集合
1.什么是集合?
Java 集合类可以用于存储数量不等的多个对象,还可用于保存具有映射关系的关联数组
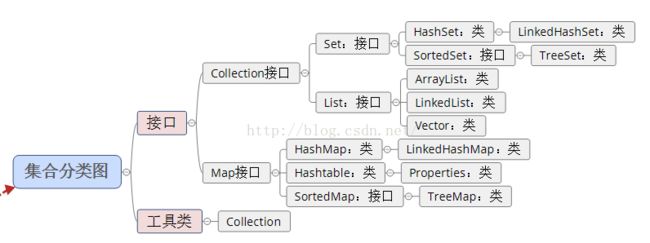
Java 集合可分为 Collection 和 Map 两种体系:
1)Collection接口:
(1)Set:元素无序、不可重复的集合 ---类似高中的“集合”
(2)List:元素有序,可重复的集合 ---”动态”数组
2)Map接口:具有映射关系“key-value对”的集合 ---类似于高中的“函数” y = f(x) (x1,y1) (x2,y2)
2.集合体系分类
3.Collection接口
1)Collection常用方法
2)集合的遍历
/*
* 遍历集合
*/
@Test
public void test(){
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(111);
collection.add("aaa");
collection.add(222);
//方法一:增强For循环
for(Object i : collection){
System.out.println("!!!" + i);
}
//方法二:使用Iterator接口的hasNext() next() 方法
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
4.List
1)ArrayList(List接口的主要实现类):其底层为数组
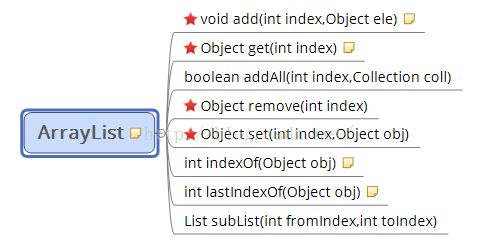
2)LinkedList:其底层数据结构为链表,插入和删除操作比较方便
3)Vector:基本上不用,线程安全
5.Set
①元素无序、不可重复的集合
②无序:是指元素在底层的存放位置是无序的
③不可重复:当向Set中添加相同元素是,后面重复的元素添加不进去
1)HashSet(主要实现类)
Person类
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Person other = (Person) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
}
test方法
/**
* 要求添加进Set中元素所在的类,一定要重写equals()和hashCode()方法
* 进而保证Set元素的不可重复性
*
* Set是如何存储元素的?使用了哈希算法
* 当向Set中添加对象时,首先调用所在类的hashCode()方法,计算此对象的哈希值,此哈希值
* 决定了此对象在Set中的存储位置,若此位置之前没有对象存储,则这个对象直接存储到该位置,若
* 此位置已有对象存储,就用equals()比较两个对象是否相同,若相同,则此对象不能存储
* >要求:hashCode()和equals()方法要一致
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
Set set = new HashSet();
set.add(111);
set.add("aaa");
set.add(new Person("xiaoming",10));
set.add(new Person("xiaoming",10));
set.add(new Person("daming",20));
System.out.println(set);
}2)LinkedHashSet
使用链表维护了元素添加进集合中的顺序,所以遍历LinkedHashSet集合元素时,就是元素的添加顺序
3)TreeSet
(1)特点:①只能添加同一种类型的元素;②可以按添加进集合的元素的顺序进行遍历,默认从小到大
(2)排序:①自然排序 ②定制排序
(3)自然排序:要求自定义类必须实现java.lang.Comparable接口并重写compareTo(Object obj)方法,并在compareTo(Object obj)方法中指定按照自定义类的那个属性进行排序
创建实现Comparable接口的实现类Person
public class Person implements Comparable{
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person() {}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Person other = (Person) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
//当向TreeSet中添加Person类对象时,依据此方法,确定按照那个属性排列
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
if(o instanceof Person){
Person person = (Person)o;
int i = this.name.compareTo(person.name);
if(i == 0){
return this.age.compareTo(person.age);
}else{
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}测试
@Test
public void test3(){
Set set = new TreeSet();
set.add(new Person("xiaoming",10));
set.add(new Person("daming",20));
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
(4)定制排序:
①创建Comparator接口对象,并重写compare(Object obj1,Object obj2)方法;
②将Comparator接口对象作为参数传递给TreeSet构造器,创建TreeSet对象;
③向TreeSet对象中添加自定义类对象
创建Custommer类
public class Custommer {
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Custommer [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public Custommer(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Custommer() {
