GeekOS源代码学习(9)project1中Init_DMA与Init_Floppy
生成project1
$ startProject project1 ./geekos-0.3.0/src/ project0
在当前目录下生成了project1目录
再来看一下main.c。
/* * GeekOS C code entry point * Copyright (c) 2001,2003,2004 David H. Hovemeyer <[email protected]> * Copyright (c) 2003, Jeffrey K. Hollingsworth <[email protected]> * Copyright (c) 2004, Iulian Neamtiu <[email protected]> * $Revision: 1.51 $ * * This is free software. You are permitted to use, * redistribute, and modify it as specified in the file "COPYING". */ #include <geekos/bootinfo.h> #include <geekos/string.h> #include <geekos/screen.h> #include <geekos/mem.h> #include <geekos/crc32.h> #include <geekos/tss.h> #include <geekos/int.h> #include <geekos/kthread.h> #include <geekos/trap.h> #include <geekos/timer.h> #include <geekos/keyboard.h> #include <geekos/dma.h> #include <geekos/ide.h> #include <geekos/floppy.h> #include <geekos/pfat.h> #include <geekos/vfs.h> /* * Define this for a self-contained boot floppy * with a PFAT filesystem. (Target "fd_aug.img" in * the makefile.) */ /*#define FD_BOOT*/ #ifdef FD_BOOT # define ROOT_DEVICE "fd0" # define ROOT_PREFIX "a" #else # define ROOT_DEVICE "ide0" # define ROOT_PREFIX "c" #endif #define INIT_PROGRAM "/" ROOT_PREFIX "/shell.exe" static void Mount_Root_Filesystem(void); static void Spawn_Init_Process(void); /* * Kernel C code entry point. * Initializes kernel subsystems, mounts filesystems, * and spawns init process. */ static void print_out(ulong_t arg) { while(1) { int key = Wait_For_Key(); int finish = ('d' | KEY_CTRL_FLAG); if( key == finish ){ Print("finish input \n"); Exit(0); }else Print("%c", key); } } void Main(struct Boot_Info* bootInfo) { Init_BSS(); Init_Screen(); Init_Mem(bootInfo); Init_CRC32(); Init_TSS(); Init_Interrupts(); Init_Scheduler(); Init_Traps(); Init_Timer(); Init_Keyboard(); Init_DMA(); Init_Floppy(); Init_IDE(); Init_PFAT(); Mount_Root_Filesystem(); Set_Current_Attr(ATTRIB(BLACK, GREEN|BRIGHT)); Print("Welcome to GeekOS!\n"); Set_Current_Attr(ATTRIB(BLACK, GRAY)); Print("call Wait_For_Key...\n"); Print("%d\n", 'd' | KEY_LCTRL ); Start_Kernel_Thread(print_out, 0, PRIORITY_NORMAL, true); <<<<<<< Your version of src/geekos/main.c // TODO("Start a kernel thread to echo pressed keys and print counts"); ======= >>>>>>> Master version of src/geekos/main.c from project1 Spawn_Init_Process(); /* Now this thread is done. */ // Exit(0); } static void Mount_Root_Filesystem(void) { if (Mount(ROOT_DEVICE, ROOT_PREFIX, "pfat") != 0) Print("Failed to mount /" ROOT_PREFIX " filesystem\n"); else Print("Mounted /" ROOT_PREFIX " filesystem!\n"); } /* Spawner is a a thread that accomodates the program to be loaded & executed * it is started from main.c */ void Spawner(unsigned long arg); static void Spawn_Init_Process(void) { /* this thread will load&run ELF files, see the rest in lprog.c */ Print("Starting the Spawner thread...\n"); Start_Kernel_Thread( Spawner, 0, PRIORITY_NORMAL, true ); }
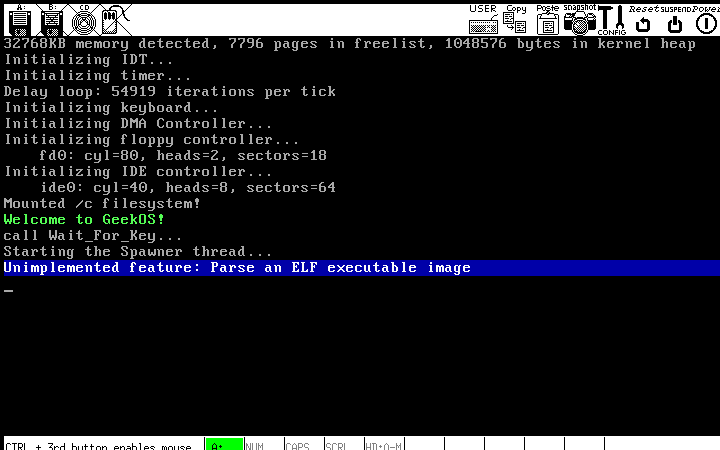
编译运行一下可以看到如下。。
ps:在build目录下的.bochsrc中有这么一行
ata0-master: type=disk, mode=flat, path="./diskc.img", cylinders=40, heads=8, spt=64
这里的柱面磁头扇区信息,我也不知道是怎么得到的,待研究。。。
project1要求你完成elf可执行文件的装载
文件./src/user/a.c会被编译成./src/user/a.exe
GeekOS在启动的时候会将a.exe读至内存,然后调用函数ELF_Executable,创建一个新的内核线程来运行此文件。
要求你完成ELF_Executable()函数的编写。
呃。。这个任务我以后再完成,我还是先来看多出来的代码吧。。
主函数Main中多了
Init_DMA();
Init_Floppy();
Init_IDE();
Init_PFAT();
Mount_Root_Filesystem();
Spawn_Init_Process();
这么几个函数。
先来看第一个函数Init_DMA吧
位于./src/geekos/dma.c
/**
* Initialize the DMA controllers.
