HDU-1023 -Train Problem II(卡特兰数)
Problem Description
As we all know the Train Problem I, the boss of the Ignatius Train Station want to know if all the trains come in strict-increasing order, how many orders that all the trains can get out of the railway.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test cases consists of a number N(1<=N<=100). The input is terminated by the end of file.
Output
For each test case, you should output how many ways that all the trains can get out of the railway.
Sample Input
1
2
3
10
Sample Output
1
2
5
16796
Hint
The result will be very large, so you may not process it by 32-bit integers.
卡特兰数
卡塔兰数是组合数学中一个常出现在各种计数问题中出现的数列。由以比利时的数学家欧仁·查理·卡塔兰 (1814–1894)命名。
卡塔兰数的一般项公式为 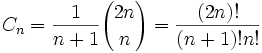 另类递归式: h(n)=((4*n-2)/(n+1))*h(n-1);
另类递归式: h(n)=((4*n-2)/(n+1))*h(n-1);
前几项为 (OEIS中的数列A000108): 1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, 16796, 58786, 208012, 742900, 2674440, 9694845, 35357670, 129644790, 477638700, 1767263190, 6564120420, 24466267020, 91482563640, 343059613650, 1289904147324, 4861946401452, …
性质
Cn的另一个表达形式为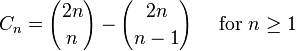 所以,Cn是一个自然数;这一点在先前的通项公式中并不显而易见。这个表达形式也是André对前一公式证明的基础。
所以,Cn是一个自然数;这一点在先前的通项公式中并不显而易见。这个表达形式也是André对前一公式证明的基础。
卡塔兰数满足以下递推关系
![]()
它也满足
![]()
这提供了一个更快速的方法来计算卡塔兰数。
卡塔兰数的渐近增长为
![]()
它的含义是左式除以右式的商趋向于1当n → ∞。(这可以用n!的斯特灵公式来证明。)
所有的奇卡塔兰数Cn都满足n = 2k − 1。所有其他的卡塔兰数都是偶数。
应用
组合数学中有非常多.的组合结构可以用卡塔兰数来计数。在Richard P. Stanley的Enumerative Combinatorics: Volume 2一书的习题中包括了66个相异的可由卡塔兰数表达的组合结构。以下用Cn=3和Cn=4举若干例:
Cn表示长度2n的dyck word的个数。Dyck word是一个有n个X和n个Y组成的字串,且所有的部分字串皆满足X的个数大于等于Y的个数。以下为长度为6的dyck words:
XXXYYY XYXXYY XYXYXY XXYYXY XXYXYY
将上例的X换成左括号,Y换成右括号,Cn表示所有包含n组括号的合法运算式的个数
((())) ()(()) ()()() (())() (()())
Cn表示所有不同构的含n个分枝结点的满二叉树的个数。(一个有根二叉树是满的当且仅当每个结点都有两个子树或没有子树。)
证明:
令1表示进栈,0表示出栈,则可转化为求一个2n位、含n个1、n个0的二进制数,满足从左往右扫描到任意一位时,经过的0数不多于1数。显然含n个1、n个0的2n位二进制数共有![]() 个,下面考虑不满足要求的数目.
个,下面考虑不满足要求的数目.
考虑一个含n个1、n个0的2n位二进制数,扫描到第2m+1位上时有m+1个0和m个1(容易证明一定存在这样的情况),则后面的0-1排列中必有n-m个1和n-m-1个0。将2m+2及其以后的部分0变成1、1变成0,则对应一个n+1个0和n-1个1的二进制数。反之亦然(相似的思路证明两者一一对应)。
从而 。证毕。
。证毕。
Cn表示所有在n × n格点中不越过对角线的单调路径的个数。一个单调路径从格点左下角出发,在格点右上角结束,每一步均为向上或向右。计算这种路径的个数等价于计算Dyck word的个数: X代表“向右”,Y代表“向上”。下图为n = 4的情况:

Cn表示通过连结顶点而将n + 2边的凸多边形分成三角形的方法个数。下图中为n = 4的情况:

Cn表示对{1, …, n}依序进出栈的置换个数。一个置换w是依序进出栈的当S(w) = (1, …, n), 其中S(w)递归定义如下:令w = unv,其中n为w的最大元素,u和v为更短的数列;再令S(w) =S(u)S(v)n,其中S为所有含一个元素的数列的单位元。
Cn表示集合{1, …, n}的不交叉划分的个数. 那么, Cn 永远不大于第n项贝尔数. Cn也表示集合{1, …, 2n}的不交叉划分的个数,其中每个段落的长度为2。综合这两个结论,可以用数学归纳法证明 that all of the free cumulants of degree more than 2 of the Wigner semicircle law are zero. This law is important in free probability theory and the theory of random matrices.
Cn表示用n个长方形填充一个高度为n的阶梯状图形的方法个数。下图为 n = 4的情况:

代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#define N 101
#define ll long long
#define base 10000
using namespace std;
ll n;
void mul(int a[], int len, int b) //大数乘法
{
int carry, i;
for (i = len-1, carry = 0; i >= 0; i--)
{
carry += b*a[i];
a[i] = carry%base;
carry /= base;
}
}
void Div(int a[], int len, int b) //大数除法
{
int div, i;
for (i = 0, div = 0; i < len; i++)
{
div = div*base + a[i];
a[i] = div/b;
div %= b;
}
}
int ans[N][N];
int main()
{
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("1.txt", "r", stdin);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int i, j;
memset(ans[1], 0, N*sizeof(int));
ans[1][N-1] = 1;
for(i = 2; i <= 100; i++)
{
memcpy(ans[i], ans[i-1], N*sizeof(int));
mul(ans[i], N, 4*i-2);
Div(ans[i], N, i+1);
}
while(cin >> n)
{
for(i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
if (ans[n][i] > 0)
break;
}
cout << ans[n][i++];
for(; i < N; i++)
{
cout << setw(4) << setfill('0')<< ans[n][i];
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}