super();
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((age == null) ? 0 : age.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Custommer other = (Custommer) obj;
if (age == null) {
if (other.age != null)
return false;
} else if (!age.equals(other.age))
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
return true;
}
}创建Comparator接口对象,并测试
/**
* 定制排序
*/
@Test
public void test4(){
//1.创建一个实现了Comparator接口的对象
Comparator com = new Comparator() {
@Override
public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) {
if(o1 instanceof Custommer && o2 instanceof Custommer){
Custommer c1 = (Custommer)o1;
Custommer c2 = (Custommer)o2;
int i = c1.getName().compareTo(c2.getName());
if(i == 0){
return c1.getAge().compareTo(c2.getAge());
}else{
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
};
//将次对象作为形参传递给TreeSet构造器中
TreeSet set = new TreeSet(com);
//向集合中添加对象元素
set.add(new Custommer("xiaoming",10));
set.add(new Custommer("xiaoming",20));
set.add(new Custommer("xiaoding",10));
Iterator iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
6.Map
1)Map概述
(1)Map与Collection并列存在。用于保存具有映射关系的数据:Key-Value
(2)Map 中的 key 和 value 都可以是任何引用类型的数据
(3)Map 中的 key 用Set来存放,不允许重复,即同一个 Map 对象所对应的类,须重写hashCode()和equals()方法。
(4)常用String类作为Map的“键”。
(5)key 和 value 之间存在单向一对一关系,即通过指定的 key 总能找到唯一的、确定的 value。
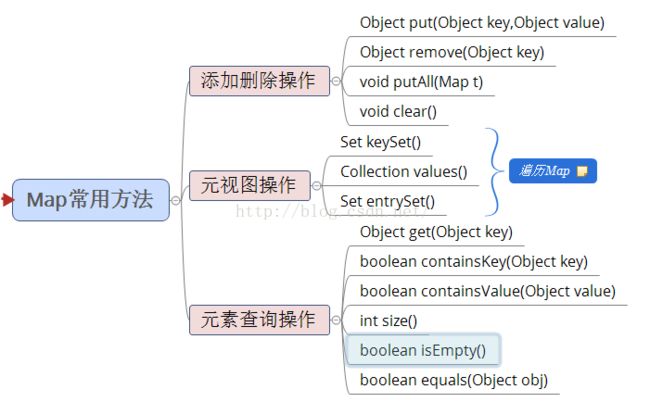
2)Map常用方法: @Test
public void test5(){
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("user", "root");
map.put("password", 123);
map.put(new Person("xiaoming",10), "example1");
//1获取Map中key集
Set keys = map.keySet();
for(Object obj : keys){
System.out.println(obj);
}
//2.获取Map中的value集
Collection values = map.values();
for(Object obj : values){
System.out.println(obj);
}
//3.获取Map中ley-value集方法一
Set entrysSet = map.entrySet();
for(Object obj : entrysSet){
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry)obj;
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
//4.获取Map中ley-value集方法二
Set set = map.keySet();
for(Object objKey : set){
Object objValue = map.get(objKey);
System.out.println(objKey + ":" + objValue);
}
}
4)HashMap
(1)key是用Set存放的,不可重复;value使用Collection存放的,可重复
(2)一个key-value对是一个Entry,Entry都是用Set来存放的也是不可重复的
(3)HashMap 判断两个 key 相等的标准是:两个 key 通过 equals() 方法返回 true,hashCode 值也相等。若key相同,只能添加最后的那个元素
(4)HashMap 判断两个 value相等的标准是:两个 value 通过 equals() 方法返回 true
5)HashTable—Properties
(1)常用来处理属性文件,它的kye和value都是String类型的
(2)常用方法:①load(InputStream is) ②String getProperty(Strng key)
@Test
public void test6() throws Exception{
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("pro.properties");
Properties pro = new Properties();
pro.load(is);
String user = pro.getProperty("user");
String password = pro.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(user + " : " + password);
}
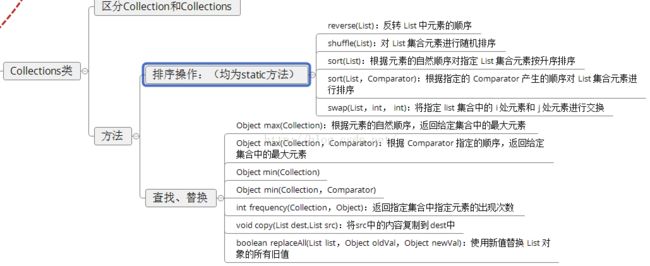
6.集合工具类(Collections)