树莓派学习笔记——定时向yeelink上传树莓派CPU温度
0 前言
本文通过python文件IO操作获得树莓派CPU温度信息,通过python request库周期性向yeelink平台上传温度,修改rc.local脚本使得该python脚本在开机时便在后台运行,向平台每5分钟上报一次温度信息。
网上查阅了很多关于linux开机启动的博文,尝试了几遍居然发现方法都无法实现开机启动效果。我想可能是操作系统或开发环境的微小差异产生的,如果发现博文中的内容存在问题,请及时留言,我查证之后定当修改。
【相关博文】
【 树莓派学习笔记——获取树莓派CPU温度】
【 树莓派学习笔记——索引博文】——更多博文请关注。
1 修改python脚本
修改【树莓派学习笔记——获取树莓派CPU温度】一文中的python脚本,由单次运行变为间隔运行,间隔时间为5分钟。由于该脚本将在后台运行,所以每次上传CPU温度参数之后,把温度参数写到同目录中的txt文件中,验证该脚本是否在成功运行,上传的参数是否正常等(yeelink平台没有列表功能,所有历史数据查看比较麻烦)
【python脚本】
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import requests
import json
import time
def main():
fileRecord = open("result.txt", "w")
fileRecord.write("connect to yeelink\n");
fileRecord.close()
while True:
# 打开文件
file = open("/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp")
# 读取结果,并转换为浮点数
temp = float(file.read()) / 1000
# 关闭文件
file.close()
# 设备URI
apiurl = 'http://api.yeelink.net/v1.1/device/1949/sensor/2510/datapoints'
# 用户密码, 指定上传编码为JSON格式
apiheaders = {'U-ApiKey': 'ffa3826972d6cc7ba5b17e104ec59fa3', 'content-type': 'application/json'}
# 字典类型数据,在post过程中被json.dumps转换为JSON格式字符串 {"value": 48.123}
payload = {'value': temp}
#发送请求
r = requests.post(apiurl, headers=apiheaders, data=json.dumps(payload))
# 向控制台打印结果
fileRecord = open("result.txt", "a")
strTime = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d:%H-%M-%S',time.localtime(time.time()))
fileRecord.writelines(strTime + "\n")
strTemp = "temp : %.1f" %temp + "\n"
fileRecord.writelines(strTemp)
fileRecord.writelines(str(r.status_code) + "\n")
fileRecord.close()
time.sleep(5*60)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
2 开机启动——增加脚本
【auto-start.sh】
#!/bin/bash
cd /home/pi/python-works/yeelink-temp
python yeelink-temp.py &
【提醒】
【1】&表示脚本后台运行
【2】sudo chmod a+x auto-start.sh
3 开机启动——修改/etc/rc.local
在exit 0之前增加一行,内容为/home/pi/path/to/auto-start.sh start,请修改为auto-start.sh所在目录。修改之后的rc.local内容如下:
#!/bin/sh -e # # rc.local # # This script is executed at the end of each multiuser runlevel. # Make sure that the script will "exit 0" on success or any other # value on error. # # In order to enable or disable this script just change the execution # bits. # # By default this script does nothing. # Print the IP address _IP=$(hostname -I) || true if [ "$_IP" ]; then printf "My IP address is %s\n" "$_IP" fi # 向yeelink上传树莓派CPU温度 /home/pi/python-works/yeelink-temp/auto-start.sh start exit 0
【必要的验证】
可通过ps指令查看该脚本是否在后台运行,保证万无一失。
ps aux | grep yeelink-temp.py
图1 ps aux执行返回结果
请注意返回结果中还包括grep过滤指令,yeelink-temp.py的PID为2836。
【可能的后悔】
如果发现调试存在问题可通过kill指令终止进程,此时yeelink-temp.py的进程PID为2836
kill -s 9 2836
4 运行结果
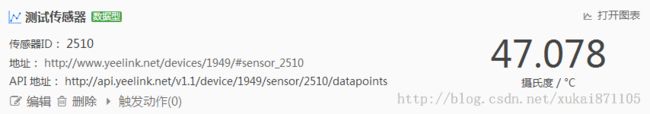
【平台查看】
图2 平台查看
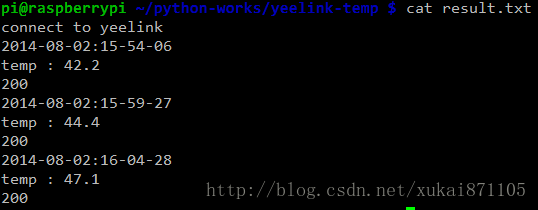
【本地查看】
本地记录被保存到result.txt文件中。在15分钟的时间内关闭了空调,室内温度快速升高,而树莓派的CPU温度由42.2上升到47.1度。
图3 本地查看
5 总结和参考资料
【1】修改rc.local可使linux在开机之后自动执行用户程序。
【2】当关闭房间空调之后,树莓派CPU温度从42.2度上升至47.1度,符合实际预期,说明实验成功了。
【3】再做一个保存温度到数据库的例子,再做一个RESTFul API读取温度历史数据的例子。
【吐槽】
yeelink平台对于历史数据的处理存在一些问题的。我本以为可以通过API把传感器的历史数据获得,并可设定查询时间,阅读了yeelink平台的文档我居然发现并没有此功能。在yeelink的用户中心中,我打开的网页调试工具,发现网页调用的API为sensor-data?sensor_id=2510×cale=3600
返回的数据为两个数组,一个代表数据点,一个为UNIX时间戳。从API和返回数据的格式上看并没有追求RESTFul结构,不知道是不是开发人员换了,所以风格变化了。
【参考资料】
【1】 树莓派 插电自动登录、自动运行程序
【1】 理解Linux系统/etc/init.d目录和/etc/rc.local脚本——CSDN博客
【2】 linux下杀死进程(kill)的N种方法 ——CSDN博客