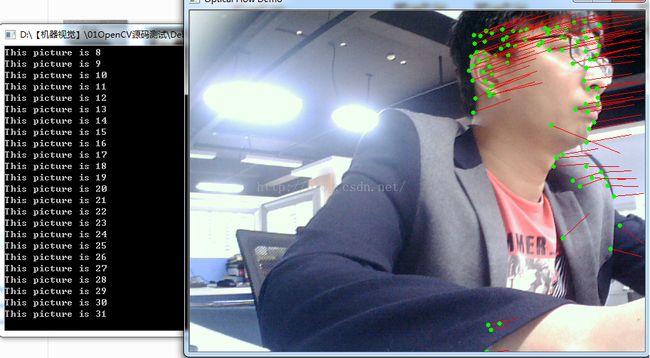
OpenCV3的第二天——光流法(Optial Flow)运动目标检测
基于特征点的跟踪算法大致可以分为两个步骤:
1)探测当前帧的特征点;
2)通过当前帧和下一帧灰度比较,估计当前帧特征点在下一帧的位置;
3)过滤位置不变的特征点,余下的点就是目标了。
特征点包括:
1、Harris
2、SURF
3、FAST
4、STAR
5、SIFT
6、ORB
7、MSER
8、GETT
9、Dense
10、SimpleBlob
光流的基本方法:
1、基于梯度
2、基于匹配
3、基于能量
4、基于相位
光流法首先假设的条件:
1、亮度恒定
2、小运动
3、空间一致
使用函数:
goodFeaturesToTrack()——寻找图像中具有大特征的角点
calcOpticalFlowPyrLK()——计算一个稀疏特征集的光流
两篇博客链接:
Opencv学习笔记(九)光流法
http://blog.csdn.net/crzy_sparrow/article/details/7407604
【算法分析】Lucas–Kanade光流算法
http://www.cnblogs.com/gnuhpc/archive/2012/12/04/2802124.html
OpenCV3编程入门——光流法的代码
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <opencv2/video/video.hpp>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void duan_OpticalFlow( Mat &frame, Mat & result);
bool addNewPoints();
bool acceptTrackedPoint(int i);
int main()
{
VideoCapture video(0);
Mat matSrc;
Mat matRst;
long lNum = 0;
if (video.isOpened())
{
while(1)
{
video >> matSrc;
if ( !matSrc.empty())
{
lNum++;
duan_OpticalFlow(matSrc, matRst);
cout << "This picture is " << lNum << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Error : Get picture is empty!" << endl;
}
}
}
else
{
cout << "Error : Open this camera is Fail!\n" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Mat curgray; //Current mat
Mat pregray; // next mat
vector<Point2f> point[2];
vector<Point2f> initPoint;
vector<Point2f> features;
int maxCount = 500; // max feature number
double qLevel = 0.01; // level
double minDist = 10.0; // Two features distance
vector<uchar> status; // find optical flow is 1
vector<float> err;
void duan_OpticalFlow( Mat &frame, Mat & result)
{
cvtColor(frame, curgray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
frame.copyTo(result);
if (addNewPoints())
{
goodFeaturesToTrack(curgray, features, maxCount,qLevel,minDist);
point[0].insert(point[0].end(), features.begin(), features.end());
initPoint.insert(initPoint.end(), features.begin(), features.end());
}
if (pregray.empty())
{
curgray.copyTo(pregray);
}
calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(pregray, curgray, point[0], point[1], status, err);
int k = 0;
for (size_t i=0; i<point[1].size(); i++)
{
if (acceptTrackedPoint(i))
{
initPoint[k] = initPoint[i];
point[1][k++] = point[1][i];
}
}
point[1].resize(k);
initPoint.resize(k);
for (size_t i=0; i<point[1].size(); i++)
{
line(result, initPoint[i], point[1][i], Scalar(0, 0, 255));
circle(result, point[1][i], 3, Scalar(0, 255, 0), -1);
}
swap(point[1], point[0]);
swap(pregray, curgray);
imshow("Optical Flow Demo", result);
waitKey(50);
}
bool addNewPoints()
{
return point[0].size() <= 10;
}
bool acceptTrackedPoint(int i)
{
return status[i] && ((abs(point[0][i].x - point[1][i].x) + abs(point[0][i].y - point[1][i].y)) > 2);
}