个流程。节点注册操作,在NodeManager类自身中。这个类中定义的基本信息如下
- //ResourceManager下资源管理器类
- public class NodeManager implements ContainerManagementProtocol {
- private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(NodeManager.class);
- private static final RecordFactory recordFactory = RecordFactoryProvider.getRecordFactory(null);
- final private String containerManagerAddress;
- //节点通信地址
- final private String nodeHttpAddress;
- //所在机架名称
- final private String rackName;
- //节点ID
- final private NodeId nodeId;
- final private Resource capability;
- Resource available = recordFactory.newRecordInstance(Resource.class);
- Resource used = recordFactory.newRecordInstance(Resource.class);
注册操作并没有独立出方法来,而是包含在了构造函数中,也就是说,当你构造新的NodeManager的时候,你已经在注册节点到ResourceTrackerService。
- public NodeManager(String hostName, int containerManagerPort, int httpPort,
- String rackName, Resource capability,
- ResourceTrackerService resourceTrackerService, RMContext rmContext)
- throws IOException, YarnException {
- this.containerManagerAddress = hostName + ":" + containerManagerPort;
- this.nodeHttpAddress = hostName + ":" + httpPort;
- this.rackName = rackName;
- this.resourceTrackerService = resourceTrackerService;
- this.capability = capability;
- Resources.addTo(available, capability);
- this.nodeId = NodeId.newInstance(hostName, containerManagerPort);
- //新建nodemanager注册请求
- RegisterNodeManagerRequest request = recordFactory
- .newRecordInstance(RegisterNodeManagerRequest.class);
- //往请求内写入状态信息
- request.setHttpPort(httpPort);
- request.setNodeId(this.nodeId);
- request.setResource(capability);
- request.setNodeId(this.nodeId);
- //调用resourceTrackerService服务对象进行节点注册操作
- resourceTrackerService.registerNodeManager(request);
- this.schedulerNode = new FiCaSchedulerNode(rmContext.getRMNodes().get(
- this.nodeId), false);
- .....
- }
- //节点资源跟踪服务,与各个节点的NodeManager通信服务
- public class ResourceTrackerService extends AbstractService implements
- ResourceTracker {
- private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(ResourceTrackerService.class);
- private static final RecordFactory recordFactory =
- RecordFactoryProvider.getRecordFactory(null);
- //资源管理器上下文
- private final RMContext rmContext;
- //节点列表管理器
- private final NodesListManager nodesListManager;
- //节点存活状态监控
- private final NMLivelinessMonitor nmLivelinessMonitor;
- //节点安全认证相关
- private final RMContainerTokenSecretManager containerTokenSecretManager;
- private final NMTokenSecretManagerInRM nmTokenSecretManager;
- //心跳间隔
- private long nextHeartBeatInterval;
- //远程RPC服务
- private Server server;
- private InetSocketAddress resourceTrackerAddress;
- private static final NodeHeartbeatResponse resync = recordFactory
- .newRecordInstance(NodeHeartbeatResponse.class);
- private static final NodeHeartbeatResponse shutDown = recordFactory
- .newRecordInstance(NodeHeartbeatResponse.class);
- //最小分配的内存的大小
- private int minAllocMb;
- //最小分配的核数大小
- private int minAllocVcores;
- //响应NodeManager的节点注册请求方法
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- @Override
- public RegisterNodeManagerResponse registerNodeManager(
- RegisterNodeManagerRequest request) throws YarnException,
- IOException {
- NodeId nodeId = request.getNodeId();
- String host = nodeId.getHost();
- .....
- // Check if this node is a 'valid' node
- //如果此节点是在exclude名单中,注册请求将会被拒绝,调用的是节点列表管理器的isValidNode方法
- if (!this.nodesListManager.isValidNode(host)) {
- String message =
- "Disallowed NodeManager from " + host
- + ", Sending SHUTDOWN signal to the NodeManager.";
- LOG.info(message);
- response.setDiagnosticsMessage(message);
- response.setNodeAction(NodeAction.SHUTDOWN);
- return response;
- }
- // Check if this node has minimum allocations
- //判断节点资源是否满足最小内存和核数的限制,如果没有同样拒绝注册
- if (capability.getMemory() < minAllocMb
- || capability.getVirtualCores() < minAllocVcores) {
- String message =
- "NodeManager from " + host
- + " doesn't satisfy minimum allocations, Sending SHUTDOWN"
- + " signal to the NodeManager.";
- LOG.info(message);
- response.setDiagnosticsMessage(message);
- response.setNodeAction(NodeAction.SHUTDOWN);
- return response;
- }
- .....
- .....
- // On every node manager register we will be clearing NMToken keys if
- // present for any running application.
- this.nmTokenSecretManager.removeNodeKey(nodeId);
- //同时将节点注册到节点存活监控线程中
- this.nmLivelinessMonitor.register(nodeId);
- String message =
- "NodeManager from node " + host + "(cmPort: " + cmPort + " httpPort: "
- + httpPort + ") " + "registered with capability: " + capability
- + ", assigned nodeId " + nodeId;
- LOG.info(message);
- response.setNodeAction(NodeAction.NORMAL);
- response.setRMIdentifier(ResourceManager.clusterTimeStamp);
- return response;
- }
- //进程存活状态监控类
- public abstract class AbstractLivelinessMonitor<O> extends AbstractService {
- ......
- private final Clock clock;
- //保存了心跳检验的结果记录
- private Map<O, Long> running = new HashMap<O, Long>();
- //更新心跳监控检测最新时间
- public synchronized void receivedPing(O ob) {
- //only put for the registered objects
- if (running.containsKey(ob)) {
- running.put(ob, clock.getTime());
- }
- }
OK,回到之前没有说清楚的NodeListManager节点列表管理器类,这个类提供了节点有效性检查的方法
- .....