*/
void Init_DMA(void)
{
Print("Initializing DMA Controller...\n");
/* Reset the controller */
Out_Byte(DMA_MASTER_CLEAR_REG, 0);
}
再看下一个函数Init_Floppy
位于./src/geekos/floppy.c
/*
* Initialize the floppy controller.
*/
void Init_Floppy(void)
{
uchar_t floppyByte;
bool ready = false;
bool good;
Print("Initializing floppy controller...\n");
/* Allocate memory for DMA transfers */
s_transferBuf = (uchar_t*) Alloc_Page();//为DMA传输分配一个页的缓冲区
/* Use CMOS to get floppy configuration */
Out_Byte(CMOS_OUT, CMOS_FLOPPY_INDEX);
floppyByte = In_Byte(CMOS_IN); //返回2个软盘类型信息
Setup_Drive_Parameters(0, (floppyByte >> 4) & 0xF);//0号软盘在高4位
Setup_Drive_Parameters(1, floppyByte & 0xF); //1号软盘在低4位
/* Install floppy interrupt handler */
Install_IRQ(FDC_IRQ, &Floppy_Interrupt_Handler); //注册软盘中断函数
Enable_IRQ(FDC_IRQ);
/* Reset and calibrate the controller. */
Disable_Interrupts();
good = Reset_Controller(); //重置软盘控制器
Enable_Interrupts();
if (!good) {
Print(" Failed to reset controller!\n");
goto done;
}
/* Reserve DMA channel 2. */
if (!Reserve_DMA(FDC_DMA)) { //重置软盘的DMA通道
Print(" Failed to reserve DMA channel\n");
goto done;
}
/*
* Driver is now ready for requests.
* Start the request processing thread.
*///现在可以访问软盘了
ready = true; //Floppy_Request_Thread是处理软盘访问的线程
Start_Kernel_Thread(Floppy_Request_Thread, 0, PRIORITY_NORMAL, true);
done:
if (!ready)
Print(" Floppy controller initialization FAILED\n");
}
Setup_Drive_Parameters位于./src/geekos/floppy.c
/*
* Initialize drive parameters based on the floppy type returned
* by the CMOS.
*/ //drive为软盘号,type是一个索引值,为软盘
static void Setup_Drive_Parameters(int drive, int type)
{
if (IS_VALID_FLOPPY_TYPE(type)) {
struct Floppy_Parameters* params = &s_floppyParamsTable[type];//得到软盘参数
char devname[BLOCKDEV_MAX_NAME_LEN+1];
int rc;
snprintf(devname, sizeof(devname), "fd%d", drive);
Print(" %s: cyl=%d, heads=%d, sectors=%d\n", devname,
params->cylinders, params->heads, params->sectors);
s_driveTable[drive].params = params;//保存软盘参数信息
/* Register the block device. *///注册块设备
rc = Register_Block_Device(devname, &s_floppyDeviceOps, drive, 0,
&s_floppyWaitQueue, &s_floppyRequestQueue);
if (rc != 0)
Print(" Error: could not create block device for %s\n", devname);
}
}
看一下Setup_Drive_Parameters中的注册块设备函数Register_Block_Device
位于./src/geekos/blockdev.c
/*
* Register a block device.
