线性表(一)——顺序表(1)
/* *Copyright (c) 2015 , 烟台大学计算机学院 *All right resvered . *文件名称: 对称矩阵压缩存储的实现与应用.cpp *作 者: 郑兆涵 *线性表(一)——顺序表 */
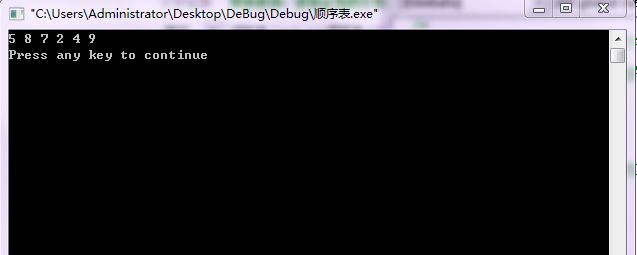
问题:测试“建立线性表”的算法CreateList,为查看建表的结果,需要实现“输出线性表”的算法DispList。
编程代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MaxSize 50
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int length;
} SqList;
//用数组创建线性表
void CreateList(SqList *&L, ElemType a[], int n)
{
int i;
L=(SqList *)malloc(sizeof(SqList));
for (i=0; i<n; i++)
L->data[i]=a[i];
L->length=n;
}
//初始化线性表InitList(L)
void InitList(SqList *&L) //引用型指针
{
L=(SqList *)malloc(sizeof(SqList));
//分配存放线性表的空间
L->length=0;
}
//销毁线性表DestroyList(L)
void DestroyList(SqList *&L)
{
free(L);
}
//判定是否为空表ListEmpty(L)
bool ListEmpty(SqList *L)
{
return(L->length==0);
}
//求线性表的长度ListLength(L)
int ListLength(SqList *L)
{
return(L->length);
}
//输出线性表DispList(L)
void DispList(SqList *L)
{
int i;
if (ListEmpty(L)) return;
for (i=0; i<L->length; i++)
printf("%d ",L->data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
//求某个数据元素值GetElem(L,i,e)
bool GetElem(SqList *L,int i,ElemType &e)
{
if (i<1 || i>L->length) return false;
e=L->data[i-1];
return true;
}
//按元素值查找LocateElem(L,e)
int LocateElem(SqList *L, ElemType e)
{
int i=0;
while (i<L->length && L->data[i]!=e) i++;
if (i>=L->length) return 0;
else return i+1;
}
//插入数据元素ListInsert(L,i,e)
bool ListInsert(SqList *&L,int i,ElemType e)
{
int j;
if (i<1 || i>L->length+1)
return false; //参数错误时返回false
i--; //将顺序表逻辑序号转化为物理序号
for (j=L->length; j>i; j--) //将data[i..n]元素后移一个位置
L->data[j]=L->data[j-1];
L->data[i]=e; //插入元素e
L->length++; //顺序表长度增1
return true; //成功插入返回true
}
//删除数据元素ListDelete(L,i,e)
bool ListDelete(SqList *&L,int i,ElemType &e)
{
int j;
if (i<1 || i>L->length) //参数错误时返回false
return false;
i--; //将顺序表逻辑序号转化为物理序号
e=L->data[i];
for (j=i; j<L->length-1; j++) //将data[i..n-1]元素前移
L->data[j]=L->data[j+1];
L->length--; //顺序表长度减1
return true; //成功删除返回true
}
int main()
{
SqList *sq;
ElemType x[6]= {5,8,7,2,4,9};
CreateList(sq, x, 6);
DispList(sq);
return 0;
}
代码解析:
针对以上的代码,对于数据结构这门课程而言,最重要的不是算法,当我们把每一个函数实现之后,例如:
(1)初始化线性表InitList(&L):构造一个空的线性表L
(2)销毁线性表DestroyList(&L):释放线性表L占用的内存空间
(3)判线性表是否为空表ListEmpty(L):若L为空表,则返回真,否则返回假
(4)求线性表的长度ListLength(L):返回L中元素个数
(5)输出线性表DispList(L):当线性表L不为空时,顺序显示L中各节点的值域
(6)求线性表L中指定位置的某个数据元素GetElem(L,i,&e):用e返回L中第 i 个元素的值
(7)查找元素LocateElem(L,e):返回线性表L中第1个与e相等的序号,找不到返回0
(8)插入元素ListInsert(&L, i, &e):在线性表L中的第i个位置插入元素e;
(9)删除元素ListDelete(&L, i, &e):在线性表L中删除第i个元素,有e返回删除的值;
(10)创建线性表CreateList(&L):创建一个线性表
这样一些代码之后,需要做初步的定义,让算法运行起来。因此,根据视频“0207”(http://www.mosoteach.cn/web/?c=res&m=index&clazz_course_id=33975A67-64CD-A0C3-9744-15346CB30B73)上所讲,在进行编译之前,需要先对所创建的线性表中的SqList进行定义,因此就需使用结构体,定义一个SqList结构体。之后需要对整个程序进行宏观定义,包括#include<stdio.h>、#include<malloc.h>、#define MaxSize 50 ,在此之后,会发现,一切就绪之后,只需要编写一个主函数,用于调用各个函数即可。