- // Check if this node is a 'valid' node
- //如果此节点是在exclude名单中,注册请求将会被拒绝,调用的是节点列表管理器的isValidNode方法
- if (!this.nodesListManager.isValidNode(host)) {
- String message =
- "Disallowed NodeManager from " + host
- + ", Sending SHUTDOWN signal to the NodeManager.";
- LOG.info(message);
- response.setDiagnosticsMessage(message);
- response.setNodeAction(NodeAction.SHUTDOWN);
- return response;
- }
- .....
- //节点列表管理器,主要是根据include白名单和exclude黑名单属性进行判断,也是一个服务
- public class NodesListManager extends AbstractService implements
- EventHandler<NodesListManagerEvent> {
- private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(NodesListManager.class);
- //节点列表读取器
- private HostsFileReader hostsReader;
- private Configuration conf;
- //不允许使用的节点列表
- private Set<RMNode> unusableRMNodesConcurrentSet = Collections
- .newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<RMNode,Boolean>());
- //资源管理上下文
- private final RMContext rmContext;
- .....
- //输入主机名,判断是否是有效的节点,
- public boolean isValidNode(String hostName) {
- synchronized (hostsReader) {
- //获取可接入和不可接入主机名列表
- Set<String> hostsList = hostsReader.getHosts();
- Set<String> excludeList = hostsReader.getExcludedHosts();
- String ip = NetUtils.normalizeHostName(hostName);
- //判断是否在相应的列表中以此判断节点是否有效
- return (hostsList.isEmpty() || hostsList.contains(hostName) || hostsList
- .contains(ip))
- && !(excludeList.contains(hostName) || excludeList.contains(ip));
- }
- }
- @Override
- protected void serviceInit(Configuration conf) throws Exception {
- this.conf = conf;
- // Read the hosts/exclude files to restrict access to the RM
- //在服务初始化的时候读取include和exclude文件信息,exclude的节点列表名单将会被RM拒绝接入
- try {
- this.hostsReader =
- new HostsFileReader(
- conf.get(YarnConfiguration.RM_NODES_INCLUDE_FILE_PATH,
- YarnConfiguration.DEFAULT_RM_NODES_INCLUDE_FILE_PATH),
- conf.get(YarnConfiguration.RM_NODES_EXCLUDE_FILE_PATH,
- YarnConfiguration.DEFAULT_RM_NODES_EXCLUDE_FILE_PATH)
- );
- //输出节点信息
- printConfiguredHosts();
- .....
节点HeartBeat心跳
心跳方法在NodeManager中有直接定义
- public class NodeManager implements ContainerManagementProtocol {
- ....
- //周期心跳方法
- public void heartbeat() throws IOException, YarnException {
- NodeStatus nodeStatus =
- org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.resourcemanager.NodeManager.createNodeStatus(
- nodeId, getContainerStatuses(containers));
- nodeStatus.setResponseId(responseID);
- NodeHeartbeatRequest request = recordFactory
- .newRecordInstance(NodeHeartbeatRequest.class);
- request.setNodeStatus(nodeStatus);
- //调用resourceTrackerService发送心跳包,并获取响应回复
- NodeHeartbeatResponse response = resourceTrackerService
- .nodeHeartbeat(request);
- responseID = response.getResponseId();
- }
- //节点心跳相应方法
- @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
- @Override
- public NodeHeartbeatResponse nodeHeartbeat(NodeHeartbeatRequest request)
- throws YarnException, IOException {
- //从心跳中获取远程节点状态信息
- NodeStatus remoteNodeStatus = request.getNodeStatus();
- /**
- * Here is the node heartbeat sequence...
- * 1. Check if it's a registered node
- * 2. Check if it's a valid (i.e. not excluded) node
- * 3. Check if it's a 'fresh' heartbeat i.e. not duplicate heartbeat
- * 4. Send healthStatus to RMNode
- */
- NodeId nodeId = remoteNodeStatus.getNodeId();
- // 1. Check if it's a registered node
- RMNode rmNode = this.rmContext.getRMNodes().get(nodeId);
- if (rmNode == null) {
- /* node does not exist */
- String message = "Node not found resyncing " + remoteNodeStatus.getNodeId();
- LOG.info(message);
- resync.setDiagnosticsMessage(message);
- return resync;
- }
- // Send ping
- //更新心跳响应最新时间
- this.nmLivelinessMonitor.receivedPing(nodeId);
- // 2. Check if it's a valid (i.e. not excluded) node
- //每次心跳检测都会检查节点是否被拉入exclude名单
- if (!this.nodesListManager.isValidNode(rmNode.getHostName())) {
- String message =
- "Disallowed NodeManager nodeId: " + nodeId + " hostname: "
- + rmNode.getNodeAddress();
- LOG.info(message);
- shutDown.setDiagnosticsMessage(message);
- //如果是被拉入,则触发节点撤销事件
- this.rmContext.getDispatcher().getEventHandler().handle(
- new RMNodeEvent(nodeId, RMNodeEventType.DECOMMISSION));
- return shutDown;
- }
- .....
- // Heartbeat response
- //设置心跳回复
- NodeHeartbeatResponse nodeHeartBeatResponse = YarnServerBuilderUtils
- .newNodeHeartbeatResponse(lastNodeHeartbeatResponse.
- getResponseId() + 1, NodeAction.NORMAL, null, null, null, null,
- nextHeartBeatInterval);
- rmNode.updateNodeHeartbeatResponseForCleanup(nodeHeartBeatResponse);