* This should be called by device drivers in their Init
* functions to register all detected devices.
* Returns 0 if successful, error code otherwise.
*/
int Register_Block_Device(const char *name, struct Block_Device_Ops *ops,
int unit, void *driverData, struct Thread_Queue *waitQueue,
struct Block_Request_List *requestQueue)
{
struct Block_Device *dev;
KASSERT(ops != 0);
KASSERT(waitQueue != 0);
KASSERT(requestQueue != 0);
dev = (struct Block_Device*) Malloc(sizeof(*dev));//分配块设备结构体
if (dev == 0)
return ENOMEM;
//初始化各个参数
strcpy(dev->name, name);
dev->ops = ops;
dev->unit = unit;
dev->inUse = false;
dev->driverData = driverData;
dev->waitQueue = waitQueue;
dev->requestQueue = requestQueue;
Mutex_Lock(&s_blockdevLock);//s_blockdevLock是用于保护块设备链表s_deviceList的互斥锁,线程要操作s_deviceList首先必须获得s_blockdevLock
/* FIXME: handle name conflict with existing device */
Debug("Registering block device %s\n", dev->name);
Add_To_Back_Of_Block_Device_List(&s_deviceList, dev);//链入到设备链表中
Mutex_Unlock(&s_blockdevLock);
return 0;
}
这里值得说明的是s_deviceList,定义在./src/geekos/blockdev.c
static struct Block_Device_List s_deviceList;
它使用了static修饰,表示s_deviceList这个变量只在这个文件中有效,对于其他文件编译出的代码是不可见的。
这里出现了互斥锁Mutex_Lock和Mutex_Unlock。
先看一下struct Mutex 类型
位于./include/geekos/synch.h
struct Mutex {
int state;
struct Kernel_Thread* owner;
struct Thread_Queue waitQueue;
};
可以看到struct Mutex有锁的状态、锁的所有者、锁的等待队列三个成员。
再来看一下锁互斥的实现。
位于./src/geekos/synch.c
/*
* Lock given mutex.
*/
void Mutex_Lock(struct Mutex* mutex)
{
KASSERT(Interrupts_Enabled());
g_preemptionDisabled = true;//禁止抢占,意思就是中断结束后只能继续运行原来的被中断进程,中断可以是时钟中断、键盘中断、软盘中断
Mutex_Lock_Imp(mutex);
g_preemptionDisabled = false;
}
/*
* Unlock given mutex.
*/
void Mutex_Unlock(struct Mutex* mutex)
{
KASSERT(Interrupts_Enabled());
g_preemptionDisabled = true;//禁止系统抢占
Mutex_Unlock_Imp(mutex);
g_preemptionDisabled = false;
}
其中又成对出现了Mutex_Lock_Imp和Mutex_Unlock_Imp。
Mutex_Lock_Imp等待并得到锁,Mutex_Unlock_Imp释放锁。
位于./src/geekos/synch.c
/*
* Lock given mutex.
* Preemption must be disabled.
*/
static __inline__ void Mutex_Lock_Imp(struct Mutex* mutex)
{
KASSERT(g_preemptionDisabled);
/* Make sure we're not already holding the mutex */
KASSERT(!IS_HELD(mutex));
/* Wait until the mutex is in an unlocked state */
while (mutex->state == MUTEX_LOCKED) {
Mutex_Wait(mutex);//休眠等待此互斥锁,并循环判断
}
/* Now it's ours! *///运行到这里说明获得了锁
mutex->state = MUTEX_LOCKED;
mutex->owner = g_currentThread;
}
/*
* Unlock given mutex.
* Preemption must be disabled.
*/
static __inline__ void Mutex_Unlock_Imp(struct Mutex* mutex)
{
KASSERT(g_preemptionDisabled);
/* Make sure mutex was actually acquired by this thread. */
KASSERT(IS_HELD(mutex));
/* Unlock the mutex. */
mutex->state = MUTEX_UNLOCKED;//解锁
mutex->owner = 0;
/*
* If there are threads waiting to acquire the mutex,
* wake one of them up. Note that it is legal to inspect
* the queue with interrupts enabled because preemption
* is disabled, and therefore we know that no thread can
* concurrently add itself to the queue.
*///若锁的等待队列非空,则唤醒等待队列上的一个线程。
if (!Is_Thread_Queue_Empty(&mutex->waitQueue)) {
Disable_Interrupts();
Wake_Up_One(&mutex->waitQueue);
Enable_Interrupts();
}
}
Mutex_Lock_Imp中的Mutex_Wait(mutex)如下
位于./src/geekos/synch.c
/*
* The mutex is currently locked.
