机器学习实战3:决策树学习笔记(python)
决策树就是在已知各种情况发生概率的情况下,通过构造决策树,评价项目风险,判断其可行性的决策分析方法,它是运用概率分析的一种图解法。
优缺点分析:
优点:计算复杂度不高,输出结果较直观,易于理解,对中间值的缺失不敏感,可以处理不相关特征数据
缺点:可能产生过度匹配
创建数据集并计算其熵值:
from math import log
import operator
def createDataSet():
dataSet = [[1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 1, 'yes'],
[1, 0, 'no'],
[0, 1, 'no'],
[0, 1, 'no']]
labels = ['no surfacing','flippers']
#change to discrete values
return dataSet, labels
myDat,labels=createDataSet()
def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
numEntries = len(dataSet)
labelCounts = {}
for featVec in dataSet: #the the number of unique elements and their occurance
currentLabel = featVec[-1]
labelCounts[currentLabel] =labelCounts.get(currentLabel,0)+1
shannonEnt = 0.0
for key in labelCounts:
prob = float(labelCounts[key])/numEntries
shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob,2) #log base 2
return shannonEnt
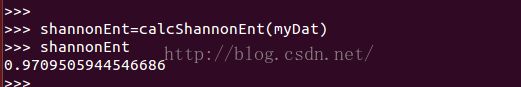
shannonEnt=calcShannonEnt(myDat)
将数据集的特征划分出来:
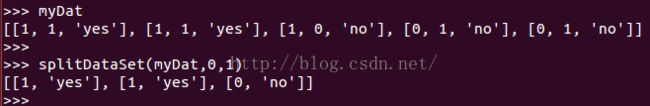
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):
retDataSet = []
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] == value:
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] #chop out axis used for splitting
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
return retDataSet
从特征中选择最好的划分方式:
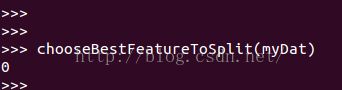
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #the last column is used for the labels
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
bestInfoGain = 0.0; bestFeature = -1
for i in range(numFeatures): #iterate over all the features
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]#create a list of all the examples of this feature
uniqueVals = set(featList) #get a set of unique values
newEntropy = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value)
prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #calculate the info gain; ie reduction in entropy
if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #compare this to the best gain so far
bestInfoGain = infoGain #if better than current best, set to best
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature #returns an integer
显示出最好的特征是第0个特征。
设计一个函数,返回出现次数最多的那个特征(后面创建树会用到该函数):
def majorityCnt(classList):
classCount={}
for vote in classList:
if vote not in classCount.keys(): classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.iteritems(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
现在进行树的创建:
def createTree(dataSet,labels):
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList):
return classList[0]#stop splitting when all of the classes are equal
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: #stop splitting when there are no more features in dataSet
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet)
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat]
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}}
del(labels[bestFeat])
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featValues)
for value in uniqueVals:
subLabels = labels[:] #copy all of labels, so trees don't mess up existing labels
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value),subLabels)
return myTree
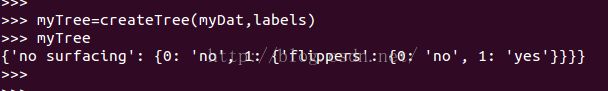
myTree=createTree(myDat,labels)
myTree
该树代表了如下这棵树: