基于密度的聚类算法(DBSCAN)的java实现
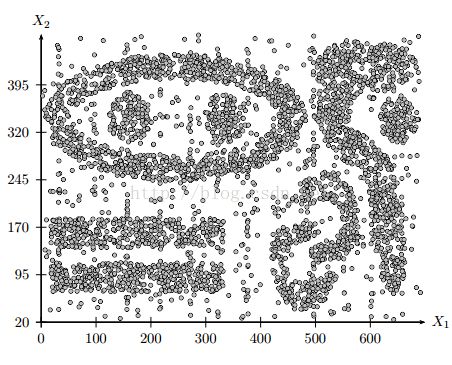
k-means和EM算法适合发现凸型的聚类(大概就是圆形,椭圆形比较规则的类),而对于非凸型的聚类,这两种方法就很难找到准确的聚类了。比如如下图:
可能来自不同类的点反而比来自相同类的点还要靠的更近。
太多的原理和算法介绍,大家可以找到很多相关资料。(推荐《Data Mining and Analysis: FundamentalConcepts and Algorithms》)。下面的代码是对基于密度聚类算法的一种实现。希望能够帮助想要学习了理解这种算法的同学。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
*
* @author aturbo
* 基于密度的聚类算法
*/
public class MyDBSCAN {
private static final double[][] points = {
{3.0, 8.04},
{4.0, 7.95},
{4.4, 8.58},
{3.6, 8.81},
{5.0, 8.33},
{6.0, 6.96},
{17.0, 4.24},
{18.0, 4.26},
{16.0, 3.84},
{17.0, 4.82},
{15.0, 5.68},
{17.0, 5.68},
{11.0, 10.68},
{13.0, 9.68},
{11.8, 10.0},
{12.0, 11.18},
{8.0, 12.0},
{9.2, 9.68},
{8.8, 11.2},
{10.0,11.4},
{7.0, 9.68},
{6.1, 10.68},
{5.70, 1.68},
{5.0, 2.68},
{12.0, 0.68}
};
private static int minpts = 6;
private static double radius = 1.3;
private static List<List<double[]>> clusters;
private static List<double[]> cores;
/**
* 欧氏距离
* @param point1
* @param point2
* @return
*/
private static double countEurDistance(double[] point1,double[] point2){
double eurDistance = 0.0;
for(int i=0;i<point1.length;i++){
eurDistance += (point1[i]-point2[i])*(point1[i]-point2[i]);
}
return Math.sqrt(eurDistance);
}
/**
* find the core points
* @param points
* @param minpts
* @param radius
* @return
*/
private static List<double[]> findCores(double[][] points,int minpts,double radius){
List<double[]> cores = new ArrayList<double[]>();
for(int i = 0; i < points.length;i++){
int pts = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < points.length;j++){
for(int k = 0; k < points[i].length;k++){
if(countEurDistance(points[i], points[j])<radius){
pts++;
}
}
}
if(pts>=minpts){
cores.add(points[i]);
}
}
return cores;
}
/**
* put the core point to cluster and get the densityconnect
*/
private static void putCoreToCluster(){
clusters = new ArrayList<List<double[]>>();
int clusterNum = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<cores.size();i++){
clusters.add(new ArrayList<double[]>());
clusters.get(clusterNum).add(cores.get(i));
densityConnected(points, cores.get(i), clusterNum);
clusterNum++;
}
}
/**
*
* @param points
* @param core
* @param clusterNum
*/
private static void densityConnected(double[][] points,double[] core,int clusterNum){
boolean isputToCluster;//是否已经归为某个类
boolean isneighbour = false;//是不是core的“邻居”
cores.remove(core);//对某个core点处理后就从core集中去掉
for(int i = 0; i < points.length;i++){
isneighbour = false;
isputToCluster = false;
for(List<double[]> cluster:clusters){
if(cluster.contains(points[i])){//如果已经归为某个类
isputToCluster = true;
break;
}
}
if(isputToCluster)continue;//已在聚类中,跳过,不处理
if(countEurDistance(points[i], core)<radius){//是目前加入的core点的“邻居”吗?,ture的话,就和这个core加入一个类
clusters.get(clusterNum).add(points[i]);
isneighbour = true;
}
if(isneighbour){//如果是邻居,才会接下来对邻居进行densityConnected处理,否则,结束这个core点的处理
if(cores.contains(points[i])){
cores.remove(points[i]);
densityConnected(points, points[i], clusterNum);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
cores = findCores(points, minpts, radius);
System.out.println("点的个数:"+points.length);
System.out.println(cores.size()+" core points:");
for(double[] core:cores){
System.out.print("[");
for(int i = 0;i< core.length;i++){
System.out.print(core[i]);
if(i!=(core.length-1))
System.out.print(",");
}
System.out.print("]");
System.out.println();
}
putCoreToCluster();
int i = 0;
for(List<double[]> cluster:clusters){
System.out.println("cluster "+ i++ +":");
for(double[] point:cluster){
System.out.println("["+point[0]+","+point[1]+"]");
}
}
int flag = 0;
for(int j = 0;j<points.length;j++){
flag = 0;
for(List<double[]> cluster:clusters){
if(cluster.contains(points[j])){
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if(flag==0)System.out.println("noise point:"+"["+points[j][0]+","+points[j][1]+"]");
}
}
}
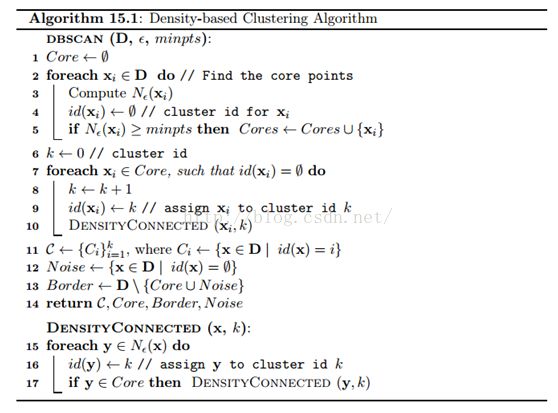
具体算法流程:
参考文献:
《Data Mining and Analysis: FundamentalConcepts and Algorithms》