* Atomically reenable preemption and wait in the
* mutex's wait queue.
*/
static void Mutex_Wait(struct Mutex *mutex)
{
KASSERT(mutex->state == MUTEX_LOCKED);
KASSERT(g_preemptionDisabled);
Disable_Interrupts();//这里关中断就保证了下面的代码一定是连续执行的,因为这里的g_preemptionDisabled是全局的,在中断处理函数中有可能发生变化。
g_preemptionDisabled = false;
Wait(&mutex->waitQueue);//在队列上等待
g_preemptionDisabled = true;
Enable_Interrupts();
}
使用Mutex与关中断的区别和联系:
共同点:都是为了保护临界区中的变量不被除此线程之外的线程修改。
区别:使用关中断保护的临界区代码执行是从头到尾的;使用Mutex保护的临界区代码执行过程中有可能被中断,但是中断过程和临界区代码没有任何耦合,中断结束后仍然返回被中断线程的临界区中继续执行。
被中断的线程并不知道产生了中断。
回到Init_Floppy中,看下一句
Install_IRQ(FDC_IRQ, &Floppy_Interrupt_Handler);
为软盘安装了中断处理函数Floppy_Interrupt_Handler
看Floppy_Interrupt_Handler
位于./src/geekos/floppy.c
/*
* Interrupt handler.
* The floppy controller generally issues an interrupt
* to notify the driver of the completion of a command.
*/
/*
* For now, we just set a flag that the driver
* can busy-wait for.
*/
static void Floppy_Interrupt_Handler(struct Interrupt_State* state)
{
Begin_IRQ(state);
Debug("Floppy_Interrupt_Handler!\n");
s_interruptOccurred = 1;
End_IRQ(state);
}
可以看到,它只是简单的将中断标志s_interruptOccurred置为1。
再往下看
Start_Kernel_Thread(Floppy_Request_Thread, 0, PRIORITY_NORMAL, true);
创建了Floppy_Request_Thread线程,用于处理用户对软盘的访问。
来看Floppy_Request_Thread
位于./src/geekos/floppy.c
/*
* This is the thread which processes floppy I/O requests.
*/
static void Floppy_Request_Thread(ulong_t arg)
{
int rc;
Debug("FRQ: Floppy request thread starting...\n");
for (;;) {
struct Block_Request *request;
/* Wait for an I/O request to arrive */
Debug("FRQ: Request thread waiting for a request\n");
request = Dequeue_Request(&s_floppyRequestQueue, &s_floppyWaitQueue);
Debug("FRQ: Got a floppy request [@%x]\n", request);
KASSERT(request->type == BLOCK_READ || request->type == BLOCK_WRITE);
/* Perform the I/O. */
if (request->type == BLOCK_READ)
rc = Floppy_Read(request->dev->unit, request->blockNum, request->buf);
else
rc = Floppy_Write(request->dev->unit, request->blockNum, request->buf);
/* Notify the requesting thread of the outcome of the I/O. */
Debug("FRQ: Notifying requesting thread...\n");
Notify_Request_Completion(request, rc == 0 ? COMPLETED : ERROR, rc);
Debug("FRQ: Completed floppy request\n");
}
}
首先来看struct Block_Request结构,用于对块的访问。
位于./include/geekos/blockdev.h
/*
* An I/O request for a block device.
*/
struct Block_Request {
struct Block_Device *dev;
enum Request_Type type;
int blockNum;
void *buf;
volatile enum Request_State state;
volatile int errorCode;
struct Thread_Queue waitQueue;
DEFINE_LINK(Block_Request_List, Block_Request);
};
再来看Dequeue_Request(&s_floppyRequestQueue, &s_floppyWaitQueue);
Dequeue_Request从队列s_floppyWaitQueue上得到块请求结构,并返回。块请求队列为空,则在floppyWaitQueue上等待。
Dequeue_Request位于./src/geekos/blockdev.c
/*
* Wait for a block request to arrive.
*/
struct Block_Request *Dequeue_Request(struct Block_Request_List *requestQueue,
struct Thread_Queue *waitQueue)
{
struct Block_Request *request;
Disable_Interrupts();
while (Is_Block_Request_List_Empty(requestQueue))
Wait(waitQueue);
request = Get_Front_Of_Block_Request_List(requestQueue);
Remove_From_Front_Of_Block_Request_List(requestQueue);
Enable_Interrupts();
return request;
}
然后根据块请求的类型来对软盘进行读或写。